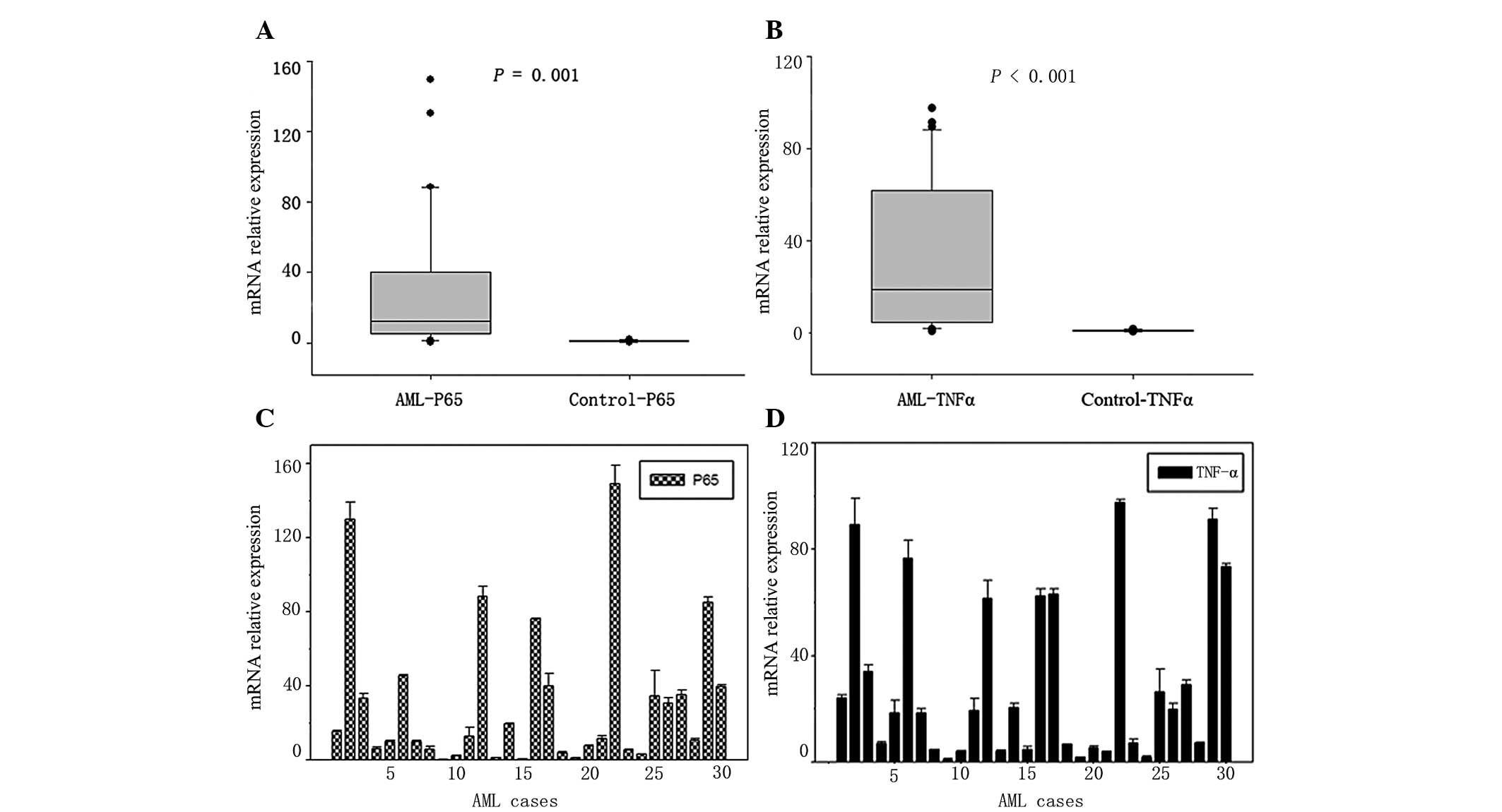
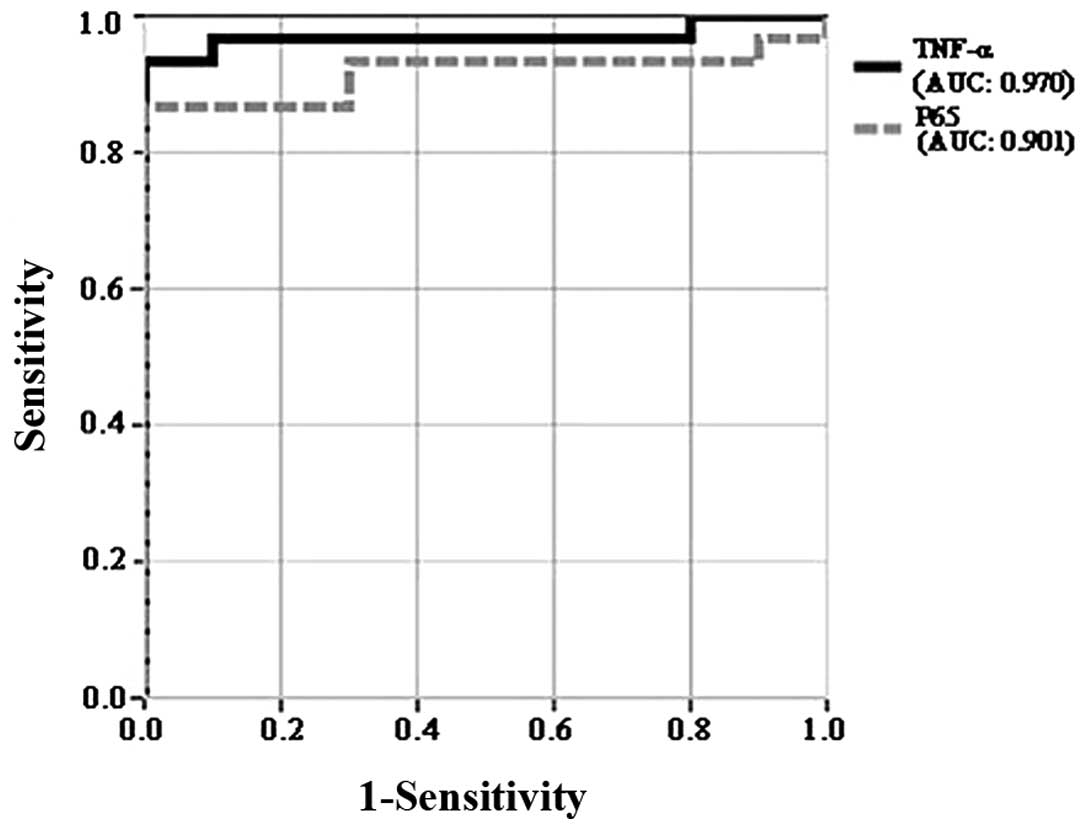
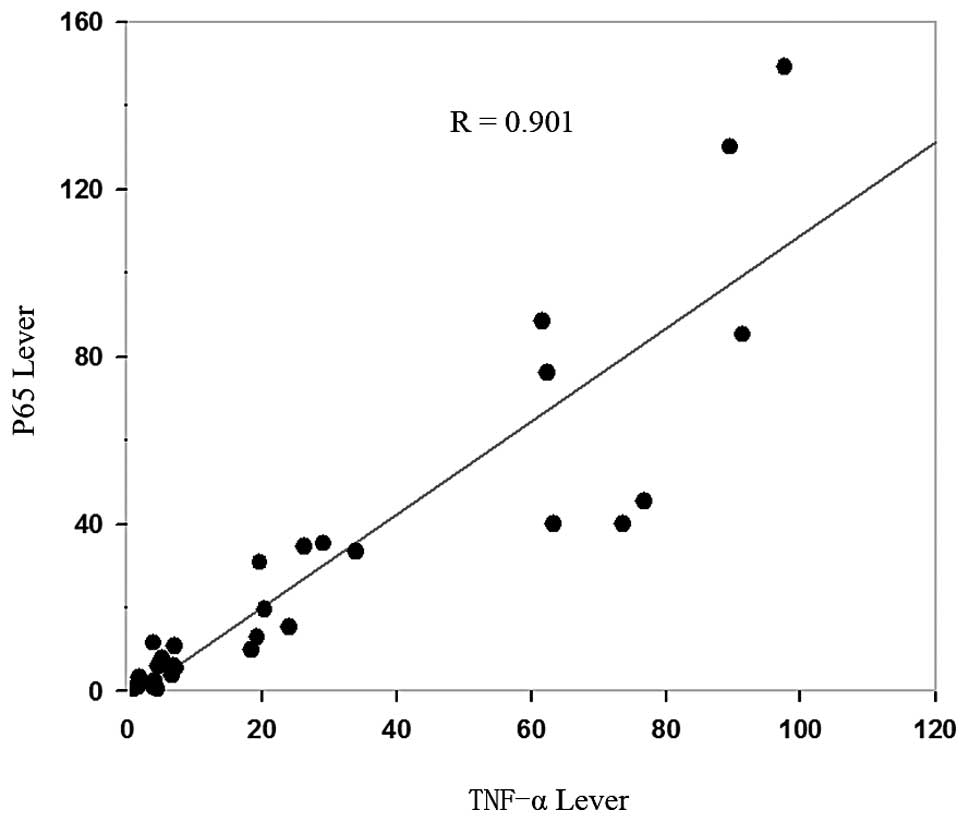
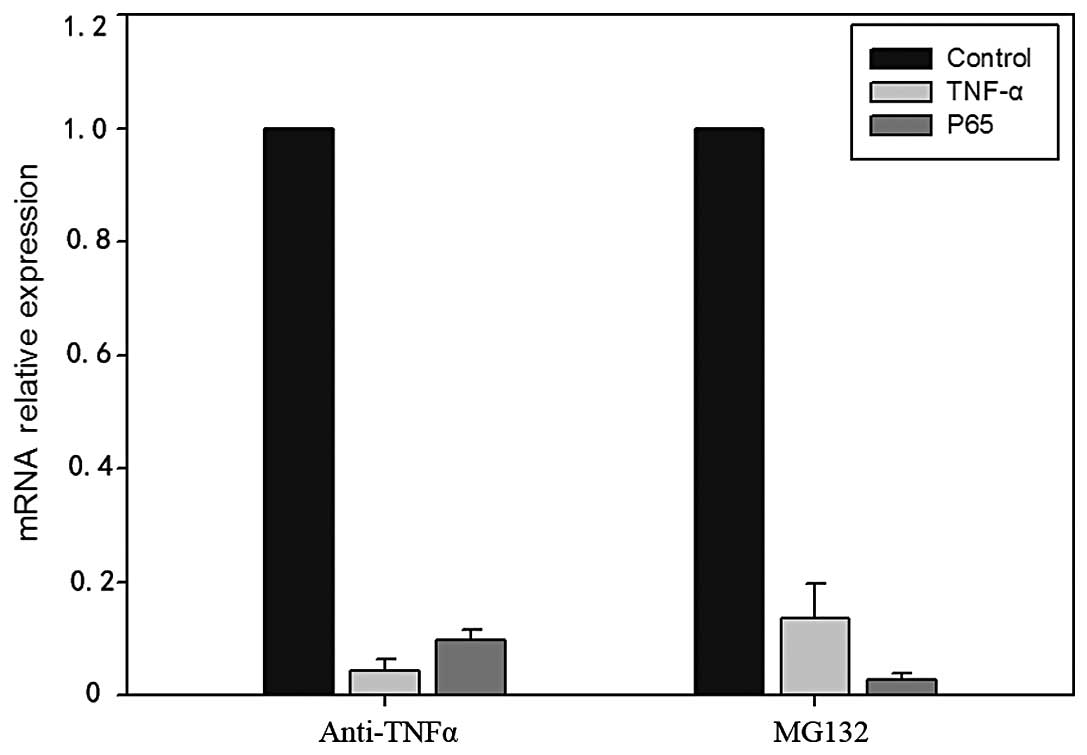
|
1
|
Larkin K and Blum W: Novel therapies in
AML: Reason for hope or just hype? Am Soc Clin Oncol Educ Book.
e341–e351. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Kohgo Y, Inamura J and Shindo M: Molecular
target drugs for AML-current state and prospects for the future.
Nihon Rinsho. 72:1063–1067. 2014.(In Japanese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Zeijlemaker W, Gratama JW and Schuurhuis
GJ: Tumor heterogeneity makes AML a ‘moving target’ for detection
of residual disease. Cytometry B Clin Cytom. 86:3–14. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Thomas R, Phuong J, McHale CM and Zhang L:
Using bioinformatic approaches to identify pathways targeted by
human leukemogens. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 9:2479–2503.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Liu YQ, Zhao FJ and Chen WQ: An analysis
of incidence and mortality of leukemia in China, 2009. Zhong Guo Ai
Zheng Yan Jiu. 22:528–534. 2013.(In Chinese).
|
|
6
|
Miyawaki S: Guideline for AML. Rinsho
Ketsueki. 54:1633–1642. 2013.(In Japanese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Levine RL: Molecular pathogenesis of AML:
Translating insights to the clinic. Best Pract Res Clin Haematol.
