|
1
|
Jemal A, Siegel R, Xu J and Ward E: Cancer
statistics, 2010. CA Cancer J Clin. 60:277–300. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Steeg PS: Metastasis suppressors alter the
signal transduction of cancer cells. Nat Rev Cancer. 3:55–63. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Winter J, Jung S, Keller S, Gregory RI and
Diederichs S: Many roads to maturity: microRNA biogenesis pathways
and their regulation. Nat Cell Biol. 11:228–234. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Esquela-Kerscher A and Slack FJ: Oncomirs
- microRNAs with a role in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 6:259–269. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Place RF, Li LC, Pookot D, Noonan EJ and
Dahiya R: MicroRNA- 373 induces expression of genes with
complementary promoter sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
105:1608–1613. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Lim LP, Lau NC, Garrett-Engele P, Grimson
A, Schelter JM, Castle J, Bartel DP, Linsley PS and Johnson JM:
Microarray analysis shows that some microRNAs downregulate large
numbers of target mRNAs. Nature. 433:769–773. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Dalmay T and Edwards DR: MicroRNAs and the
hallmarks of cancer. Oncogene. 25:6170–6175. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Fish JE, Santoro MM, Morton SU, Yu S, Yeh
RF, Wythe JD, Ivey KN, Bruneau BG, Stainier DY and Srivastava D:
miR-126 regulates angiogenic signaling and vascular integrity. Dev
Cell. 15:272–284. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Wang S, Aurora AB, Johnson BA, Qi X,
McAnally J, Hill JA, Richardson JA, Bassel-Duby R and Olson EN: The
endothelial-specific microRNA miR-126 governs vascular integrity
and angiogenesis. Dev Cell. 15:261–271. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Tavazoie SF, Alarcón C, Oskarsson T, Padua
D, Wang Q, Bos PD, Gerald WL and Massagué J: Endogenous human
microRNAs that suppress breast cancer metastasis. Nature.
451:147–152. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Hamada S, Satoh K, Fujibuchi W, Hirota M,
Kanno A, Unno J, Masamune A, Kikuta K, Kume K and Shimosegawa T:
MiR-126 acts as a tumor suppressor in pancreatic cancer cells via
the regulation of ADAM9. Mol Cancer Res. 10:3–10. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Feng R, Chen X, Yu Y, Su L, Yu B, Li J,
Cai Q, Yan M, Liu B and Zhu Z: miR-126 functions as a tumour
suppressor in human gastric cancer. Cancer Lett. 298:50–63. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Donnem T, Fenton CG, Lonvik K, Berg T,
Eklo K, Andersen S, Stenvold H, Al-Shibli K, Al-Saad S, Bremnes RM
and Busund LT: MicroRNA signatures in tumor tissue related to
angiogenesis in non-small cell lung cancer. PLoS One. 7:e296712012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Jiao LR, Frampton AE, Jacob J, Pellegrino
L, Krell J, Giamas G, Tsim N, Vlavianos P, Cohen P, Ahmad R, Keller
A, Habib NA, Stebbing J and Castellano L: MicroRNAs targeting
oncogenes are down-regulated in pancreatic malignant transformation
from benign tumors. PLoS One. 7:e320682012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Miko E, Margitai Z, Czimmerer Z, Várkonyi
I, Dezso B, Lányi A, Bacsó Z and Scholtz B: miR-126 inhibits
proliferation of small cell lung cancer cells by targeting SLC7A5.
