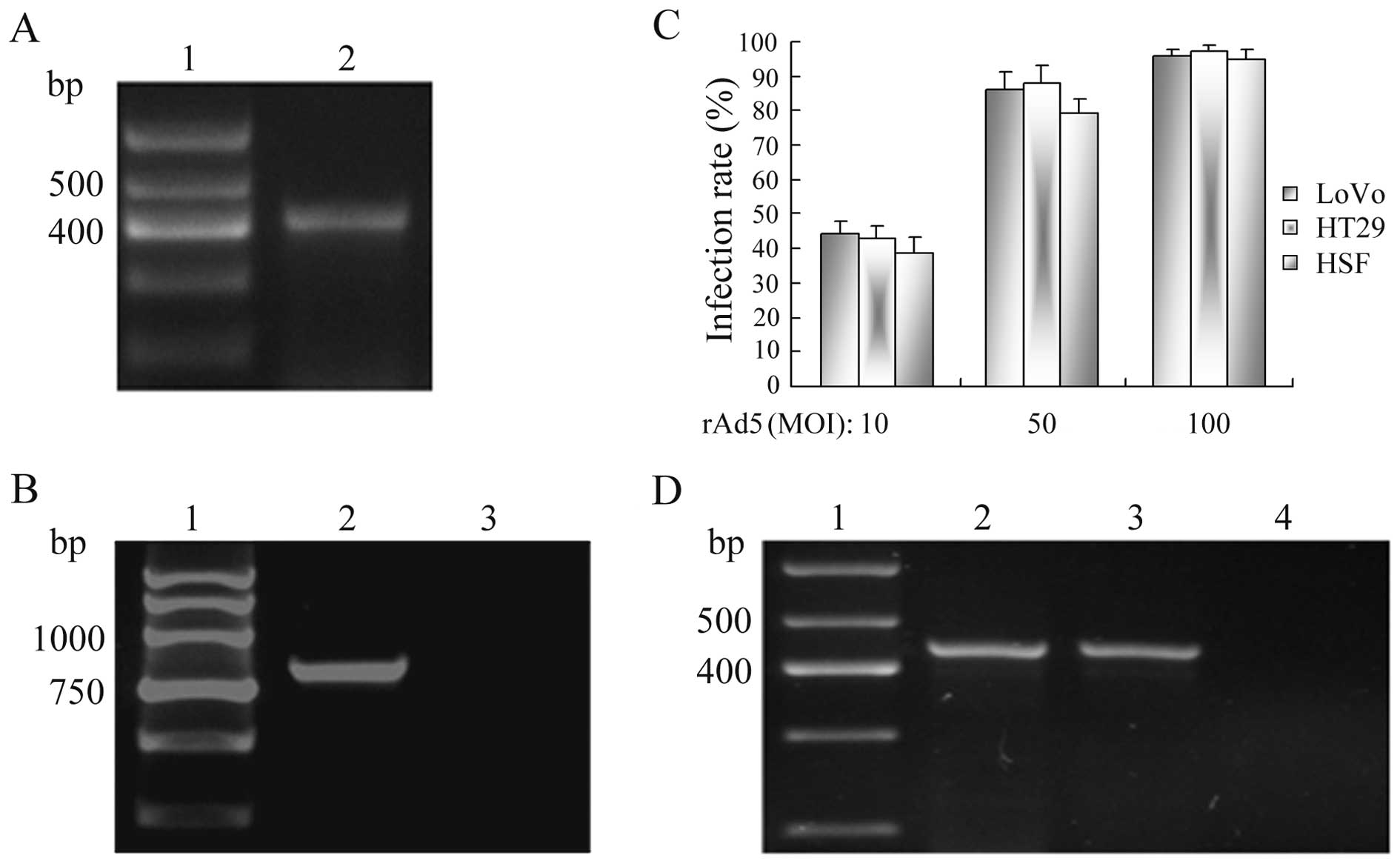
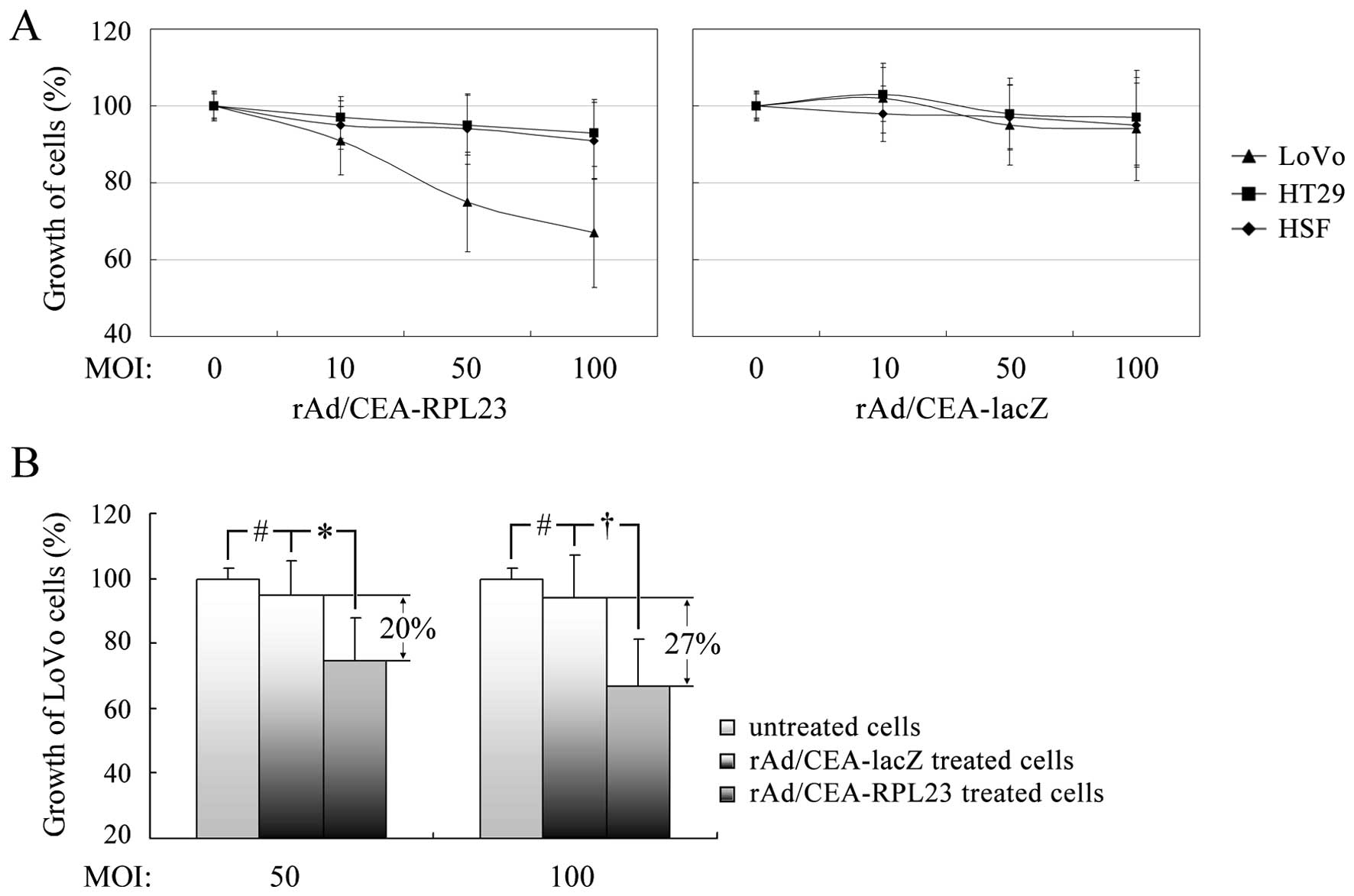
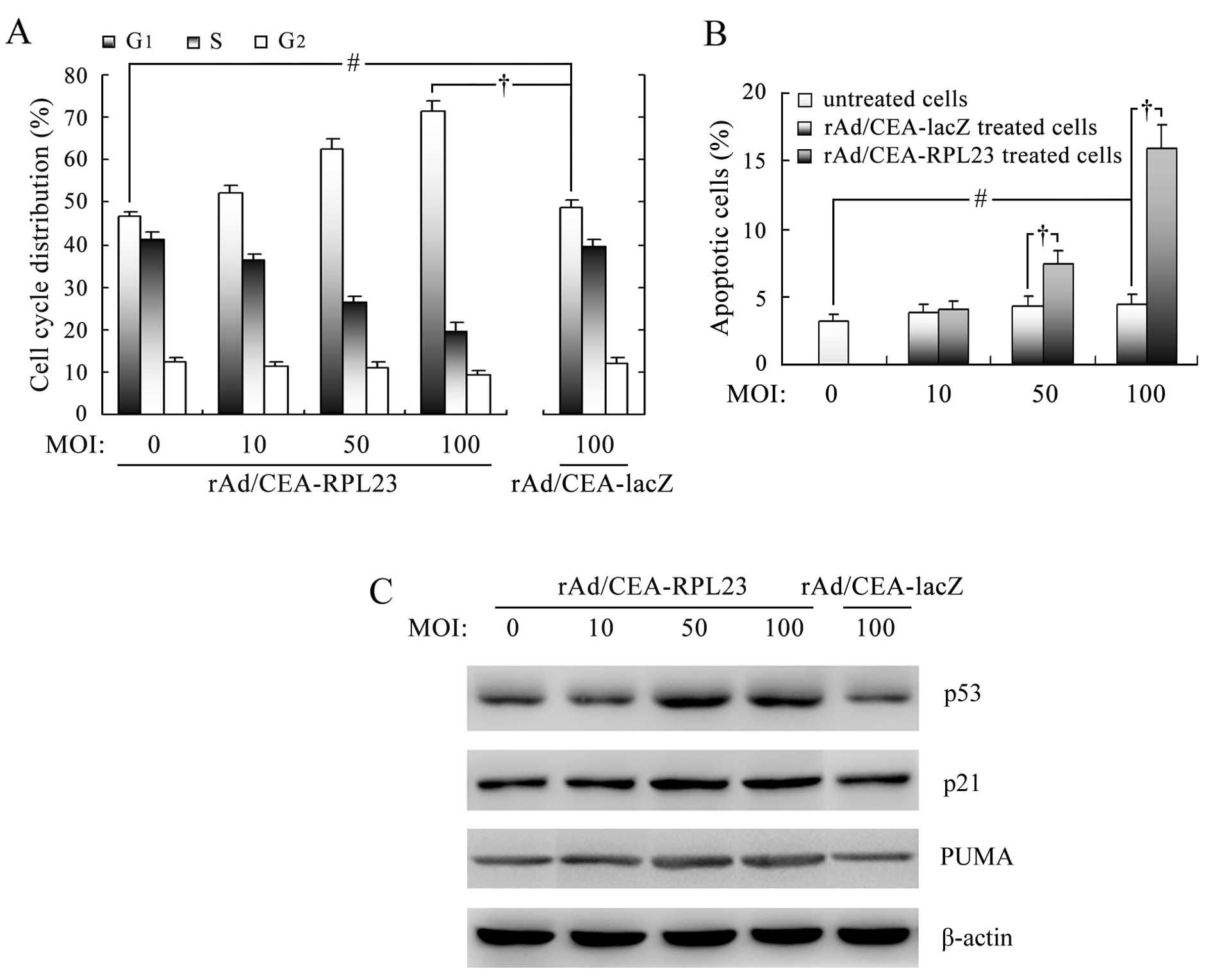
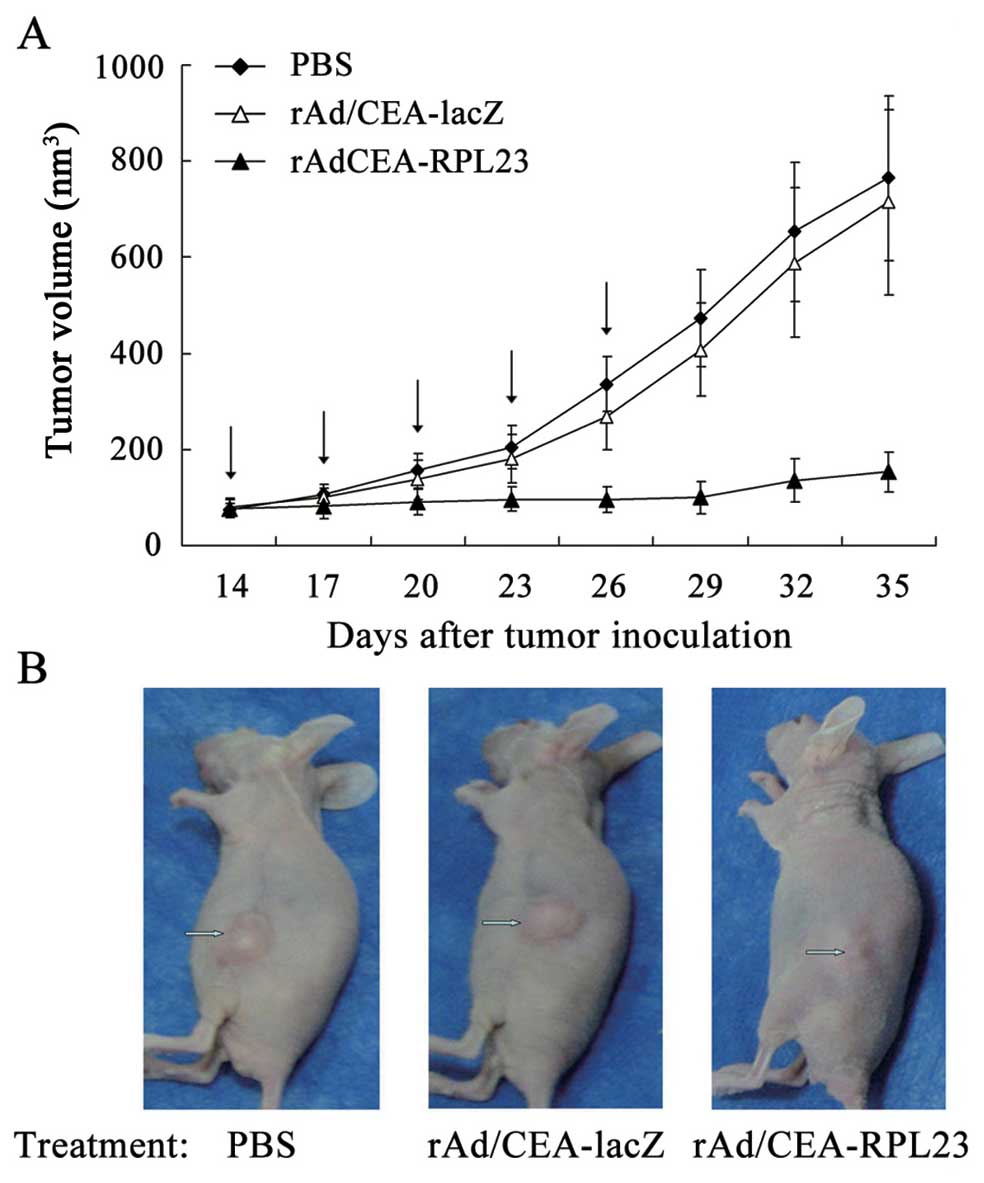
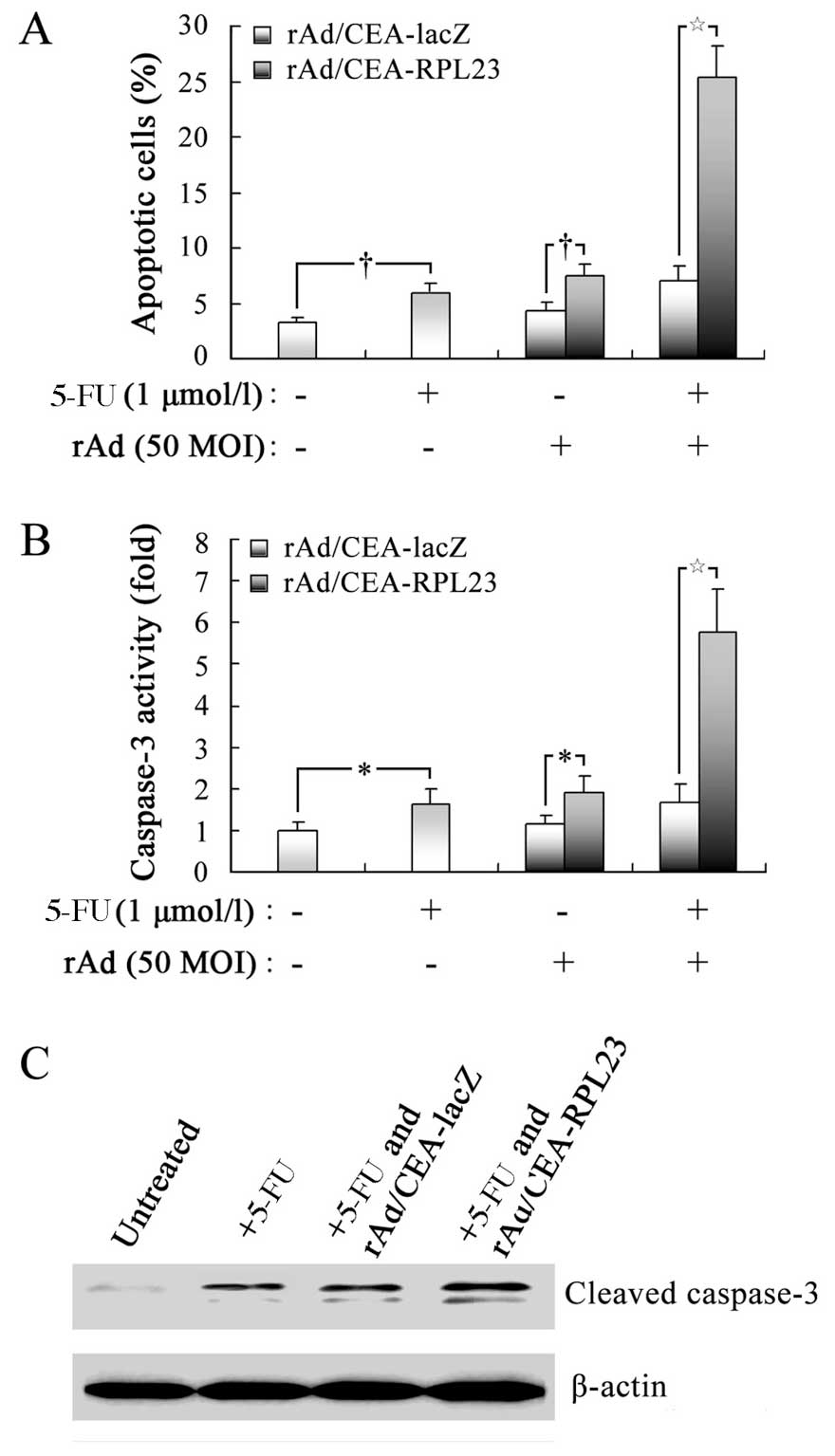
