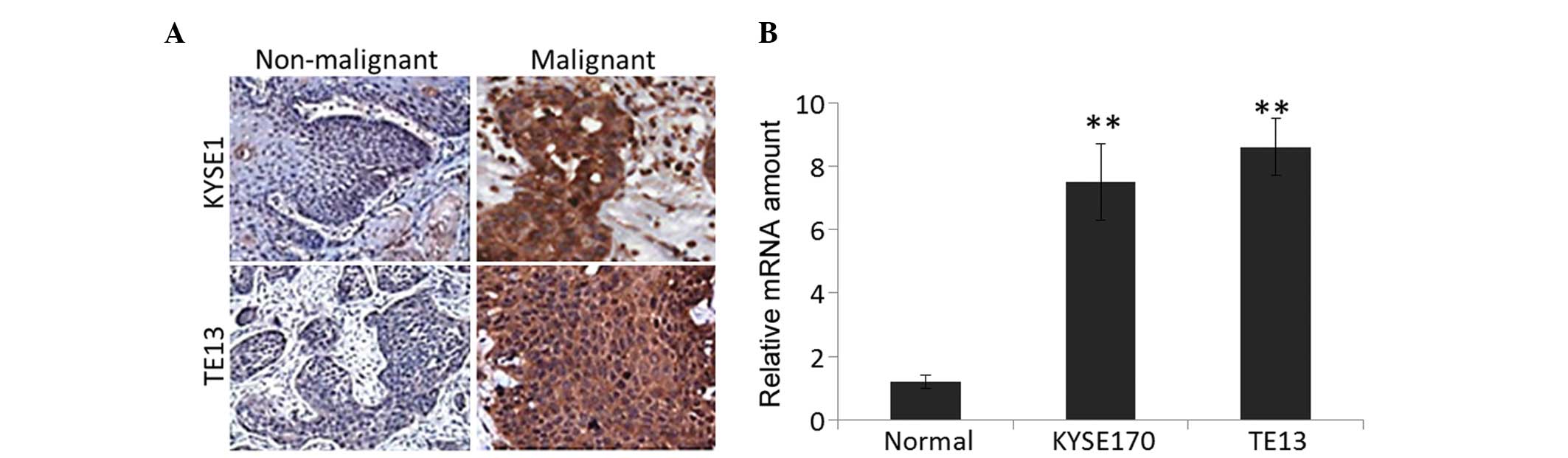
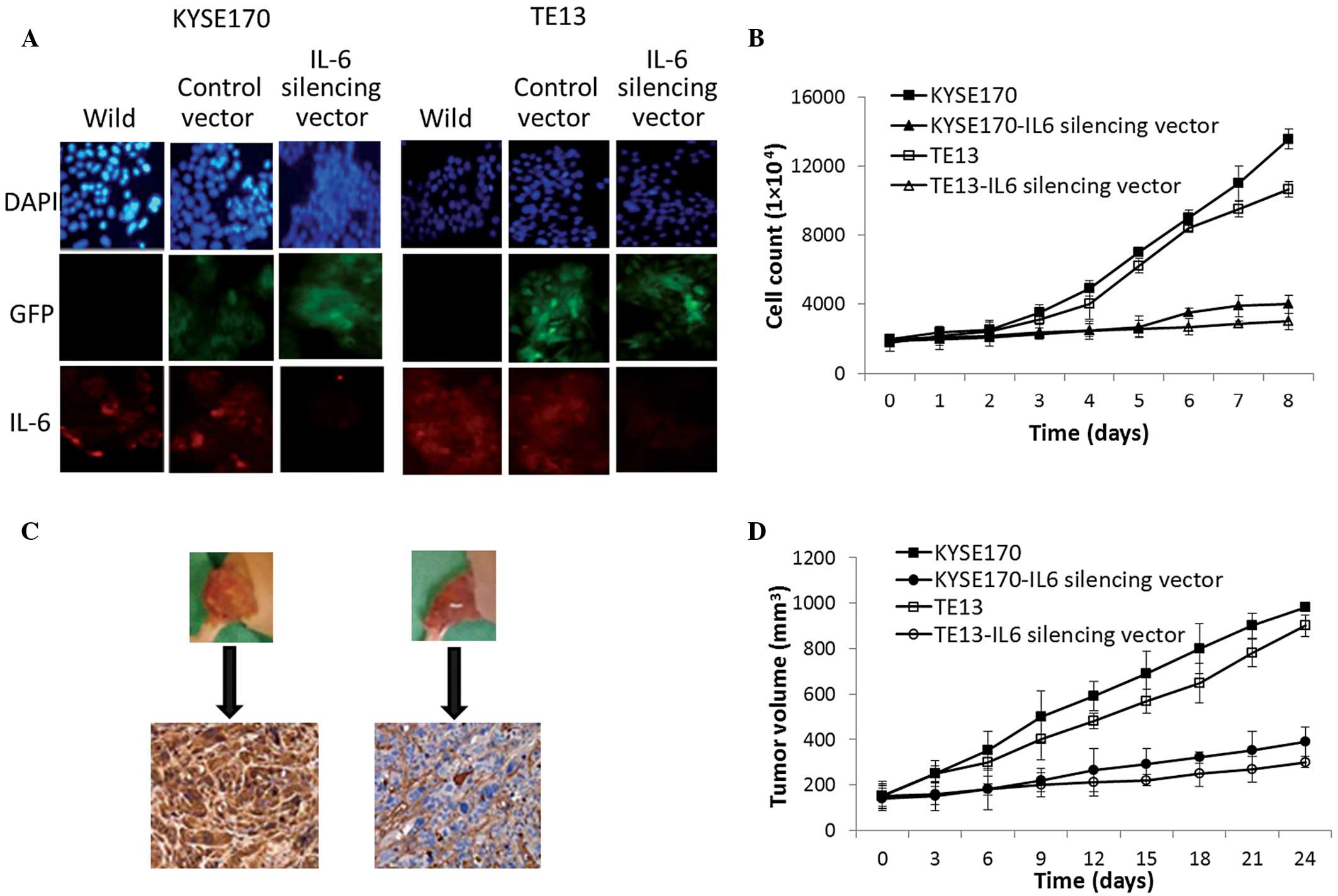
|
1
|
Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward
E and Forman D: Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin.
61:69–90. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Sarwar Shahbaz CM, Luketich JD, Landreneau
RJ and Abbas G: Esophageal cancer, An update. Int J Surg.
8:417–422. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Jemal A, Siegel R, Ward E, Hao Y, Xu J and
Thun MJ: Cancer statistics, 2009. CA Cancer J Clin. 59:225–249.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Allum WH, Stenning SP, Bancewicz J, Clark
PI and Langley RE: Long-term results of a randomized trial of
surgery with or without preoperative chemotherapy in esophageal
cancer. J Clin Oncol. 27:5062–5067. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Sjoquist KM, Burmeister BH, Smithers BM,
Zalcberg JR, Simes RJ, Barbour A and Gebski V: Australasian
Gastro-Intestinal Trials Group: Survival after neoadjuvant
chemotherapy or chemoradiotherapy for resectable oesophageal
carcinoma. An updated meta-analysis. Lancet Oncol. 12:681–692.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Chen WQ, Zheng RS, Zhang SW, Li N, Zhao P,
Li GL, Wu LY and He J: Report of incidence and mortality in china
cancer registries, 2008. Chin J Cancer Res. 24:171–180. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Liu Q, Li R, Zhu Z, Qian X, Guan W, Yu L,
Yang M, Jiang X and Liu B: Enhanced antitumor efficacy,
biodistribution and penetration of docetaxel-loaded biodegradable
nanoparticles. Int J Pharm. 430:350–358. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Coussens LM and Werb Z: Inflammation and
