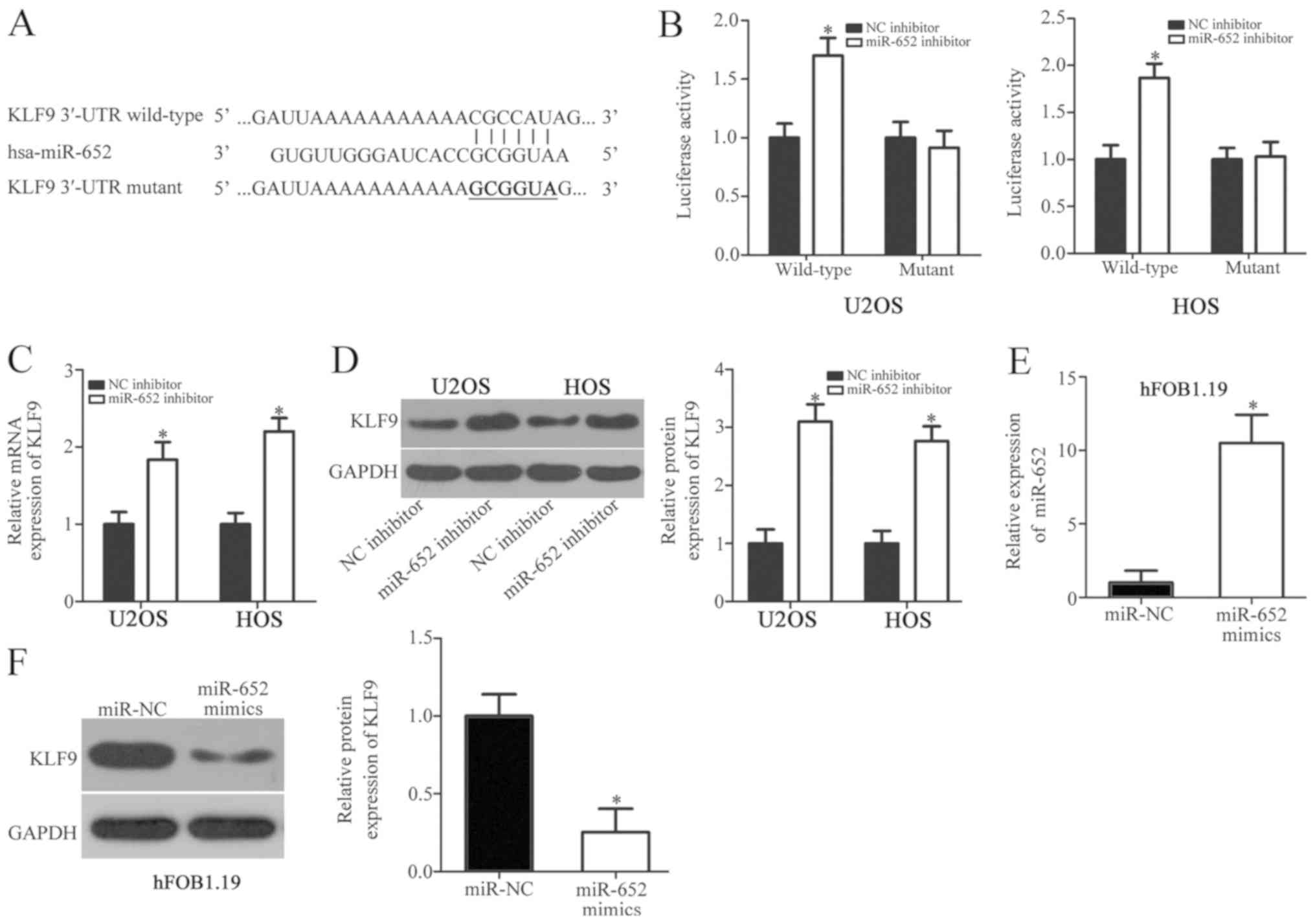
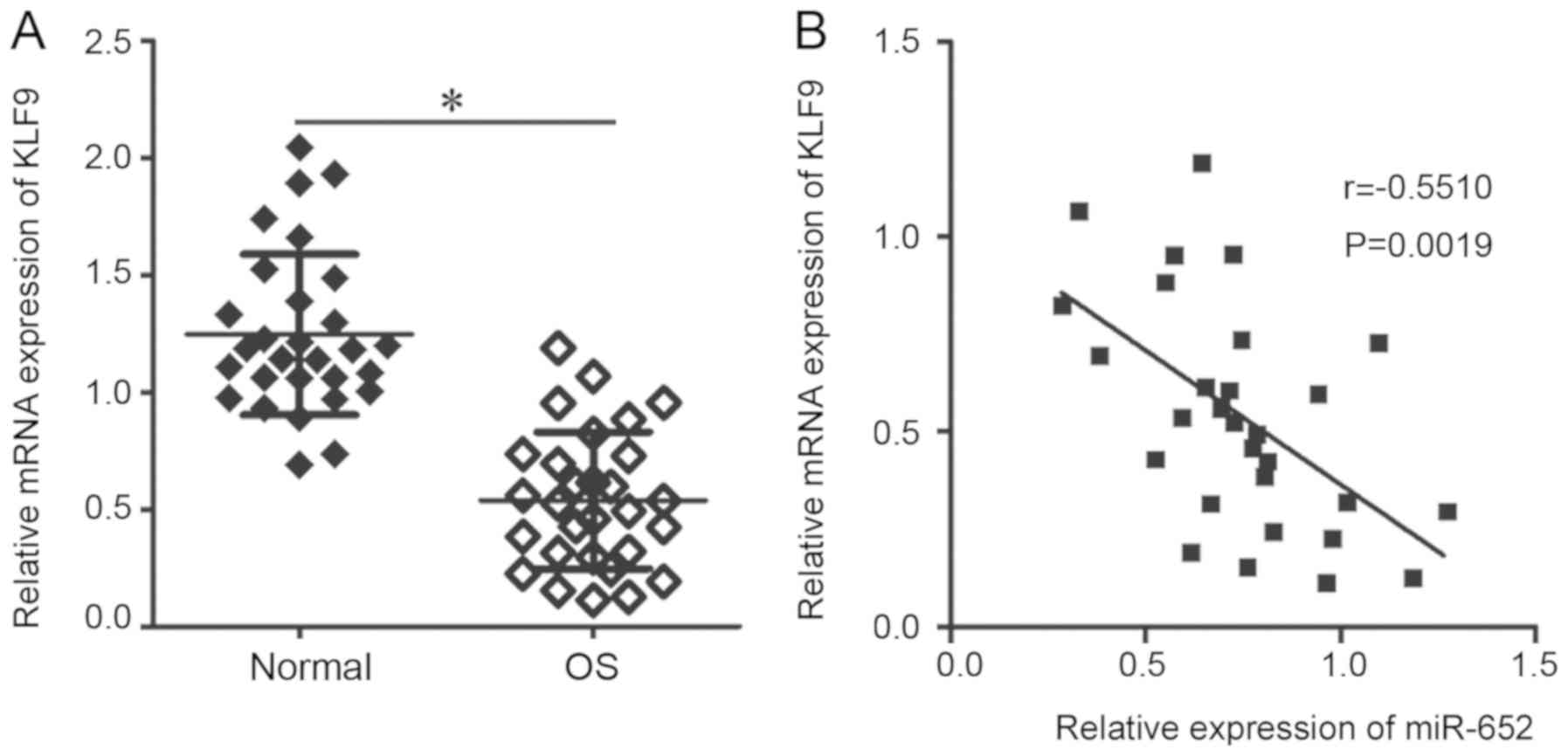
|
1
|
Ando K, Mori K, Verrecchia F, Marc B,
Redini F and Heymann D: Molecular alterations associated with
osteosarcoma development. Sarcoma. 2012(523432)2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Picci P: Osteosarcoma (osteogenic
sarcoma). Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2(6)2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Tan ML, Choong PF and Dass CR:
Osteosarcoma: Conventional treatment vs. Gene therapy. Cancer Biol
Ther. 8:106–117. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Ferrari S, Palmerini E, Staals EL, Mercuri
M, Franco B, Picci P and Bacci G: The treatment of nonmetastatic
high grade osteosarcoma of the extremity: Review of the italian
rizzoli experience. Impact on the future. Cancer Treat Res.
152:275–287. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Pan Y, Lu L, Chen J, Zhong Y and Dai Z:
Identification of potential crucial genes and construction of
MicroRNA-MRNA negative regulatory networks in osteosarcoma.
Hereditas. 155(21)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
To KK, Tong CW, Wu M and Cho WC: MicroRNAs
in the prognosis and therapy of colorectal cancer: From bench to
bedside. World J Gastroenterol. 24:2949–2973. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Yuan HL, Wang T and Zhang KH: MicroRNAs as
potential biomarkers for diagnosis, therapy and prognosis of
gastric cancer. Onco Targets Ther. 11:3891–3900. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Sharma N and Baruah MM: The microRNA
signatures: Aberrantly expressed miRNAs in prostate cancer. Clin
Transl Oncol. 21:126–144. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Han K, Chen X, Bian N, Ma B, Yang T, Cai
C, Fan Q, Zhou Y and Zhao TB: MicroRNA profiling identifies MiR-195
suppresses osteosarcoma cell metastasis by targeting CCND1.
Oncotarget. 6:8875–8889. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Bartel DP: MicroRNAs: Genomics,
biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 116:281–297.
2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Chen X, Jia C, Jia C, Jin X and Gu X:
MicroRNA-374a Inhibits aggressive tumor biological behavior in
bladder carcinoma by suppressing wnt/β-Catenin signaling. Cell
Physiol Biochem. 48:815–826. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Tao Y, Ma C, Fan Q, Wang Y, Han T and Sun
C: MicroRNA-1296 facilitates proliferation, migration and invasion
of colorectal cancer cells by targeting SFPQ. J Cancer.
