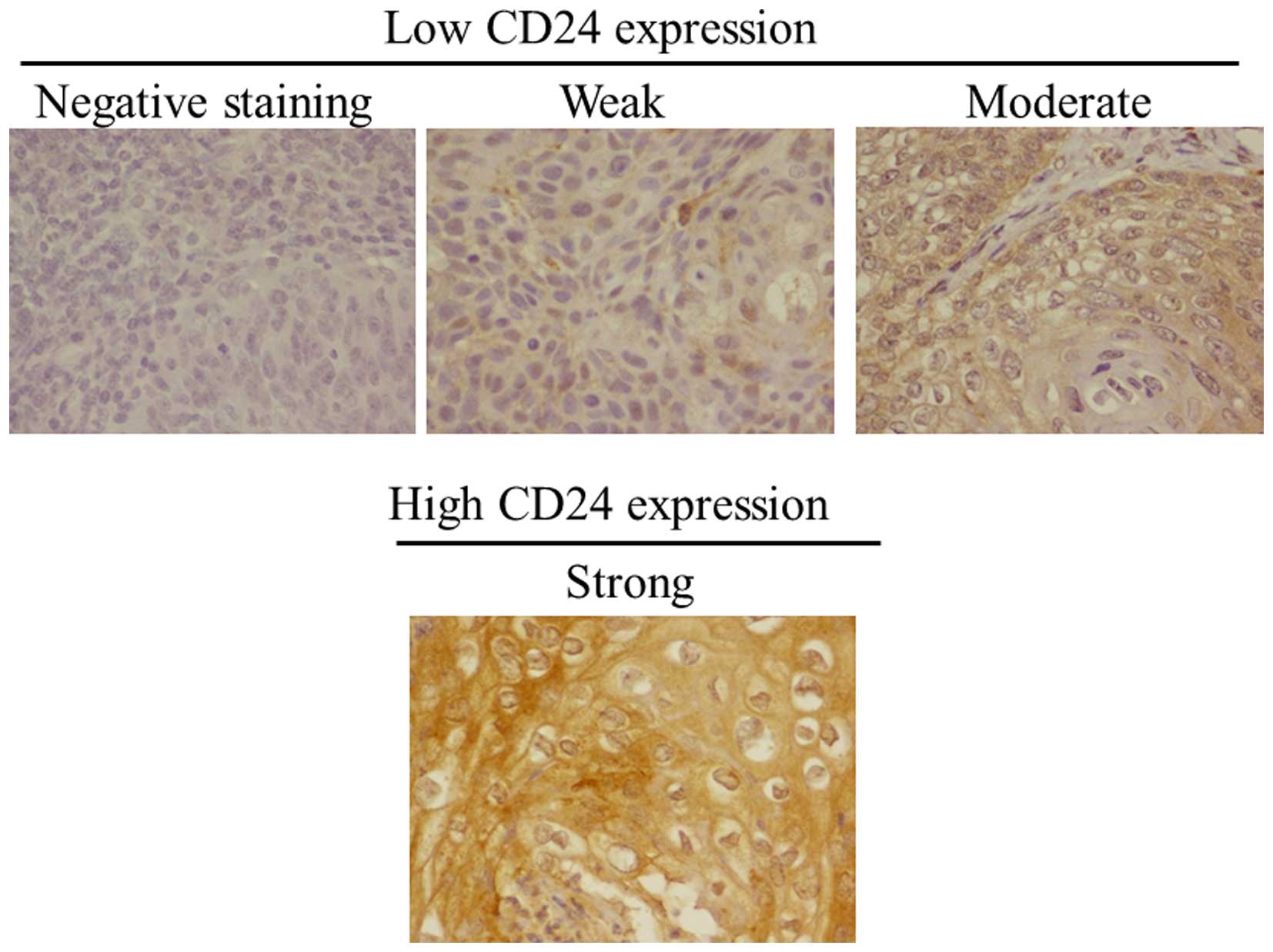
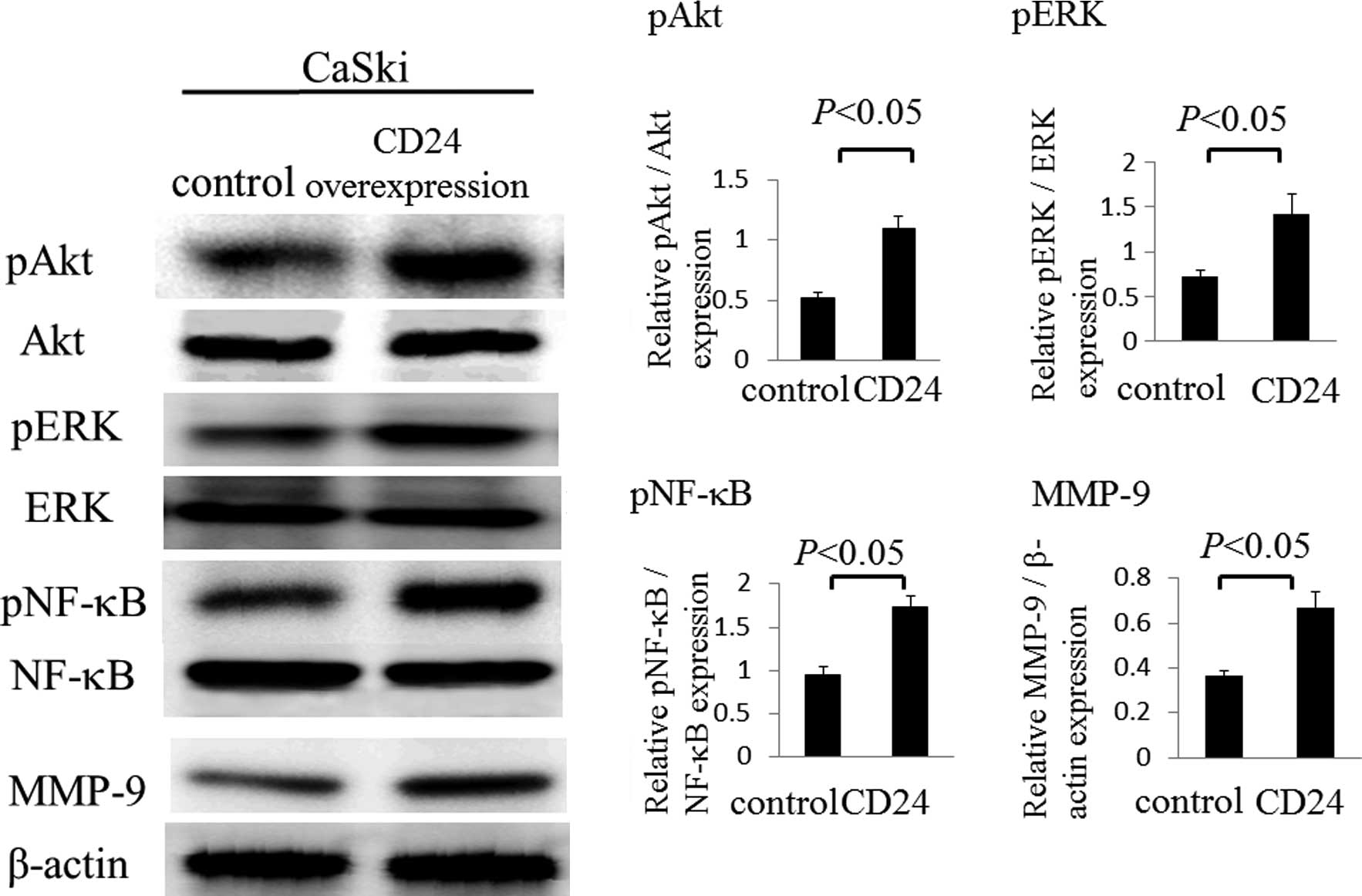
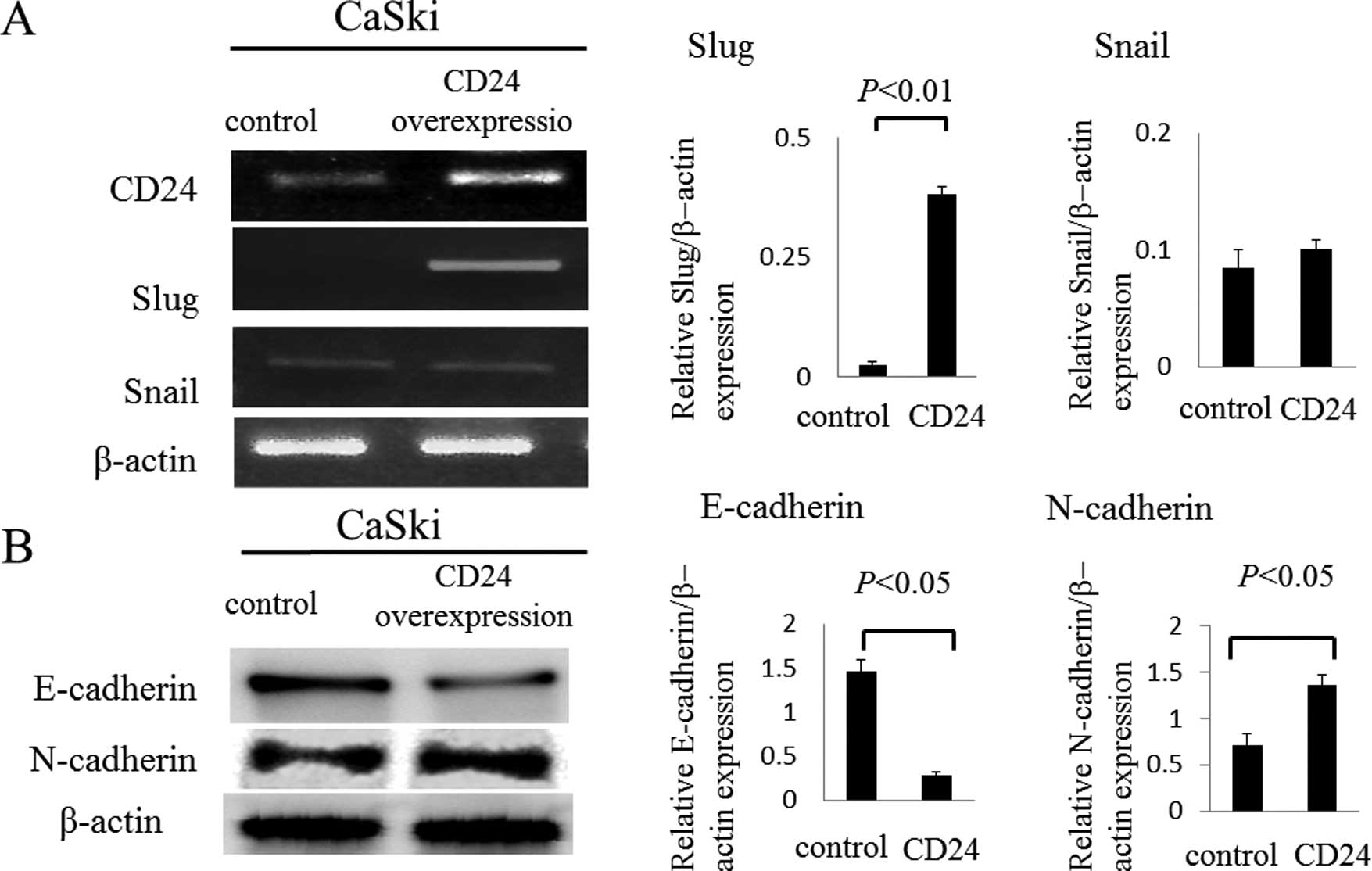
|
1
|
Forouzanfar MH, Foreman KJ, Delossantos
AM, Lozano R, Lopez AD, Murray CJ and Naghavi M: Breast and
cervical cancer in 187 countries between 1980 and 2010: A
systematic analysis. Lancet. 378:1461–1484. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Kay R, Rosten PM and Humphries RK: CD24, a
signal transducer modulating B cell activation responses, is a very
short peptide with a glycosyl phosphatidylinositol membrane anchor.
J Immunol. 147:1412–1416. 1991.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Aigner S, Ruppert M, Hubbe M, Sammar M,