26:245–248. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Al-Ali HK, Jaekel N and Niederwieser D:
The role of hypomethylating agents in the treatment of elderly
patients with AML. J Geriatr Oncol. 5:89–105. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Kamieńska E, Ociepa T, Wysocki M, Kurylak
A, Matysiak M, Urasiński T, Urasińska E and Domagała W: Activation
of NF-kB in leukemic cells in response to initial prednisone
therapy in children with acute lymphoblastic leukaemia: Relation to
other prognostic factors. Pol J Pathol. 62:5–11. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Giuliani C, Napolitano G, Bucci I, Montani
V and Monaco F: Nf-kB transcription factor: Role in the
pathogenesis of inflammatory, autoimmune and neoplastic diseases
and therapy implications. Clin Ter. 152:249–253. 2001.(In Italian).
PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Baud V and Jacque E: The alternative NF-kB
activation pathway and cancer: friend or foe? Med Sci (Paris).
24:1083–1088. 2008.(In French). View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Schulz U, Munker R, Ertl B, Holler E and
Kolb HJ: Different types of human leukemias express the message for
TNF-alpha and interleukin-10. Eur J Med Res. 6:359–363.
2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Sun Y, Mi W, Cai J, Ying W, Liu F, Lu H,
Qiao Y, Jia W, Bi X, Lu N, et al: Quantitative proteomic signature
of liver cancer cells: Tissue transglutaminase 2 could be a novel
protein candidate of human hepatocellular carcinoma. J Proteome
Res. 7:3847–3859. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Zor T and Zvi S: Linearization of the
Bradford protein assay increases its sensitivity: Theoretical and
experimental studies. Anal Biochem. 236:302–308. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Karatas OF, Guzel E, Suer I, Ekici ID,
Caskurlu T, Creighton CJ, Ittmann M and Ozen M: miR-1 and miR-133b
are differentially expressed in patients with recurrent prostate
cancer. PLoS One. 9:e986752014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Morotti A, Cilloni D, Pautasso M, Messa F,
Arruga F, Defilippi I, Carturan S, Catalano R, Rosso V, Chiarenza
A, et al: NF-kB inhibition as a strategy to enhance
etoposide-induced apoptosis in K562 cell line. Am J Hematol.
81:938–945. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Abdullah M, Rani AA, Sudoyo AW, Makmun D,
Handjari DR and Hernowo BS: Expression of NF-kB and COX2 in
colorectal cancer among native Indonesians: The role of
inflammation in colorectal carcinogenesis. Acta Med Indones.
45:187–192. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Guzman ML, Neering SJ, Upchurch D, Grimes
B, Howard DS, Rizzieri DA, Luger SM and Jordan CT: Nuclear
factor-kappaB is constitutively activated in primitive human acute
myelogenous leukemia cells. Blood. 98:2301–2307. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Choi S, Park YS, Koga T, Treloar A and Kim
KC: TNF-α is a key regulator of MUC1, an anti-inflammatory
molecule, during airway Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection. Am J
Respir Cell Mol Biol. 44:255–260. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Zhu M, Zhu Y and Lance P: TNF α-activated
stromal COX-2 signalling promotes proliferative and invasive
potential of colon cancer epithelial cells. Cell Prolif.
46:374–381. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Rivas MA, Carnevale RP, Proietti CJ,
Rosemblit C, Beguelin W, Salatino M, Charreau EH, Frahm I, Sapia S,
Brouckaert P, et al: TNF alpha acting on TNFR1 promotes breast
cancer growth via p42/P44 MAPK, JNK, Akt and NF-kappa B-dependent
pathways. Exp Cell Res. 314:509–529. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Lee YR, Yu HN, Noh EM, Youn HJ, Song EK,
Han MK, Park CS, Kim BS, Park YS, Park BK, et al: TNF-alpha
upregulates PTEN via NF-kappaB signaling pathways in human leukemic
cells. Exp Mol Med. 39:121–127. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Kagoya Y, Yoshimi A, Kataoka K, Nakagawa
M, Kumano K, Arai S, Kobayashi H, Saito T, Iwakura Y and Kurokawa
M: Positive feedback between NF-κB and TNF-α promotes
leukemia-initiating cell capacity. J Clin Invest. 124:528–542.
2014. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|