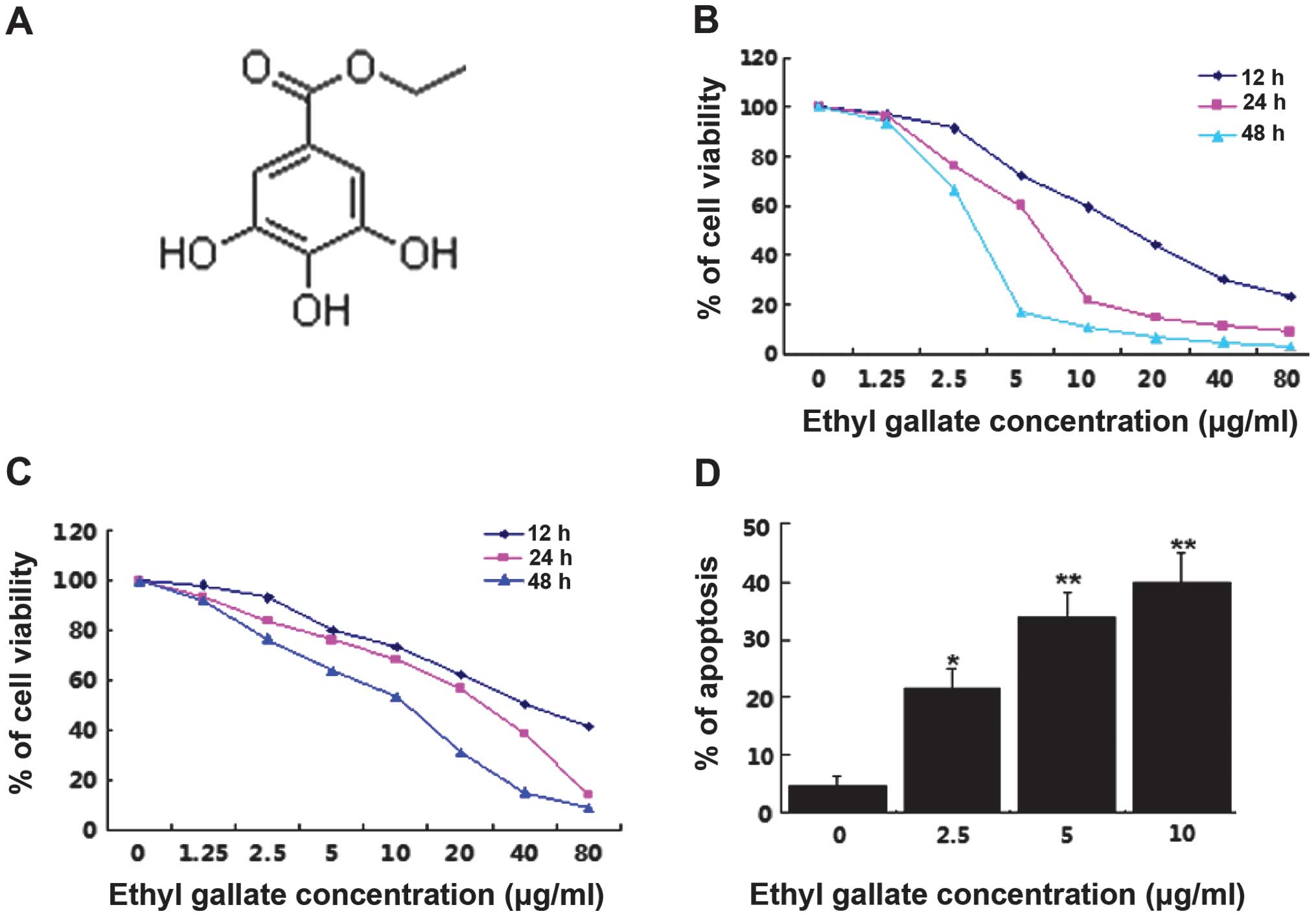
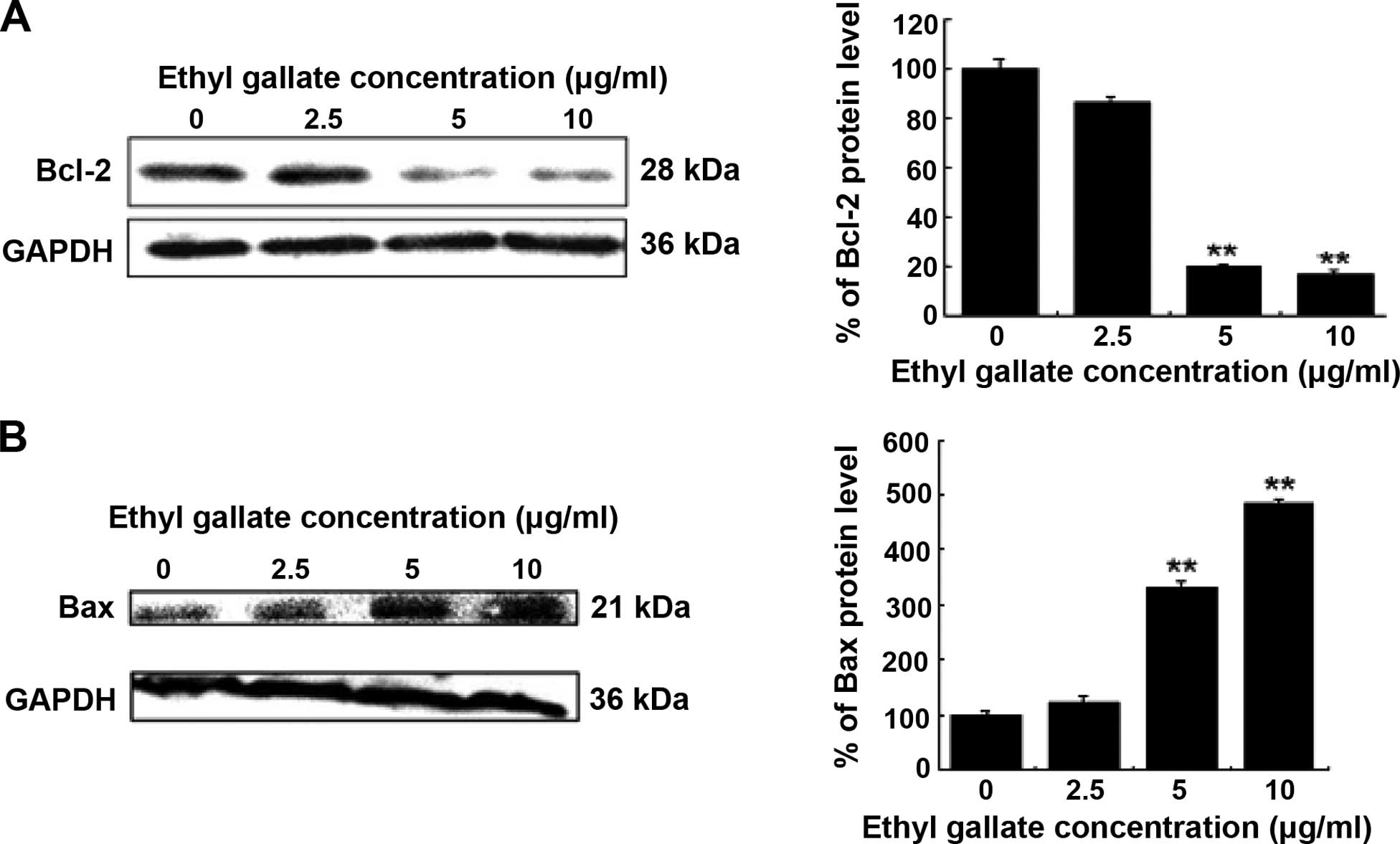
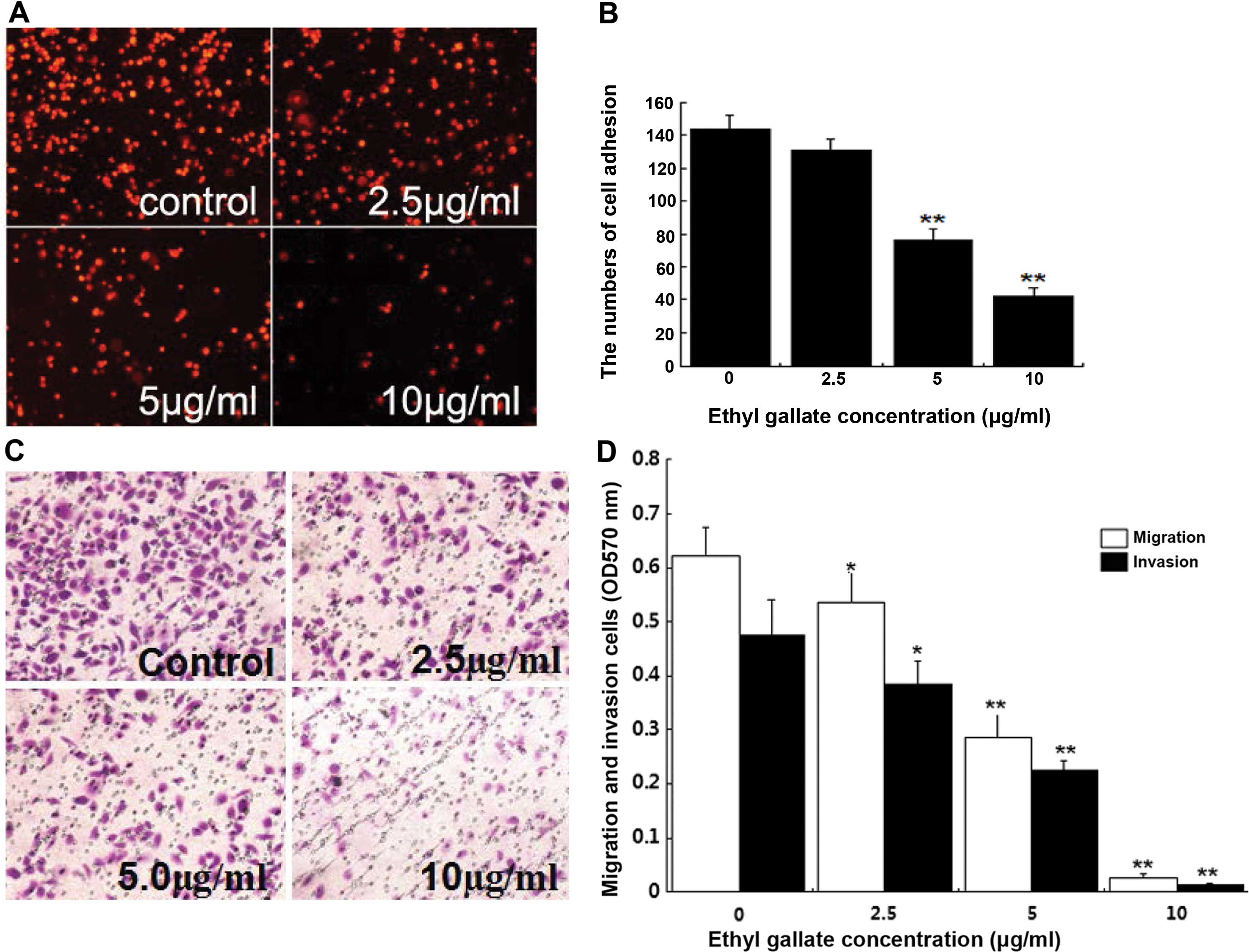
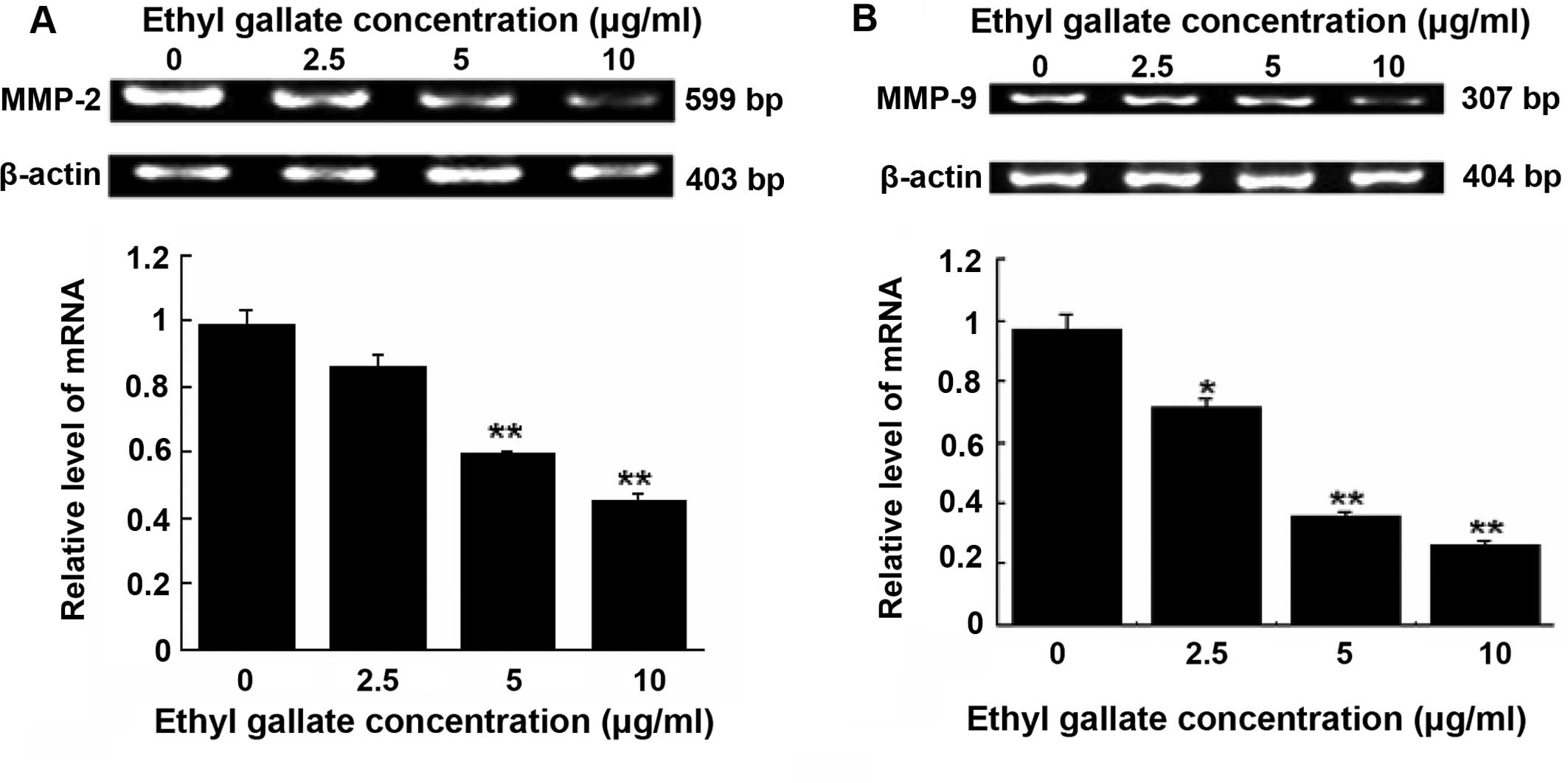
|
1
|
Cleator S, Heller W and Coombes RC:
Triple-negative breast cancer: therapeutic options. Lancet Oncol.
8:235–244. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
van de Rijn M, Perou CM, Tibshirani R, et
al: Expression of cytokeratins 17 and 5 identifies a group of
breast carcinomas with poor clinical outcome. Am J Pathol.
161:1991–1996. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Foulkes WD, Brunet JS, Stefansson IM, et
al: The prognostic implication of the basal-like (cyclin
Ehigh/p27low/p53+/glomeruloid-microvascular-proliferation+)
phenotype of BRCA1-related breast cancer. Cancer Res. 64:830–835.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Folgueras AR, Pendás AM, Sánchez LM and
López-Otín C: Matrix metalloproteinases in cancer: from new
functions to improved inhibition strategies. Int J Dev Biol.
