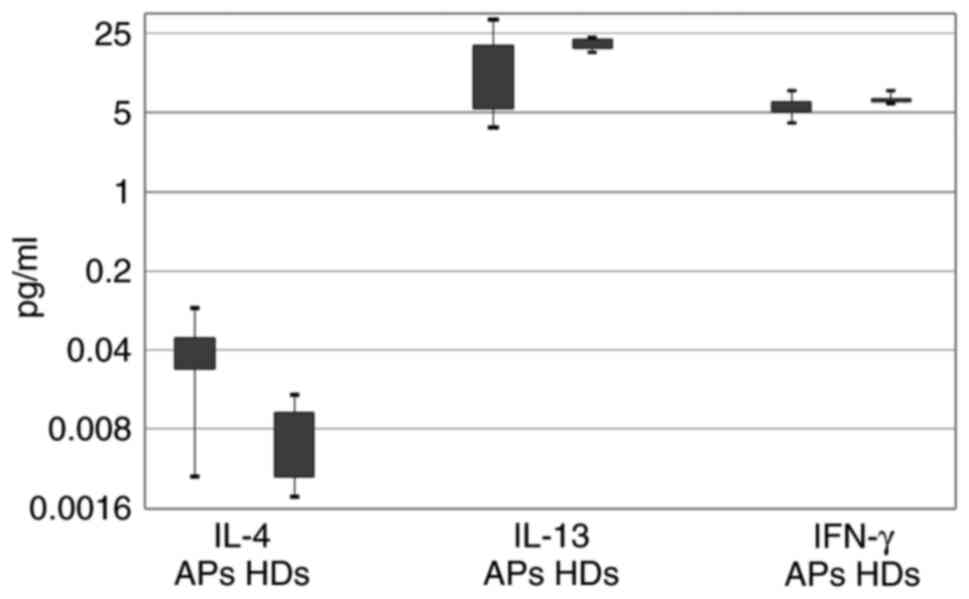
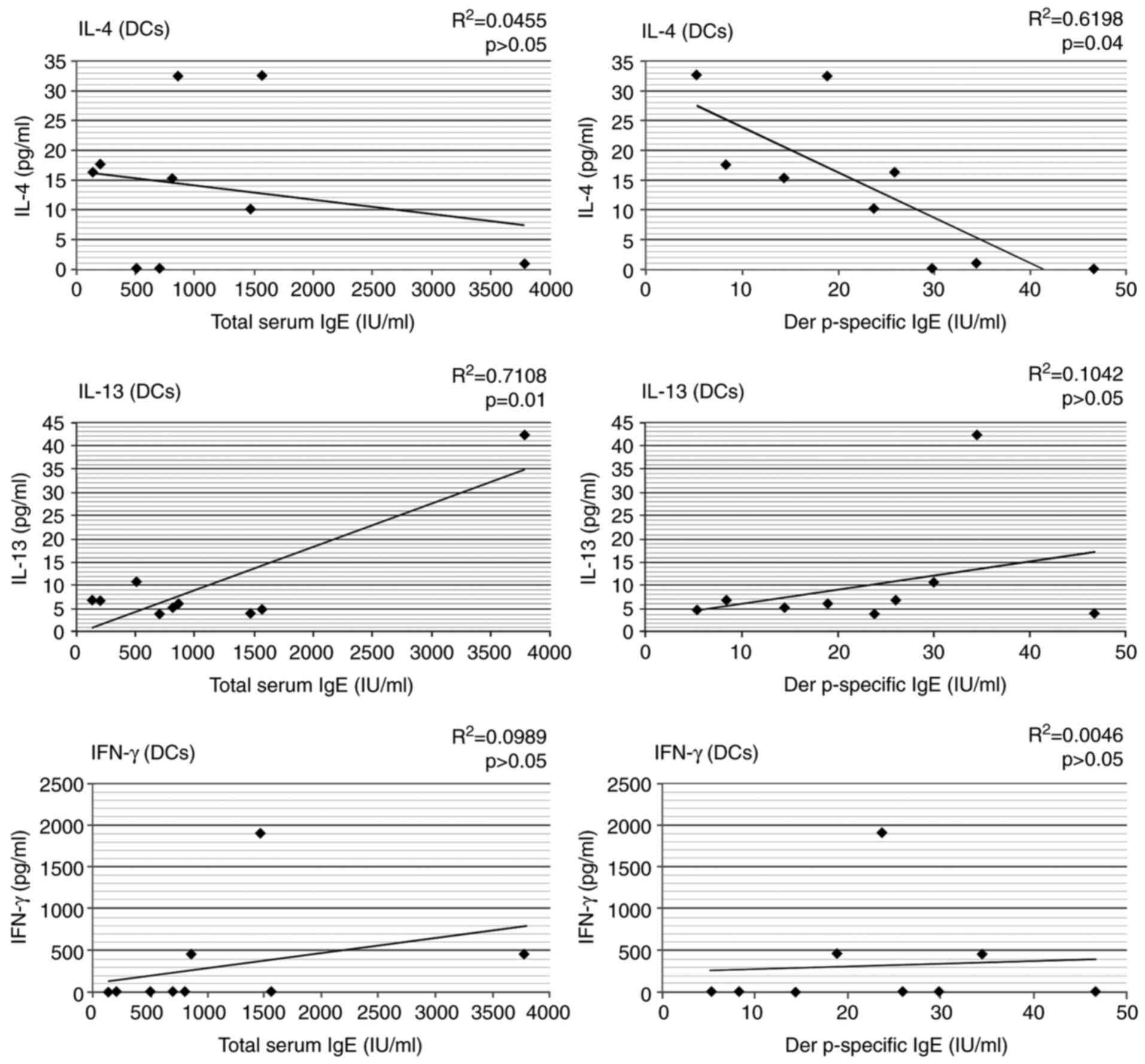
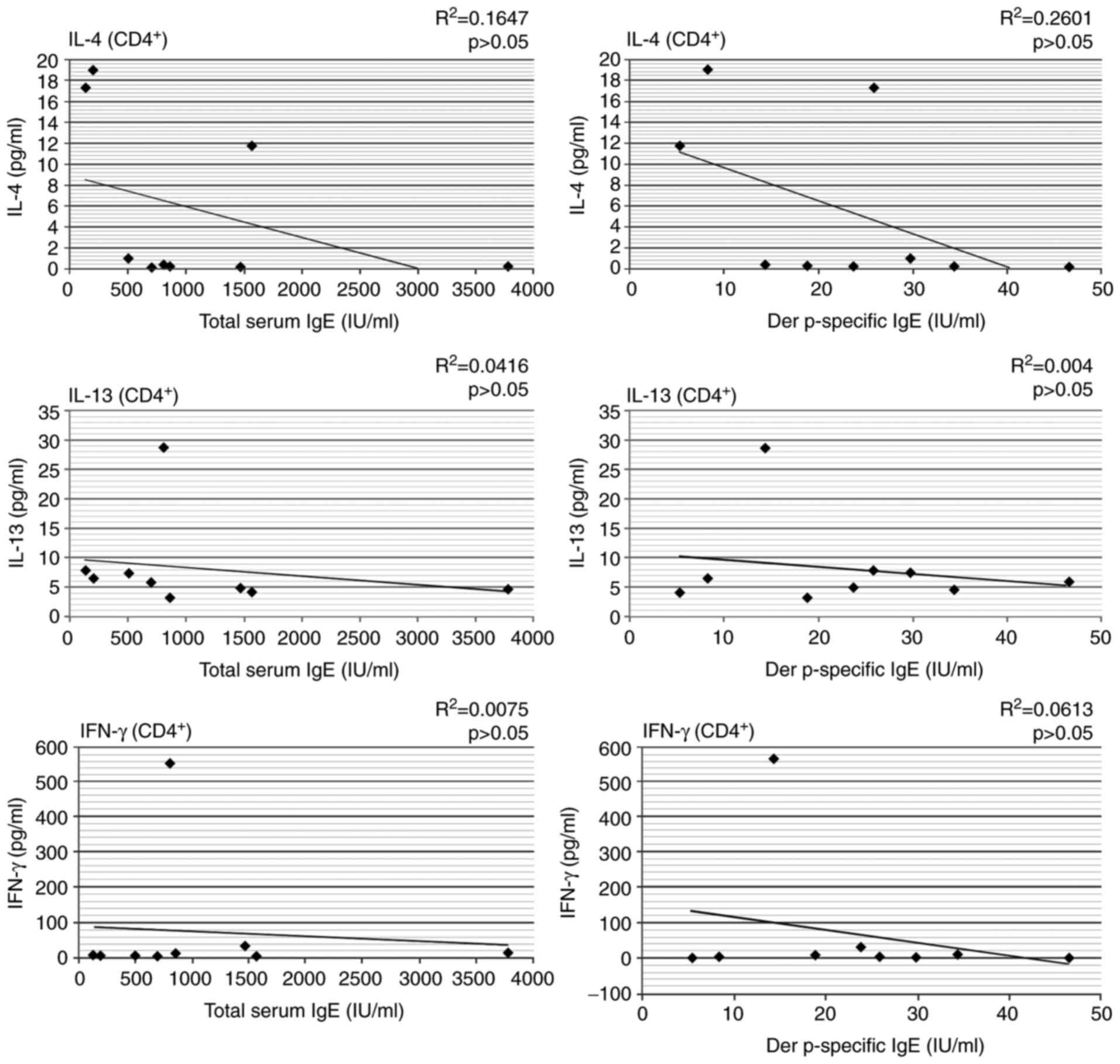
|
1
|
Larché M, Robinson DS and Kay AB: The role
of T lymphocytes in the pathogenesis of asthma. J Allergy Clin
Immunol. 111:450–464. 2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Olsson A, Cagnoni F, Dignetti P, Melioli G
and Canonica GW: Low concentrations of cytokines produced by
allergen-stimulated peripheral blood mononuclear cells have potent
effects on nasal polyp-derived fibroblasts. Clin Exp Immunol.
