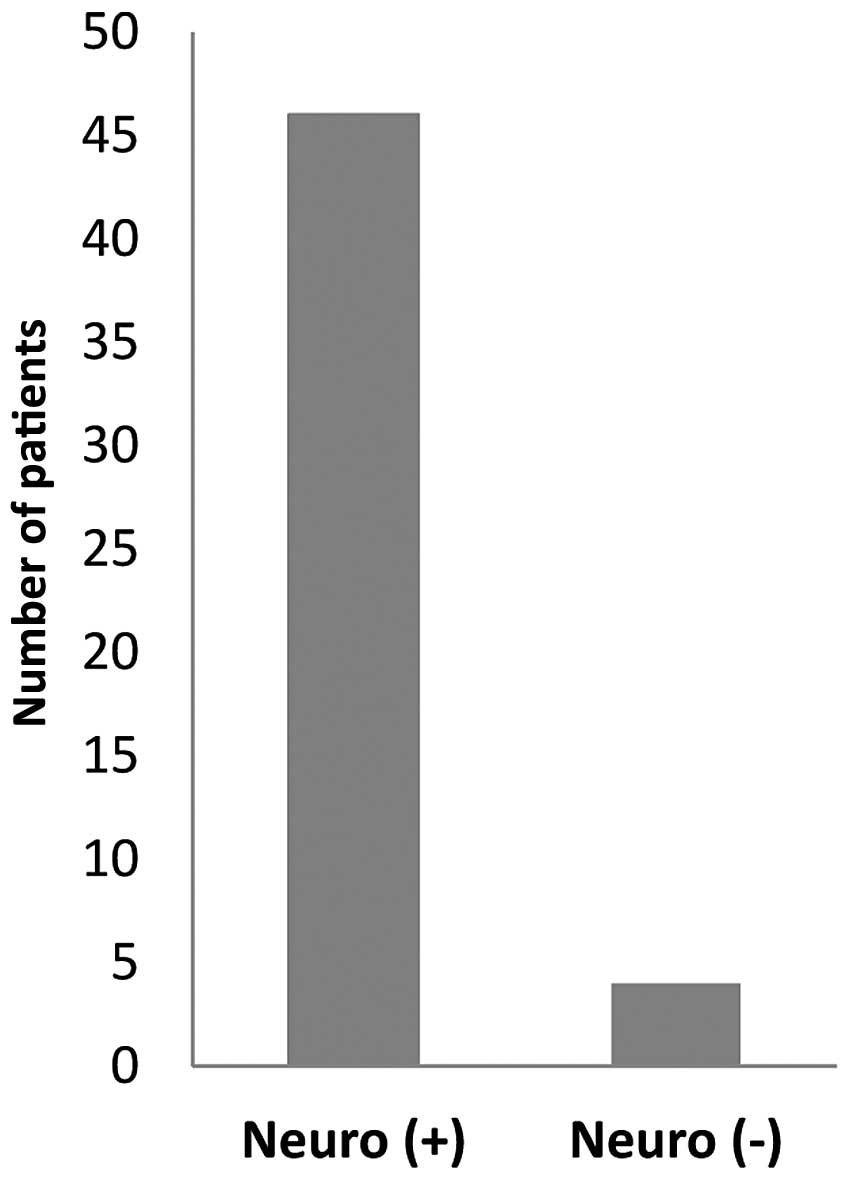
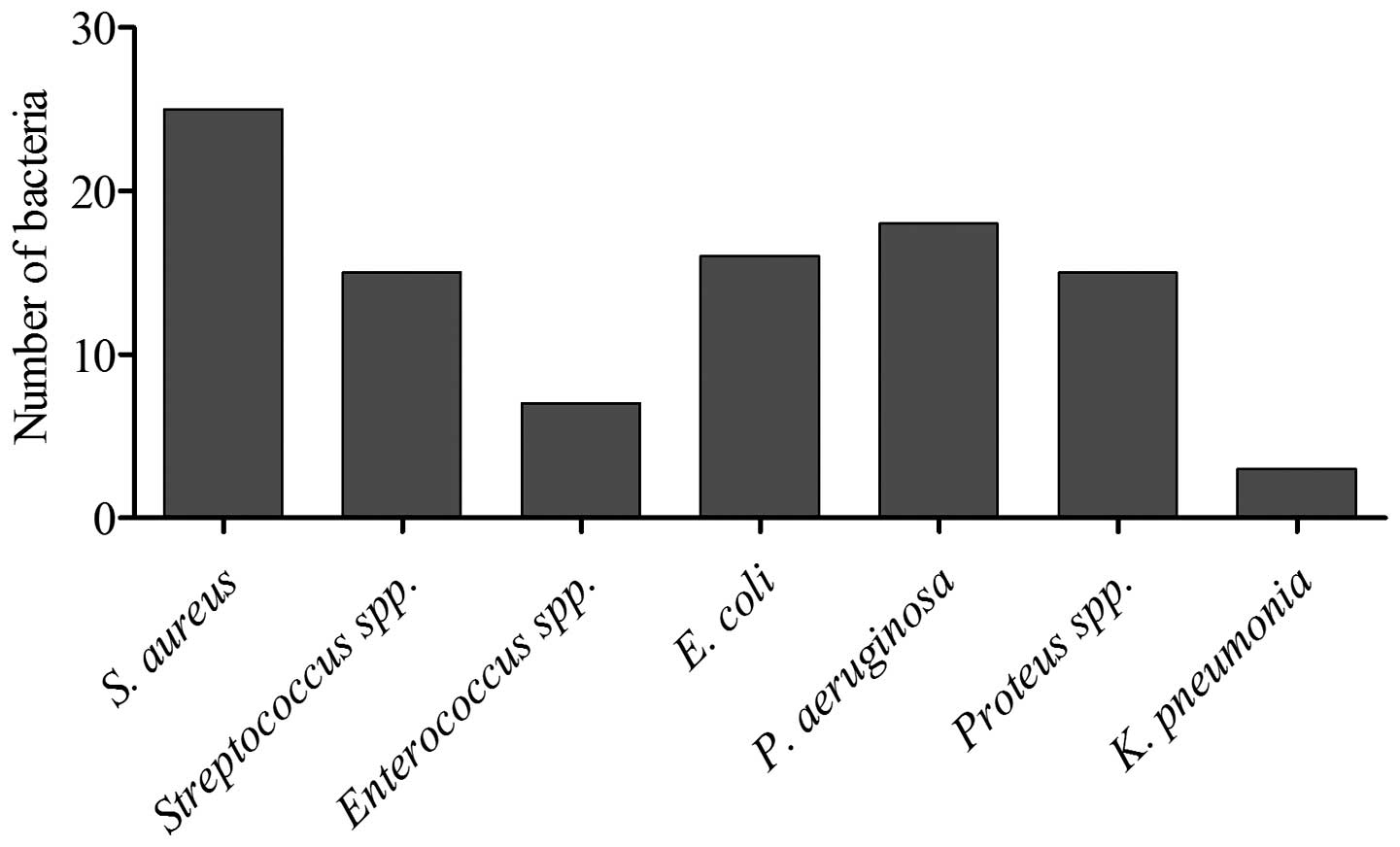
|
1
|
Singh N, Armstrong DG and Lipsky BA:
Preventing foot ulcers in patients with diabetes. JAMA.
293:217–228. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Mutlu F, Bener A, Eliyan A, Delghan H,
Nofal E, Shalabi L and Wadi N: Projection of Diabetes Burden
through 2025 and Contributing Risk Factors of Changing Disease
Prevalence: An Emerging Public Health Problem. J Diabetes Metab.
5:3412014.
|
|
3
|
Forouhi NG and Wareham NJ: Epidemiology of
diabetes. Medicine. 38:602–606. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Cusick M, Meleth AD, Agrón E, Fisher MR,
Reed GF, Knatterud GL, Barton FB, Davis MD, Ferris FL and Chew EY:
Early Treatment Diabetic Retinopathy Study Research Group:
Associations of mortality and diabetes complications in patients
with type 1 and type 2 diabetes: Early treatment diabetic
retinopathy study report no. 27. Diabetes Care. 28:617–625. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Clayton W and Elasy TA: A Review of the
Pathophysiology, Classification, and Treatment of Foot Ulcers in
Diabetic Patients. Clin Diabetes. 27:52–58. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Fowler MJ: Microvascular and macrovascular
complications of diabetes. Clinical diabetes. 26:77–82. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Bowler PG, Duerden BI and Armstrong DG:
Wound microbiology and associated approaches to wound management.