FEBS Lett. 585:1191–1196. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
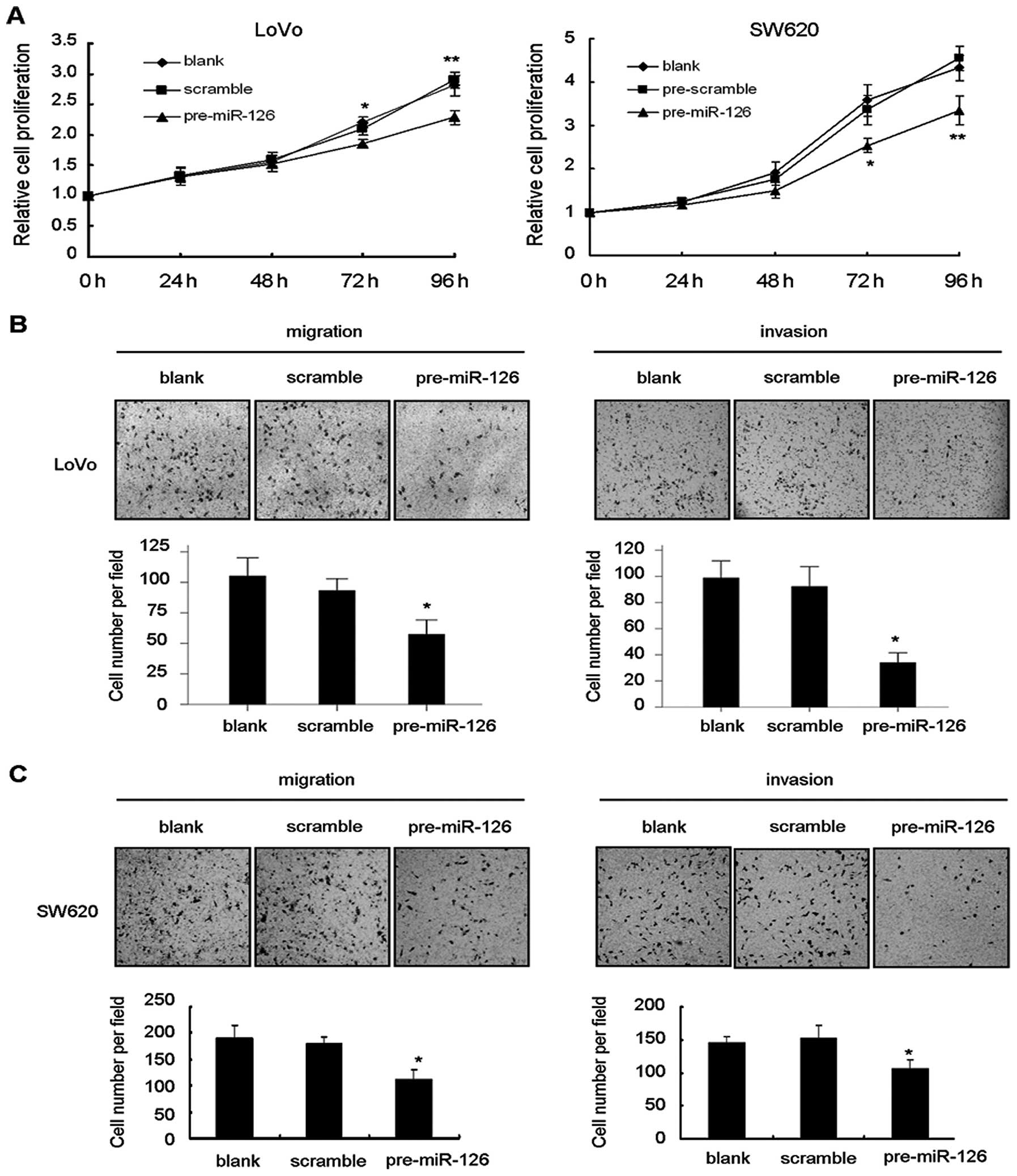
Crawford M, Brawner E, Batte K, Yu L,
Hunter MG, Otterson GA, Nuovo G, Marsh CB and Nana-Sinkam SP:
MicroRNA-126 inhibits invasion in non-small cell lung carcinoma
cell lines. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 373:607–612. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Otsubo T, Akiyama Y, Hashimoto Y, Shimada
S, Goto K and Yuasa Y: MicroRNA-126 inhibits SOX2 expression and
contributes to gastric carcinogenesis. PLoS One. 6:e166172011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Watahiki A and Wang Y, Morris J, Dennis K,
O’Dwyer HM, Gleave M, Gout PW and Wang Y: MicroRNAs associated with
metastatic prostate cancer. PLoS One. 6:e249502011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Ferrara N and Kerbel RS: Angiogenesis as a
therapeutic target. Nature. 438:967–974. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Grothey A and Galanis E: Targeting
