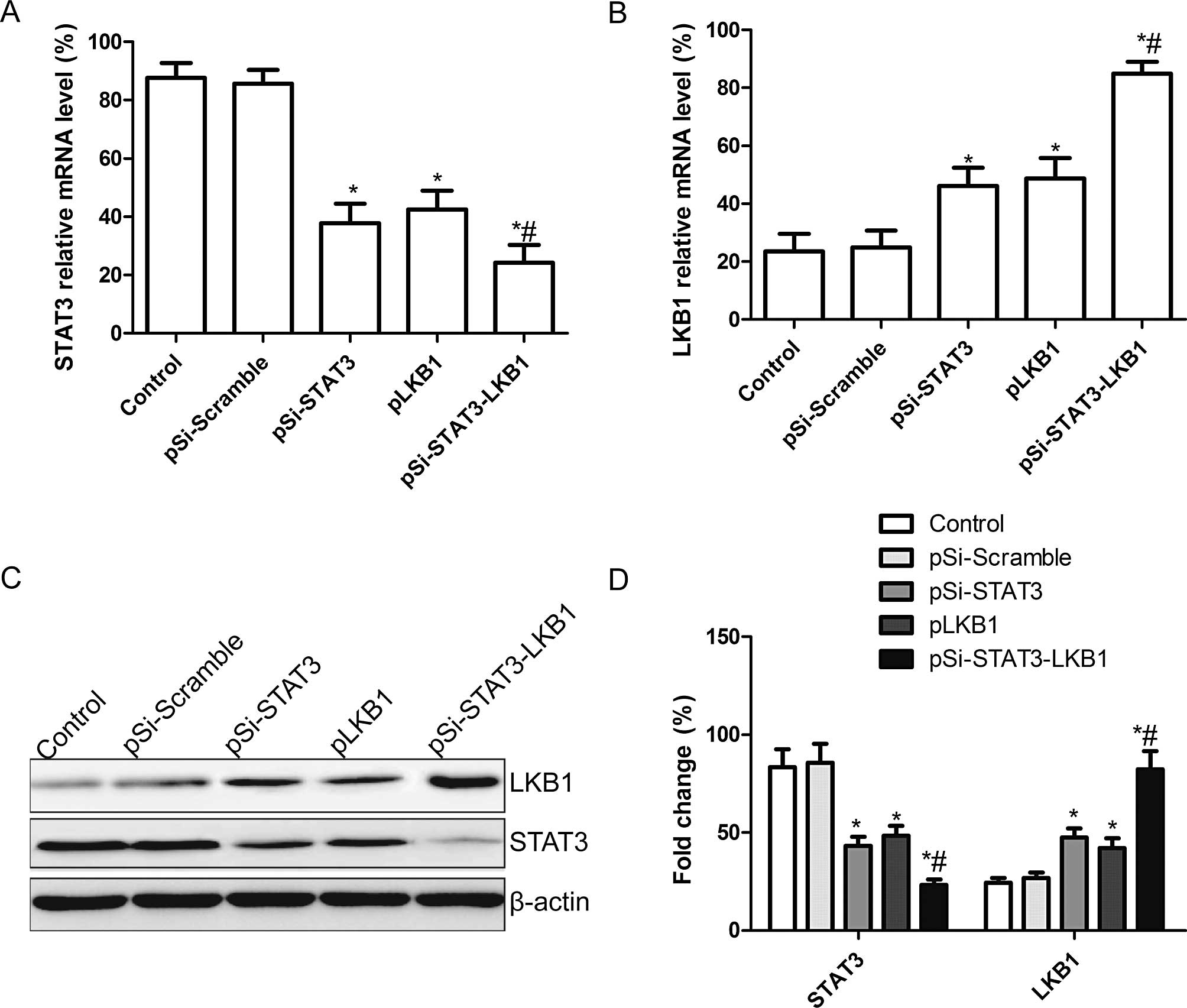
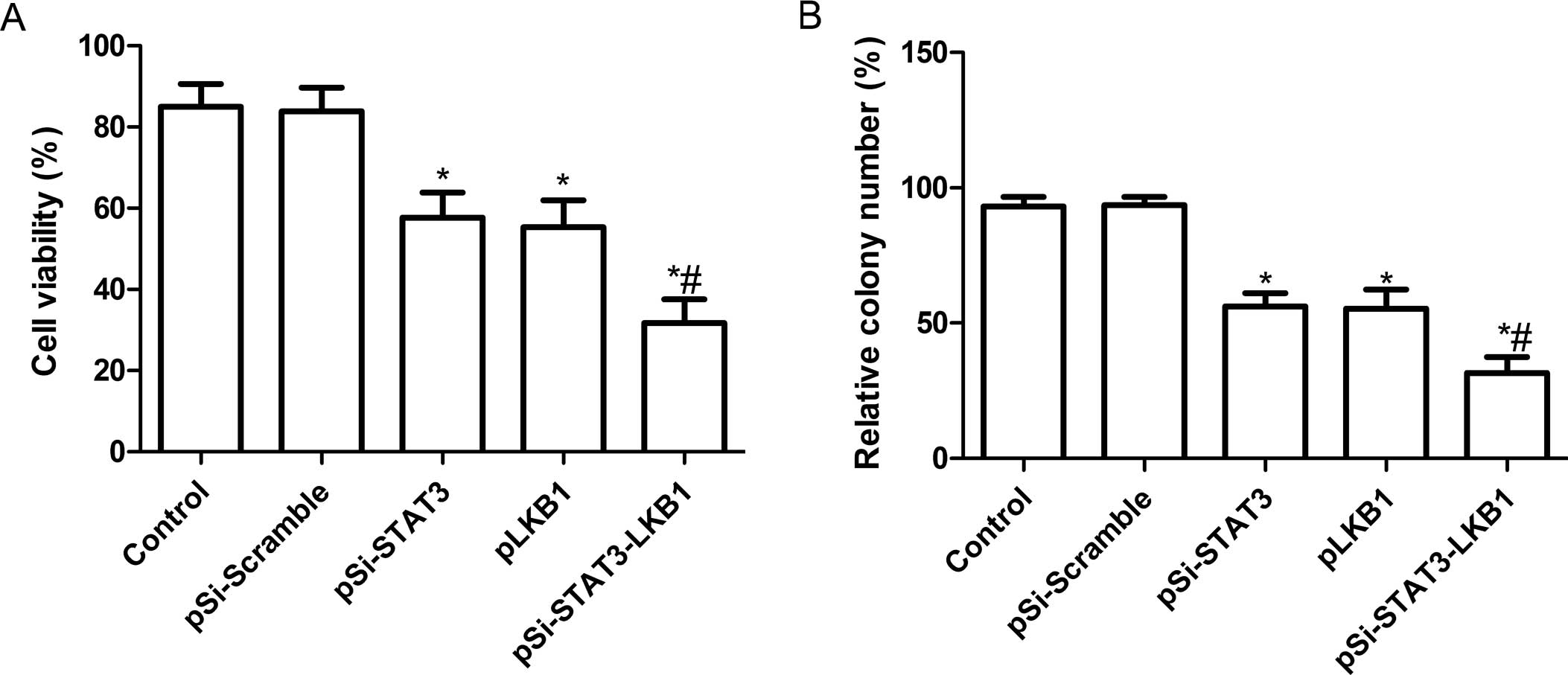
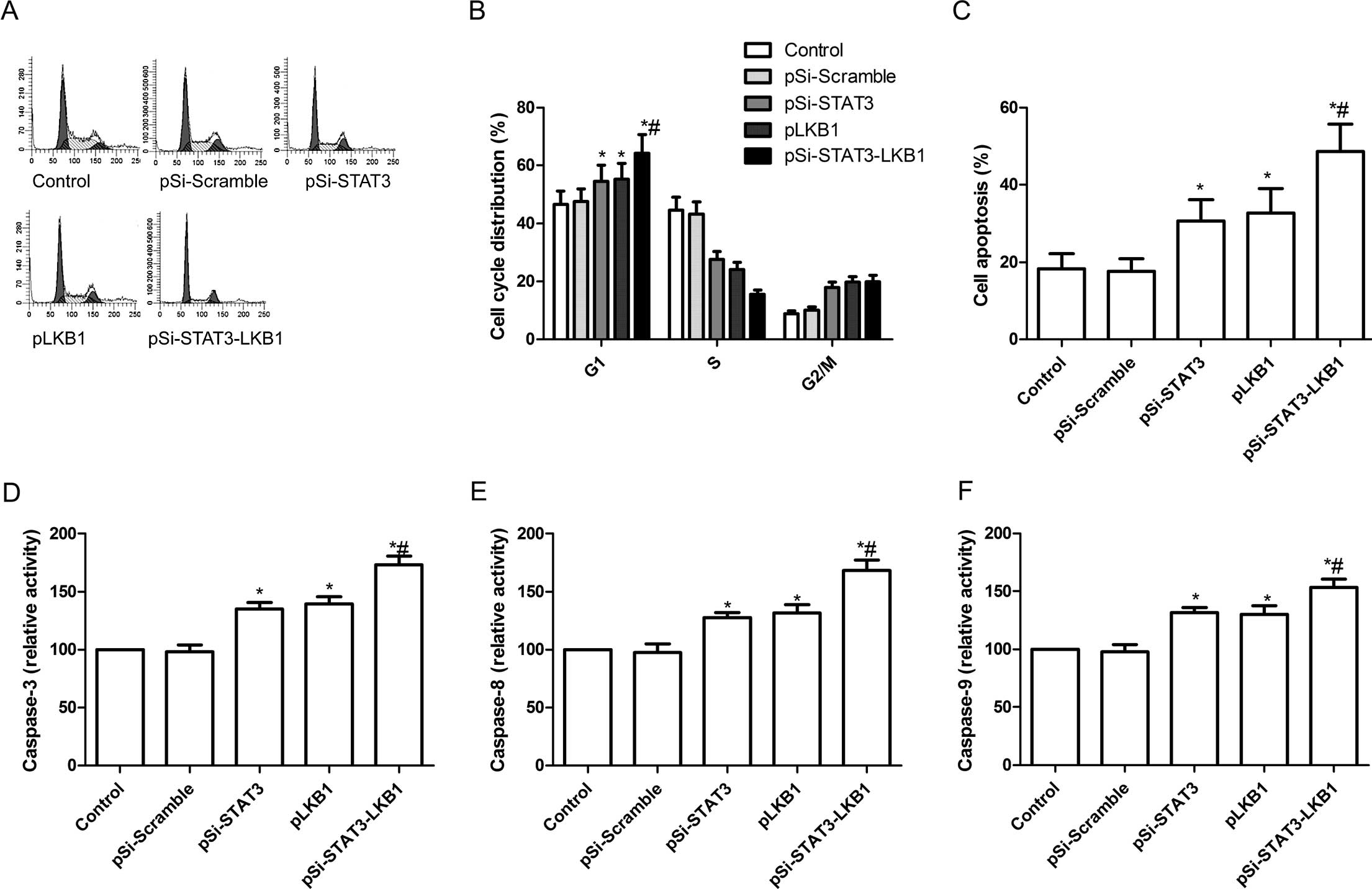
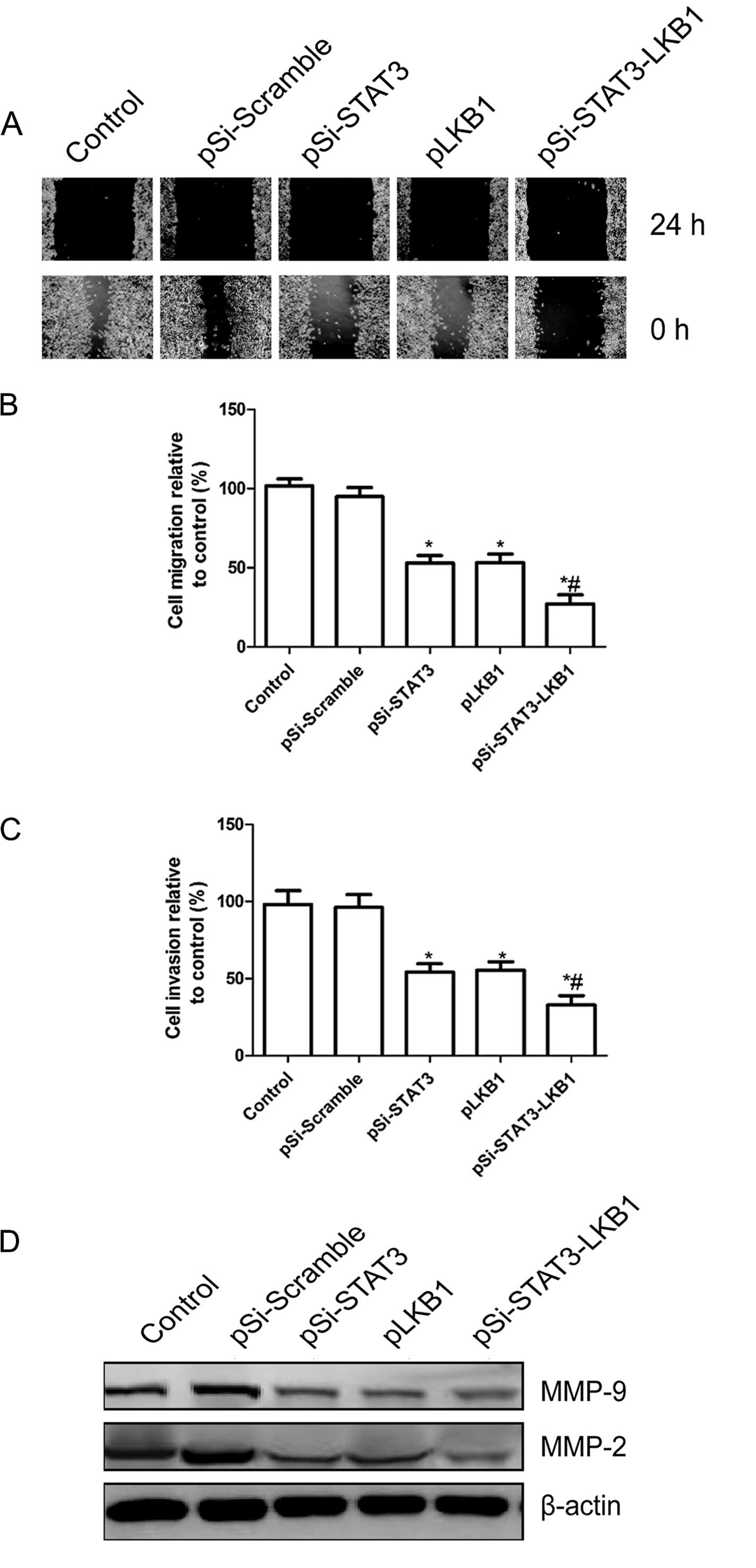
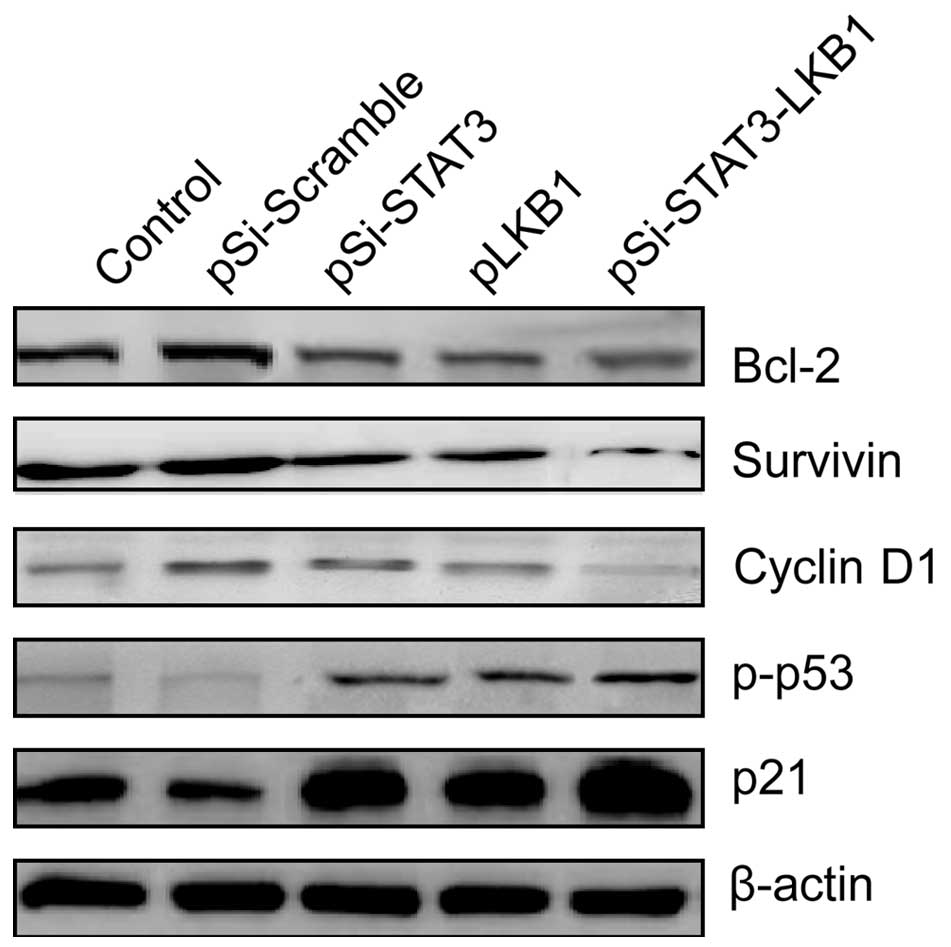
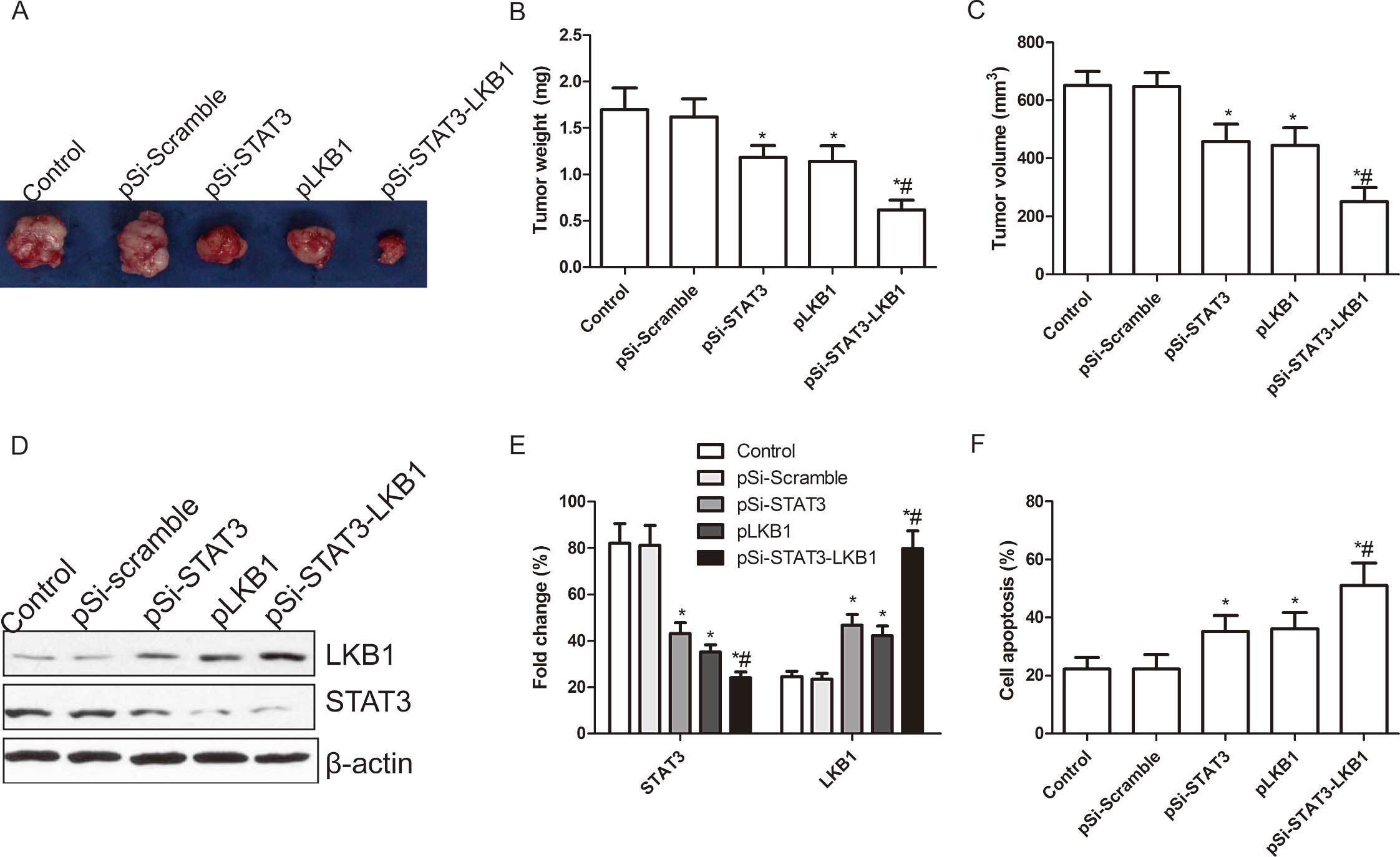
|
1
|
Siegel R, Naishadham D and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J Clin. 62:10–29. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Cannistra SA: Cancer of the ovary. N Engl
J Med. 351:2519–2529. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Kipps E, Tan DS and Kaye SB: Meeting the
challenge of ascites in ovarian cancer: new avenues for therapy and