Clin Microbiol Rev. 14:244–269. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Argoff CE, Cole BE, Fishbain DA and Irving
GA: Diabetic peripheral neuropathic pain: Clinical and
quality-of-life issues. Mayo Clin Proc. 81(Suppl 4): S3–S11. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Podwall D and Gooch C: Diabetic
neuropathy: Clinical features, etiology, and therapy. Curr Neurol
Neurosci Rep. 4:55–61. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Delamaire M, Maugendre D, Moreno M, Le
Goff MC, Allannic H and Genetet B: Impaired leucocyte functions in
diabetic patients. Diabet Med. 14:29–34. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Siitonen OI, Niskanen LK, Laakso M,
Siitonen JT and Pyörälä K: Lower-extremity amputations in diabetic
and nondiabetic patients: A population-based study in eastern
Finland. Diabetes care. 16:16–20. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Trautner C, Haastert B, Giani G and Berger
M: Incidence of lower limb amputations and diabetes. Diabetes care.
19:1006–1009. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Paneni F, Beckman JA, Creager MA and
Cosentino F: Diabetes and vascular disease: Pathophysiology,
clinical consequences, and medical therapy. Eur Heart J.
34:2436–2443. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Reiber GE: Epidemiology of foot ulcers and
amputations in the diabetic foot. The diabetic foot. 6:13–32.
2001.
|
|
15
|
Tiwari S, Pratyush DD, Dwivedi A, Gupta
SK, Rai M and Singh SK: Microbiological and clinical
characteristics of diabetic foot infections in northern India. J
Infec Dev Ctries. 6:329–332. 2012.
|
|
16
|
Lipsky B, Pecoraro R and Wheat L: The
diabetic foot. Soft tissue and bone infection. Infect Dis Clin
North Am. 4:409–432. 1990.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Frykberg RG: An evidence-based approach to
diabetic foot infections. Am J Surg. 186(Suppl): S44–S54. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Benwan K, Al Mulla A and Rotimi VO: A
study of the microbiology of diabetic foot infections in a teaching
hospital in Kuwait. J Infect Public Health. 5:1–8. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Roberts RR, Hota B, Ahmad I, Scott RD 2nd,
Foster SD, Abbasi F, Schabowski S, Kampe LM, Ciavarella GG, Supino
M, et al: Hospital and societal costs of antimicrobial-resistant
infections in a Chicago teaching hospital: Implications for
antibiotic stewardship. Clin Infect Dis. 49:1175–1184. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Cosgrove SE, Sakoulas G, Perencevich EN,
Schwaber MJ, Karchmer AW and Carmeli Y: Comparison of mortality
associated with methicillin-resistant and methicillin-susceptible
Staphylococcus aureus bacteremia: A meta-analysis. Clin Infect Dis.
36:53–59. 2003. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Grundmann H, Aires-de-Sousa M, Boyce J and
Tiemersma E: Emergence and resurgence of meticillin-resistant
Staphylococcus aureus as a public-health threat. Lancet.
368:874–885. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Askari E, Soleymani F, Arianpoor A,
Tabatabai SM, Amini A and Nasab Naderi M: Epidemiology of
mecA-methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) in Iran: A
systematic review and meta-analysis. Iran J Basic Med Sci.
15:1010–1019. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Poole K: Resistance to beta-lactam
antibiotics. Cell Mol Life Sci. 61:2200–2223. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Bonnet R: Growing group of
extended-spectrum beta-lactamases: The CTX-M enzymes. Antimicrob
Agents Chemother. 48:1–14. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Perez F, Endimiani A, Hujer KM and Bonomo
RA: The continuing challenge of ESBLs. Curr Opin Pharmacol.
7:459–469. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Walsh TR, Toleman MA, Poirel L and
Nordmann P: Metallo-beta-lactamases: The quiet before the storm?
