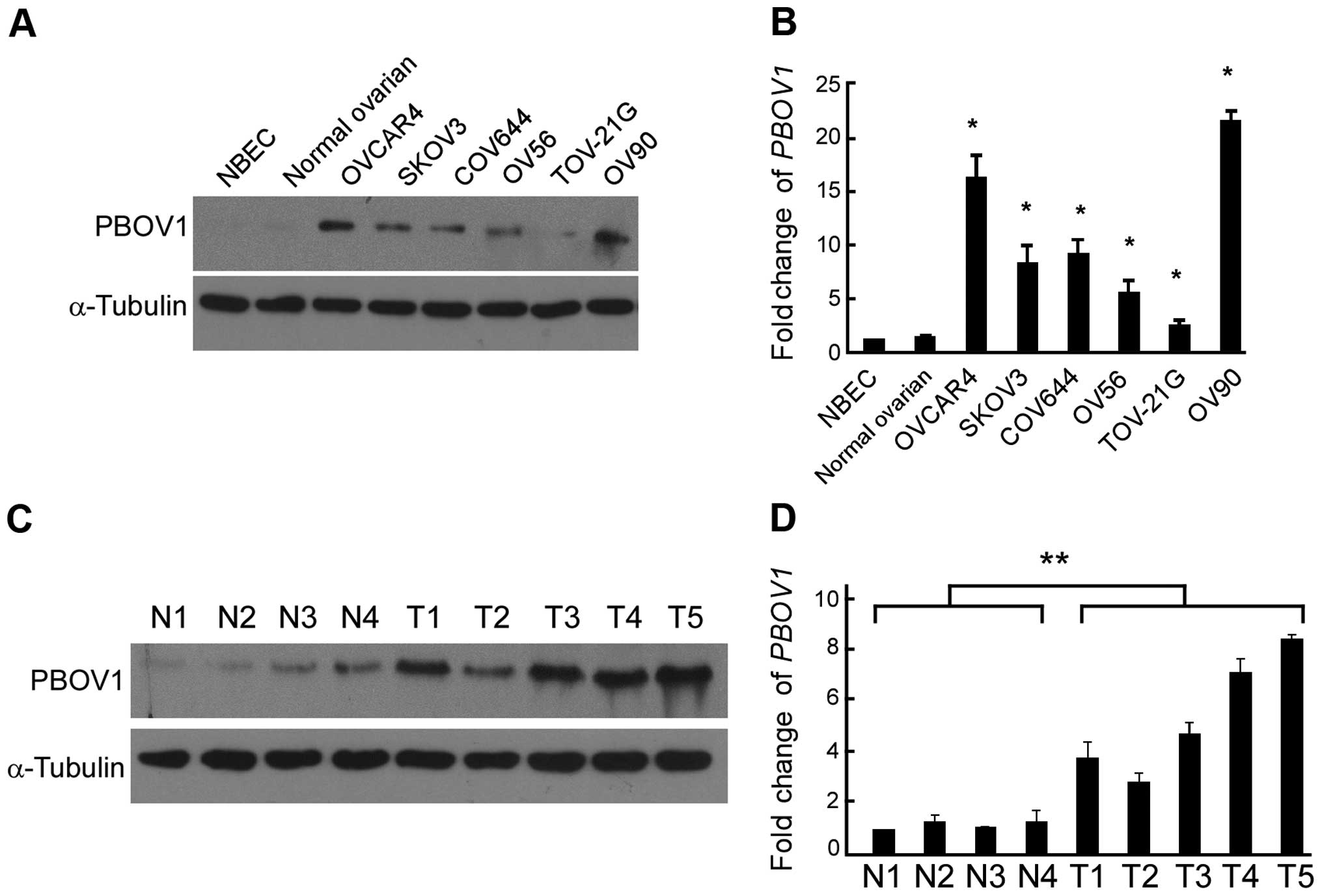
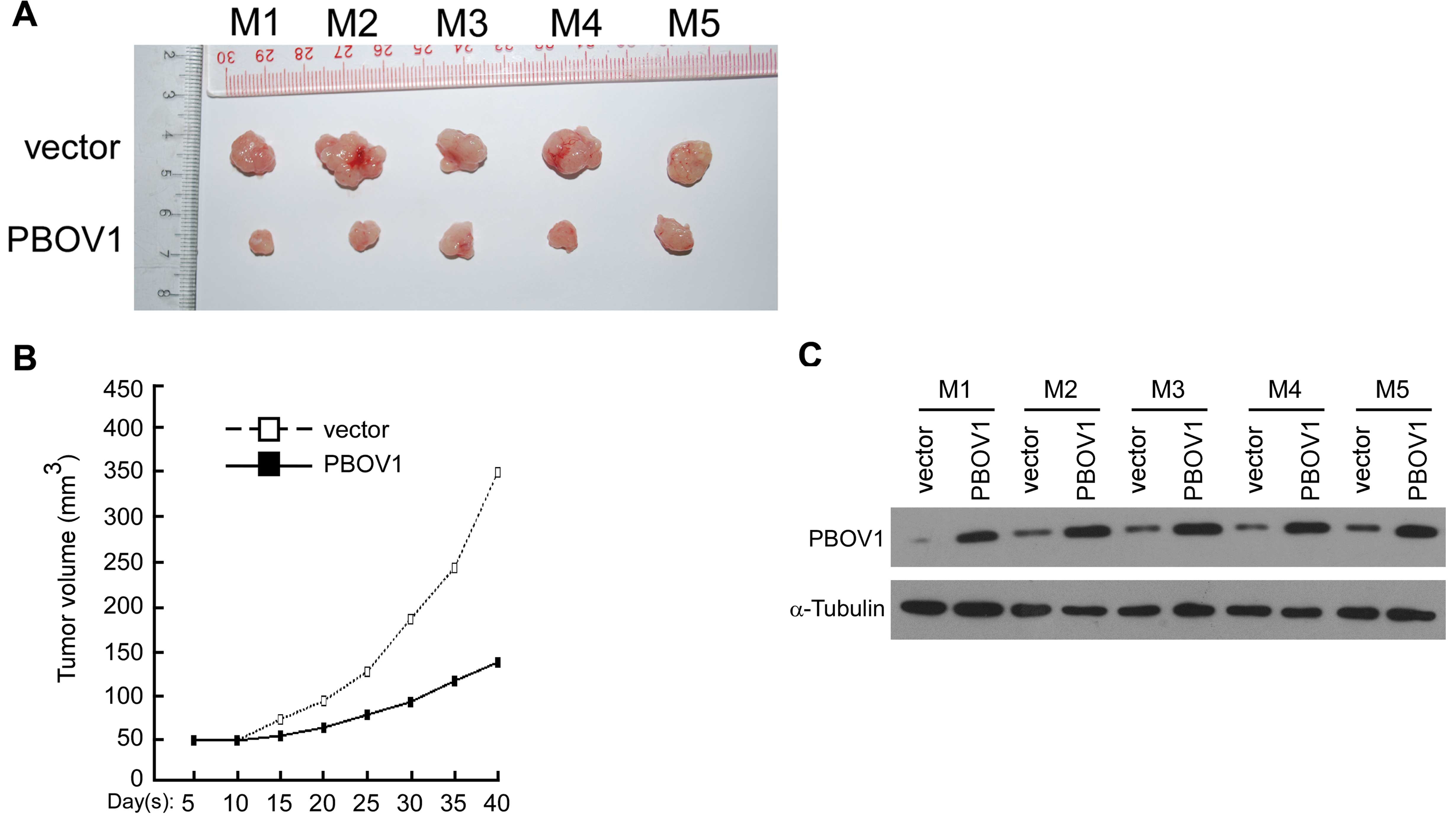
|
1
|
Whitmore SE, Rosenshein NB and Provost TT:
Ovarian cancer in patients with dermatomyositis. Medicine
(Baltimore). 73:153–160. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Markman M, Webster K, Zanotti K, Peterson
G, Kulp B and Belinson J: Survival following the documentation of
platinum and taxane resistance in ovarian cancer: A single
institution experience involving multiple phase 2 clinical trials.