Sthoeger Z, Butcher EC, Vestweber D and Altevogt P: Heat stable
antigen (mouse CD24) supports myeloid cell binding to endothelial
and platelet P-selectin. Int Immunol. 7:1557–1565. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Lee KM, Ju JH, Jang K, Yang W, Yi JY, Noh
DY and Shin I: CD24 regulates cell proliferation and transforming
growth factor β-induced epithelial to mesenchymal transition
through modulation of integrin β1 stability. Cell Signal.
24:2132–2142. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Aigner S, Sthoeger ZM, Fogel M, Weber E,
Zarn J, Ruppert M, Zeller Y, Vestweber D, Stahel R, Sammar M, et
al: CD24, a mucin-type glycoprotein, is a ligand for P-selectin on
human tumor cells. Blood. 89:3385–3395. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Sammar M, Aigner S and Altevogt P:
Heat-stable antigen (mouse CD24) in the brain: Dual but distinct
interaction with P-selectin and L1. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1337:287–294. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
King JB, von Furstenberg RJ, Smith BJ,
McNaughton KK, Galanko JA and Henning SJ: CD24 can be used to
isolate Lgr5+ putative colonic epithelial stem cells in
mice. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 303:G443–G452. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Li J, Li C, Yuan H and Gong F: Clinical
value of CD24 expression in retinoblastoma. J Biomed Biotechnol.
