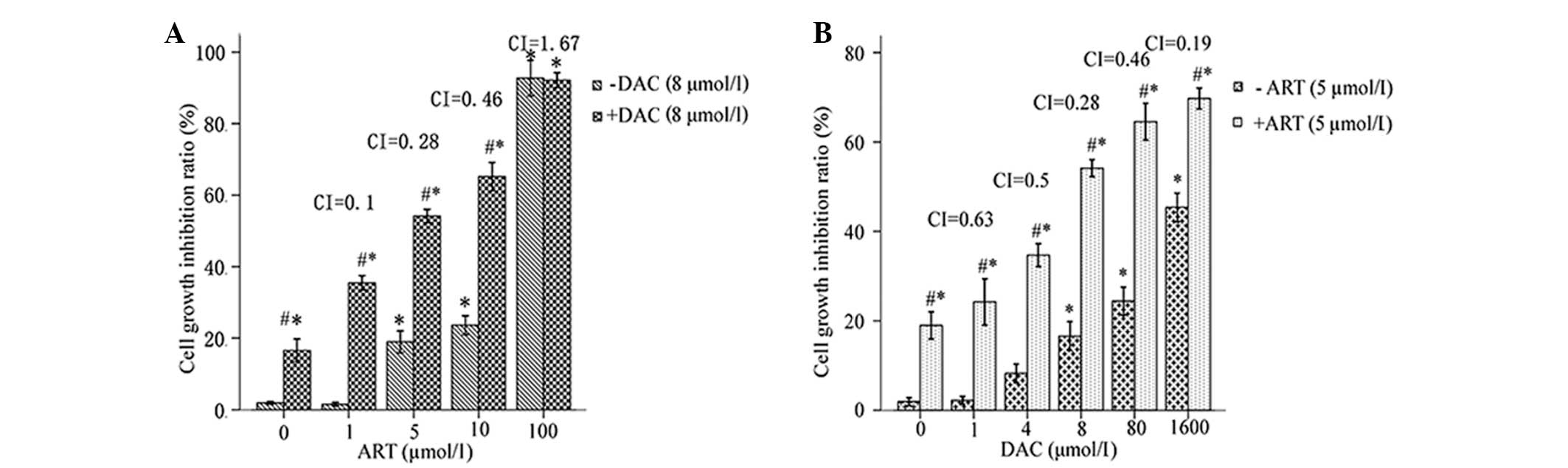
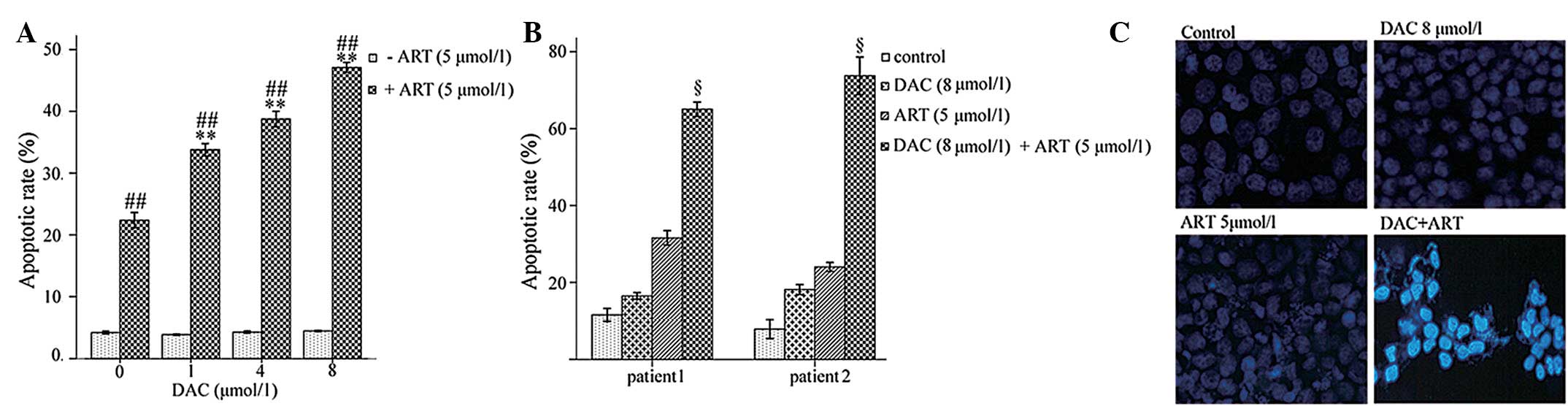
|
1
|
Fenaux P, Mufti GJ, Hellstrom-Lindberg E,
et al: Efficacy of azacitidine compared with that of conventional
care regimens in the treatment of higher-risk myelodysplastic
syndromes: a randomised, open-label, phase III study. Lancet Oncol.