Gynecol Oncol. 93:699–701. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
No authors listed. Debulking surgery in
ovarian cancer. J Clin Oncol. 4:1716–1717. 1986.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Rossing MA, Wicklund KG, Cushing-Haugen KL
and Weiss NS: Predictive value of symptoms for early detection of
ovarian cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst. 102:222–229. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Chudecka-Głaz AM, Cymbaluk-Płoska AA,
Menkiszak JL, Sompolska-Rzechuła AM, Tołoczko-Grabarek AI and
Rzepka-Górska IA: Serum He4, CA125, YKL-40, bcl-2, cathepsin-L and
prediction optimal debulking surgery, response to chemotherapy in
ovarian cancer. J Ovarian Res. 7:622014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
DiSaia PJ and Bloss JD: Treatment of
ovarian cancer: New strategies. Gynecol Oncol. 90:S24–S32. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Mantha S, Sarasohn D, Ma W, Devlin SM, Chi
DS, Roche KL, Suidan RS, Woo K and Soff GA: Ovarian vein thrombosis
after debulking surgery for ovarian cancer: Epidemiology and
clinical significance. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 213:208.e1–e4. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Krukovskaia LL, Samusik ND, Shilov ES,
Polev DE and Kozlov AP: Tumor-specific expression of PBOV1, a new
gene in evolution. Vopr Onkol. 56:327–332. 2010.In Russian.
|
|
9
|
Kamagata C, Tsuji N, Kondoh K, Sasaki M,
Kobayashi D, Yagihashi A and Watanabe N: Enhanced expression of the
uROC28 gene in human breast cancer: Relationship to ERBB2 gene
expression. Anticancer Res. 22:4087–4091. 2002.
|
|
10
|
Doak SH, Jenkins SA, Hurle RA, Varma M,
Hawizy A, Kynaston HG and Parry JM: Bone morphogenic factor gene
dosage abnormalities in prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia and
prostate cancer. Cancer Genet Cytogenet. 176:161–165. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Loizidou MA, Cariolou MA, Neuhausen SL,
Newbold RF, Bashiardes E, Marcou Y, Michael T, Daniel M, Kakouri E,
Papadopoulos P, et al: Genetic variation in genes interacting with
BRCA1/2 and risk of breast cancer in the Cypriot population. Breast
Cancer Res Treat. 121:147–156. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Samusik N, Krukovskaya L, Meln I, Shilov E
and Kozlov AP: PBOV1 is a human de novo gene with tumor-specific
expression that is associated with a positive clinical outcome of
cancer. PLoS One. 8:e561622013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Li J, Zhang N, Song LB, Liao WT, Jiang LL,
Gong LY, Wu J, Yuan J, Zhang HZ, Zeng MS, et al: Astrocyte elevated
gene-1 is a novel prognostic marker for breast cancer progression
and overall patient survival. Clin Cancer Res. 14:3319–3326. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Hahn WC, Dessain SK, Brooks MW, King JE,
Elenbaas B, Sabatini DM, DeCaprio JA and Weinberg RA: Enumeration
of the simian virus 40 early region elements necessary for human
cell transformation. Mol Cell Biol. 22:2111–2123. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Zhang Z, Li J, Zheng H, Yu C, Chen J, Liu
Z, Li M, Zeng M, Zhou F and Song L: Expression and cytoplasmic
localization of SAM68 is a significant and independent prognostic
marker for renal cell carcinoma. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev.