cancer. Nature. 420:860–867. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Balkwill F and Mantovani A: Inflammation
and cancer: Back to Virchow? Lancet. 357:539–545. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Gonda TA, Tu S and Wang TC: Chronic
inflammation, the tumor microenvironment and carcinogenesis. Cell
Cycle. 8:2005–2013. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Abdel-Latif MM, Duggan S, Reynolds JV and
Kelleher D: Inflammation and esophageal carcinogenesis. Curr Opin
Pharmacol. 9:396–404. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Schafer ZT and Brugge JS: IL-6 involvement
in epithelial cancers. J Clin Invest. 117:3660–3663. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Akira S, Taga T and Kishimoto T:
Interleukin-6 in biology and medicine. Adv Immunol. 54:1–78. 1993.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Chen CC, Chen WC, Lu CH, Wang WH, Lin PY,
Lee KD and Chen MF: Significance of interleukin-6 signaling in the
resistance of pharyngeal cancer to irradiation and the epidermal
growth factor receptor inhibitor. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys.
76:1214–1224. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Santer FR, Malinowska K, Culig Z and
Cavarretta IT: Interleukin-6 trans-signalling differentially
regulates proliferation, migration, adhesion and maspin expression
in human prostate cancer cells. Endocr Relat Cancer. 17:241–253.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Kishimoto T: Interleukin-6:F rom basic
science to medicine - 40 years in immunology. Annu Rev Immunol.