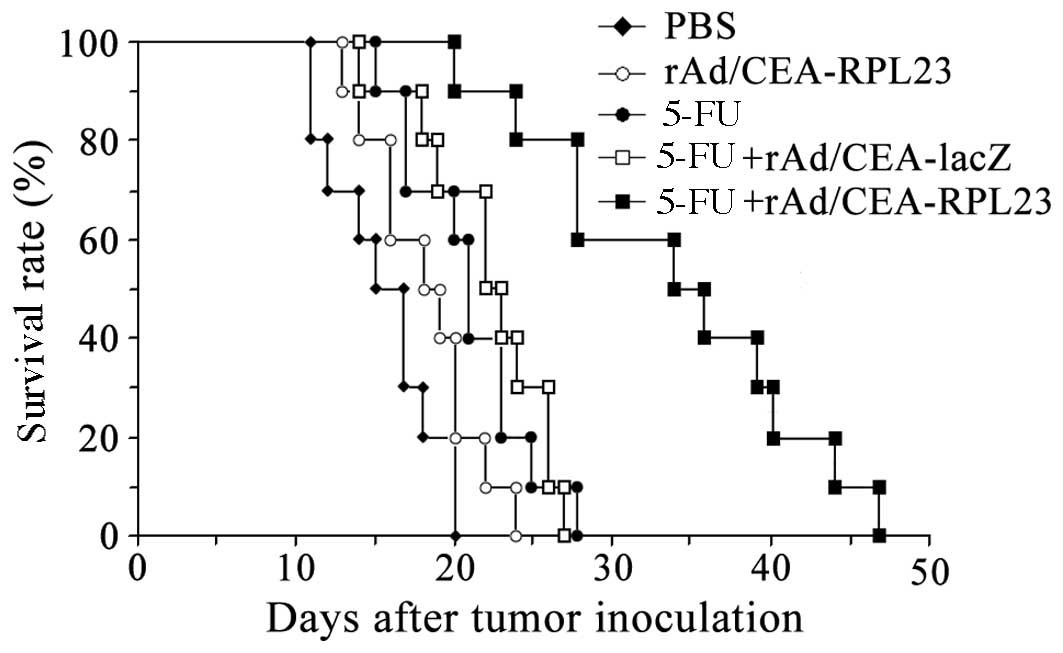
|
1
|
Selivanova G: Wild type p53 reactivation:
from lab bench to clinic. FEBS Lett. 588:2628–2638. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Khoo KH, Verma CS and Lane DP: Drugging
the p53 pathway: understanding the route to clinical efficacy. Nat
Rev Drug Discov. 13:217–236. 2014. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Kruse JP and Gu W: Modes of p53
regulation. Cell. 137:609–622. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Freedman DA, Wu L and Levine AJ: Functions
of the MDM2 oncoprotein. Cell Mol Life Sci. 55:96–107. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Wang W and El-Deiry WS: Restoration of p53
to limit tumor growth. Curr Opin Oncol. 20:90–96. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Momand J, Jung D, Wilczynski S and Niland
J: The MDM2 gene amplification database. Nucleic Acids Res.