10:223–232. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Stankov K, Bogdanovic G, Kojic V, et al:
Expression analysis of genes involved in epigenetic regulation and
apoptosis in human malignant haematopoietic cell lines treated with
5-azacytidine. J BUON. 16:116–122. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Saunthararajah Y, Triozzi P, Rini B, et
al: p53-independent, normal stem cell sparing epigenetic
differentiation therapy for myeloid and other malignancies. Semin
Oncol. 39:97–108. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Lin J, Yao DM, Qian J, et al: Recurrent
DNMT3A R882 mutations in Chinese patients with acute myeloid
leukemia and myelodysplastic syndrome. PLoS One. 6:e269062011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Walter MJ, Ding L, Shen D, et al:
Recurrent DNMT3A mutations in patients with myelodysplastic
syndromes. Leukemia. 25:1153–1158. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Shih AH, Abdel-Wahab O, Patel JP and
Levine RL: The role of mutations in epigenetic regulators in
myeloid malignancies. Nat Rev Cancer. 12:599–612. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Faderl S, Garcia-Manero G, Jabbour E, et
al: A randomized study of 2 dose levels of intravenous clofarabine
in the treatment of patients with higher-risk myelodysplastic
syndrome. Cancer. 118:722–728. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Piekarz RL and Bates SE: Epigenetic
modifiers: basic understanding and clinical development. Clin
Cancer Res. 15:3918–3926. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Cheng JC, Matsen CB, Gonzales FA, et al:
Inhibition of DNA methylation and reactivation of silenced genes by
zebularine. J Natl Cancer Inst. 95:399–409. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Robak T: New nucleoside analogs for
patients with hematological malignancies. Expert Opin Investig
Drugs. 20:343–359. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Flotho C, Claus R, Batz C, et al: The DNA
methyltransferase inhibitors azacitidine, decitabine and zebularine
exert differential effects on cancer gene expression in acute
myeloid leukemia cells. Leukemia. 23:1019–1028. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Gotze K, Platzbecker U, Giagounidis A, et
al: Azacitidine for treatment of patients with myelodysplastic
syndromes (MDS): practical recommendations of the German MDS Study
Group. Ann Hematol. 89:841–850. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Klisovic RB, Stock W, Cataland S, et al: A
phase I biological study of MG98, an oligodeoxynucleotide antisense
to DNA methyltransferase 1, in patients with high-risk
myelodysplasia and acute myeloid leukemia. Clin Cancer Res.
14:2444–2449. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Yang X, Lay F, Han H and Jones PA:
Targeting DNA methylation for epigenetic therapy. Trends Pharmacol
Sci. 31:536–546. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Qin T, Castoro R, El Ahdab S, et al:
Mechanisms of resistance to decitabine in the myelodysplastic
syndrome. PLoS One. 6:e233722011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Efferth T, Giaisi M, Merling A, Krammer PH
and Li-Weber M: Artesunate induces ROS-mediated apoptosis in
doxorubicin-resistant T leukemia cells. PLoS One. 2:e6932007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Mercer AE, Copple IM, Maggs JL, O'Neill PM
and Park BK: The role of heme and the mitochondrion in the chemical
and molecular mechanisms of mammalian cell death induced by the
artemisinin antimalarials. J Biol Chem. 286:987–996. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Kondo A, Yamashita T, Tamura H, et al:
Interferon-gamma and tumor necrosis factor-alpha induce an
immunoinhibitory molecule, B7-H1, via nuclear factor-kappaB
activation in blasts in myelodysplastic syndromes. Blood.
116:1124–1131. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Thanaketpaisarn O, Waiwut P, Sakurai H and
Saiki I: Artesunate enhances TRAIL-induced apoptosis in human
cervical carcinoma cells through inhibition of the NF-ĸB and
PI3K/Akt signaling pathways. Int J Oncol. 39:279–285.
2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Chou TC and Talalay P: Analysis of
combined drug effects: a new look at a very old problem. Trends
Phamacol Sci. 4:450–454. 1983. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Chen H, Shi L, Yang X, Li S, Guo X and Pan
L: Artesunate inhibiting angiogenesis induced by human myeloma
RPMI8226 cells. Int J Hematol. 92:587–597. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Wang Y, Han Y, Yang Y, et al: Effect of
interaction of magnetic nanoparticles of
Fe3O4 and artesunate on apoptosis of K562
cells. Int J Nanomedicine. 6:1185–1192. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|