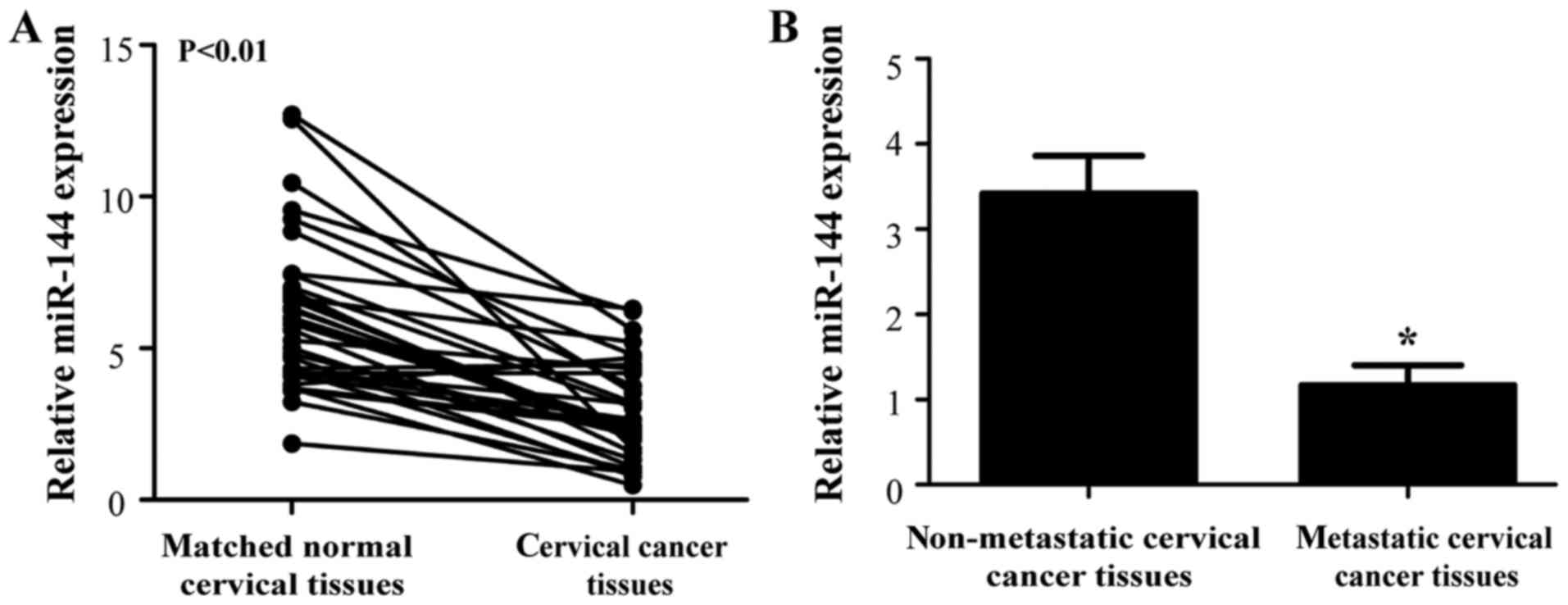
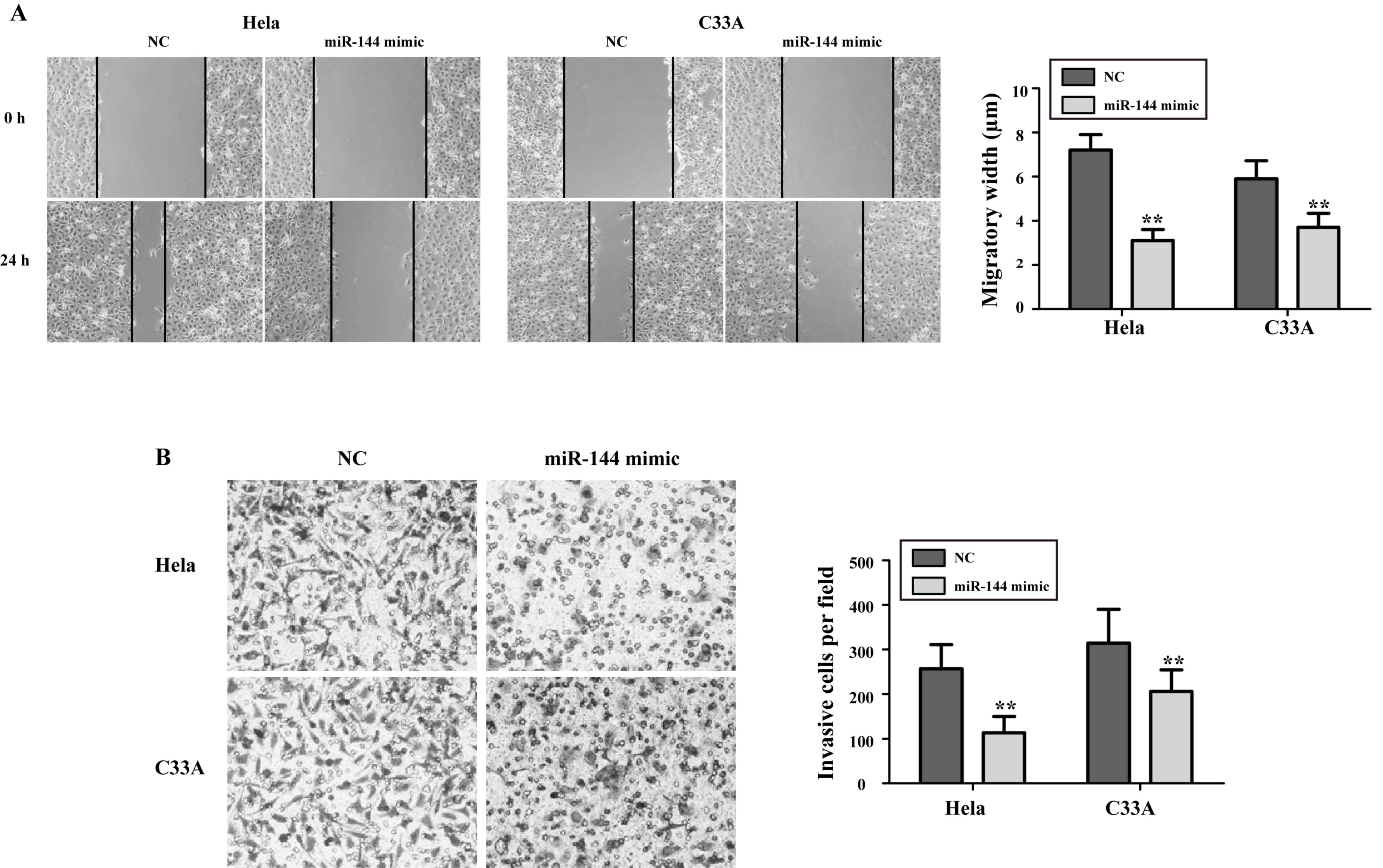
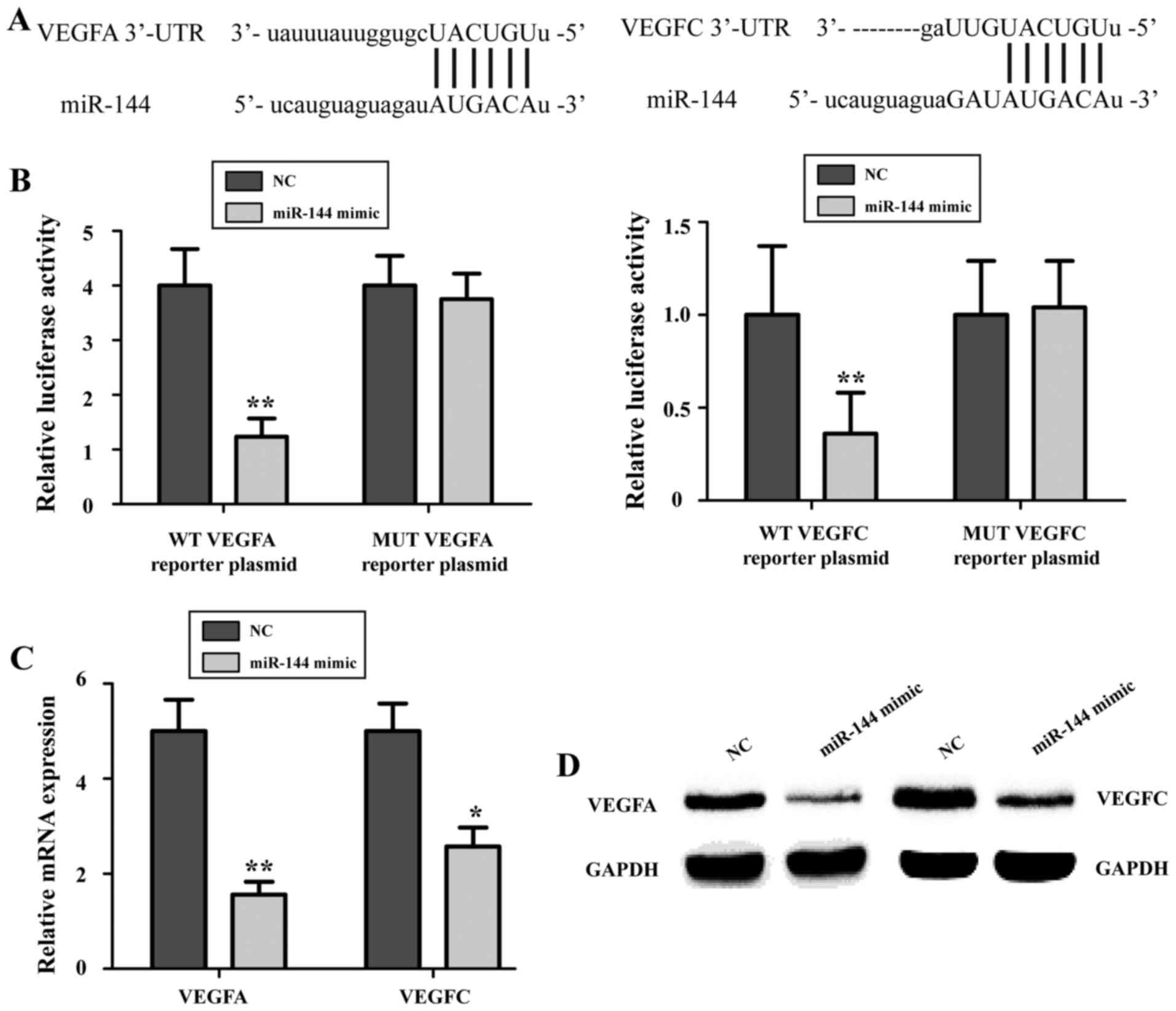
|
1
|
Siegel R, Ma J, Zou Z and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2014. CA Cancer J Clin. 64:9–29. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward
E and Forman D: Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin.
61:69–90. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Hildesheim A and Wang SS: Host and viral
genetics and risk of cervical cancer: A review. Virus Res.
89:229–240. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Castellsagué X: Natural history and
epidemiology of HPV infection and cervical cancer. Gynecol Oncol.
110(3 Suppl 2): S4–S7. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Du CX and Wang Y: Expression of P-Akt,
NFkappaB and their correlation with human papillomavirus infection
in cervical carcinoma. Eur J Gynaecol Oncol. 33:274–277.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Bartel DP: MicroRNAs: Target recognition
and regulatory functions. Cell. 136:215–233. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Moreno-Moya JM, Vilella F and Simón C:
MicroRNA: Key gene expression regulators. Fertil Steril.
