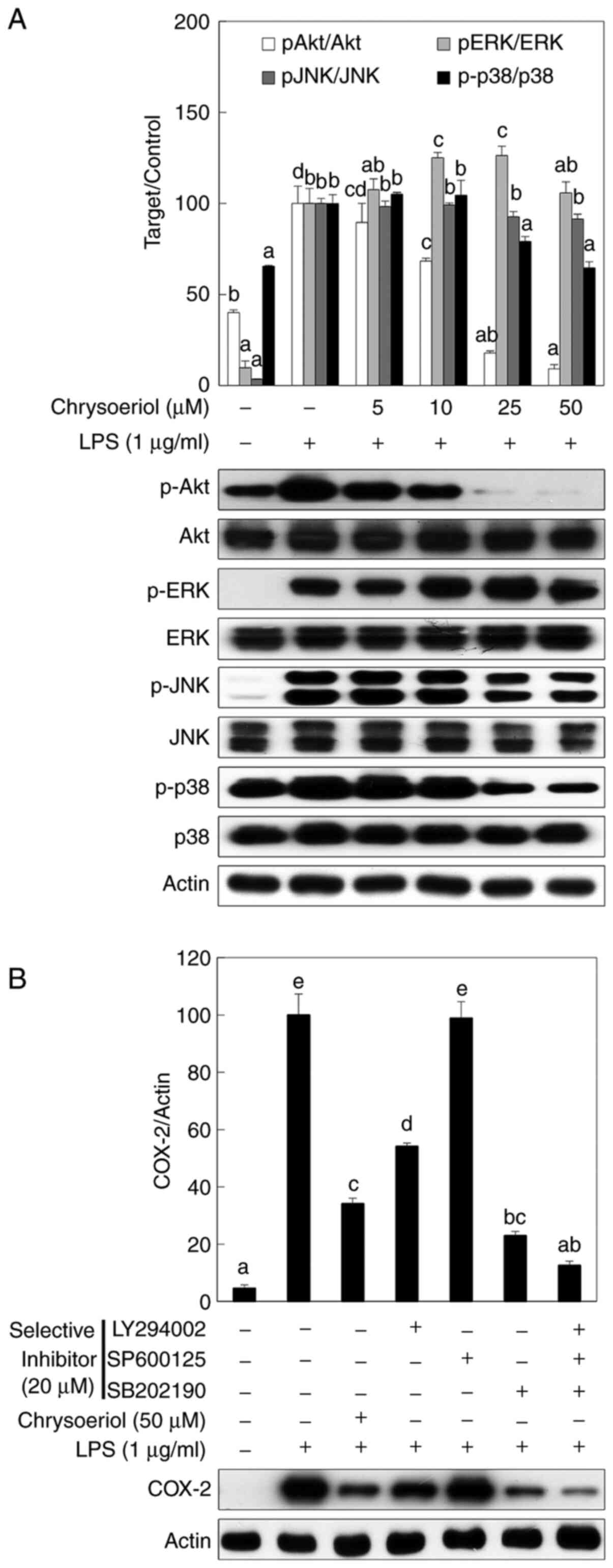
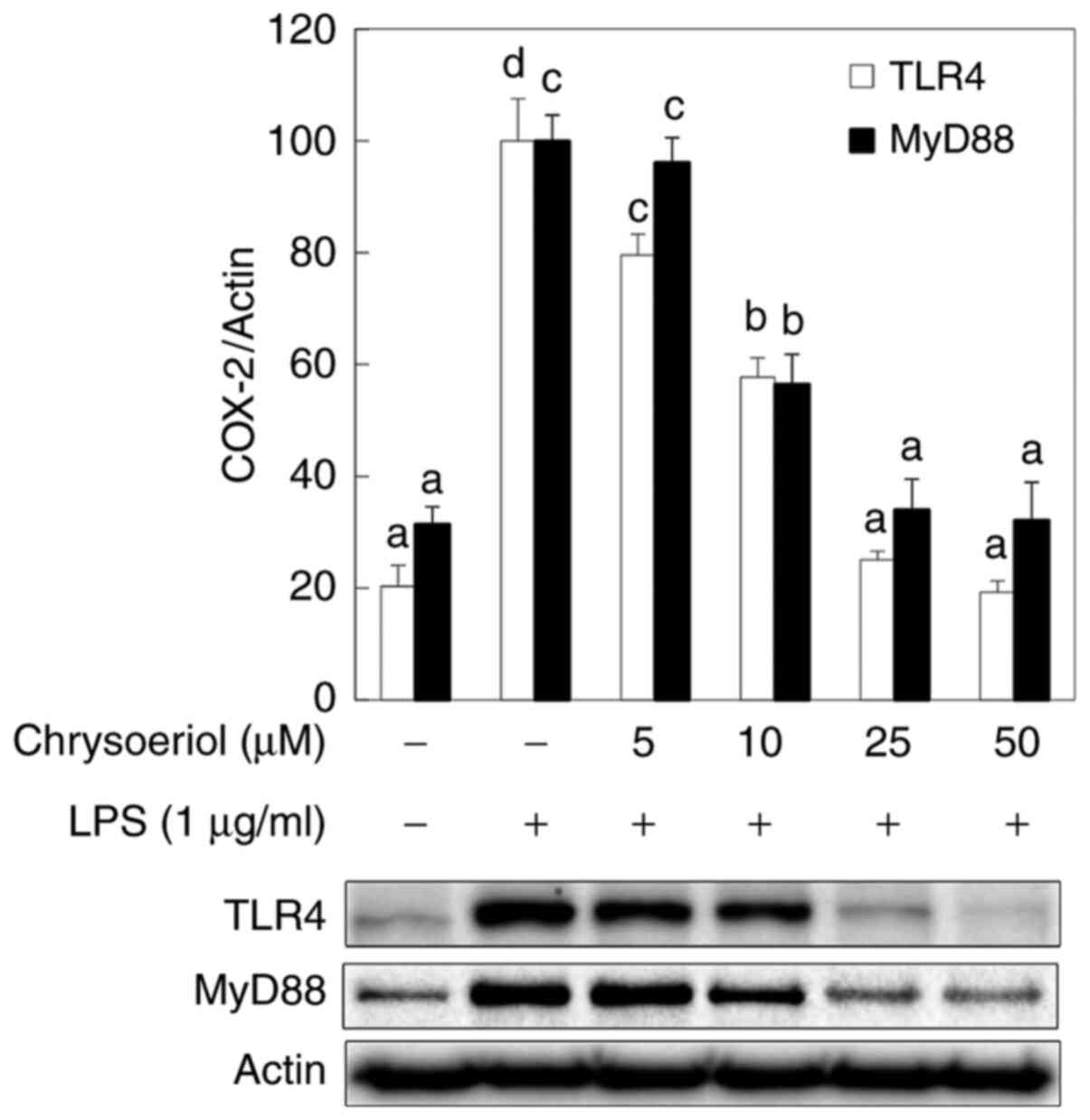
|
1
|
Kunnumakkara AB, Sailo BL, Banik K, Harsha
C, Prasad S, Gupta SC, Bharti AC and Aggarwal BB: Chronic diseases,
inflammation, and spices: How are they linked? J Transl Med.
16(14)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Kundu JK and Surh YJ: Inflammation:
Gearing the journey to cancer. Mutat Res. 659:15–30.
2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Sukketsiri W, Tanasawet S, Moolsap F,
Tantisira MH, Hutamekalin P and Tipmanee V: ECa 233 suppresses
LPS-induced proinflammatory responses in macrophages via
suppressing ERK1/2, p38 MAPK and akt pathways. Biol Pharm Bull.
42:1358–1365. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Park SA, Kim EH, Na HK and Surh YJ: KG-135
inhibits COX-2 expression by blocking the activation of JNK and
AP-1 in phorbol ester-stimulated human breast epithelial cells. Ann
NY Acad Sci. 1095:545–553. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Na HK and Surh YJ: Intracellular signaling
network as a prime chemopreventive target of (-)-epigallocatechin
gallate. Mol Nutr Food Res. 50:152–159. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Kim JH, Na HK, Pak YK, Lee YS, Lee SJ,
Moon A and Surh YJ: Roles of ERK and p38 mitogen-activated protein
kinases in phorbol ester-induced NF-kappaB activation and COX-2
expression in human breast epithelial cells. Chem Biol Interact.