research. Nat Rev Cancer. 13:273–282. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Telleria CM: Repopulation of ovarian
cancer cells after chemotherapy. Cancer Growth Metastasis. 6:15–21.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Duan Z, Foster R, Bell DA, et al: Signal
transducers and activators of transcription 3 pathway activation in
drug-resistant ovarian cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 12:5055–5063. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Darnell JE Jr: STATs and gene regulation.
Science. 277:1630–1635. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Lu Y, Fukuyama S, Yoshida R, et al: Loss
of SOCS3 gene expression converts STAT3 function from
anti-apoptotic to proapoptotic. J Biol Chem. 281:36683–36690. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Yu H and Jove R: The STATs of cancer - new
molecular targets come of age. Nat Rev Cancer. 4:97–105. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Catlett-Falcone R, Landowski TH, Oshiro
MM, et al: Constitutive activation of Stat3 signaling confers
resistance to apoptosis in human U266 myeloma cells. Immunity.
10:105–115. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Grandis JR, Drenning SD, Zeng Q, et al:
Constitutive activation of Stat3 signaling abrogates apoptosis in
squamous cell carcinogenesis in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
97:4227–4232. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Yan X, Fraser M, Qiu Q and Tsang BK:
Over-expression of PTEN sensitizes human ovarian cancer cells to
cisplatin-induced apoptosis in a p53-dependent manner. Gynecol
Oncol. 102:348–355. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Epling-Burnette PK, Liu JH,
Catlett-Falcone R, et al: Inhibition of STAT3 signaling leads to
apoptosis of leukemic large granular lymphocytes and decreased
Mcl-1 expression. J Clin Invest. 107:351–362. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Mora LB, Buettner R, Seigne J, et al:
Constitutive activation of Stat3 in human prostate tumors and cell
lines: direct inhibition of Stat3 signaling induces apoptosis of
prostate cancer cells. Cancer Res. 62:6659–6666. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Scholz A, Heinze S, Detjen KM, et al:
Activated signal transducer and activator of transcription 3
(STAT3) supports the malignant phenotype of human pancreatic
cancer. Gastroenterology. 125:891–905. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Song L, Turkson J, Karras JG, Jove R and
Haura EB: Activation of Stat3 by receptor tyrosine kinases and
cytokines regulates survival in human non-small cell carcinoma
cells. Oncogene. 22:4150–4165. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Kanda N, Seno H, Konda Y, et al: STAT3 is
constitutively activated and supports cell survival in association
with survivin expression in gastric cancer cells. Oncogene.
23:4921–4929. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Li L and Shaw PE: Autocrine-mediated
activation of STAT3 correlates with cell proliferation in breast
carcinoma lines. J Biol Chem. 277:17397–17405. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Aittomäki S and Pesu M: Therapeutic
targeting of the Jak/STAT pathway. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol.