132:254–260. 2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Leru PM: Eosinophilic disorders:
Evaluation of current classification and diagnostic criteria,
proposal of a practical diagnostic algorithm. Clin Transl Allergy.
9(36)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Brightling CE, Symon FA, Birring SS,
Bradding P, Pavord ID and Wardlaw AJ: TH2 cytokine expression in
bronchoalveolar lavage fluid T lymphocytes and bronchial submucosa
is a feature of asthma and eosinophilic bronchitis. J Allergy Clin
Immunol. 110:899–905. 2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Tang M, Kemp A and Varigos G: IL-4 and
interferon-γ production in children with atopic disease. Clin Exp
Immunol. 92:120–124. 1993.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Agache I, Doros IC, Leru PM, Bucur I,
Poenaru M and Sarafoleanu C: MP-AzeFlu provides rapid and effective
allergic rhinitis control: Results of a non-interventional study in
Romania. Rhinology. 56:33–41. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Leru PM, Eftimie AM and Thibaudon M: First
allergenic pollen monitoring in Bucharest and results of three
years collaboration with European aerobiology specialists. Rom J
Intern Med. 56:27–33. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Perkins C, Wills-Karp E and Finkelman FD:
IL-4 induces IL-13-independent allergic airway inflammation. J
Allergy Clin Immunol. 118:410–419. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Saha SK, Berry MA, Parker D, Siddiqui S,
Morgan A, May R, Monk P, Bradding P, Wardlaw AJ, Pavord ID and
Brightling CE: Increased sputum and bronchial biopsy IL-13
expression in severe asthma. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 121:685–691.
2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Yanagawa H, Sone S, Haku T, Mizuno K, Yano
S, Ohmoto Y and Ogura T: Contrasting effect of interleukin-13 on
interleukin-l receptor agonist and proinflammatory cytokme
production by human alveolar makrophages. Am J Respir Cell Mol
Biol. 12:71–76. 1995.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Morawetz RA, Gabriele L, Rizzo LV,
Noben-Trauth N, Kühn R, Rajewsky K, Müller W, Doherty TM, Finkelman
F, Coffman RL and Morse HC III: Interleukin (IL)-4-independent
immunoglobulin class switch to immunoglobulin (Ig)E in the mouse. J
Exp Med. 184:1651–1661. 1996.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Ngoc LP, Gold DR, Tzianabos AO, Weiss ST
and Celedon JC: Cytokines, allergy and asthma. Curr Opin Allergy
Clin Immunol. 5:161–166. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Coyle AJ, Tsuyuki S, Bertrand C, Huang S,
Aguet M, Alkan SS and Anderson GP: Mice lacking the IFN-gamma
receptor have impaired ability to resolve a lung eosinophilic
inflammatory response associated with a prolonged capacity of T
cells to exhibit a Th2 cytokine profile. J Immunol. 156:2680–2685.
