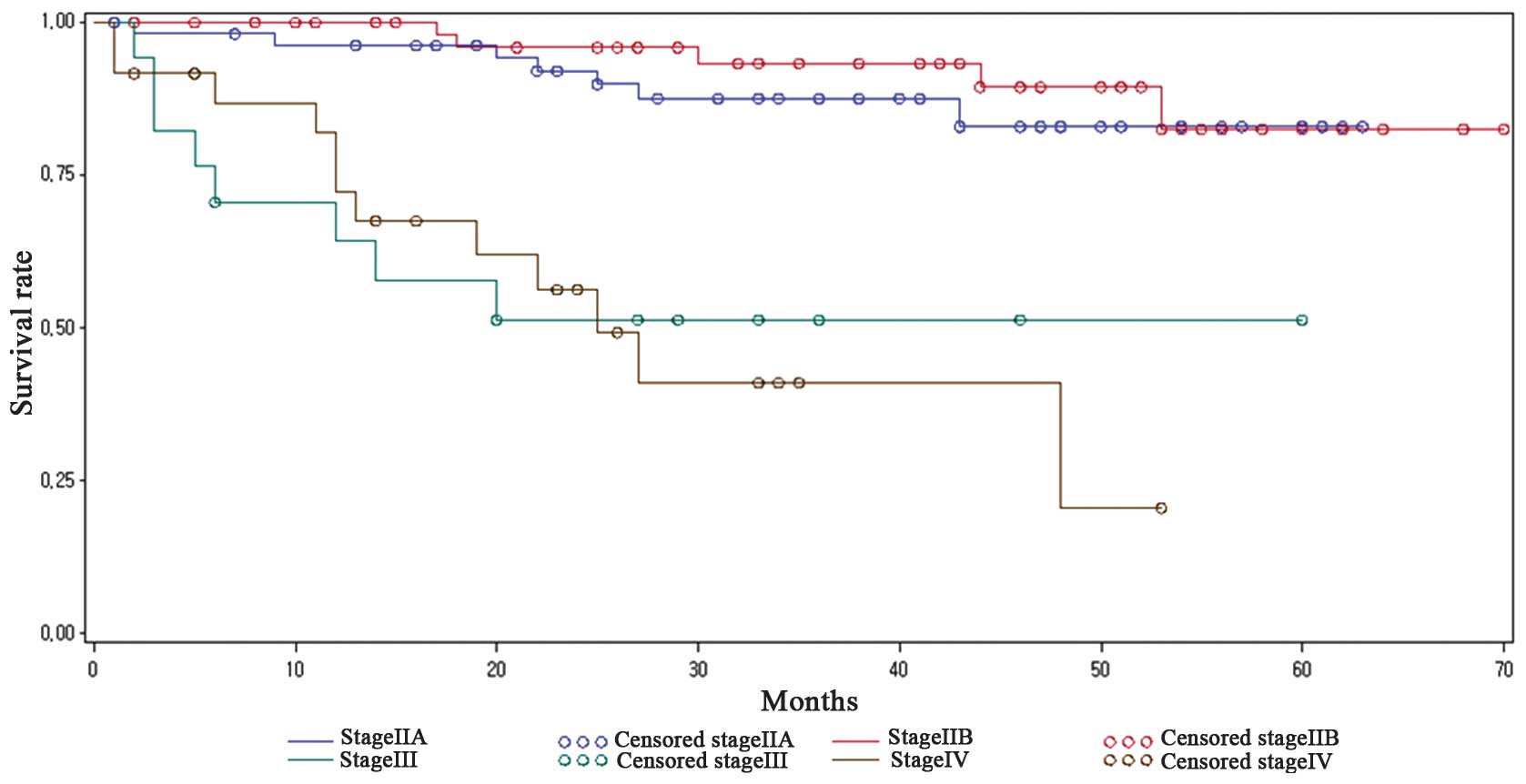
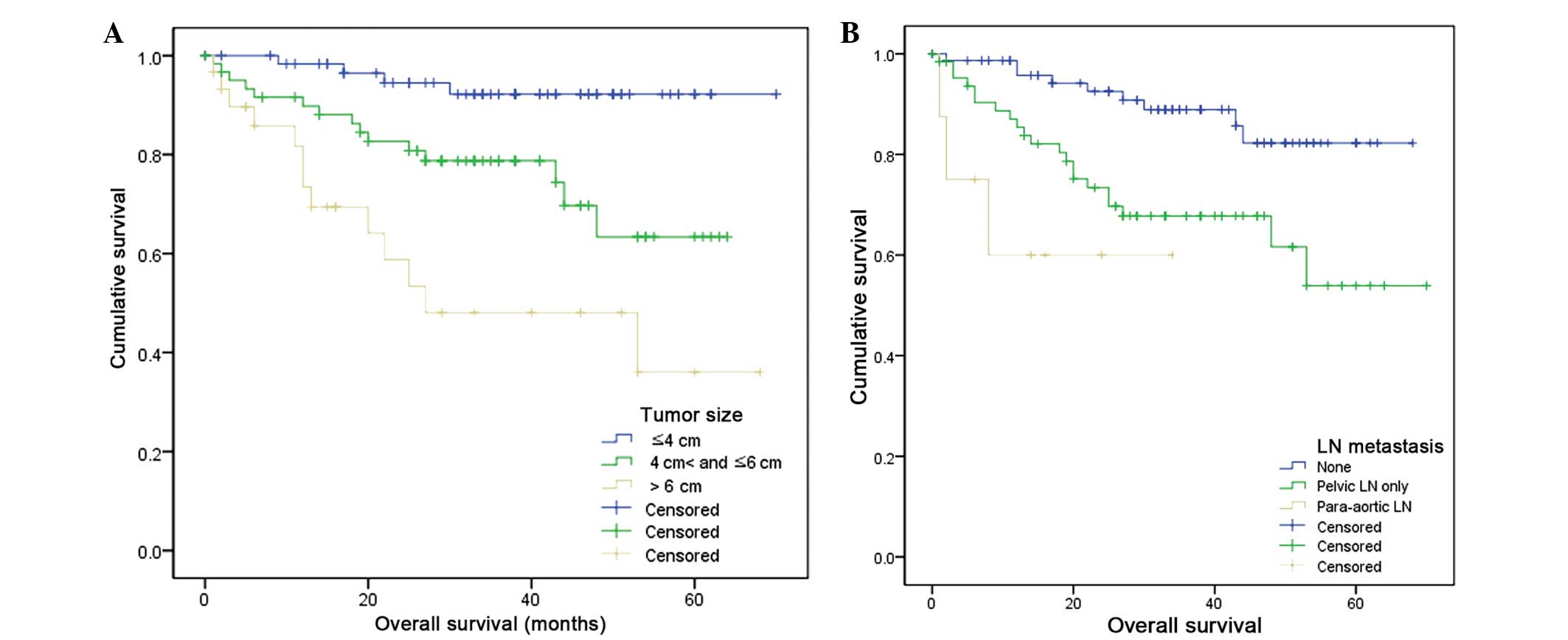
|
1
|
Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Ervik M, et al:
GLOBOCAN 2008: Cancer incidence, mortality and prevalence
worldwide. IARC Press; Lyon: 2008
|
|
2
|
Pecorelli S: Revised FIGO staging for
carcinoma of the vulva, cervix, and endometrium. Int J Gynaecol
Obstet. 105:103–104. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Lilic V, Lilic G, Filipovic S, Milosevic
J, Tasic M and Stojilijkovic M: Modern treatment of invasive
carcinoma of the uterine cervix. J BUON. 14:587–592.
2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Keys HM, Bundy BN, Stehman FB, et al:
Cisplatin, radiation, and adjuvant hysterectomy compared with
radiation and adjuvant hysterectomy for bulky stage IB cervical
carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 340:1154–1161. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Morris M, Eifel PJ, Lu J, et al: Pelvic
radiation with concurrent chemotherapy compared with pelvic and
para-aortic radiation for high-risk cervical cancer. N Engl J Med.
340:1137–1143. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Rose PG, Bundy BN, Watkins EB, et al:
Concurrent cisplatin-based radiotherapy and chemotherapy for
locally advanced cervical cancer. N Engl J Med. 340:1144–1153.
