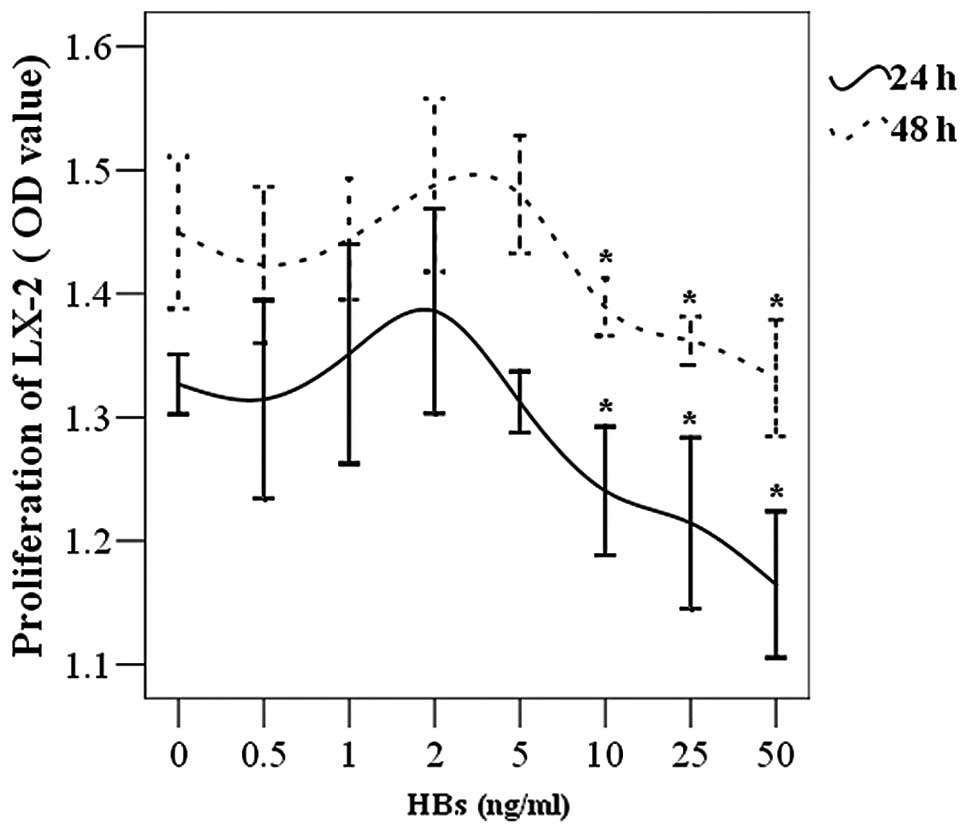
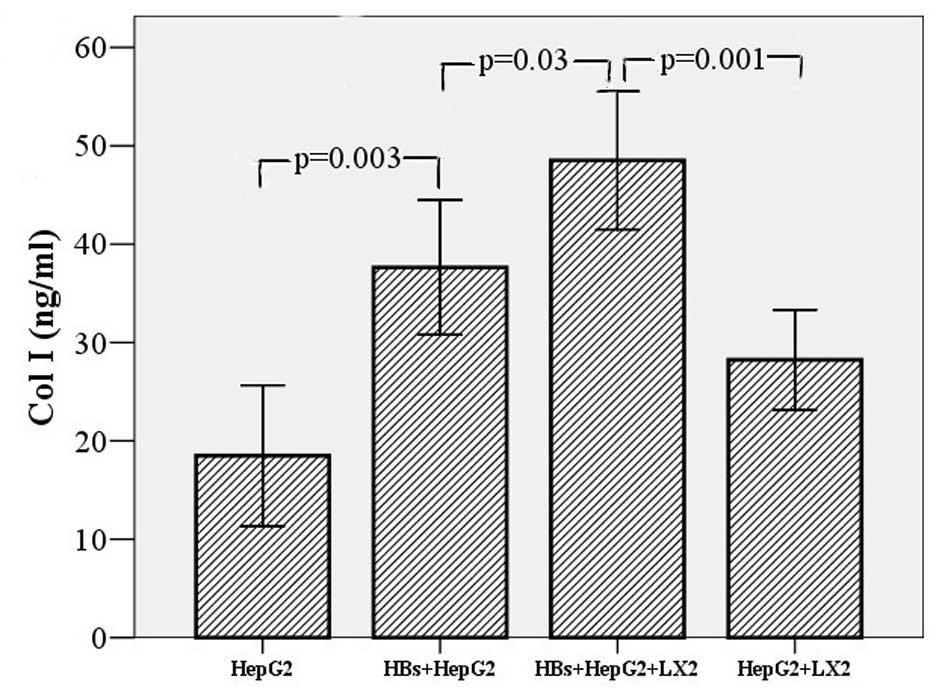
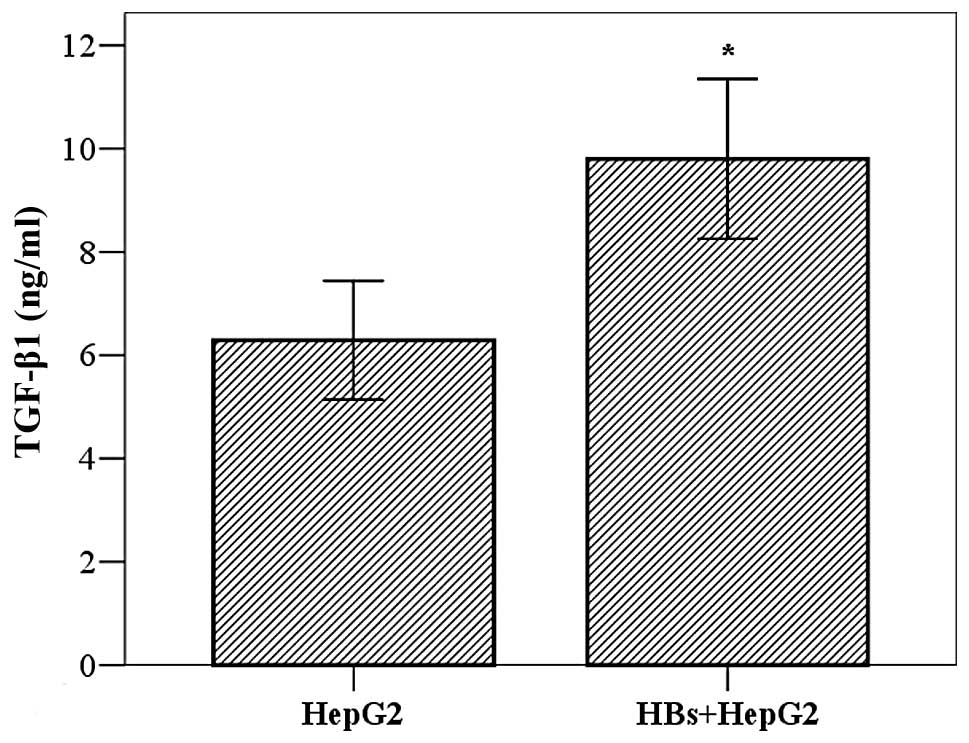
|
1
|
Ocama P, Opio CK and Lee WM: Hepatitis B
virus infection: current status. Am J Med. 118:14132005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Lavanchy D: Hepatitis B virus
epidemiology, disease burden, treatment, and current and emerging
prevention and control measures. J Viral Hepat. 11:97–107. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Kao JH and Chen DS: Global control of
hepatitis B virus infection. Lancet Infect Dis. 2:395–403. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Lee WM: Hepatitis B virus infection. N
Engl J Med. 337:1733–1745. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Ganem D and Prince AM: Hepatitis B virus
infection - natural history and clinical consequences. N Engl J
Med. 350:1118–1129. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Wright TL: Introduction to chronic
hepatitis B infection. Am J Gastroenterol. 101(Suppl 1): S1–S6.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Eng FJ and Friedman SL: Fibrogenesis I.
New insights into hepatic stellate cell activation: the simple
becomes complex. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol.
279:G7–G11. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Friedman SL: Molecular regulation of
hepatic fibrosis, an integrated cellular response to tissue injury.
