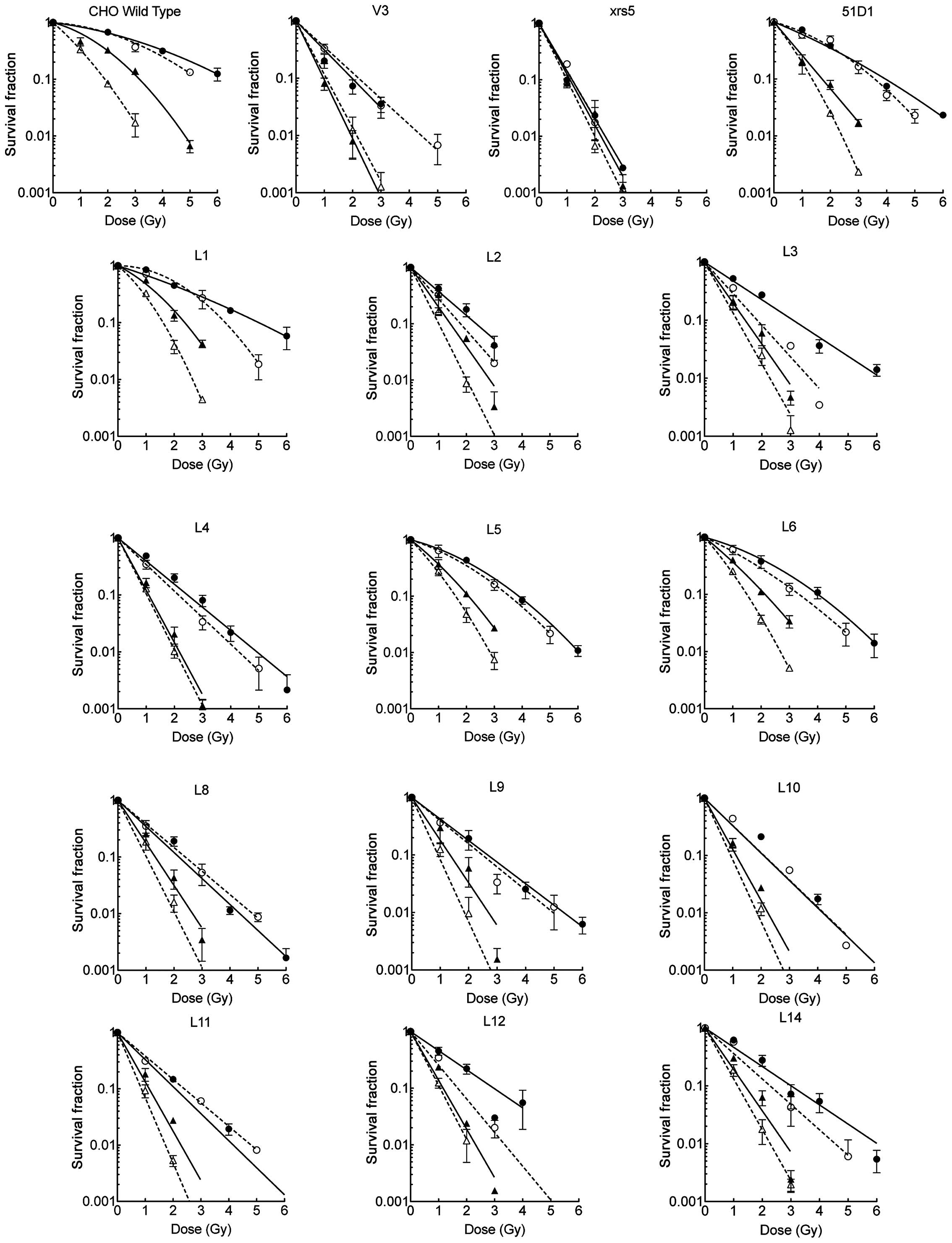
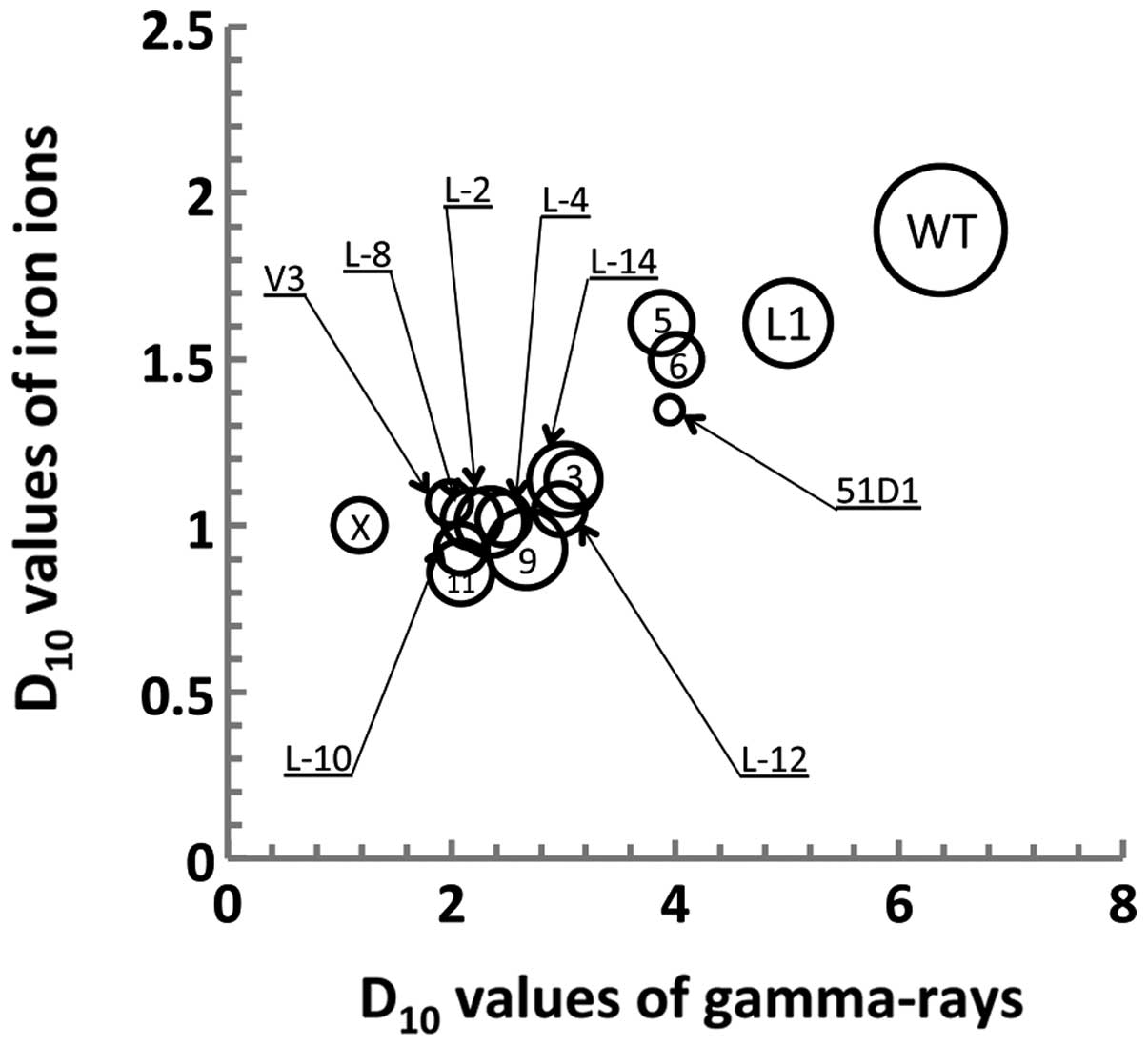
Spandidos Publications style
Cartwright IM, Bell JJ, Maeda J, Genet MD, Romero A, Fujii Y, Fujimori A, Kitamuta H, Kamada T, Chen DJ, Chen DJ, et al: Effects of targeted phosphorylation site mutations in the DNA-PKcs phosphorylation domain on low and high LET radiation sensitivity. Oncol Lett 9: 1621-1627, 2015.
APA
Cartwright, I.M., Bell, J.J., Maeda, J., Genet, M.D., Romero, A., Fujii, Y. ... Kato, T.A. (2015). Effects of targeted phosphorylation site mutations in the DNA-PKcs phosphorylation domain on low and high LET radiation sensitivity. Oncology Letters, 9, 1621-1627. https://doi.org/10.3892/ol.2015.2974
MLA
Cartwright, I. M., Bell, J. J., Maeda, J., Genet, M. D., Romero, A., Fujii, Y., Fujimori, A., Kitamuta, H., Kamada, T., Chen, D. J., Kato, T. A."Effects of targeted phosphorylation site mutations in the DNA-PKcs phosphorylation domain on low and high LET radiation sensitivity". Oncology Letters 9.4 (2015): 1621-1627.
Chicago
Cartwright, I. M., Bell, J. J., Maeda, J., Genet, M. D., Romero, A., Fujii, Y., Fujimori, A., Kitamuta, H., Kamada, T., Chen, D. J., Kato, T. A."Effects of targeted phosphorylation site mutations in the DNA-PKcs phosphorylation domain on low and high LET radiation sensitivity". Oncology Letters 9, no. 4 (2015): 1621-1627. https://doi.org/10.3892/ol.2015.2974