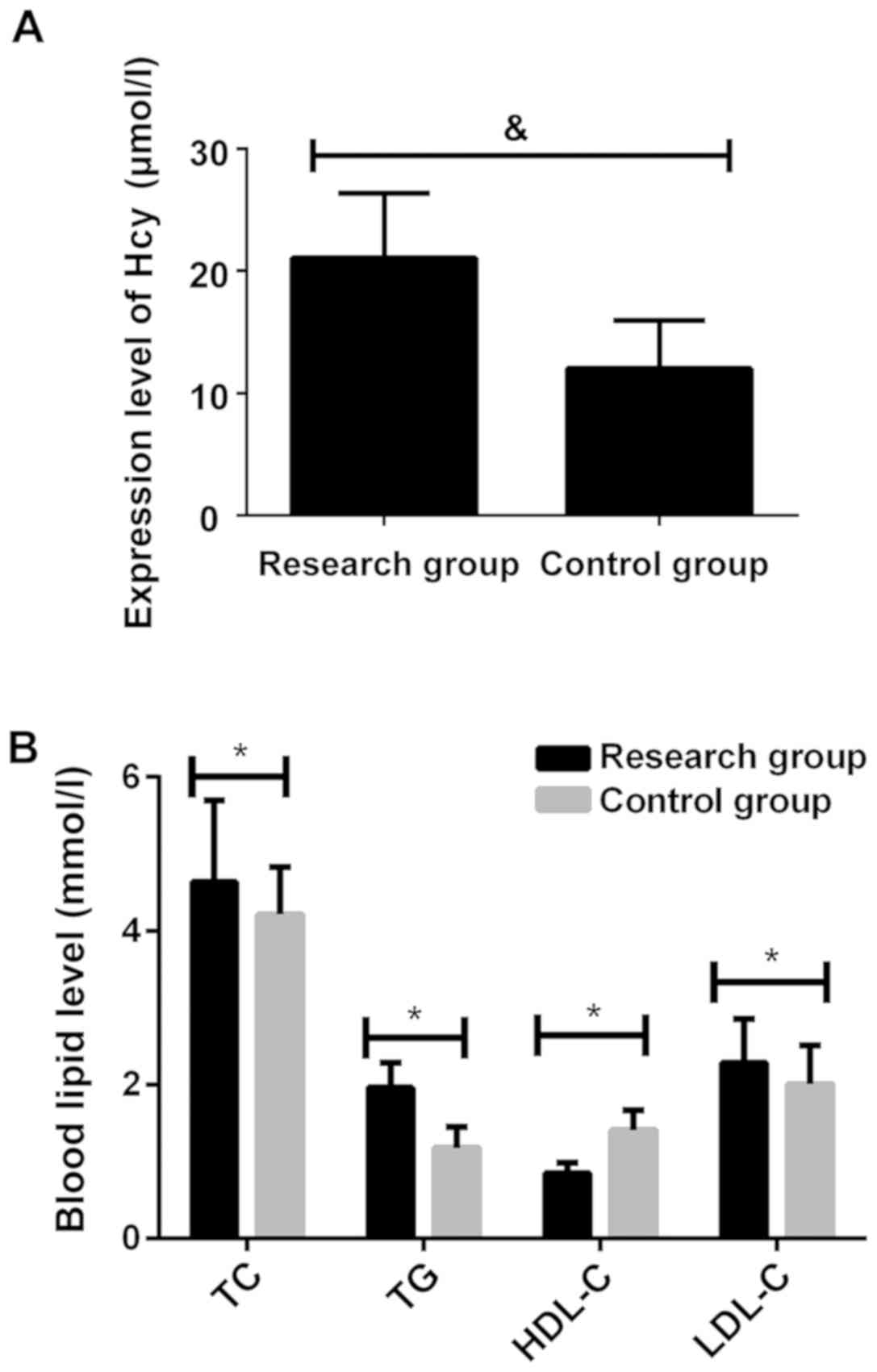
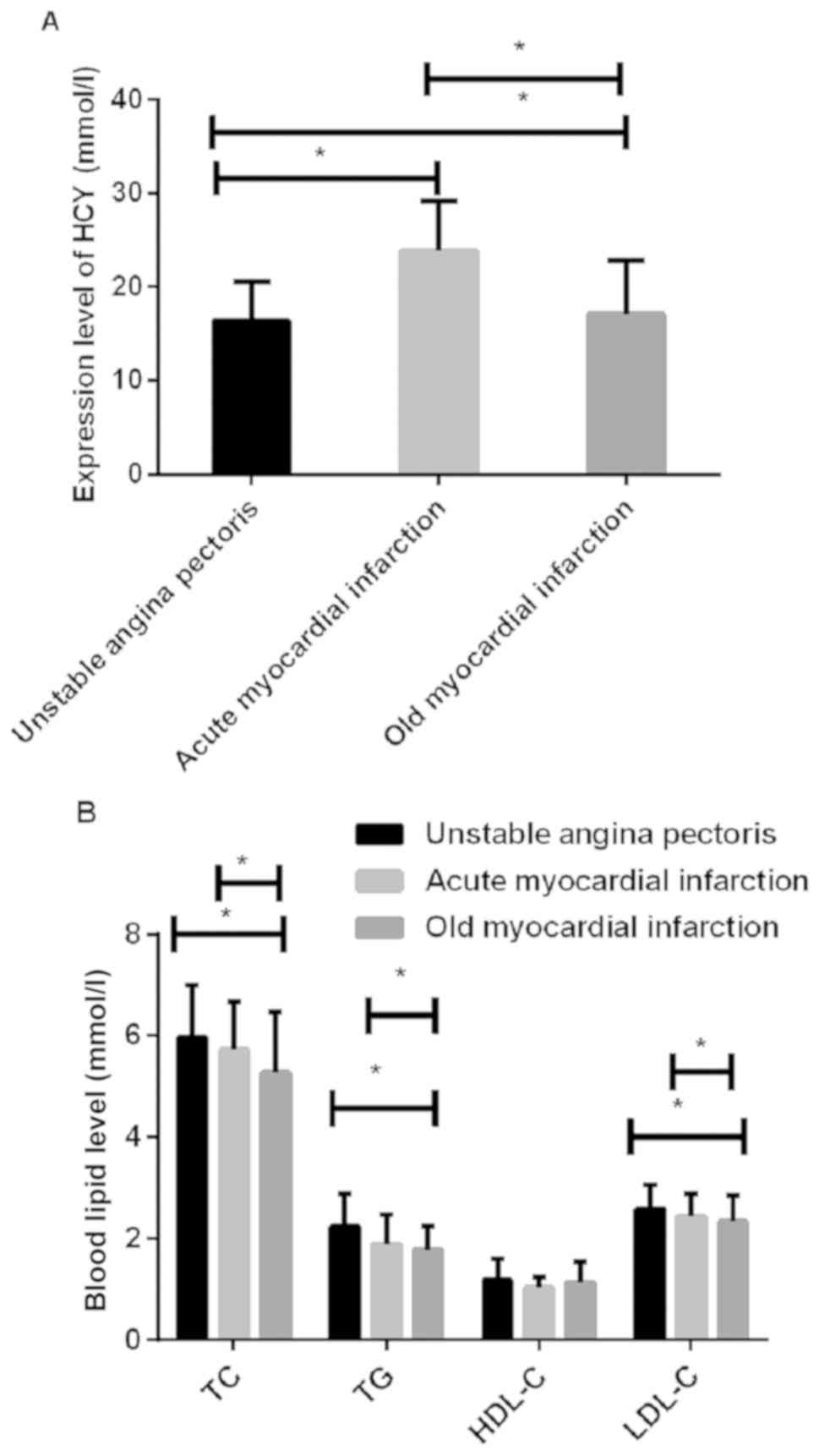
|
1
|
Zhong Y, Wang N, Xu H, Hou X, Xu P and
Zhou Z: Ischemia-modified albumin in stable coronary
atherosclerotic heart disease: Clinical diagnosis and risk
stratification. Coron Artery Dis. 23:538–541. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Su Z, Zhang S, Hou Y, Zhang L, Liao L, Xia
Q, Xiao C, Meng H and Yan Y: A preliminary study of single
nucleotide polymorphisms of lipoprotein lipase gene in coronary
atherosclerotic heart disease. Zhonghua Yi Xue Yi Chuan Xue Za Zhi.