J Biol Chem. 275:2247–2250. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Poynard T, Mathurin P, Lai CL, et al: A
comparison of fibrosis progression in chronic liver diseases. J
Hepatol. 38:257–265. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Norton PA, Reis HM, Prince S, et al:
Activation of fibronectin gene expression by hepatitis B virus x
antigen. J Viral Hepat. 11:332–341. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Guo GH, Tan DM, Zhu PA and Liu F:
Hepatitis B virus X protein promotes proliferation and upregulates
TGF-beta1 and CTGF in human hepatic stellate cell line, LX-2.
Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int. 8:59–64. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Martin-Vilchez S, Sanz-Cameno P,
Rodriguez-Munoz Y, et al: The hepatitis B virus X protein induces
paracrine activation of human hepatic stellate cells. Hepatology.
47:1872–1883. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Zan Y, Zhang Y and Tien P: Hepatitis B
virus e antigen induces activation of rat hepatic stellate cells.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 435:391–396. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Chen HY, Wang XZ and Chen ZX: Expression
of the hepatitis B virus X gene in liver cells promotes the
proliferation and migration of co-cultured hepatic stellate cells.
World Chin J Digestol. 20:721–728. 2012.(In Chinese).
|
|
15
|
Liu X, Zhu ST, You H, Cong M, Liu TH, Wang
BE and Jia JD: Hepatitis B virus infects hepatic stellate cells and
affects their proliferation and expression of collagen type I. Chin
Med J (Engl). 122:1455–1461. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Beasley RP, Shiao IS, Wu TC and Hwang LY:
Hepatoma in an HBsAg carrier - seven years after perinatal
infection. J Pediatr. 101:83–84. 1982.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Lupberger J and Hildt E: Hepatitis B
virus-induced oncogenesis. World J Gastroenterol. 13:74–81. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Chevaliez S: Is HBsAg quantification
ready, for prime time? Clin Res Hepatol Gastroenterol. Aug
7–2013.(Epub ahead of print). View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Mazzocca A, Sciammetta SC, Carloni V, et
al: Binding of hepatitis C virus envelope protein E2 to CD81
up-regulates matrix metalloproteinase-2 in human hepatic stellate
cells. J Biol Chem. 280:11329–11339. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Xu L, Hui AY, Albanis E, et al: Human
hepatic stellate cell lines, LX-1 and LX-2: new tools for analysis
of hepatic fibrosis. Gut. 54:142–151. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Gabele E, Brenner DA and Rippe RA: Liver
fibrosis: signals leading to the amplification of the fibrogenic
hepatic stellate cell. Front Biosci. 8:d69–d77. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Kato J, Sato Y, Inui N, et al: Ethanol
induces transforming growth factor-alpha expression in hepatocytes,
leading to stimulation of collagen synthesis by hepatic stellate
cells. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 27(Suppl 8): 58S–63S. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Parkes JG and Templeton DM: Modulation of
stellate cell proliferation and gene expression by rat hepatocytes:
effect of toxic iron overload. Toxicol Lett. 144:225–233. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Zeisberg M, Yang C, Martino M, et al:
Fibroblasts derive from hepatocytes in liver fibrosis via
epithelial to mesenchymal transition. J Biol Chem. 282:23337–23347.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Tseng TC, Liu CJ, Yang HC, et al: Serum
hepatitis B surface antigen levels help predict disease progression
in patients with low hepatitis B virus loads. Hepatology.
57:441–450. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Martinot-Peignoux M, Lapalus M, Asselah T
and Marcellin P: The role of HBsAg quantification for monitoring
natural history and treatment outcome. Liver Int. 33(Suppl 1):
125–132. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Liao R, Wu H, Yi Y, et al: Clinical
significance and gene expression study of human hepatic stellate
cells in HBV related-hepatocellular carcinoma. J Exp Clin Cancer
Res. 32:222013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Greupink R, Bakker HI, Bouma W, et al: The
antiproliferative drug doxorubicin inhibits liver fibrosis in bile
duct-ligated rats and can be selectively delivered to hepatic
stellate cells in vivo. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 317:514–521. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|