1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Tang ML, Kemp AS, Thorburn J and Hill DJ:
Reduced interferon-gamma secretion in neonates and subsequent
atopy. Lancet. 344:983–985. 1994.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Ten Hacken NH, Oosterhoff Y, Kauffman HF,
Guevarra L, Satoh T, Tollerud DJ and Postma DS: Elevated serum
interferon-gamma in atopic asthma correlates with increased airways
responsiveness and circadian peak expiratory flow variation. Eur
Respir J. 11:312–316. 1998.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Brunner PM, Guttman-Yassky E and Leung DY:
The immunology of atopic dermatitis and its reversibility with
broad-spectrum and targeted therapies. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 139
(Suppl 4):S65–S76. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Solomon I, Ilie MA, Draghici C, Voiculescu
VM, Căruntu C, Boda D and Zurac S: The impact of lifestyle factors
on evolution of atopic dermatitis: An alternative approach. Exp
Ther Med. 17:1078–1084. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Hamilton JD, Suárez-Fariñas M, Dhingra N,
Cardinale I, Li X, Kostic A, Ming JE, Radin AR, Krueger JG, Graham
N, et al: Dupilumab improves the molecular signature in skin of
patients with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis. J Allergy Clin
Immunol. 134:1293–1300. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Hamilton J, Hamon S, Simpson E, Chaudhry
U, Swanson B, Zhang R, Graham N, Pirozzi G, Ardeleanu M and Rizova
E: 372 The effect of dupilumab on biomarkers in a randomized phase
2b clinical trial in adults with moderate-to-severe atopic
dermatitis. J Invest Dermatol. 136: (Suppl 2)(S224)2016.
|
|
20
|
Eshtiaghi P and Gooderham MJ: Dupilumab:
An evidence-based review of its potential in the treatment of
atopic dermatitis. Core Evid. 13:13–20. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Castro M, Corren J, Pavord ID, Maspero J,
Wenzel S, Rabe KF, Busse WW, Ford L, Sher L, FitzGerald JM, et al:
Dupilumab efficacy and safety in moderate-to-severe uncontrolled
asthma. N Engl J Med. 378:2486–2496. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Verheugen G: Commission directive
2005/28/EC laying down principles and guidelines for good clinical
practice as regards investigational medicinal products for human
use, as well as the requirements for authorization of the
manufacturing or importation of such products. Off J Eur Union.
91:13–19. 2005.
|
|
23
|
International Council on Harmonisation of
Technical Requirements for Registration of Pharmaceuticals for
Human Use (ICH). Retrieved from urihttps://www.ema.europa.eu/en/partners-networks/international-activities/multilateral-organisations-initiatives/international-council-harmonisation-technical-requirements-registration-pharmaceuticals-human-use#ich-guidelines-and-technical-requirements-sectionsimplehttps://www.ema.europa.eu/en/partners-networks/international-activities/multilateral-organisations-initiatives/international-council-harmonisation-technical-requirements-registration-pharmaceuticals-human-use#ich-guidelines-and-technical-requirements-section.
|
|
24
|
World Medical Association Declaration of
Helsinki. Recommendations Guiding Physicians in Biomedical Research
Involving Human Subjects. JAMA. 277:925–926.
1997.doi:10.1001/jama.1997.03540350075038.
|
|
25
|
Brożek JL, Bousquet J, Agache I, Agarwal
A, Bachert C, Bosnic-Anticevich S, Brignardello-Petersen R,
Canonica GW, Casale T, Chavannes NH, et al: Allergic rhinitis and
its impact on asthma (ARIA) guidelines-2016 revision. J Allergy
Clin Immunol. 140:950–958. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Global strategy for asthma management and
prevention. Global Initiative for Asthma (GINA), 2018. URL:
urihttp://www.ginasthma.orgsimplehttp://www.ginasthma.org.
|
|
27
|
Pawankar R: Inflammatory mechanisms in
allergic rhinitis. Curr Opin Allergy Clin Immunol. 7:1–4.
2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Leru PM and Deleanu DM: Romanian
allergology in the actual European context. Rom J Intern Med.
53:111–117. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Leru PM, Eftimie AM, Anton VF and
Thibaudon M: Five-year data on pollen monitoring, distribution and
health impact of allergenic plants in Bucharest and the
Southeastern region of Romania. Medicina (Kaunas).
55(140)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Frieri M: Advances in the understanding of
allergic asthma. Allergy Asthma Proc. 28:614–619. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Leru PM: Drug allergies in primary care
practice in Romania: A questionnaire-based survey. Allergy Asthma
Clin Immunol. 10(16)2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Tavakkol Afshari J, Farid Hosseini R,
Hosseini Farahabadi S, Heydarian F, Boskabady MH, Khoshnavaz R,
Razavi A, Ghayoor Karimiani E and Ghasemi G: Association of the
expression of IL-4 and IL-13 genes, IL-4 and IgE serum levels with
allergic asthma. Iran J Allergy Asthma Immunol. 6:67–72.