angiogenesis: progress with anti-VEGF treatment with large
molecules. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 6:507–518. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
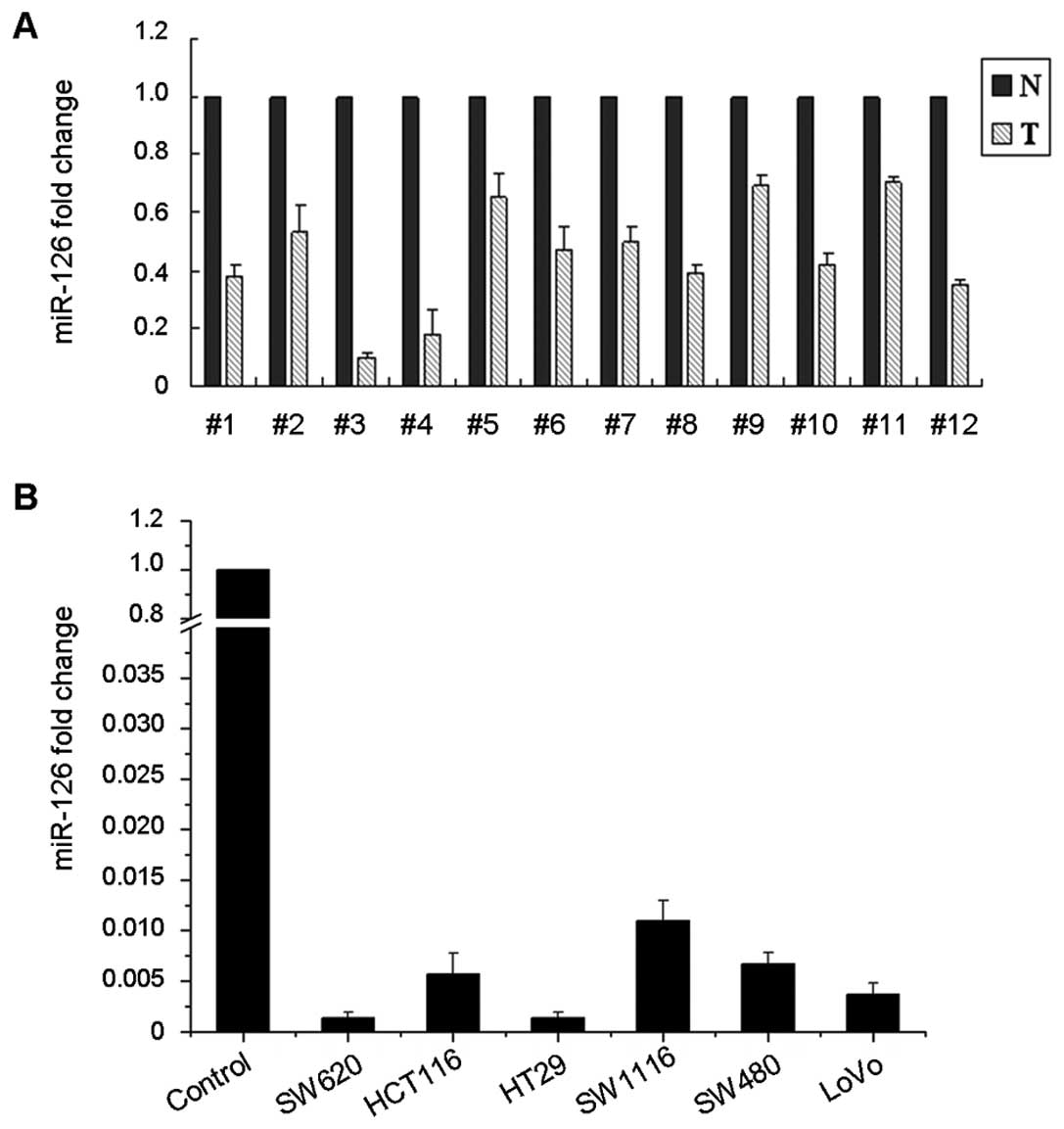
Li XM, Wang AM, Zhang J and Yi H:
Down-regulation of miR-126 expression in colorectal cancer and its
clinical significance. Med Oncol. 28:1054–1057. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Saito Y, Friedman JM, Chihara Y, Egger G,
Chuang JC and Liang G: Epigenetic therapy upregulates the tumor
suppressor microRNA-126 and its host gene EGFL7 in human
cancer cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 379:726–731. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Watanabe K, Emoto N, Hamano E, Sunohara M,
Kawakami M, Kage H, Kitano K, Nakajima J, Goto A, Fukayama M,
Nagase T, Yatomi Y, Ohishi N and Takai D: Genome structure-based
screening identified epigenetically silenced microRNA associated
with invasiveness in non-small-cell lung cancer. Int J Cancer.