2012:1580842012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Deng J, Gao G, Wang L, Wang T, Yu J and
Zhao Z: CD24 expression as a marker for predicting clinical outcome
in human gliomas. J Biomed Biotechnol. 2012:5171722012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Hira SK and Manna PP: Down regulation of
CD24 and HER-2/neu in breast carcinoma cells by activated human
dendritic cell. Role of STAT3. Cell Immunol. 275:69–79. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Shi Y, Gong HL, Zhou L, Tian J and Wang Y:
CD24: A novel cancer biomarker in laryngeal squamous cell
carcinoma. ORL. J Otorhinolaryngol Relat Spec. 74:78–85. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Su N, Peng L, Xia B, Zhao Y, Xu A, Wang J,
Wang X and Jiang B: Lyn is involved in CD24-induced ERK1/2
activation in colorectal cancer. Mol Cancer. 11:432012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Zhu J, Zhang G and Lu H: CD24, COX-2, and
p53 in epithelial ovarian cancer and its clinical significance.
Front Biosci. 4:2745–2751. 2012. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Liu C, Zheng S, Shen H, Xu K, Chen J, Li
H, Xu Y, Xu A, Chen B, Kaku H, et al: Clinical significance of CD24
as a predictor of bladder cancer recurrence. Oncol Lett. 6:96–100.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Blechschmidt K, Sassen S, Schmalfeldt B,
Schuster T, Höfler H and Becker KF: The E-cadherin repressor Snail
is associated with lower overall survival of ovarian cancer
patients. Br J Cancer. 98:489–495. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Wang W, Wang X, Peng L, Deng Q, Liang Y,
Qing H and Jiang B: CD24-dependent MAPK pathway activation is
required for colorectal cancer cell proliferation. Cancer Sci.
101:112–119. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Kang KS, Choi YP, Gao MQ, Kang S, Kim BG,
Lee JH, Kwon MJ, Shin YK and Cho NH: CD24+ ovary cancer
cells exhibit an invasive mesenchymal phenotype. Biochem Biophys
Res Commun. 432:333–338. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Lee SH, Kim H, Hwang JH, Shin E, Lee HS,
Hwang DW, Cho JY, Yoon YS, Han HS and Cha BH: CD24 and S100A4
expression in resectable pancreatic cancers with earlier disease
recurrence and poor survival. Pancreas. 43:380–388. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Zhang Y, Wei J, Wang H, Xue X, An Y, Tang
D, Yuan Z, Wang F, Wu J, Zhang J, et al: Epithelial mesenchymal
transition correlates with CD24+CD44+ and
CD133+ cells in pancreatic cancer. Oncol Rep.
27:1599–1605. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Lim J, Lee KM, Shim J and Shin I: CD24
regulates stemness and the epithelial to mesenchymal transition
through modulation of Notch1 mRNA stability by p38MAPK. Arch
Biochem Biophys. 558:120–126. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Jaggupilli A and Elkord E: Significance of
CD44 and CD24 as cancer stem cell markers: An enduring ambiguity.
Clin Dev Immunol. 2012:7080362012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Newman H, Shapira S, Spierer O, Kraus S,
Rosner M, Pri-Chen S, Loewenstein A, Arber N and Barak A:
Involvement of CD24 in angiogenesis in a mouse model of
oxygen-induced retinopathy. Curr Eye Res. 37:532–539. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Rasheed ZA and Matsui W: Biological and
clinical relevance of stem cells in pancreatic adenocarcinoma. J
Gastroenterol Hepatol. 27(Suppl 2): S15–S18. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Keysar SB and Jimeno A: More than markers:
Biological significance of cancer stem cell-defining molecules. Mol
Cancer Ther. 9:2450–2457. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Kemper K, Grandela C and Medema JP:
Molecular identification and targeting of colorectal cancer stem
cells. Oncotarget. 1:387–395. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Zou GM: Cancer initiating cells or cancer
stem cells in the gastrointestinal tract and liver. J Cell Physiol.
217:598–604. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Tang J, Cai H, Lin L, Xie P, Zhong W and
Tang M: Increased expression of CD24 is associated with tumor
progression and prognosis in patients suffering osteosarcoma. Clin
Transl Oncol. 15:541–547. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Wu JX, Zhao YY, Wu X and An HX:
Clinicopathological and prognostic significance of CD24
overexpression in patients with gastric cancer: A meta-analysis.
PLoS One. 9:e1147462014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Lee JM, Dedhar S, Kalluri R and Thompson
EW: The epithelial-mesenchymal transition: New insights in
signaling, development, and disease. J Cell Biol. 172:973–981.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Thiery JP, Acloque H, Huang RY and Nieto
MA: Epithelial-mesenchymal transitions in development and disease.
Cell. 139:871–890. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Peinado H, Olmeda D and Cano A: Snail, Zeb
and bHLH factors in tumour progression: An alliance against the
epithelial phenotype? Nat Rev Cancer. 7:415–428. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Maeda M, Johnson KR and Wheelock MJ:
Cadherin switching: essential for behavioral but not morphological
changes during an epithelium-to-mesenchyme transition. J Cell Sci.
118:873–887. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|