2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Boyton RJ and Altamann DM: Asthma: New
developments in cytokine regulation. Clin Exp Immunol. 136:13–14.
2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Davoodi P, Mahesh PA, Holla AD,
Vijayakumar GS, Jayaraj BS, Chandrashekara S and Ramachandra NB:
Serum levels of interleukin-13 and interferon-gamma from adult
patients with asthma in Mysore. Cytokine. 60:431–437.
2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Ceylan E, Bulut S, Yılmaz M, Örün H,
Karadağ F, Ömürlü İK, Kırdar S and Karul A: The levels of serum
biomarkers in stable asthma patients with comorbidities. Iran J
Allergy Asthma Immunol. 18:27–37. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Zhou B, Comeau MR, De Smedt T, Liggitt HD,
Dahl ME, Lewis DB, Gyarmati D, Aye T, Campbell DJ and Ziegler SF:
Thymic stromal lymphopoietin as a key initiator of allergic airway
inflammation in mice. Nat Immunol. 6:1047–1053. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Luttmann W, Matthiesen T, Matthys H and
Virchow JC Jr: Synergistic effects of interleukin-4 or
interleukin-13 and tumor necrosis factor-alpha on eosinophil
activation in vitro. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 20:474–480.
1999.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Leru PM: Eosinophilia and
hypereosinophilic disorders-update on etiopathogeny, classification
and clinical approach. Rom J Intern Med. 53:289–295.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Fish SC, Donaldson DD, Goldman SJ,
Williams CM and Kasaian MT: IgE generation and mast cell effector
function in mice deficient in IL-4 and IL-13. J Immunol.
174:7716–7724. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Gandhi NA, Pirozzi G and Graham NMH:
Commonality of the IL-4/IL-13 pathway in atopic diseases. Expert
Rev Clin Immunol. 13:425–437. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Bagnasco D, Ferrando M, Varricchi G,
Passalacqua G and Canonica GW: A critical evaluation of anti-IL-13
and anti-IL-4 strategies in severe asthma. Int Arch Allergy
Immunol. 170:122–131. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Albanesi C, Scarponi C, Cavani A, Federici
M, Nasorri F and Girolomoni G: Interleukin-17 is produced by both
Th1 and Th2 lymphocytes, and modulates interferon-gamma- and
interleukin-4-induced activation of human keratinocytes. J Invest
Dermatol. 115:81–87. 2000.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Morse HC III, McCarty T, Giese NA,
Taddesse-Heath L and Grusby MJ: STAT6-deficient mice exhibit normal
induction of murine AIDS and expression of immunoglobulin E
following infection with LP-BM5 murine leukemia viruses. J Virol.
73:7093–7095. 1999.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Antczak A, Domańska-Senderowska D, Górski
P, Pastuszak-Lewandoska D, Nielepkowicz-Goździńska A, Szewczyk K,
Kurmanowska Z, Kiszałkiewicz J and Brzeziańska-Lasota E: Analysis
of changes in expression of IL-4/IL-13/STAT6 pathway and
correlation with the selected clinical parameters in patients with
atopic asthma. Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol. 29:195–204.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Kabesch M, Schedel M, Carr D, Woitsch B,
Fritzsch C, Weiland SK and von Mutius E: IL-4/IL-13 pathway
genetics strongly influence serum IgE levels and childhood asthma.
J Allergy Clin Immunol. 117:269–274. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Brusselle G, Kips J, Joos G, Bluethmann H
and Pauwels R: Allergen-induced airway inflammation and bronchial
responsiveness in wild-type and interleukin-4-deficient mice. Am J
Respir Cell Mol Biol. 12:254–259. 1995.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Billiau A and Dijkmans R:
Interferon-gamma: Mechanism of action and therapeutic potential.
Biochem Pharmacol. 40:1433–1439. 1990.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Cho SH, Stanciu LA, Begishivili T, Bates
PJ, Holgate ST and Johnston SL: Peripheral blood CD4+
and CD8+ T cell type 1 and type 2 cytokine production in
atopic asthmatic and normal subjects. Clin Exp Allergy. 32:427–433.
2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Stanciu LA, Shute J, Holgate ST and
Djukanović R: Production of IL-8 and IL-4 by positively and
negatively selected CD4+ and CD8+ human T
cells following a four-step cell separation method including
magnetic cell sorting (MACS). J Immunol Methods. 189:107–115.
1996.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|