130:2580–2590. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Roccaro AM, Hideshima T, Raje N, Kumar S,
Ishitsuka K, Yasui H, Shiraish N, Ribatti D, Nico B, Vacca A,
Dammacco F, Richardson PG and Anderson KC: Bortezomib mediates
antiangiogenesis in multiple myeloma via direct and indirect
effects on endothelial cells. Cancer Res. 66:184–191. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Kloosterman WP and Plasterk RH: The
diverse functions of microRNAs in animal development and disease.
Dev Cell. 11:441–450. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Weis SM and Cheresh DA: Tumor
angiogenesis: molecular pathways and therapeutic targets. Nat Med.
17:1359–1370. 2011. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Gaziel-Sovran A, Segura MF, Di Micco R,
Collins MK, Hanniford D, Vega-Saenz de Miera E, Rakus JF, Dankert
JF, Shang S, Kerbel RS, Bhardwaj N, Shao Y, Darvishian F, Zavadil
J, Erlebacher A, Mahal LK, Osman I and Hernando E:
MiR-30b/30d regulation of GalNAc transferases enhances
invasion and immunosuppression during metastasis. Cancer Cell.
20:104–118. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Yang CH, Yue J, Pfeffer SR, Handorf CR and
Pfeffer LM: MicroRNA-21 regulates the metastatic behavior of B16
melanoma cells. J Biol Chem. 286:39172–39178. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Fang JH, Zhou HC, Zeng C, Yang J, Liu Y,
Huang X, Zhang JP, Guan XY and Zhuang SM: MicroRNA-29b suppresses
tumor angiogenesis, invasion, and metastasis by regulating matrix
metalloproteinase 2 expression. Hepatology. 54:1729–1740. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Xu Y, Zhao F, Wang Z, Song Y, Luo Y, Zhang
X, Jiang L, Sun Z, Miao Z and Xu H: MicroRNA-335 acts as a
metastasis suppressor in gastric cancer by targeting Bcl-w and
specificity protein 1. Oncogene. 31:1398–1407. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Wang S and Olson EN: AngiomiRs - key
