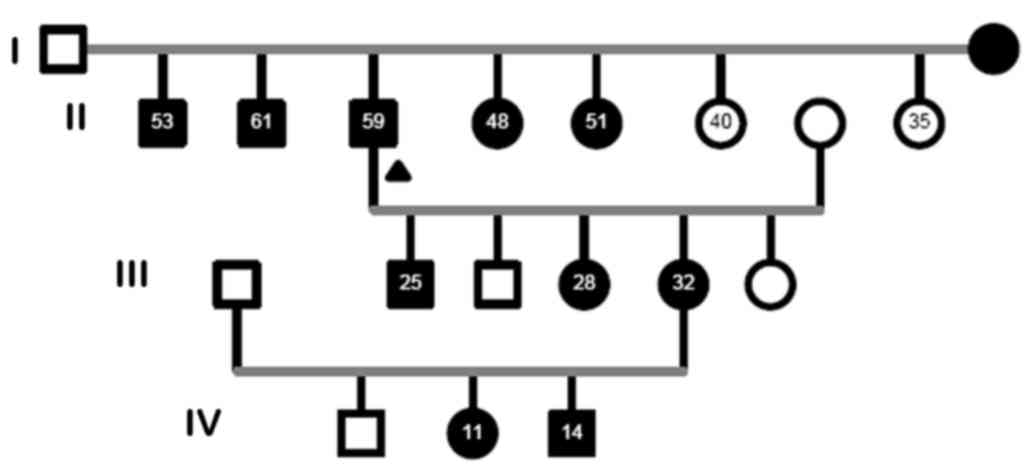
|
1
|
Trujillano D, Bullich G, Ossowski S,
Ballarín J, Torra R, Estivill X and Ars E: Diagnosis of autosomal
dominant polycystic kidney disease using efficient PKD1 and PKD2
targeted next-generation sequencing. Mol Genet Genomic Med.
2:412–421. 2014. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Wilson PD: Polycystic kidney disease. N
Engl J Med. 350:151–164. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Srivastava A and Patel N: Autosomal
dominant polycystic kidney disease. Am Fam Physician. 90:303–307.
2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Kurashige M, Hanaoka K, Imamura M, Udagawa
T, Kawaguchi Y, Hasegawa T, Hosoya T, Yokoo T and Maeda S: A
comprehensive search for mutations in the PKD1 and PKD2 in Japanese
subjects with autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease. Clin
Genet. 87:266–272. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Germino GG, Weinstat-Saslow D, Himmelbauer
H, Gillespie GA, Somlo S, Wirth B, Barton N, Harris KL, Frischauf
AM and Reeders ST: The gene for autosomal dominant polycystic
kidney disease lies in a 750-kb CpG-rich region. Genomics.
13:144–151. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Cornec-Le Gall E, Audrézet MP, Le Meur Y,
Chen JM and Férec C: Genetics and pathogenesis of autosomal
dominant polycystic kidney disease: 20 years on. Hum Mutat.
35:1393–1406. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Hughes J, Ward CJ, Peral B, Aspinwall R,
Clark K, San Millán JL, Gamble V and Harris PC: The polycystic
kidney disease 1 (PKD1) gene encodes a novel protein with multiple
cell recognition domains. Nat Genet. 10:151–160. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Nims N, Vassmer D and Maser RL:
Transmembrane domain analysis of polycystin-1, the product of the
polycystic kidney disease-1 (PKD1) gene: Evidence for 11
membrane-spanning domains. Biochemistry. 42:13035–13048. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Pei Y, Obaji J, Dupuis A, Paterson AD,
Magistroni R, Dicks E, Parfrey P, Cramer B, Coto E, Torra R, et al:
Unified criteria for ultrasonographic diagnosis of ADPKD. J Am Soc
Nephrol. 20:205–212. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Tan AY, Michaeel A, Liu G, Elemento O,
Blumenfeld J, Donahue S, Parker T, Levine D and Rennert H:
Molecular diagnosis of autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease
using next-generation sequencing. J Mol Diagn. 16:216–228. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Ding L and Zhang S, Qiu W, Xiao C, Wu S,
Zhang G, Cheng L and Zhang S: Novel mutations of PKD1 gene in
Chinese patients with autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease.
Nephrol Dial Transplant. 17:75–80. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Yu C, Yang Y, Zou L, Hu Z, Li J, Liu Y, Ma
Y, Ma M, Su D and Zhang S: Identification of novel mutations in
Chinese Hans with autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease. BMC
Med Genet. 12:1642011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Liu G, Tan AY, Michaeel A, Blumenfeld J,
Donahue S, Bobb W, Parker T, Levine D and Rennert H: Development
and validation of a whole genome amplification long-range PCR
sequencing method for ADPKD genotyping of low-level DNA samples.
Gene. 550:131–135. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Yang T, Meng Y, Wei X, Shen J, Zhang M, Qi
C, Wang C, Liu J, Ma M and Huang S: Identification of novel
mutations of PKD1 gene in Chinese patients with autosomal dominant
polycystic kidney disease by targeted next-generation sequencing.