101:1516–1523. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Ventura A and Jacks T: MicroRNAs and
cancer: Short RNAs go a long way. Cell. 136:586–591. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Bartels CL and Tsongalis GJ: MicroRNAs:
Novel biomarkers for human cancer. Clin Chem. 55:623–631. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Wang X, Tang S, Le SY, Lu R, Rader JS,
Meyers C and Zheng ZM: Aberrant expression of oncogenic and
tumor-suppressive microRNAs in cervical cancer is required for
cancer cell growth. PLoS One. 3:e25572008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Ambros V: The functions of animal
microRNAs. Nature. 431:350–355. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Wang X and Xia Y: microRNA-328 inhibits
cervical cancer cell proliferation and tumorigenesis by targeting
TCF7L2. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 475:169–175. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Ye H, Yu X, Xia J, Tang X, Tang L and Chen
F: MiR-486-3p targeting ECM1 represses cell proliferation and
metastasis in cervical cancer. Biomed Pharmacother. 80:109–114.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Zhou JY, Zheng SR, Liu J, Shi R, Yu HL and
Wei M: MiR-519d facilitates the progression and metastasis of
cervical cancer through direct targeting Smad7. Cancer Cell Int.
16:212016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Cheng YX, Zhang QF, Hong L, Pan F, Huang
JL, Li BS and Hu M: MicroRNA-200b suppresses cell invasion and
metastasis by inhibiting the epithelial-mesenchymal transition in
cervical carcinoma. Mol Med Rep. 13:3155–3160. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Dore LC, Amigo JD, Dos Santos CO, Zhang Z,
Gai X, Tobias JW, Yu D, Klein AM, Dorman C, Wu W, et al: A
GATA-1-regulated microRNA locus essential for erythropoiesis. Proc
Natl Acad Sci USA. 105:pp. 3333–3338. 2008; View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Lawrie CH: microRNA expression in
erythropoiesis and erythroid disorders. Br J Haematol. 150:144–151.
2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Cao T, Li H, Hu Y, Ma D and Cai X: miR-144
suppresses the proliferation and metastasis of hepatocellular
carcinoma by targeting E2F3. Tumour Biol. 35:10759–10764. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Cai SD, Chen JS, Xi ZW, Zhang LJ, Niu ML
and Gao ZY: MicroRNA144 inhibits migration and proliferation in
rectal cancer by downregulating ROCK-1. Mol Med Rep. 12:7396–7402.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Wang H, Wang A, Hu Z, Xu X, Liu Z and Wang
Z: A Critical role of miR-144 in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma
proliferation and invasion. Cancer Immunol Res. 4:337–344. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Ding H, Wu YL, Wang YX and Zhu FF:
Characterization of the microRNA expression profile of cervical
squamous cell carcinoma metastases. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev.
15:1675–1679. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Du L, Lei Y, Li D, Qiu X and Liang B:
Value of magnetic resonance imaging in preoperative staging of
endometrial carcinoma according to International Federation of
Gynecology and Obstetrics (2009) staging criteria. Nan Fang Yi Ke
Da Xue Xue Bao. 32:1048–1051. 2012.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Schmittgen TD and Livak KJ: Analyzing
real-time PCR data by the comparative C(T) method. Nat Protoc.
3:1101–1108. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Wang LQ, Zhang Y, Yan H, Liu KJ and Zhang
S: MicroRNA-373 functions as an oncogene and targets YOD1 gene in
cervical cancer. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 459:515–520. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Schickel R, Boyerinas B, Park SM and Peter
ME: MicroRNAs: Key players in the immune system, differentiation,
tumorigenesis and cell death. Oncogene. 27:5959–5974. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Chen B, Hou Z, Li C and Tong Y: MiRNA-494
inhibits metastasis of cervical cancer through Pttg1. Tumour Biol.
36:7143–7149. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Wang N, Wei H, Yin D, Lu Y, Zhang Y, Zhang
Q, Ma X and Zhang S: MicroRNA-195 inhibits proliferation of
cervical cancer cells by targeting cyclin D1a. Tumour Biol.