regulators of angiogenesis. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 19:205–211. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Png KJ, Halberg N, Yoshida M and Tavazoie
SF: A microRNA regulon that mediates endothelial recruitment and
metastasis by cancer cells. Nature. 481:190–194. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
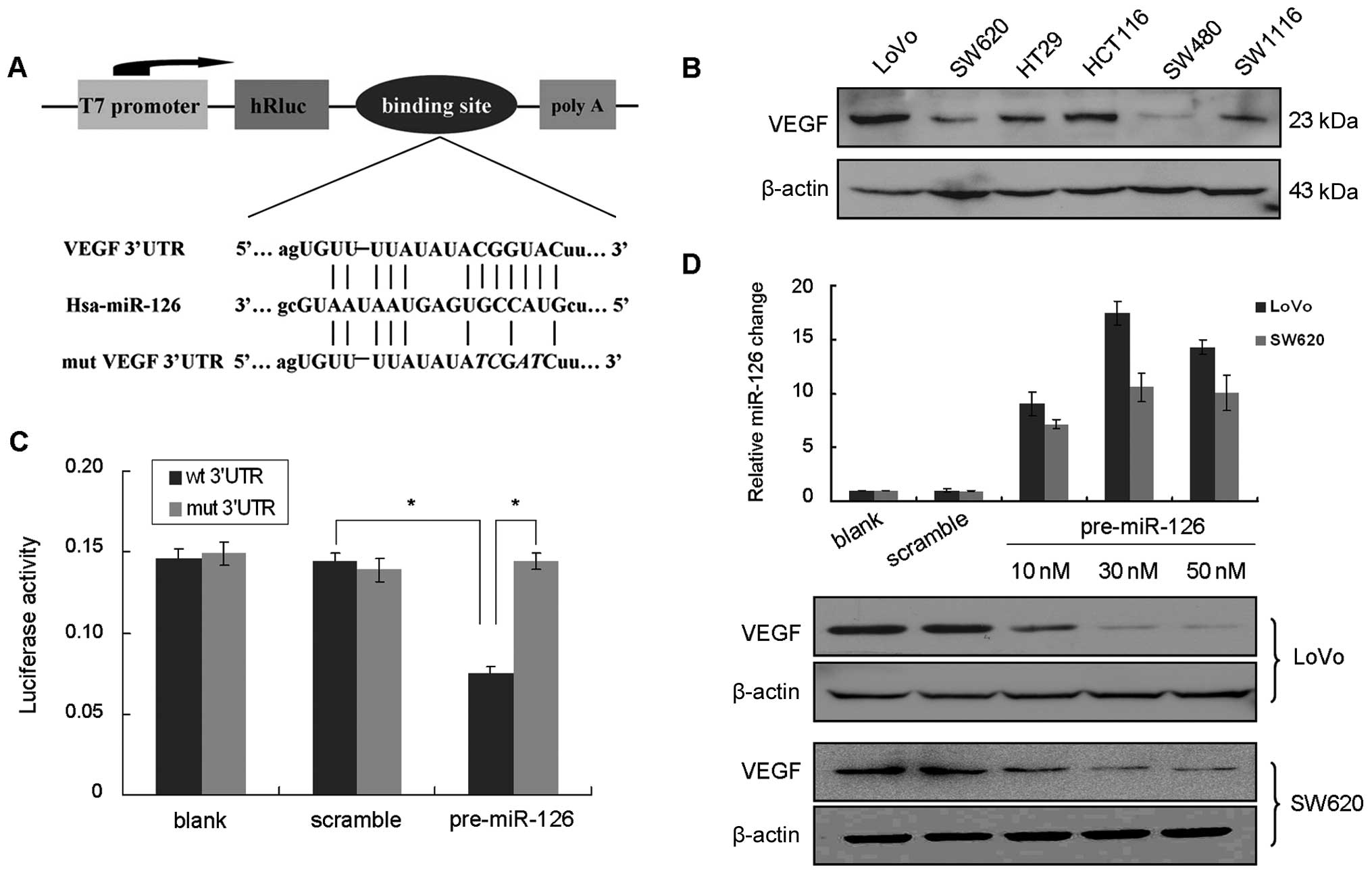
Zhu X, Li H, Long L, Hui L, Chen H, Wang
X, Shen H and Xu W: miR-126 enhances the sensitivity of non-small
cell lung cancer cells to anticancer agents by targeting vascular
endothelial growth factor A. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin. 44:519–526.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
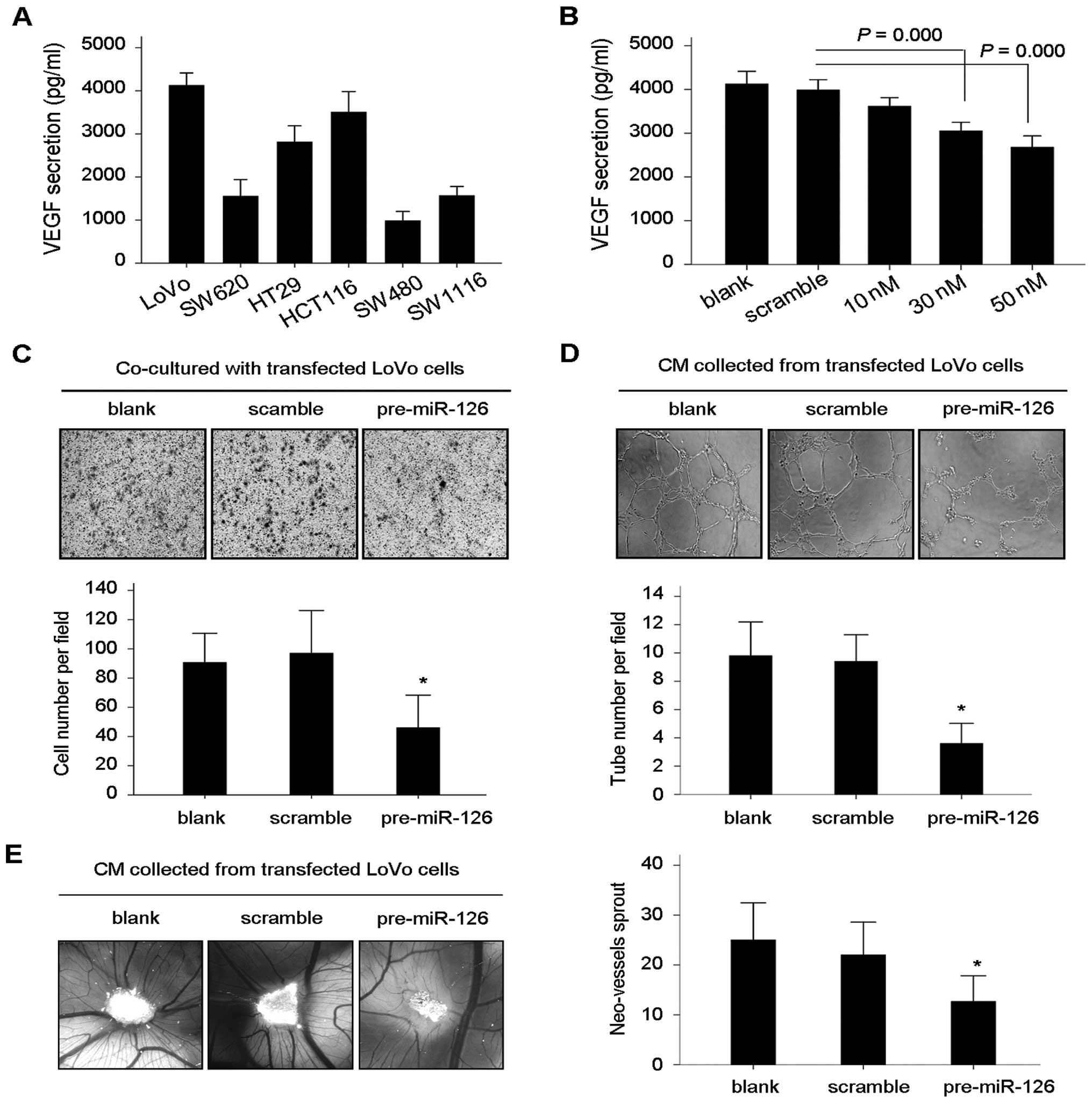
Stoeltzing O, Liu W, Reinmuth N, Parikh A,
Ahmad SA, Jung YD, Fan F and Ellis LM: Angiogenesis and
antiangiogenic therapy of colon cancer liver metastasis. Ann Surg
Oncol. 10:722–733. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Fan F, Wey JS, McCarty MF, Belcheva A, Liu
WB, Bauer TW, Somcio RJ, Wu Y, Hooper A, Hicklin DJ and Ellis LM:
Expression and function of vascular endothelial growth factor
receptor-1 on human colorectal cancer cells. Oncogene.
24:2647–2653. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Esteller M: Epigenetics in cancer. N Engl
J Med. 358:1148–1159. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Lujambio A, Calin GA, Villanueva A, Ropero
S, Sánchez-Céspedes M, Blanco D, Montuenga LM, Rossi S, Nicoloso
MS, Faller WJ, Gallagher WM, Eccles SA, Croce CM and Esteller M: A
microRNA DNA methylation signature for human cancer metastasis.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 105:13556–13561. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Toyota M, Suzuki H, Sasaki Y, Maruyama R,