48:411–424. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Lin YC, Tsai PH, Lin CY, Cheng CH, Lin TH,
Lee KP, Huang KY, Chen SH, Hwang JJ, Kandaswami CC and Lee MT:
Impact of flavonoids on matrix metalloproteinase secretion and
invadopodia formation in highly invasive A431-III cancer cells.
PLoS One. 8:e719032013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Liu Y, Cao W, Zhang B, Liu YQ, Wang ZY, Wu
YP, Yu XJ, Zhang XD, Ming PH, Zhou GB and Huang L: The natural
compound magnolol inhibits invasion and exhibits potential in human
breast cancer therapy. Sci Rep. 3:30982013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Ho YC, Yang SF, Peng CY, Chou MY and Chang
YC: Epigallocatechin-3-gallate inhibits the invasion of human oral
cancer cells and decreases the productions of matrix
metalloproteinases and urokinase-plasminogen activator. J Oral
Pathol Med. 36:588–593. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Lee WJ, Chen WK, Wang CJ, Lin WL and Tseng
TH: Apigenin inhibits HGF-promoted invasive growth and metastasis
involving blocking PI3K/Akt pathway and β4 integrin function in
MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol.
226:178–191. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Qin GW and Xu RS: Recent advances on
bioactive natural products from Chinese medicinal plants. Med Res
Rev. 18:375–382. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Wang YB, Huang R, Wang HB, Jin HZ, Lou LG
and Qin GW: Diterpenoids from the roots of Euphorbia fischeriana. J
Nat Prod. 69:967–970. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Shi HM, Williams ID, Sung HH, Zhu HX, Ip
NY and Min ZD: Cytotoxic diterpenoids from the roots of Euphorbia
ebracteolata. Planta Med. 71:349–354. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Wang JH, Zhang K, Niu HY, Shu LH, Yue DM,
Li D and He P: Jolkinolide B from Euphorbia fischeriana Steud
induces in human leukemic cells apoptosis via JAK2/STAT3 pathways.
Int J Clin Pharmacol Ther. 51:170–178. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Yan SS, Li Y, Wang Y, Shen SS, Gu Y, Wang
HB, Qin GW and Yu Q: 17- Acetoxyjolkinolide B irreversibly inhibits
IκB kinase and induces apoptosis of tumor cells. Mol Cancer Ther.
7:1523–1532. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Wang JH, Zhou YJ, Bai X and He P:
Jolkinolide B from Euphorbia fischeriana Steud induces apoptosis in
human leukemic U937 cells through PI3K/Akt and XIAP pathways. Mol
Cells. 32:451–457. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Wang Y, Ma X, Yan S, Shen S, Zhu H, Gu Y,
Wang H, Qin G and Yu Q: 17-Hydroxy-jolkinolide B inhibits signal
transducers and activators of transcription 3 signaling by
covalently cross-linking Janus kinases and induces apoptosis of
human cancer cells. Cancer Res. 69:7302–7310. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Chaffer CL and Weinberg RA: A perspective
on cancer cell metastasis. Science. 331:1559–1564. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Hung SH, Shen KH, Wu CH, Liu CL and Shih
YW: α-Mangostin suppresses PC-3 human prostate carcinoma cell
metastasis by inhibiting matrix metalloproteinase-2/9 and
urokinase-plasminogen expression through the JNK signaling pathway.
J Agric Food Chem. 57:1291–1298. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Chen PN, Chu SC, Chiou HL, Kuo WH, Chiang
CL and Hsieh YS: Mulberry anthocyanins, cyanidin 3-rutinoside and
cyanidin 3-glucoside, exhibited an inhibitory effect on the
migration and invasion of a human lung cancer cell line. Cancer
Lett. 235:248–259. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Azios NG and Dharmawardhane SF:
Resveratrol and estradiol exert disparate effects on cell
migration, cell surface actin structures, and focal adhesion
assembly in MDA-MB-231 human breast cancer cells. Neoplasia.