Clin Chim Acta. 433:12–19. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Rossetti S, Hopp K, Sikkink RA, Sundsbak
JL, Lee YK, Kubly V, Eckloff BW, Ward CJ, Winearls CG, Torres VE
and Harris PC: Identification of gene mutations in autosomal
dominant polycystic kidney disease through targeted resequencing. J
Am Soc Nephrol. 23:915–933. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Eisenberger T, Decker C, Hiersche M,
Hamann RC, Decker E, Neuber S, Frank V, Bolz HJ, Fehrenbach H, Pape
L, et al: An efficient and comprehensive strategy for genetic
diagnostics of polycystic kidney disease. PloS One.
10:e01166802015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Edrees BM, Athar M, Al-Allaf FA, Taher MM,
Khan W, Bouazzaoui A, Al-Harbi N, Safar R, Al-Edressi H, Alansary
K, et al: Next-generation sequencing for molecular diagnosis of
autosomal recessive polycystic kidney disease. Gene. 591:214–226.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Harris PC and Hopp K: The mutation, a key
determinant of phenotype in ADPKD. J Am Soc Nephrol. 24:868–870.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Li J, Yu C, Tao Y, Yang Y, Hu Z and Zhang
S: Putative mutation of PKD1 gene responsible for autosomal
dominant polycystic kidney disease in a Chinese family. Int J Urol.
18:240–242. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Gout AM, Martin NC, Brown AF and Ravine D:
PKDB: Polycystic kidney disease mutation database-a gene variant
database for autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease. Hum
Mutat. 28:654–659. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Ravine D, Gibson RN, Walker RG, Sheffield
LJ, Kincaid-Smith P and Danks DM: Evaluation of ultrasonographic
diagnostic criteria for autosomal dominant polycystic kidney
disease 1. Lancet. 343:824–827. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Sambrook J and Russell DW: Purification of
nucleic acids by extraction with phenol: Chloroform. CSH Protoc.
2006.pdb.prot44552006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Stenson PD, Mort M, Ball EV, Howells K,
Phillips AD, Thomas NS and Cooper DN: The human gene mutation
database: 2008 update. Genome Med. 1:132009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Schwarz JM, Rödelsperger C, Schuelke M and
Seelow D: MutationTaster evaluates disease-causing potential of
sequence alterations. Nat Methods. 7:575–576. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Kumar P, Henikoff S and Ng PC: Predicting
the effects of coding non-synonymous variants on protein function
using the SIFT algorithm. Nat Protoc. 4:1073–1081. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Adzhubei IA, Schmidt S, Peshkin L,
Ramensky VE, Gerasimova A, Bork P, Kondrashov AS and Sunyaev SR: A
method and server for predicting damaging missense mutations. Nat
Methods. 7:248–249. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Desmet FO, Hamroun D, Lalande M,
Collod-Béroud G, Claustres M and Béroud C: Human Splicing Finder:
An online bioinformatics tool to predict splicing signals. Nucleic
Acids Res. 37:e672009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Rossetti S, Chauveau D, Walker D,
Saggar-Malik A, Winearls CG, Torres VE and Harris PC: A complete
mutation screen of the ADPKD genes by DHPLC. Kidney Int.
61:1588–1599. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Kinoshita M, Higashihara E, Kawano H,
Higashiyama R, Koga D, Fukui T, Gondo N, Oka T, Kawahara K, Rigo K,
et al: Technical evaluation: Identification of pathogenic mutations
in PKD1 and PKD2 in patients with autosomal dominant polycystic
kidney disease by next-generation sequencing and use of a
comprehensive new classification system. PloS One. 11:e01662882016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Flaherty L, Bryda EC, Collins D, Rudofsky
U and Montgomery JC: New mouse model for polycystic kidney disease
with both recessive and dominant gene effects. Kidney Int.
47:552–558. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Cornec-Le Gall E, Audrézet MP, Chen JM,
Hourmant M, Morin MP, Perrichot R, Charasse C, Whebe B, Renaudineau
E, Jousset P, et al: Type of PKD1 mutation influences renal outcome
in ADPKD. J Am Soc Nephrol. 24:1006–1013. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Heyer CM, Sundsbak JL, Abebe KZ, Chapman
AB, Torres VE, Grantham JJ, Bae KT, Schrier RW, Perrone RD, Braun
WE, et al: Predicted mutation strength of nontruncating PKD1
mutations aids genotype-phenotype correlations in autosomal
dominant polycystic kidney disease. J Am Soc Nephrol. 27:2872–2884.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Sherry ST, Ward MH, Kholodov M, Baker J,
Phan L, Smigielski EM and Sirotkin K: dbSNP: The NCBI database of
genetic variation. Nucleic Acids Res. 29:308–311. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Gainullin VG, Hopp K, Ward CJ, Hommerding
CJ and Harris PC: Polycystin-1 maturation requires polycystin-2 in
a dose-dependent manner. J Clin Invest. 125:607–620. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Siva N: 1000 Genomes project. Nat
Biotechnol. 26:2562008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|