18:2685–2693. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Song L, Wang L, Li Y, Xiong H, Wu J, Li J
and Li M: Sam68 up-regulation correlates with, and its
down-regulation inhibits, proliferation and tumourigenicity of
breast cancer cells. J Pathol. 222:227–237. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Verkooijen HM, Koot VC, Fioretta G, van
der Heiden M, Schipper ME, Rapiti E, Peeters PH, Peterse JL and
Bouchardy C: Hormone replacement therapy, mammography screening and
changing age-specific incidence rates of breast cancer: An
ecological study comparing two european populations. Breast Cancer
Res Treat. 107:389–395. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Moran-Santa Maria MM, Flanagan J and Brady
K: Ovarian hormones and drug abuse. Curr Psychiatry Rep.
16:5112014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
McCullough ML, Patel AV, Patel R,
Rodriguez C, Feigelson HS, Bandera EV, Gansler T, Thun MJ and Calle
EE: Body mass and endometrial cancer risk by hormone replacement
therapy and cancer subtype. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev.
17:73–79. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Ansari J, Hussain SA, Zarkar A, Tanguay
JS, Bliss J and Glaholm J: Docetaxel chemotherapy for metastatic
hormone refractory prostate cancer as first-line palliative
chemotherapy and subsequent re-treatment: Birmingham experience.
Oncol Rep. 20:891–896. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Markman M, Glass T, Smith HO, Hatch KD,
Weiss GR, Taylor SA, Goodwin JW and Alberts DS: Phase II trial of
single agent carboplatin followed by dose-intense paclitaxel,
followed by maintenance paclitaxel therapy in stage IV ovarian,
fallopian tube, and peritoneal cancers: A Southwest Oncology Group
trial. Gynecol Oncol. 88:282–288. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Coleman RE: Current and future status of
adjuvant therapy for breast cancer. Cancer. 97(Suppl 3): 880–886.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Izadi-Mood N, Sarmadi S and Sanii S:
Strategies in the histologic diagnosis of low-grade glandular
endometrial neoplasm. Curr Opin Obstet Gynecol. 22:43–50. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Rochefort H, Chalbos D, Cunat S, Lucas A,
Platet N and Garcia M: Estrogen regulated proteases and
antiproteases in ovarian and breast cancer cells. J Steroid Biochem
Mol Biol. 76:119–124. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Elguero S, Patel B and Liu JH:
Misperception of estrogen activity in patients treated with an
estrogen receptor antagonist. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 211:e1–e2. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Krichevsky AM, King KS, Donahue CP,
Khrapko K and Kosik KS: A microRNA array reveals extensive
regulation of microRNAs during brain development. RNA. 9:1274–1281.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Kawasaki H and Taira K: Hes1 is a target
of microRNA-23 during retinoic-acid-induced neuronal
differentiation of NT2 cells. Nature. 423:838–842. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Li J, Liang S, Yu H, Zhang J, Ma D and Lu
X: An inhibitory effect of miR-22 on cell migration and invasion in
ovarian cancer. Gynecol Oncol. 119:543–548. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Hu X, Macdonald DM, Huettner PC, Feng Z,
El Naqa IM, Schwarz JK, Mutch DG, Grigsby PW, Powell SN and Wang X:
A miR-200 microRNA cluster as prognostic marker in advanced ovarian
cancer. Gynecol Oncol. 114:457–464. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Giannakakis A, Sandaltzopoulos R, Greshock
J, Liang S, Huang J, Hasegawa K, Li C, O'Brien-Jenkins A, Katsaros
D, Weber BL, et al: miR-210 links hypoxia with cell cycle
regulation and is deleted in human epithelial ovarian cancer.
Cancer Biol Ther. 7:255–264. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Bhattacharya R, Nicoloso M, Arvizo R, Wang
E, Cortez A, Rossi S, Calin GA and Mukherjee P: miR-15a and miR-16
control Bmi-1 expression in ovarian cancer. Cancer Res.
69:9090–9095. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|