26:3453–3459. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Zhao Y, Aguilar A, Bernard D and Wang S:
Small-molecule inhibitors of the MDM2-p53 protein-protein
interaction (MDM2 inhibitors) in clinical trials for cancer
treatment. J Med Chem. 58:1038–1052. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Lu C and El-Deiry WS: Targeting p53 for
enhanced radio- and chemo-sensitivity. Apoptosis. 14:597–606. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Dai MS, Zeng SX, Jin Y, Sun XX, David L
and Lu H: Ribosomal protein L23 activates p53 by inhibiting MDM2
function in response to ribosomal perturbation but not to
translation inhibition. Mol Cell Biol. 24:7654–7668. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Jin A, Itahana K, O’Keefe K and Zhang Y:
Inhibition of HDM2 and activation of p53 by ribosomal protein L23.
Mol Cell Biol. 24:7669–7680. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Pocard M, Chevillard S, Villaudy J, Poupon
MF, Dutrillaux B and Remvikos Y: Different p53 mutations produce
distinct effects on the ability of colon carcinoma cells to become
blocked at the G1/S boundary after irradiation. Oncogene.
12:875–882. 1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Shi MD, Lin HH, Lee YC, Chao JK, Lin RA
and Chen JH: Inhibition of cell-cycle progression in human
colorectal carcinoma Lovo cells by andrographolide. Chem Biol
Interact. 174:201–210. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Zhang NH, Song LB, Wu XJ, Li RP, Zeng MS,
Zhu XF, Wan DS, Liu Q, Zeng YX and Zhang XS: Proteasome inhibitor
MG-132 modifies coxsackie and adenovirus receptor expression in
colon cancer cell line Lovo. Cell Cycle. 7:925–933. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Kim HJ, Cho HI, Han YH, Park SY, Kim DW,
Lee DG, Kim JH, Shin WS, Paik SY, Kim CC, et al: Efficient
transduction with recombinant adenovirus in EBV-transformed B
lymphoblastoid cell lines. J Biochem Mol Biol. 37:376–382. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Zhang Y, Shi Y, Li X, Du R, Luo G, Xia L,
Du W, Chen B, Zhai H, Wu K, et al: Proteasome inhibitor MG132
reverses multidrug resistance of gastric cancer through enhancing
apoptosis and inhibiting P-gp. Cancer Biol Ther. 7:540–546. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Li X, Zhang Y, Xiong C, Jin H, Jing B,
Zhang Y and Fan D: Overexpression of a new gene P28GANK confers
multidrug resistance of gastric cancer cells. Cancer Invest.