37:4711–4720. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Shao Y, Li P, Zhu ST, Yue JP, Ji XJ, Ma D,
Wang L, Wang YJ, Zong Y, Wu YD and Zhang ST: MiR-26a and miR-144
inhibit proliferation and metastasis of esophageal squamous cell
cancer by inhibiting cyclooxygenase-2. Oncotarget. 7:15173–15186.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Wu X, Cui CL, Chen WL, Fu ZY, Cui XY and
Gong X: miR-144 suppresses the growth and metastasis of laryngeal
squamous cell carcinoma by targeting IRS1. Am J Transl Res. 8:1–11.
2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Zhang SY, Lu ZM, Lin YF, Chen LS, Luo XN,
Song XH, Chen SH and Wu YL: miR-144-3p, a tumor suppressive
microRNA targeting ETS-1 in laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma.
Oncotarget. 7:11637–11650. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Guo Y, Ying L, Tian Y, Yang P, Zhu Y, Wang
Z, Qiu F and Lin J: miR-144 downregulation increases bladder cancer
cell proliferation by targeting EZH2 and regulating Wnt signaling.
FEBS J. 280:4531–4538. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Wilting SM, Miok V, Jaspers A, Boon D,
Sørgård H, Lando M, Snoek BC, van Wieringen WN, Meijer CJ, Lyng H,
et al: Aberrant methylation-mediated silencing of microRNAs
contributes to HPV-induced anchorage independence. Oncotarget.
7:43805–43819. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Wang W, Zhou X and Wei M: MicroRNA-144
suppresses osteosarcoma growth and metastasis by targeting ROCK1
and ROCK2. Oncotarget. 6:10297–10308. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Matsushita R, Seki N, Chiyomaru T,
Inoguchi S, Ishihara T, Goto Y, Nishikawa R, Mataki H, Tatarano S,
Itesako T, et al: Tumour-suppressive microRNA-144-5p directly
targets CCNE1/2 as potential prognostic markers in bladder cancer.
Br J Cancer. 113:282–289. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Goel HL and Mercurio AM: VEGF targets the
tumour cell. Nat Rev Cancer. 13:871–882. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Fu Z, Chen D, Cheng H and Wang F:
Hypoxia-inducible factor-1α protects cervical carcinoma cells from
apoptosis induced by radiation via modulation of vascular
endothelial growth factor and p53 under hypoxia. Med Sci Monit.
21:318–325. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Tsuda N, Watari H and Ushijima K:
Chemotherapy and molecular targeting therapy for recurrent cervical
cancer. Chin J Cancer Res. 28:241–253. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Cai Y, Li H and Zhang Y: Downregulation of
microRNA-206 suppresses clear cell renal carcinoma proliferation
and invasion by targeting vascular endothelial growth factor A.
Oncol Rep. 35:1778–1786. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Liu Z, Wang J, Mao Y, Zou B and Fan X:
MicroRNA-101 suppresses migration and invasion via targeting
vascular endothelial growth factor-C in hepatocellular carcinoma
cells. Oncol Lett. 11:433–438. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Chen L, Wu YY, Liu P, Wang J, Wang G, Qin
J, Zhou J and Zhu J: Down-regulation of HPV18 E6, E7, or VEGF
expression attenuates malignant biological behavior of human
cervical cancer cells. Med Oncol. 28 Suppl 1:S528–S539. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Liu J, Cheng Y, He M and Yao S: Vascular
endothelial growth factor C enhances cervical cancer cell
invasiveness via upregulation of galectin-3 protein. Gynecol
Endocrinol. 30:461–465. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Chen H, Suo K, Cheng Y, Zheng B and Xu L:
Vascular endothelial growth factor C enhances cervical cancer
migration and invasion via activation of focal adhesion kinase.
Gynecol Endocrinol. 29:20–24. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|