1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Whitney CW, Sause W, Bundy BN, et al:
Randomized comparison of fluorouracil plus cisplatin versus
hydroxyurea as an adjunct to radiation therapy in stage IIB-IVA
carcinoma of the cervix with negative para-aortic lymph nodes: a
Gynecologic Oncology Group and Southwest Oncology Group study. J
Clin Oncol. 17:1339–1348. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Kupets R and Covens A: Is the
International Federation of Gynecology and Obstetrics staging
system for cervical carcinoma able to predict survival in patients
with cervical carcinoma?: an assessment of clinimetric properties.
Cancer. 92:796–804. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Noguchi H, Shiozawa I, Sakai Y, Yamazaki T
and Fukuta T: Pelvic lymph node metastasis of uterine cervical
cancer. Gynecol Oncol. 27:150–158. 1987. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Avall-Lundqvist EH, Sjövall K, Nilsson BR
and Eneroth PH: Prognostic significance of pretreatment serum
levels of squamous cell carcinoma antigen and CA 125 in cervical
carcinoma. Eur J Cancer. 28A:1695–1702. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Rutledge FN, Mitchell MF, Munsell M, Bass
S, McGuffee V and Atkinson EN: Youth as a prognostic factor in
carcinoma of the cervix: a matched analysis. Gynecol Oncol.
44:123–130. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Kosary CL: FIGO stage, histology,
histologic grade, age and race as prognostic factors in determining
survival for cancers of the female gynecological system: an
analysis of 1973–87 SEER cases of cancers of the endometrium,
cervix, ovary, vulva, and vagina. Semin Surg Oncol. 10:31–46. 1994.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Brewster WR, DiSaia PJ, Monk BJ, Ziogas A,
Yamada SD and Anton-Culver H: Young age as a prognostic factor in
cervical cancer: results of a population-based study. Am J Obstet
Gynecol. 180:1464–1467. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Ishikawa H, Nakanishi T, Inoue T and
Kuzuya K: Prognostic factors of adenocarcinoma of the uterine
cervix. Gynecol Oncol. 73:42–46. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Wagenaar HC, Trimbos JB, Postema S, et al:
Tumor diameter and volume assessed by magnetic resonance imaging in
the prediction of outcome for invasive cervical cancer. Gynecol
Oncol. 82:474–482. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Miller TR and Grigsby PW: Measurement of
tumor volume by PET to evaluate prognosis in patients with advanced
cervical cancer treated by radiation therapy. Int J Radiat Oncol
Biol Phys. 53:353–359. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Tseng JY, Yen MS, Twu NF, et al:
Prognostic nomogram for overall survival in stage IIB-IVA cervical
cancer patients treated with concurrent chemoradiotherapy. Am J
Obstet Gynecol. 202:174. e171–177. 2010.
|
|
18
|
Van Nagell JR Jr, Roddick JW Jr and Lowin
DM: The staging of cervical cancer: inevitable discrepancies
between clinical staging and pathologic findinges. Am J Obstet
Gynecol. 110:973–978. 1971.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Averette HE, Ford JH Jr, Dudan RC,
Girtanner RE, Hoskins WJ and Lutz MH: Staging of cervical cancer.
Clin Obstet Gynecol. 18:215–232. 1975. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Lagasse LD, Creasman WT, Shingleton HM,
Ford JH and Blessing JA: Results and complications of operative
staging in cervical cancer: experience of the Gynecologic Oncology
Group. Gynecol Oncol. 9:90–98. 1980. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Seo Y, Yoo SY, Kim MS, et al: Nomogram
prediction of overall survival after curative irradiation for
uterine cervical cancer. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 79:782–787.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Behtash N, Karimi Zarchi M and Deldar M:
Preoperative prognostic factors and effects of adjuvant therapy on
outcomes of early stage cervical cancer in Iran. Asian Pac J Cancer
Prev. 10:613–618. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Angioli R, Plotti F, Montera R, et al:
Neoadjuvant chemotherapy plus radical surgery followed by
chemotherapy in locally advanced cervical cancer. Gynecol Oncol.