171:133–141. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Kawamori T, Rao CV, Seibert K and Reddy
BS: Chemopreventive activity of celecoxib, a specific
cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitor, against colon carcinogenesis. Cancer
Res. 58:409–412. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Choi CW, Jung HA, Kang SS and Choi JS:
Antioxidant constituents and a new triterpenoid glycoside from flos
lonicerae. Arch Pharm Res. 30:1–7. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Schinella GR, Giner RM, Recio MC,
Mordujovich de Buschiazzo P, Rios JL and Manez S: Anti-inflammatory
effects of South American Tanacetum vulgare. J Pharm Pharmacol.
50:1069–1074. 1998.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Abu Zarga M, Qauasmeh R, Sabri S, Munsoor
M and Abdalla S: Chemical constituents of artemisia arborescens and
the effect of the aqueous extract on rat isolated smooth muscle.
Planta Med. 61:242–245. 1995.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Han LK, Sumiyoshi M, Zheng YN, Okuda H and
Kimura Y: Anti-obesity action of salix matsudana leaves (Part 2).
Isolation of anti-obesity effectors from polyphenol fractions of
salix matsudana. Phytother Res. 17:1195–1198. 2003.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Mishra B, Priyadarsini KI, Kumar MS,
Unnikrishnan MK and Mohan H: Effect of O-glycosilation on the
antioxidant activity and free radical reactions of a plant
flavonoid, chrysoeriol. Bioorg Med Chem. 11:2677–2685.