Clin Microbiol Rev. 18:306–325. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Shahi SK, Singh VK and Kumar A: Detection
of Escherichia coli and associated β-lactamases genes from diabetic
foot ulcers by multiplex PCR and molecular modeling and docking of
SHV-1, TEM-1, and OXA-1 β-lactamases with clindamycin and
piperacillin-tazobactam. PLoS One. 8:e682342013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Oyibo SO, Jude EB, Tarawneh I, Nguyen HC,
Harkless LB and Boulton AJ: A comparison of two diabetic foot ulcer
classification systems: The Wagner and the University of Texas
wound classification systems. Diabetes care. 24:84–88. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Bauer AW, Perry DM and Kirby WM:
Single-disk antibiotic-sensitivity testing of Staphylococci: An
analysis of technique and results. AMA Arch Intern Med.
104:208–216. 1959. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Clinical and Laboratory Standards
Institute (CLSI). Performance Standards for Antimicrobial
Susceptibility Testing: Twenty-first Informational Supplement
(M100-S21) (Wayne, PA). CLSI. 2011.
|
|
31
|
Singhal S, Mathur T, Khan S, Upadhyay DJ,
Chugh S, Gaind R and Rattan A: Evaluation of methods for AmpC
beta-lactamase in gram negative clinical isolates from tertiary
care hospitals. Indian J Med Microbiol. 23:120–124. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Yong D, Lee K, Yum JH, Shin HB, Rossolini
GM and Chong Y: Imipenem-EDTA disk method for differentiation of
metallo-beta-lactamase-producing clinical isolates of Pseudomonas
spp. and Acinetobacter spp. J Clin Microbiol. 40:3798–3801. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Shahcheraghi F, Nikbin VS and Feizabadi
MM: Prevalence of ESBLs genes among multidrug-resistant isolates of
Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolated from patients in Tehran. Microb
Drug Resist. 15:37–39. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Fang H, Ataker F, Hedin G and Dornbusch K:
Molecular epidemiology of extended-spectrum beta-lactamases among
Escherichia coli isolates collected in a Swedish hospital and its
associated health care facilities from 2001 to 2006. J Clin
Microbiol. 46:707–712. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Dallenne C, Da Costa A, Decré D, Favier C
and Arlet G: Development of a set of multiplex PCR assays for the
detection of genes encoding important beta-lactamases in
Enterobacteriaceae. J Antimicrob Chemother. 65:490–495. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Boyd DA, Tyler S, Christianson S, McGeer
A, Muller MP, Willey BM, Bryce E, Gardam M, Nordmann P and Mulvey
MR: Complete nucleotide sequence of a 92-kilobase plasmid harboring
the CTX-M-15 extended-spectrum beta-lactamase involved in an
outbreak in long-term-care facilities in Toronto, Canada.
Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 48:3758–3764. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Monstein HJ, Ostholm-Balkhed A, Nilsson M,
Nilsson M, Dornbusch K and Nilsson L: Multiplex PCR amplification
assay for the detection of blaSHV, blaTEM and blaCTX-M genes in
Enterobacteriaceae. APMIS. 115:1400–1408. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Rodrigues BT, Gilhotra RA, Vangaveti VN
and Malabu UH: Prevalence and risk factors of lower limb amputation
amongst diabetic food ulcer patients at the Townsville Hospital.
Annals of the ACTM. 15:572014.
|
|
39
|
Stockl K, Vanderplas A, Tafesse E and
Chang E: Costs of lower-extremity ulcers among patients with
diabetes. Diabetes Care. 27:2129–2134. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Gardner SE, Hillis SL, Heilmann K, Segre
JA and Grice EA: The neuropathic diabetic foot ulcer microbiome is
associated with clinical factors. Diabetes. 62:923–930. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Lipsky BA, Berendt AR, Deery HG, Embil JM,
Joseph WS, Karchmer AW, LeFrock JL, Lew DP, Mader JT, Norden C, et
al: Diagnosis and treatment of diabetic foot infections. Clin
Infect Dis. 39:885–910. 2004. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Monteiro-Soares M, Boyko EJ, Ribeiro J,
Ribeiro I and Dinis-Ribeiro M: Risk stratification systems for
diabetic foot ulcers: A systematic review. Diabetologia.