23:1–21. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Guo Y, Xu F, Lu T, Duan Z and Zhang Z:
Interleukin-6 signaling pathway in targeted therapy for cancer.
Cancer Treat Rev. 38:904–910. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Stahl M: Is there any role for surgery in
the multidisciplinary treatment of esophageal cancer? Ann Oncol.
21((Suppl 7)): vii283–vii285. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Trikha M, Corringham R, Klein B and Rossi
JF: Targeted anti-interleukin-6 monoclonal antibody therapy for
cancer, A review of the rationale and clinical evidence. Clin
Cancer Res. 9:4653–4665. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Leu CM, Wong FH, Chang C, Huang SF and Hu
CP: Interleukin-6 acts as an antiapoptotic factor in human
esophageal carcinoma cells through the activation of both STAT3 and
mitogen-activated protein kinase pathways. Oncogene. 22:7809–7818.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Chen MF, Lee KD, Lu MS, Chen CC, Hsieh MJ,
Liu YH, Lin PY and Chen WC: The predictive role of E2-EPF ubiquitin
carrier protein in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. J Mol Med
(Berl). 87:307–320. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Thiery JP: Epithelial-mesenchymal
transitions in tumour progression. Nat Rev Cancer. 2:442–454. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Scott DW and Gascoyne RD: The tumour
microenvironment in B cell lymphomas. Nat Rev Cancer. 14:517–534.
2014. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
McConkey DJ, Choi W, Marquis L, Martin F,
Williams MB, Shah J, Svatek R, Das A, Adam L, Kamat A, et al: Role
of epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT) in drug sensitivity
and metastasis in bladder cancer. Cancer Metastasis Rev.
28:335–344. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Tartour E, Pere H, Maillere B, Terme M,
Merillon N, Taieb J, Sandoval F, Quintin-Colonna F, Lacerda K,
Karadimou A, et al: Angiogenesis and immunity: A bidirectional link
potentially relevant for the monitoring of antiangiogenic therapy
and the development of novel therapeutic combination with
immunotherapy. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 30:83–95. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Sharma S, Sharma MC and Sarkar C:
Morphology of angiogenesis in human cancer, A conceptual overview,
histoprognostic perspective and significance of neoangiogenesis.
Histopathology. 46:481–489. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Landskron G, De la Fuente M, Thuwajit C
and Hermoso MA: Chronic inflammation and cytokines in the tumor
microenvironment. J Immunol Res. 2014:2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Sepúlveda P, Encabo A, Carbonell-Uberos F
and Miñana MD: BCL-2 expression is mainly regulated by JAK/STAT3
pathway in human CD34+ hematopoietic cells. Cell Death Differ.
14:378–380. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Aggarwal BBA, Kunnumakkara AB, Harikumar
KB, Gupta SR, Tharakan ST, Koca C, Dey S and Sung B: Signal
transducer and activator of transcription-3, inflammation, and
cancer, How intimate is the relationship? Ann N Y Acad Sci.
1171:59–76. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Levy DE and Darnell JE Jr: Stats:
Transcriptional control and biological impact. Nat Rev Mol Cell
Biol. 3:651–662. 2002. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Bromberg J: Stat proteins and oncogenesis.
J Clin Invest. 109:1139–1142. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Bishop JL, Thaper D and Zoubeidi A: The
multifaceted roles of STAT3 signaling in the progression of
prostate cancer. Cancers (Basel). 6:829–859. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Chen MF, Lu MS, Lin PY, Chen PT, Chen WC
and Lee KD: The role of DNA methyltransferase 3b in esophageal
squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer. 118:4074–4089. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Sarvaiya PJ, Guo D, Ulasov I, Gabikian P
and Lesniak MS: Chemokines in tumor progression and metastasis.
Oncotarget. 4:2171–2185. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Schindler C, Levy DE and Decker T:
JAK-STAT signaling, From interferons to cytokines. J Biol Chem.
282:20059–20063. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Mian BM, Dinney CP, Bermejo CE, Sweeney P,
Tellez C, Yang XD, Gudas JM, McConkey DJ and Bar-Eli M: Fully human
anti-interleukin 8 antibody inhibits tumor growth in orthotopic
bladder cancer xenografts via down-regulation of matrix
metalloproteases and nuclear factor-kappaB. Clin Cancer Res.
9:3167–3175. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|