114:18–23. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Huang K, Li LA, Meng YG, You YQ, Fu XY and
Song L: Arctigenin promotes apoptosis in ovarian cancer cells via
the iNOS/NO/STAT3/survivin signalling. Basic Clin Pharmacol
Toxicol. May 19–2014.(Epub ahead of print). View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Han Z, Feng J, Hong Z, et al: Silencing of
the STAT3 signaling pathway reverses the inherent and induced
chemoresistance of human ovarian cancer cells. Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 435:188–194. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Jiang Q, Dai L, Cheng L, et al: Efficient
inhibition of intraperitoneal ovarian cancer growth in nude mice by
liposomal delivery of short hairpin RNA against STAT3. J Obstet
Gynaecol Res. 39:701–709. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Zhang L, Gao L, Li Y, et al: Effects of
plasmid-based Stat3-specific short hairpin RNA and GRIM-19 on PC-3M
tumor cell growth. Clin Cancer Res. 14:559–568. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Elbashir SM, Harborth J, Weber K and
Tuschl T: Analysis of gene function in somatic mammalian cells
using small interfering RNAs. Methods. 26:199–213. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Hemminki A, Markie D, Tomlinson I, et al:
A serine/threonine kinase gene defective in Peutz-Jeghers syndrome.
Nature. 391:184–187. 1998. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Esteller M, Avizienyte E, Corn PG, et al:
Epigenetic inactivation of LKB1 in primary tumors associated with
the Peutz-Jeghers syndrome. Oncogene. 19:164–168. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Andrade-Vieira R, Xu Z, Colp P and
Marignani PA: Loss of LKB1 expression reduces the latency of
ErbB2-mediated mammary gland tumorigenesis, promoting changes in
metabolic pathways. PLoS One. 8:e565672013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Zhuang Z, Wang K, Cheng X, et al: LKB1
inhibits breast cancer partially through repressing the Hedgehog
signaling pathway. PLoS One. 8:e674312013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Wang YQ, Dai WM, Chu XY, Yang B, Zhao M
and Sun Y: Downregulation of LKB1 suppresses Stat3 activity to
promote the proliferation of esophageal carcinoma cells. Mol Med
Rep. 9:2400–2404. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Wang GM, Ren ZX, Wang PS, et al:
Plasmid-based Stat3-specific siRNA and GRIM-19 inhibit the growth
of thyroid cancer cells in vitro and in vivo. Oncol Rep.
32:573–580. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Du Y, Shi A, Han B, et al: COX-2 silencing
enhances tamoxifen antitumor activity in breast cancer in vivo and
in vitro. Int J Oncol. 44:1385–1393. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Wen LJ, Gao LF, Jin CS, et al: Small
interfering RNA survivin and GRIM-19 co-expression salmonella
plasmid inhibited the growth of laryngeal cancer cells in vitro and
in vivo. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 6:2071–2081. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Li X, Li Y, Hu J, et al: Plasmid-based
E6-specific siRNA and co-expression of wild-type p53 suppresses the
growth of cervical cancer in vitro and in vivo. Cancer Lett.
335:242–250. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Li L, Yu C, Ren J, et al: Synergistic
effects of eukaryotic coexpression plasmid carrying LKB1 and FUS1
genes on lung cancer in vitro and in vivo. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol.
140:895–907. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Tiainen M, Vaahtomeri K, Ylikorkala A and
Mäkelä TP: Growth arrest by the LKB1 tumor suppressor: induction of
p21WAF1/CIP1. Hum Mol Genet. 11:1497–1504.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Tiainen M, Ylikorkala A and Mäkelä TP:
Growth suppression by Lkb1 is mediated by a G1 cell
cycle arrest. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 96:9248–9251. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Kim DW, Chung HK, Park KC, et al: Tumor
suppressor LKB1 inhibits activation of signal transducer and
activator of tran scription 3 (STAT3) by thyroid oncogenic tyrosine
kinase rearranged in transformation (RET)/papillary thyroid
carcinoma (PTC). Mol Endocrinol. 21:3039–3049. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Braicu EI, Gasimli K, Richter R, et al:
Role of serum VEGFA, TIMP2, MMP2 and MMP9 in monitoring response to
adjuvant radiochemotherapy in patients with primary cervical cancer
- results of a companion protocol of the randomized NOGGO-AGO phase
III clinical trial. Anticancer Res. 34:385–391. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Ou W, Ye S, Yang W, et al: Enhanced
antitumor effect of cisplatin in human NSCLC cells by tumor
suppressor LKB1. Cancer Gene Ther. 19:489–498. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|