17:157–160. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Lyu Y, Jiang X and Dai W: The roles of a
novel inflammatory neopterin in subjects with coronary
atherosclerotic heart disease. Int Immunopharmacol. 24:169–172.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Ozkan Y, Ozkan E and Simşek B: Plasma
total homocysteine and cysteine levels as cardiovascular risk
factors in coronary heart disease. Int J Cardiol. 82:269–277. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Mayer O Jr, Simon J, Holubec L, Pikner R,
Vobrubová I and Trefil L: Fibrate treatment and prevalence risk of
mild hyperhomocysteinaemia in clinical coronary heart disease
patients. Eur J Cardiovasc Prev Rehabil. 11:244–249. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Naureen A, Munazza B, Shaheen R, Khan SA
and Fatima F: Serum homocysteine as a risk factor for coronary
heart disease. J Ayub Med Coll Abbottabad. 24:59–62.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Wang P, Liu J, Lv X, Liu Y, Zhao Y and Guo
W: A naphthalimide-based glyoxal hydrazone for selective
fluorescence turn-on sensing of Cys and Hcy. Org Lett. 14:520–523.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Nabipour I, Vahdat K, Jafari SM, Amiri M,
Shafeiae E, Riazi A, Amini AL, Pazoki R and Sanjdideh Z:
Correlation of hyperhomocysteinaemia and Chlamydia
pneumoniae IgG seropositivity with coronary artery disease in a
general population. Heart Lung Circ. 16:416–422. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Sainani GS and Sainani R: Homocysteine and
its role in the pathogenesis of atherosclerotic vascular disease. J
Assoc Physicians India. 50 Suppl:16–23. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Zhang HJ, Han P, Sun SY, Wang LY, Yan B,
Zhang JH, Zhang W, Yang SY and Li XJ: Attenuated associations
between increasing BMI and unfavorable lipid profiles in Chinese
Buddhist vegetarians. Asia Pac J Clin Nutr. 22:249–256.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Sierakowska-Fijalek A, Kaczmarek P, Pokoca
L, Smorag I, Wosik-Erenbek M and Baj Z: Homocystein serum levels
and lipid parameters in children with atherosclerosis risk factors.
Pol Merkur Lekarski. 22:146–149. 2007.(In Polish). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Wenger NK, Shaw LJ and Vaccarino V:
Coronary heart disease in women: Update 2008. Clin Pharmacol Ther.
83:37–51. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Aronow WS: Association between plasma
homocysteine and vascular atherosclerotic disease in older persons.
Prev Cardiol. 3:89–91. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Doncheva N, Penkov A, Velcheva A, Boev M,
Popov B and Niagolov Y: Study of homocysteine concentration in
coronary heart disease patients and comparison of two determination
methods. Ann Nutr Metab. 51:82–87. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Isaacs A, Willems SM, Bos D, Dehghan A,
Hofman A, Ikram MA, Uitterlinden AG, Oostra BA, Franco OH, Witteman
JC, et al: Risk scores of common genetic variants for lipid levels
influence atherosclerosis and incident coronary heart disease.
Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 33:2233–2239. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Granberry MC, Smith ES III and Talley JD:
Raising HDL-C to prevent atherosclerotic events. J Ark Med Soc.
96:378–379. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Asztalos BF, Roheim PS, Milani RL, Lefevre
M, McNamara JR, Horvath KV and Schaefer EJ: Distribution of
ApoA-I-containing HDL subpopulations in patients with coronary
heart disease. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 20:2670–2676. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Paavola T, Kangas-Kontio T, Salonurmi T,
Kuusisto S, Huusko T, Savolainen MJ and Kakko S: Plasma levels of
antibodies against oxidized LDL are inherited but not associated
with HDL-cholesterol level in families with early coronary heart
disease. Atherosclerosis. 224:123–128. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Christensen B, Landaas S, Stensvold I,
Djurovic S, Retterstøl L, Ringstad J, Berg K and Thelle DS: Whole
blood folate, homocysteine in serum, and risk of first acute
myocardial infarction. Atherosclerosis. 147:317–326. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Huang T, Yuan G, Zhang Z, Zou Z and Li D:
Cardiovascular pathogenesis in hyperhomocysteinemia. Asia Pac J
Clin Nutr. 17:8–16. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Menezes AR, Lavie CJ, Milani RV, Arena RA
and Church TS: Cardiac rehabilitation and exercise therapy in the
elderly: Should we invest in the aged? J Geriatr Cardiol. 9:68–75.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Bruce IN: ‘Not only…but also’: Factors
that contribute to accelerated atherosclerosis and premature
coronary heart disease in systemic lupus erythematosus.
Rheumatology (Oxford). 44:1492–1502. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Lynch J, Davey Smith G, Harper S and
Bainbridge K: Explaining the social gradient in coronary heart
disease: Comparing relative and absolute risk approaches. J
Epidemiol Community Health. 60:436–441. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Marijon E, Trinquart L, Jani D, Jourdier
H, Garbarz E, Mocumbi AO, Celermajer DS and Ferreira B: Coronary
heart disease and associated risk factors in sub-Saharan Africans.
J Hum Hypertens. 21:411–414. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Maas AH, van der Schouw YT, Beijerinck D,
Deurenberg JJ, Mali WP and van der Graaf Y: Arterial calcifications
seen on mammograms: Cardiovascular risk factors, pregnancy, and
lactation. Radiology. 240:33–38. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|