7:128–140. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Kessenbrock K, Plaks V and Werb Z: Matrix
metalloproteinases: regulators of the tumor microenvironment. Cell.
141:52–67. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Das R, Philip S, Mahabeleshwar GH, Bulbule
A and Kundu GC: Osteopontin: it’s role in regulation of cell
motility and nuclear factor κB-mediated urokinase type plasminogen
activator expression. IUBMB Life. 57:441–447. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Lu KW, Tsai ML, Chen JC, Hsu SC, Hsia TC,
Lin MW, Huang AC, Chang YH, Ip SW, Lu HF and Chung JG: Gypenosides
inhibited invasion and migration of human tongue cancer SCC4 cells
through down-regulation of NFκB and matrix metalloproteinase-9.
Anticancer Res. 28:1093–1099. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Park SY, Kim JH, Lee YJ, Lee SJ and Kim Y:
Surfactin suppresses TPA-induced breast cancer cell invasion
through the inhibition of MMP-9 expression. Int J Oncol.
42:287–296. 2013.
|
|
24
|
Hojilla CV, Mohammed FF and Khokha R:
Matrix metalloproteinases and their tissue inhibitors direct cell
fate during cancer development. Br J Cancer. 89:1817–1821. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Kim Y, Kang H, Jang SW and Ko J: Celastrol
inhibits breast cancer cell invasion via suppression of
NF-κB-mediated matrix metalloproteinase-9 expression. Cell Physiol
Biochem. 28:175–184. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Rangaswami H, Bulbule A and Kundu GC:
Nuclear factor-inducing kinase plays a crucial role in
osteopontin-induced MAPK/IκBα kinase-dependent nuclear factor
κB-mediated promatrix metalloproteinase-9 activation. J Biol Chem.
279:38921–38935. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Yamaguchi N, Ito T, Azuma S, Ito E, Honma
R, Yanagisawa Y, Nishikawa A, Kawamura M, Imai J, Watanabe S, Semba
K and Inoue J: Constitutive activation of nuclear factor-κB is
preferentially involved in the proliferation of basal-like subtype
breast cancer cell lines. Cancer Sci. 100:1668–1674. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Kang H, Lee M, Choi KC, Shin DM, Ko J and
Jang SW: N-(4-hydroxyphenyl)retinamide inhibits breast cancer cell
invasion through suppressing NF-KB activation and inhibiting matrix
metalloproteinase-9 expression. J Cell Biochem. 113:2845–2855.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Thangapazham RL, Passi N and Maheshwari
RK: Green tea polyphenol and epigallocatechin gallate induce
apoptosis and inhibit invasion in human breast cancer cells. Cancer
Biol Ther. 6:1938–1943. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Viatour P, Bentires-Alj M, Chariot A,
Deregowski V, de Leval L, Merville MP and Bours V: NF-κB2/p100
induces Bcl-2 expression. Leukemia. 17:1349–1356. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Marsden VS, O’Connor L, O’Reilly LA, Silke
J, Metcalf D, Ekert PG, Huang DC, Cecconi F, Kuida K, Tomaselli KJ,
Roy S, Nicholson DW, Vaux DL, Bouillet P, Adams JM and Strasser A:
Apoptosis initiated by Bcl-2-regulated caspase activation
independently of the cytochrome c/Apaf-1/caspase-9 apoptosome.
Nature. 419:634–637. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Emi M, Kim R, Tanabe K, Uchida Y and Toge
T: Targeted therapy against Bcl-2-related proteins in breast cancer
cells. Breast Cancer Res. 7:940–952. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Patel JB, Mehta J, Belosay A, Sabnis G,
Khandelwal A, Brodie AM, Soprano DR and Njar VC: Novel retinoic
acid metabolism blocking agents have potent inhibitory activities
on human breast cancer cells and tumour growth. Br J Cancer.
96:1204–1215. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Aggarwal BB: Nuclear factor-κB: the enemy
within. Cancer Cell. 6:203–208. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|