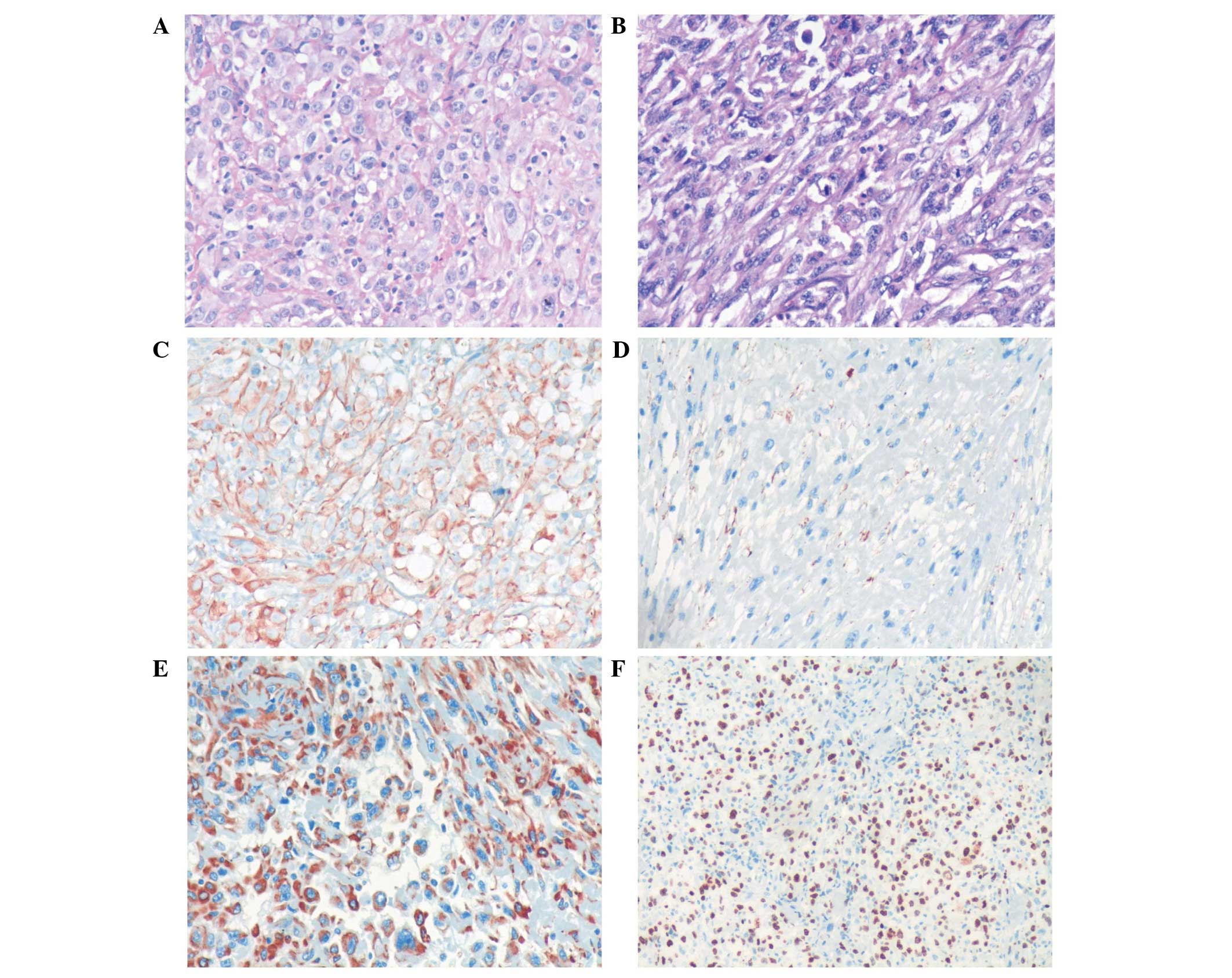
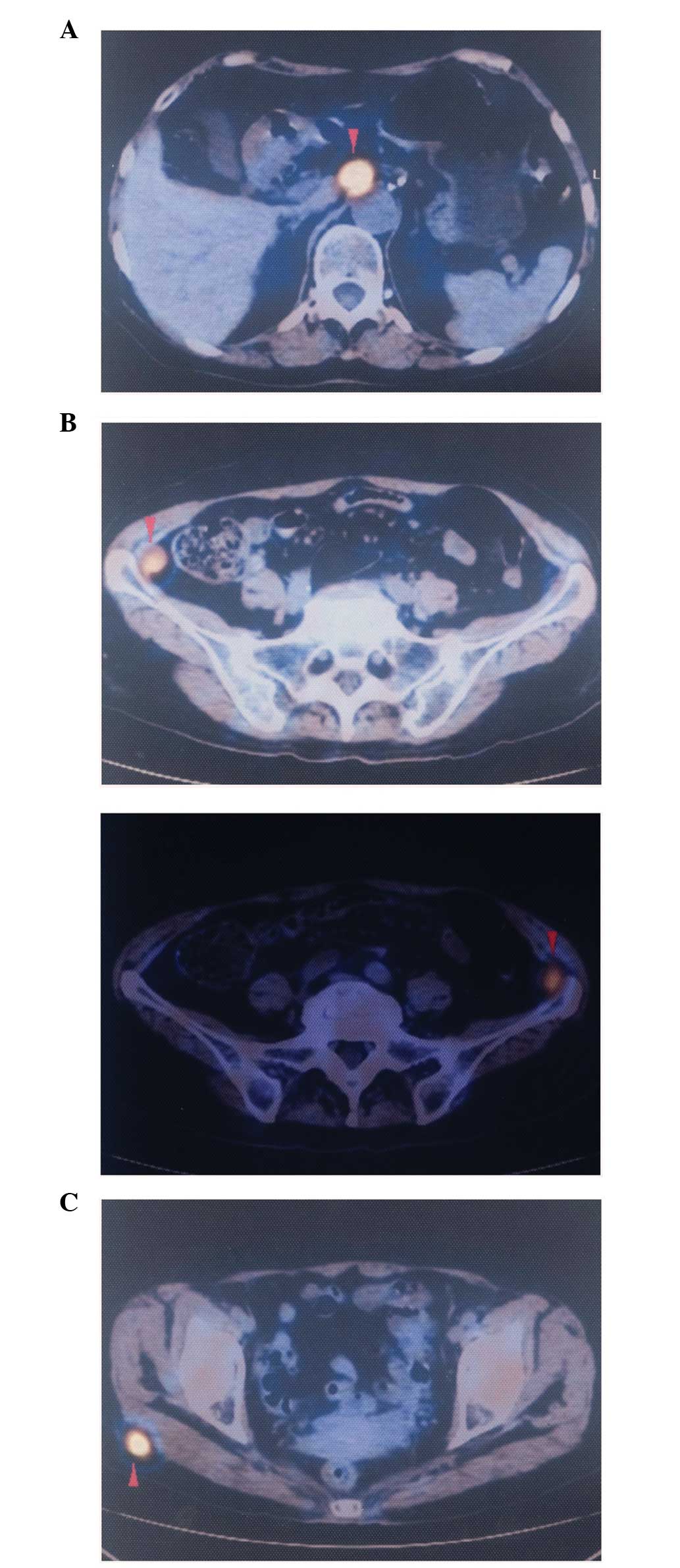
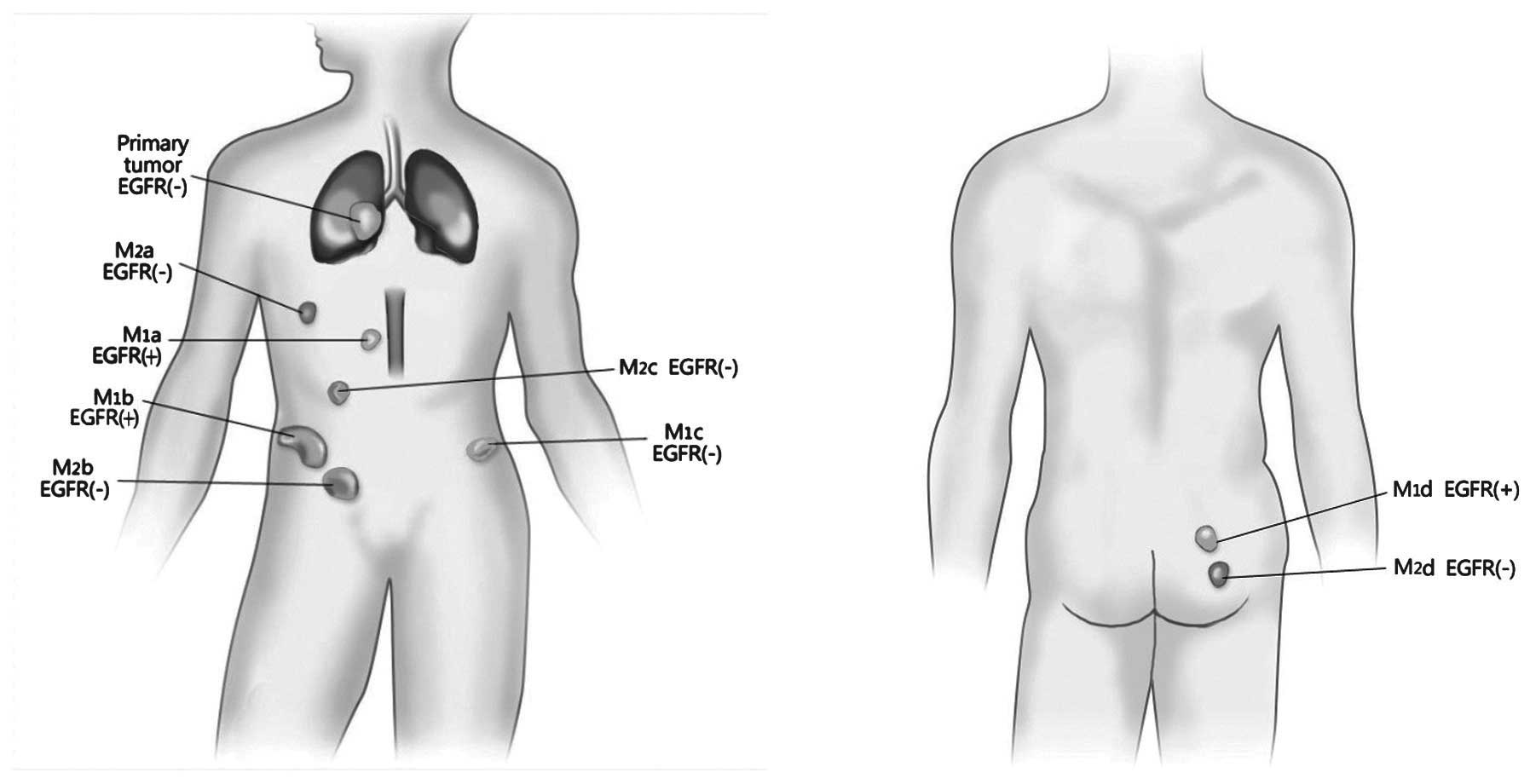
|
1
|
Park JS, Lee Y, Han J, et al:
Clinicopathologic outcomes of curative resection for sarcomatoid
carcinoma of the lung. Oncology. 11:206–213. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Zhou Z, Jiang GN, Yang TS, et al: Analysis
for the prognosis of patients with pulmonary carcinosarcoma. Zhong
Guo Ai Zheng Za Zhi. 20:59–61. 2010.
|
|
3
|
Fishback NF, Travis WD, Moran CA, et al:
Pleomorphic (spindle/giant cell) carcinoma of the lung. A
clinicopathologic correlation of 78 cases. Cancer. 73:2936–2945.
