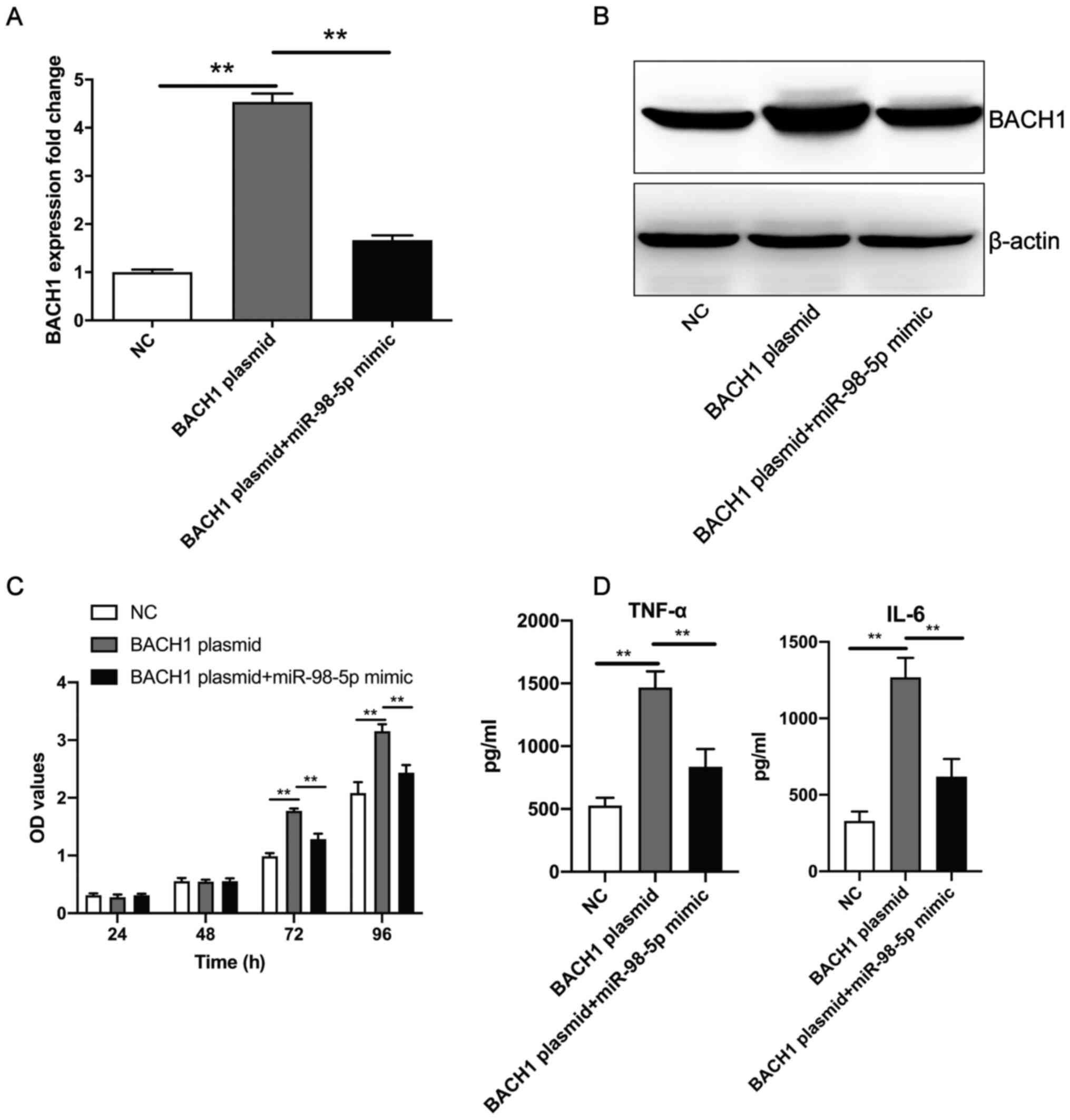
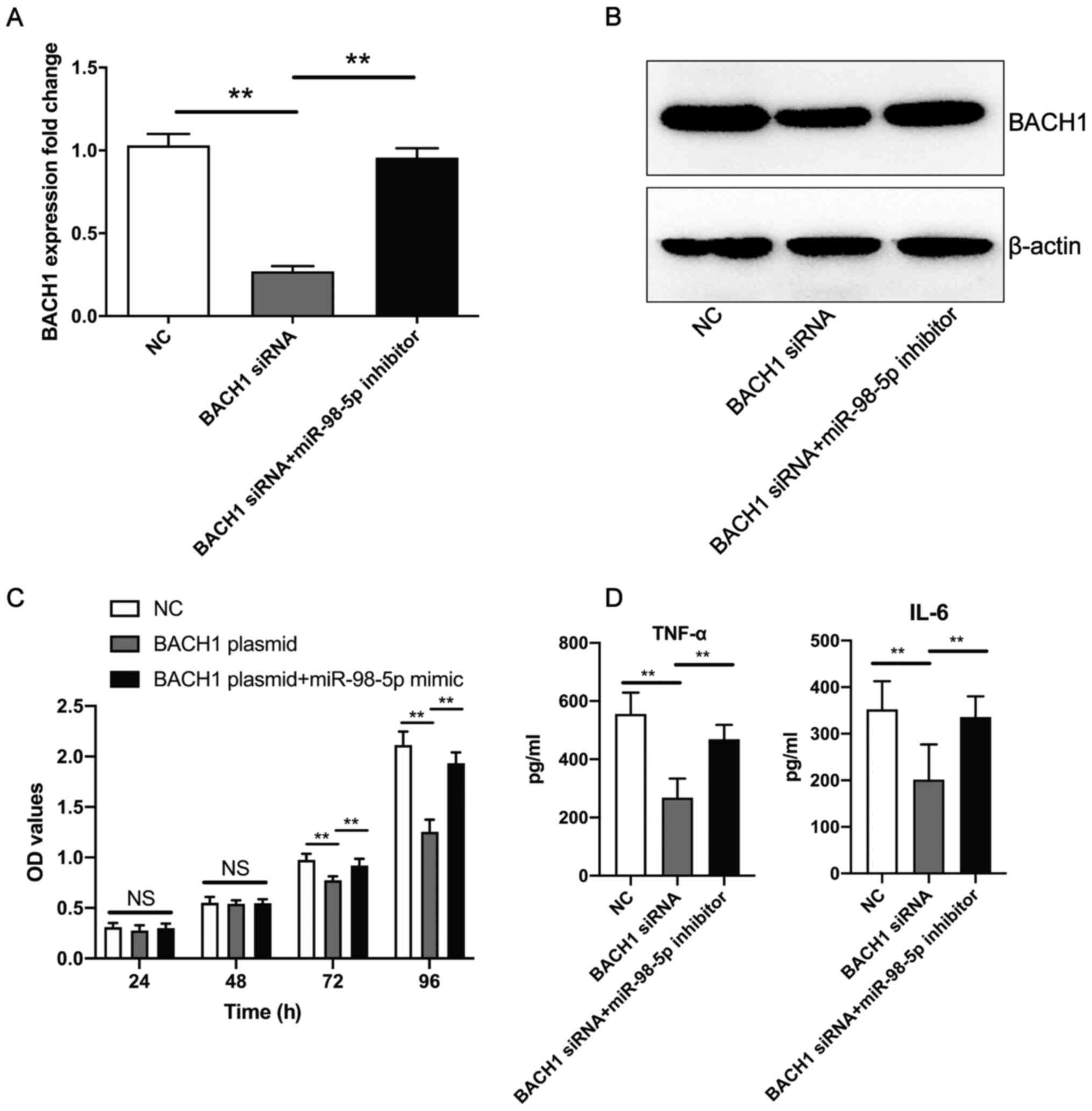
|
1
|
Talotta R, Atzeni F and Laska MJ:
Therapeutic peptides for the treatment of systemic lupus
erythematosus: A place in therapy. Expert Opin Investig Drugs.
29:845–867. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Ramanujam M, Steffgen J, Visvanathan S,
Mohan C, Fine JS and Putterman C: Phoenix from the flames:
Rediscovering the role of the CD40-CD40L pathway in systemic lupus
erythematosus and lupus nephritis. Autoimmun Rev.
19(102668)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Wang SF, Chen YH, Chen DQ, Liu ZZ, Xu F,
Zeng CH and Hu WX: Mesangial proliferative lupus nephritis with
podocytopathy: A special entity of lupus nephritis. Lupus.
27:303–311. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Wofsy D, Hillson JL and Diamond B:
Comparison of alternative primary outcome measures for use in lupus
nephritis clinical trials. Arthritis Rheum. 65:1586–1591.
2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Wright RD, Dimou P, Northey SJ and
Beresford MW: Mesangial cells are key contributors to the fibrotic
damage seen in the lupus nephritis glomerulus. J Inflamm (Lond).
16(22)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Sung SJ and Fu SM: Interactions among
glomerulus infiltrating macrophages and intrinsic cells via
cytokines in chronic lupus glomerulonephritis. J Autoimmun.
106(102331)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Kong J, Li L, Lu Z, Song J, Yan J, Yang J,
Gu Z and Da Z: Microrna-155 suppresses mesangial cell proliferation
and tgf-β1 production via inhibiting cxcr5-erk signaling pathway in
lupus nephritis. Inflammation. 42:255–263. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Chen CC, Chang ZY, Tsai FJ and Chen SY:
Resveratrol pretreatment ameliorates concanavalin a-induced
advanced renal glomerulosclerosis in aged mice through upregulation
of sirtuin 1-mediated klotho expression. Int J Mol Sci.
21(21)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Honarpisheh M, Köhler P, von Rauchhaupt E
and Lech M: The involvement of micrornas in modulation of innate
and adaptive immunity in systemic lupus erythematosus and lupus
nephritis. J Immunol Res. 2018(4126106)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Krol J, Loedige I and Filipowicz W: The
widespread regulation of microRNA biogenesis, function and decay.