Imai K, Shinomura Y and Tokino T: Epigenetic silencing of
microRNA-34b/c and B-cell translocation gene 4
is associated with CpG island methylation in colorectal cancer.
Cancer Res. 68:4123–4132. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Huang YW, Liu JC, Deatherage DE, Luo J,
Mutch DG, Goodfellow PJ, Miller DS and Huang TH: Epigenetic
repression of microRNA-129-2 leads to overexpression of SOX4
oncogene in endometrial cancer. Cancer Res. 69:9038–9046. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Saito Y and Jones PA: Epigenetic
activation of tumor suppressor microRNAs in human cancer cells.
Cell Cycle. 5:2220–2222. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Nguyen DX, Bos PD and Massagué J:
Metastasis: from dissemination to organ-specific colonization. Nat
Rev Cancer. 9:274–284. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Hurst DR, Edmonds MD and Welch DR:
Metastamir: the field of metastasis-regulatory microRNA is
spreading. Cancer Res. 69:7495–7498. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Wang P, Zou F, Zhang X, Li H, Dulak A,
Tomko RJ Jr, Lazo JS, Wang Z, Zhang L and Yu J: microRNA-21
negatively regulates Cdc25A and cell cycle progression in colon
cancer cells. Cancer Res. 69:8157–8165. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Asangani IA, Rasheed SA, Nikolova SA,
Leupold JH, Colburn NH, Post S and Allgayer H: MicroRNA-21 (miR-21)
post-transcriptionally downregulates tumor suppressor Pdcd4 and
stimulates invasion, intravasation and metastasis in colorectal
cancer. Oncogene. 27:2128–2136. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Gregory PA, Bert AG, Paterson EL, Barry
SC, Tsykin A, Farshid G, Vadas MA, Khew-Goodall Y and Goodall GJ:
The miR-200 family and miR-205 regulate epithelial to mesenchymal
transition by targeting ZEB1 and SIP1. Nat Cell Biol. 10:593–601.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|