127:290–296. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Lapitan MC and Buckley BS: Impact of
palliative urinary diversion by percutaneous nephrostomy drainage
and ureteral stenting among patients with advanced cervical cancer
and obstructive uropathy: a prospective cohort. J Obstet Gynaecol
Res. 37:1061–1070. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Sardi JE, Giaroli A, Sananes C, et al:
Long-term follow-up of the first randomized trial using neoadjuvant
chemotherapy in stage Ib squamous carcinoma of the cervix: the
final results. Gynecol Oncol. 67:61–69. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Harima Y, Sawada S, Nagata K, Sougawa M
and Ohnishi T: Human papilloma virus (HPV) DNA associated with
prognosis of cervical cancer after radiotherapy. Int J Radiat Oncol
Biol Phys. 52:1345–1351. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Riou G, Favre M, Jeannel D, Bourhis J, Le
Doussal V and Orth G: Association between poor prognosis in
early-stage invasive cervical carcinomas and non-detection of HPV
DNA. Lancet. 335:1171–1174. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Higgins GD, Davy M, Roder D, Uzelin DM,
Phillips GE and Burrell CJ: Increased age and mortality associated
with cervical carcinomas negative for human papillomavirus RNA.
Lancet. 338:910–913. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Ikenberg H, Sauerbrei W, Schottmüller U,
Spitz C and Pfleiderer A: Human papillomavirus DNA in cervical
carcinoma - correlation with clinical data and influence on
prognosis. Int J Cancer. 59:322–326. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Rose BR, Thompson CH, Cossart YE, Elliot
PE and Tattersall MH: Papillomavirus DNA and prognosis in cervical
cancer. Lancet. 337:4891991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Lombard I, Vincent-Salomon A, Validire P,
et al: Human papillomavirus genotype as a major determinant of the
course of cervical cancer. J Clin Oncol. 16:2613–2619.
1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Burger RA, Monk BJ, Kurosaki T, et al:
Human papillomavirus type 18: association with poor prognosis in
early stage cervical cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst. 88:1361–1368.
1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Nakanishi T, Ishikawa H, Suzuki Y, Inoue
T, Nakamura S and Kuzuya K: A comparison of prognoses of pathologic
stage Ib adenocarcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma of the uterine
cervix. Gynecol Oncol. 79:289–293. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Eifel PJ, Burke TW, Morris M and Smith TL:
Adenocarcinoma as an independent risk factor for disease recurrence
in patients with stage IB cervical carcinoma. Gynecol Oncol.
59:38–44. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Sigurdsson K, Hrafnkelsson J, Geirsson G,
Gudmundsson J and Salvarsdóttir A: Screening as a prognostic factor
in cervical cancer: analysis of survival and prognostic factors
based on Icelandic population data, 1964–1988. Gynecol Oncol.
43:64–70. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Hricak H, Gatsonis C, Chi DS, et al:
American College of Radiology Imaging Network 6651; Gynecologic
Oncology Group 183: Role of imaging in pretreatment evaluation of
early invasive cervical cancer: results of the intergroup study
American College of Radiology Imaging Network 6651 - Gynecologic
Oncology Group 183. J Clin Oncol. 23:9329–9337. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Subak LL, Hricak H, Powell CB, Azizi L and
Stern JL: Cervical carcinoma: computed tomography and magnetic
resonance imaging for preoperative staging. Obstet Gynecol.
86:43–50. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Gadducci A, Tana R, Cosio S and Genazzani
AR: The serum assay of tumour markers in the prognostic evaluation,
treatment monitoring and follow-up of patients with cervical
cancer: a review of the literature. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol.
66:10–20. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Takeda M, Sakuragi N, Okamoto K, et al:
Preoperative serum SCC, CA125, and CA19-9 levels and lymph node
status in squamous cell carcinoma of the uterine cervix. Acta
Obstet Gynecol Scand. 81:451–457. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Kapp DS, Fischer D, Gutierrez E, Kohorn EI
and Schwartz PE: Pretreatment prognostic factors in carcinoma of
the uterine cervix: a multivariable analysis of the effect of age,
stage, histology and blood counts on survival. Int J Radiat Oncol
Biol Phys. 9:445–455. 1983. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Boss EA, Barentsz JO, Massuger LF and
Boonstra H: The role of MR imaging in invasive cervical carcinoma.
Eur Radiol. 10:256–270. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Kidd EA, El Naqa I, Siegel BA, Dehdashti F
and Grigsby PW: FDG-PET-based prognostic nomograms for locally
advanced cervical cancer. Gynecol Oncol. 127:136–140. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|