54:1190–1199. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
James GA, Swogger E, Wolcott R, Pulcini
ED, Secor P, Sestrich J, Costerton JW and Stewart PS: Biofilms in
chronic wounds. Wound Repair Regen. 16:37–44. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Mantey I, Hill R, Foster A, Wilson S, Wade
JJ and Edmonds ME: Infection of foot ulcers with Staphylococcus
aureus associated with increased mortality in diabetic patients.
Commun Dis Public Health. 3:288–290. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Dang CN, Prasad YD, Boulton AJ and Jude
EB: Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in the diabetic
foot clinic: A worsening problem. Diabet Med. 20:159–161. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Gadepalli R, Dhawan B, Sreenivas V, Kapil
A, Ammini AC and Chaudhry R: A clinico-microbiological study of
diabetic foot ulcers in an Indian tertiary care hospital. Diabetes
care. 29:1727–1732. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Trivedi U, Parameswaran S, Armstrong A,
Burgueno-Vega D, Griswold J, Dissanaike S and Rumbaugh KP:
Prevalence of Multiple Antibiotic Resistant Infections in Diabetic
versus Nondiabetic Wounds. J Pathog. 2014:1730532014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Richard JL, Sotto A and Lavigne JP: New
insights in diabetic foot infection. World J Diabetes. 2:24–32.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Satola SW, Lessa FC, Ray SM, Bulens SN,
Lynfield R, Schaffner W, Dumyati G, Nadle J and Patel JB: Active
Bacterial Core surveillance (ABCs) MRSA Investigators: Clinical and
laboratory characteristics of invasive infections due to
methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus isolates demonstrating
a vancomycin MIC of 2 micrograms per milliliter: Lack of effect of
heteroresistant vancomycin-intermediate S. aureus phenotype. J Clin
Microbiol. 49:1583–1587. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Harish BN, Menezes GA, Shekatkar S and
Parija SC: Extended-spectrum beta-lactamase-producing Klebsiella
pneumoniae from blood culture. J Med Microbiol. 56:999–1000. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Parveen RM, Khan MA, Menezes GA, Harish
BN, Parija SC and Hays JP: Extended-spectrum β-lactamase producing
Klebsiella pneumoniae from blood cultures in Puducherry, India.
Indian J Med Res. 134:392–395. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Umadevi S, Joseph NM, Kumari K, Easow JM,
Kumar S, Stephen S, Srirangaraj S and Raj S: Detection of extended
spectrum beta lactamases, AmpC beta lactamases and
metallobetalactamases in clinical isolates of ceftazidime resistant
Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Braz J Microbiol. 42:1284–1288.
2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Saderi H, Karimi Z, Owlia P, Bahar MA and
Rad SMBA: phenotypic detection of metallo-beta-lactamase producing
Pseudomonas aeruginosa strains isolated from burned patients.
Iranian Journal of Pathology. 3:20–24. 2008.
|
|
54
|
Bukhari SZ, Ahmed S and Zia N:
Antimicrobial susceptibility pattern of Staphylococcus aureus on
clinical isolates and efficacy of laboratory tests to diagnose
MRSA: MRSA: A multi-centre study. J Ayub Med Coll Abbottabad.
23:139–142. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Šeputienė V, Linkevičius M, Bogdaitė A,
Povilonis J, Plančiūnienė R, Giedraitiene A, Pavilonis A and
Sužiedėlienė E: Molecular characterization of extended-spectrum
β-lactamase-producing Escherichia coli and Klebsiella pneumoniae
isolates from hospitals in Lithuania. J Med Microbiol.
59:1263–1265. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Bali EB, Accedil L and Sultan N:
Phenotypic and molecular characterization of SHV, TEM, CTX-M and
extended-spectrum-lactamase produced by Escherichia coli,
Acinobacter baumannii and Klebsiella isolates in a Turkish
hospital. African Journal of Microbiology Research. 4:650–654.
2010.
|
|
57
|
Umadevi S, Kandhakumari G, Joseph NM,
Kumar S, Easow JM, Stephen S and Singh UK: Prevalence and
antimicrobial susceptibility pattern of ESBL producing gram
negative bacilli. J Clin Diagn Res. 5:236–239. 2011.
|