27:129–139. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Li Y, Chen Y, Dilley J, Arroyo T, Ko D,
Working P and Yu DC: Carcinoembryonic antigen-producing
cell-specific oncolytic adenovirus, OV798, for colorectal cancer
therapy. Mol Cancer Ther. 2:1003–1009. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Cao G, Kuriyama S, Gao J, Kikukawa M, Cui
L, Nakatani T, Zhang X, Tsujinoue H, Pan X, Fukui H, et al:
Effective and safe gene therapy for colorectal carcinoma using the
cytosine deaminase gene directed by the carcinoembryonic antigen
promoter. Gene Ther. 6:83–90. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Schrewe H, Thompson J, Bona M, Hefta LJ,
Maruya A, Hassauer M, Shively JE, von Kleist S and Zimmermann W:
Cloning of the complete gene for carcinoembryonic antigen: analysis
of its promoter indicates a region conveying cell type-specific
expression. Mol Cell Biol. 10:2738–2748. 1990.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Qiao J, Doubrovin M, Sauter BV, Huang Y,
Guo ZS, Balatoni J, Akhurst T, Blasberg RG, Tjuvajev JG, Chen SH,
et al: Tumor-specific transcriptional targeting of suicide gene
therapy. Gene Ther. 9:168–175. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Ueda K, Iwahashi M, Nakamori M, Nakamura
M, Matsuura I, Ojima T and Yamaue H: Improvement of
carcinoembryonic antigen-specific prodrug gene therapy for
experimental colon cancer. Surgery. 133:309–317. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Dabrowska A, Szary J, Kowalczuk M, Szala S
and Ugorski M: CEA-negative glioblastoma and melanoma cells are
sensitive to cytosine deaminase/5-fluorocytosine therapy directed
by the carcinoembryonic antigen promoter. Acta Biochim Pol.
51:723–732. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Chen X, Bargonetti J and Prives C: p53,
through p21 (WAF1/CIP1), induces cyclin D1 synthesis. Cancer Res.
55:4257–4263. 1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Yu J and Zhang L: No PUMA, no death:
implications for p53-dependent apoptosis. Cancer Cell. 4:248–249.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Sobrero A, Kerr D, Glimelius B, Van Cutsem
E, Milano G, Pritchard DM, Rougier P and Aapro M: New directions in
the treatment of colorectal cancer: a look to the future. Eur J
Cancer. 36:559–566. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Kuribayashi K, Mayes PA and El-Deiry WS:
What are caspases 3 and 7 doing upstream of the mitochondria?
Cancer Biol Ther. 5:763–765. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Vogelstein B, Lane D and Levine AJ:
Surfing the p53 network. Nature. 408:307–310. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Rayburn E, Zhang R, He J and Wang H: MDM2
and human malignancies: expression, clinical pathology, prognostic
markers, and implications for chemotherapy. Curr Cancer Drug
Targets. 5:27–41. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Shangary S and Wang S: Small-molecule
inhibitors of the MDM2-p53 protein-protein interaction to
reactivate p53 function: a novel approach for cancer therapy. Annu
Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 49:223–241. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
30
|
Wang W, Rastinejad F and El-Deiry WS:
Restoring p53-dependent tumor suppression. Cancer Biol Ther.
2(Suppl 1): S55–S63. 2003. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Deng X, Kim M, Vandier D, Jung YJ,
Rikiyama T, Sgagias MK, Goldsmith M and Cowan KH: Recombinant
adenovirus-mediated p14(ARF) overexpression sensitizes human breast
cancer cells to cisplatin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 296:792–798.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Hemmati PG, Gillissen B, von Haefen C,
Wendt J, Stärck L, Güner D, Dörken B and Daniel PT:
Adenovirus-mediated overexpression of p14(ARF) induces p53 and
Bax-independent apoptosis. Oncogene. 21:3149–3161. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Kaeser MD, Pebernard S and Iggo RD:
Regulation of p53 stability and function in HCT116 colon cancer
cells. J Biol Chem. 279:7598–7605. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Sun XX, Dai MS and Lu H: 5-fluorouracil
activation of p53 involves an MDM2-ribosomal protein interaction. J
Biol Chem. 282:8052–8059. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Wang H, Oliver P, Zhang Z, Agrawal S and
Zhang R: Chemo-sensitization and radiosensitization of human cancer
by antisense anti-MDM2 oligonucleotides: in vitro and in vivo
activities and mechanisms. Ann NY Acad Sci. 1002:217–235. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Gu L, Findley HW and Zhou M: MDM2 induces
NF-kappaB/p65 expression transcriptionally through Sp1-binding
sites: a novel, p53-independent role of MDM2 in doxorubicin
resistance in acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Blood. 99:3367–3375.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Cheney MD, McKenzie PP, Volk EL, Fan L and
Harris LC: MDM2 displays differential activities dependent upon the
activation status of NFkappaB. Cancer Biol Ther. 7:38–44. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Shen HM and Tergaonkar V: NFkappaB
signaling in carcinogenesis and as a potential molecular target for
cancer therapy. Apoptosis. 14:348–363. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|