2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Choi DY, Lee JY, Kim MR, Woo ER, Kim YG
and Kang KW: Chrysoeriol potently inhibits the induction of nitric
oxide synthase by blocking AP-1 activation. J Biomed Sci.
12:949–959. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Kim JH, Cho YH, Park SM, Lee KE, Lee JJ,
Lee BC, Pyo HB, Song KS, Park HD and Yun YP: Antioxidants and
inhibitor of matrix metalloproteinase-1 expression from leaves of
Zostera marina L. Arch Pharm Res. 27:177–183. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Park CM and Song YS: Luteolin and
luteolin-7-O-glucoside inhibit lipopolysaccharide-induced
inflammatory responses through modulation of NF-kB/AP-1/PI3K-Akt
signaling cascades in RAW 264.7 cells. Nutr Res Pract. 7:423–429.
2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Bak MJ, Truong VL, Kang HS, Jun M and
Jeong WS: Anti-inflammatory effect of procyanidins from wild grape
(Vitis amurensis) seeds in LPS-induced RAW 264.7 cells. Oxid Med
Cell Longev. 2013(409321)2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Chun J, Choi RJ, Khan S, Lee DS, Kim YC,
Nam YJ, Lee DU and Kim YS: Alantolactone suppresses inducible
nitric oxide synthase and cyclooxygenase-2 expression by
down-regulating NF-kB, MAPK and AP-1 via the MyD88 signaling
pathway in LPS-activated RAW 264.7 cells. Int Immunopharmacol.
14:375–383. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Jeong D, Dong GZ, Lee HJ and Ryu JH:
Anti-inflammatory compounds from atractylodes macrocephala.
Molecules. 24(1859)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Xie WL, Chipman JG, Robertson DL, Erikson
RL and Simmons DL: Expression of a mitogen-responsive gene encoding
prostaglandin synthase is regulated by mRNA splicing. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 88:2692–2696. 1991.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Yang Y, Zhou X, Xiao M, Hong Z, Gong Q,
Jiang L and Zhou J: Discovery of chrysoeriol, a PI3K-AKT-mTOR
pathway inhibitor with potent antitumor activity against human
multiple myeloma cells in vitro. J Huazhong Univ Sci Technolog Med
Sci. 30:734–740. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Medzhitov R: Origin and physiological
roles of inflammation. Nature. 454:428–435. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Tabas I and Glass CK: Anti-inflammatory
therapy in chronic disease: Challenges and opportunities. Science.
339:166–172. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Qian C, Liu J and Cao X: Innate signaling
in the inflammatory immune disorders. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev.
25:731–738. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Schindler SM, Little JP and Klegeris A:
Microparticles: A new perspective in central nervous system
disorders. Biomed Res Int. 2014(756327)2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Van Dyke TE and van Winkelhoff AJ:
Infection and inflammatory mechanisms. J Periodontol. 84 (Suppl
4):S1–S7. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Meng F and Lowell CA: Lipopolysaccharide
(LPS)-induced macrophage activation and signal transduction in the
absence of Src-family kinases Hck, Fgr, and Lyn. J Exp Med.
185:1661–1670. 1997.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Roy A, Srivastava M, Saqib U, Liu D,
Faisal SM, Sugathan S, Bishnoi S and Baig MS: Potential therapeutic
targets for inflammation in toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4)-mediated
signaling pathways. Int Immunopharmacol. 40:79–89. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Hu W, Wu L, Qiang Q, Ji L, Wang X, Luo H,
Wu H, Jiang Y, Wang G and Shen T: The dichloromethane fraction from
Mahonia bealei (Fort.) Carr. leaves exerts an anti-inflammatory
effect both in vitro and in vivo. J Ethnopharmacol. 188:134–143.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Wang J, Kang YX, Pan W, Lei W, Feng B and
Wang XJ: Enhancement of anti-inflammatory activity of curcumin
using phosphatidylserine-containing nanoparticles in cultured
macrophages. Int J Mol Sci. 17(969)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Surh YJ: Cancer chemoprevention with
dietary phytochemicals. Nat Rev Cancer. 3:768–780. 2003.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Endale M, Park SC, Kim S, Kim SH, Yang Y,
Cho JY and Rhee MH: Quercetin disrupts tyrosine-phosphorylated
phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase and myeloid differentiation factor-88
association, and inhibits MAPK/AP-1 and IKK/NF-kB-induced
inflammatory mediators production in RAW 264.7 cells.
Immunobiology. 218:1452–1467. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Chen K, Huang J, Gong W, Iribarren P,
Dunlop NM and Wang JM: Toll-like receptors in inflammation,
infection and cancer. Int Immunopharmacol. 7:1271–1285.
2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Dauphinee SM and Karsan A:
Lipopolysaccharide signaling in endothelial cells. Lab Invest.
86:9–22. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|