1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Nakajima M, Kasai T, Hashimoto H, et al:
Sarcomatoid carcinoma of the lung: a clinicopathologic study of 37
cases. Cancer. 86:608–616. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Beasley MB, Brambilla E and Travis WD: The
2004 World Health Organization classification of lung tumors. Semin
Roentgenol. 40:90–97. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Venissac N, Pop D, Lassalle S, et al:
Sarcomatoid lung cancer (spindle/giant cells): an aggressive
disease? J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 134:619–623. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Brambilla E, Travis WD, Colby TV, Corrin B
and Shimosato Y: The new World Health Organization classification
of lung tumours. Eur Respir J. 18:1059–1068. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Homman T, Doki Y, Tsuda M, et al:
Uncontrollable midbrain hemorrhage due to brain metastasis of
pulmonary pleomorphic carcinoma. Kyobu Geka. 61:335–339. 2008.[(In
Japanese)]. PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Petrov DB, Vlassov VI, Kalaydjiev GT,
Plochev MA, Obretenov ED, Stanoev VI and Danon SE: Primary
pulmonary sarcomas and carcinosarcomas - postoperative results and
comparative survival analysis. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 23:461–466.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Shi YK: NCCN clinical practice guidelines
in non-small cell lung cancer V.2.2008. Zhong Hua Zhong Liu Za Zhi.
30:397–400. 2008.
|
|
11
|
Italiano A, Cortot AB, Ilie M, et al: EGFR
and KRAS status of primary sarcomatoid carcinomas of the lung:
implications for anti-EGFR treatment of a rare lung malignancy. Int
J Cancer. 125:2479–2482. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Leone A, Graziano P, Gasbarra R, et al:
Identification of EGFR mutations in lung sarcomatoid carcinoma. Int
J Cancer. 128:732–735. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Ushiki A, Koizumi T, Kobayashi N, et al:
Genetic heterogeneity of EGFR mutation in pleomorphic carcinoma of
the lung: response to gefitinib and clinical outcome. Jpn J Clin
Oncol. 39:267–270. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Taniguchi K, Okami J, Kodama K, et al:
Intratumor heterogeneity of epidermal growth factor receptor
mutations in lung cancer and its correlation to the response to
gefitinib. Cancer Sci. 99:929–935. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Tomonaga N, Nakamura Y, Yamaguchi H, et
al: Analysis of intratumor heterogeneity of EGFR mutations in
mixed-type lung adenocarcinoma. Clin Lung Cancer. 14:521–526. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Gow CH, Chang YL, Hsu YC, et al:
Comparison of epidermal growth factor receptor mutations between
primary and corresponding metastatic tumors in tyrosine kinase
inhibitor-naive non-small-cell lung cancer. Ann Oncol. 20:696–702.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Schmid K, Oehl N, Wrba F, et al:
EGFR/KRAS/BRAF mutations in primary lung adenocarcinomas and
corresponding locoregional lymph node metastases. Clin Cancer Res.
15:4554–4560. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Sun L, Zhang Q, Luan H, et al: Comparison
of KRAS and EGFR gene status between primary non-small cell lung
cancer and local lymph node metastases: implications for clinical
practice. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 30:302011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Fang Q, Zhang L, Wang S and Ou W:
Discordance of epidermal growth factor receptor mutations between
primary and corresponding metastatic tumors in non-small cell lung
cancer. Zhongguo Fei Ai Za Zhi. 14:518–522. 2011.[(In Chinese)].
PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Gerlinger M, Rowan AJ, Horswell S, et al:
Intratumor heterogeneity and branched evolution revealed by
multiregion sequencing. N Engl J Med. 366:883–892. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Sequist LV, Waltman BA, Dias-Santagata D,
et al: Genotypic and histological evolution of lung cancers
acquiring resistance to EGFR inhibitors. Sci Transl Med.
3:75ra262011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|