Nat Rev Genet. 11:597–610. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Wang Y, Bao W, Liu Y, Wang S, Xu S, Li X,
Li Y and Wu S: miR-98-5p contributes to cisplatin resistance in
epithelial ovarian cancer by suppressing miR-152 biogenesis via
targeting Dicer1. Cell Death Dis. 9(447)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Yuan S, Tang C, Chen D, Li F, Huang M, Ye
J, He Z, Li W, Chen Y, Lin X, et al: Mir-98 modulates cytokine
production from human PBMCS in systemic lupus erythematosus by
targeting IL-6 mRNA. J Immunol Res. 2019(9827574)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Xie L and Xu J: Role of mir-98 and its
underlying mechanisms in systemic lupus erythematosus. J Rheumatol.
45:1397–1405. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Wang Y, Yu F, Song D, Wang SX and Zhao MH:
Podocyte involvement in lupus nephritis based on the 2003 ISN/RPS
system: A large cohort study from a single centre. Rheumatology
(Oxford). 53:1235–1244. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Xu J, Xu G, Zhang T, Chen T, Zhao W and
Wang G: NFIL3 Acts as a Nuclear Factor to Increase Osteosarcoma
Progression. BioMed Res Int. 2019(4068521)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 25:402–408.
2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Mohr AM and Mott JL: Overview of microRNA
biology. Semin Liver Dis. 35:3–11. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Zhang L, Zhang X and Si F: MicroRNA-124
represents a novel diagnostic marker in human lupus nephritis and
plays an inhibitory effect on the growth and inflammation of renal
mesangial cells by targeting TRAF6. Int J Clin Exp Pathol.
12:1578–1588. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Pan Y, Pan YM, Liu FT, Xu SL, Gu JT, Hang
PZ and Du ZM: MicroRNA-98 ameliorates doxorubicin-induced
cardiotoxicity via regulating caspase-8 dependent Fas/RIP3 pathway.
Environ Toxicol Pharmacol. 85(103624)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Wang Q, Wei S, Zhou H, Li L, Zhou S, Shi
C, Shi Y, Qiu J and Lu L: MicroRNA-98 Inhibits Hepatic Stellate
Cell Activation and Attenuates Liver Fibrosis by Regulating HLF
Expression. Front Cell Dev Biol. 8(513)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Zeng Y, Feng Z, Liao Y, Yang M, Bai Y and
He Z: Diminution of microRNA-98 alleviates renal fibrosis in
diabetic nephropathy by elevating Nedd4L and inactivating
TGF-β/Smad2/3 pathway. Cell Cycle. 19:3406–3418. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Sun X, Li X, Ma S, Guo Y and Li Y:
MicroRNA-98-5p ameliorates oxygen-glucose deprivation/reoxygenation
(OGD/R)-induced neuronal injury by inhibiting Bach1 and promoting
Nrf2/ARE signaling. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 507:114–121.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Patil SL, Palat A, Pan Y, Rajapakshe K,
Mirchandani R, Bondesson M, Yustein JT, Coarfa C and Gunaratne PH:
MicroRNA-509-3p inhibits cellular migration, invasion, and
proliferation, and sensitizes osteosarcoma to cisplatin. Sci Rep.
9(19089)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Kanezaki R, Toki T, Yokoyama M, Yomogida
K, Sugiyama K, Yamamoto M, Igarashi K and Ito E: Transcription
factor BACH1 is recruited to the nucleus by its novel alternative
spliced isoform. J Biol Chem. 276:7278–7284. 2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Warnatz HJ, Schmidt D, Manke T, Piccini I,
Sultan M, Borodina T, Balzereit D, Wruck W, Soldatov A, Vingron M,
et al: The BTB and CNC homology 1 (BACH1) target genes are involved
in the oxidative stress response and in control of the cell cycle.
J Biol Chem. 286:23521–23532. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Kishimoto D, Kirino Y, Tamura M, Takeno M,
Kunishita Y, Takase-Minegishi K, Nakano H, Kato I, Nagahama K,
Yoshimi R, et al: Dysregulated heme oxygenase-1low M2-like
macrophages augment lupus nephritis via Bach1 induced by type I
interferons. Arthritis Res Ther. 20(64)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Yap DYH, Yung S, Lee P, Yam IYL, Tam C,
Tang C and Chan TM: B Cell Subsets and Cellular Signatures and
Disease Relapse in Lupus Nephritis. Front Immunol.
11(1732)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Liu Y, Yu C, Ji K, Wang X, Li X, Xie H,
Wang Y, Huang Y, Qi D and Fan H: Quercetin reduces TNF-α-induced
mesangial cell proliferation and inhibits PTX3 production:
Involvement of NF-κB signaling pathway. Phytother Res.
33:2401–2408. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Sun J, Guo S, Niu F, Liu D and Zhuang Y:
Complement 1q protects MRL/lpr mice against lupus nephritis via
inhibiting the nuclear factor-κB pathway. Mol Med Rep.
22:5436–5443. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|