9:2317–2326. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Yang JZ, Bian L, Hou JG and Wang HY:
MiR-550a-3p promotes non-small cell lung cancer cell proliferation
and metastasis through down-regulating TIMP2. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol
Sci. 22:4156–4165. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Wu Y, Huang J, Xu H and Gong Z:
Over-Expression of MiR-15a-3p enhances the radiosensitivity of
cervical cancer by targeting tumor protein D52. Biomed
Pharmacother. 105:1325–1334. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Leichter AL, Sullivan MJ, Eccles MR and
Chatterjee A: MicroRNA expression pat terns and signalling pathways
in the development and progression of childhood solid tumours. Mol
Cancer. 16(15)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Kim YH, Goh TS, Lee CS, Oh SO, Kim JI,
Jeung SH and Pak K: Prognostic value of microRNAs in osteosarcoma:
A meta-analysis. Oncotarget. 8:8726–8737. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Wang Z, Zheng C, Jiang K, He J, Cao X and
Wu S: MicroRNA-503 suppresses cell proliferation and invasion in
osteosarcoma via targeting insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor.
Exp Ther Med. 14:1547–1553. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Ma C, Han J, Dong D and Wang N:
MicroRNA-152 suppresses human osteosarcoma cell proliferation and
invasion by targeting E2F transcription factor 3. Oncol Res.
26:765–773. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Liu K, Sun X, Zhang Y, Liu L and Yuan Q:
MiR-598: A tumor suppressor with biomarker significance in
osteosarcoma. Life Sci. 188:141–148. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Deng S, Li X, Niu Y, Zhu S, Jin Y, Deng S,
Chen J, Liu Y, He C, Yin T, et al: MiR-652 inhibits acidic
microenvironment-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition of
pancreatic cancer cells by targeting ZEB1. Oncotarget.
6:39661–39675. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Yang W, Zhou C, Luo M, Shi X, Li Y, Sun Z,
Zhou F, Chen Z and He J: MiR-652-3p is upregulated in non-small
cell lung cancer and promotes proliferation and metastasis by
directly targeting Lgl1. Oncotarget. 7:16703–16715. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408.
2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Peng N, Miao Z, Wang L, Liu B, Wang G and
Guo X: MiR-378 promotes the cell proliferation of osteosarcoma
through down-regulating the expression of kruppel-like factor 9.
Biochem Cell Biol. 96:515–521. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Sampson VB, Yoo S, Kumar A, Vetter NS and
Kolb EA: MicroRNAs and potential targets in osteosarcoma: Review.
Front Pediatr. 3(69)2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Smolle MA, Leithner A, Posch F, Szkandera
J, Liegl-Atzwanger B and Pichler M: MicroRNAs in different
histologies of soft tissue sarcoma: A comprehensive review. Int J
Mol Sci. 18(E1960)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Yao J, Zhang P, Li J and Xu W:
MicroRNA-215 acts as a tumor suppressor in breast cancer by
targeting AKT serine/threonine kinase 1. Oncol Lett. 14:1097–1104.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
McConnell BB and Yang VW: Mammalian
kruppel-like factors in health and diseases. Physiol Rev.
90:1337–1381. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Mao Z, Fan X, Zhang J, Wang X, Ma X,
Michalski CW and Zhang Y: KLF9 is a prognostic indicator in human
pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Anticancer Res. 37:3795–3799.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Sun J, Wang B and Liu Y, Zhang L, Ma A,
Yang Z, Ji Y and Liu Y: Transcription factor KLF9 suppresses the
growth of hepatocellular carcinoma cells vivo and positively
regulates p53 expression. Cancer Lett. 355:25–33. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Kang L, Lu B, Xu J, Hu H and Lai M:
Downregulation of kruppel-like factor 9 in human colorectal cancer.
Pathol Int. 58:334–338. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Shen P, Sun J, Xu G, Zhang L, Yang Z, Xia
S, Wang Y, Liu Y and Shi G: KLF9, a transcription factor induced in
flutamide-caused cell apoptosis, inhibits AKT activation and
suppresses tumor growth of prostate cancer cells. Prostate.
74:946–958. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Bai XY, Li S, Wang M, Li X, Yang Y, Xu Z,
Li B, Li Y, Xia K, Chen H and Wu H: Kruppel-like factor 9
down-regulates matrix metalloproteinase 9 transcription and
suppresses human breast cancer invasion. Cancer Lett. 412:224–235.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Huang S, Wang C, Yi Y, Sun X, Luo M, Zhou
Z, Li J, Cai Y, Jiang X and Ke Y: Kruppel-like factor 9 inhibits
glioma cell proliferation and tumorigenicity via downregulation of
miR-21. Cancer Lett. 356:547–555. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Zhang QH, Dou HT, Tang YJ, Su S and Liu
PS: Lentivirus-mediated knockdown of Kruppel-like factor 9 inhibits
the growth of ovarian cancer. Arch Gynecol Obstet. 291:377–382.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|