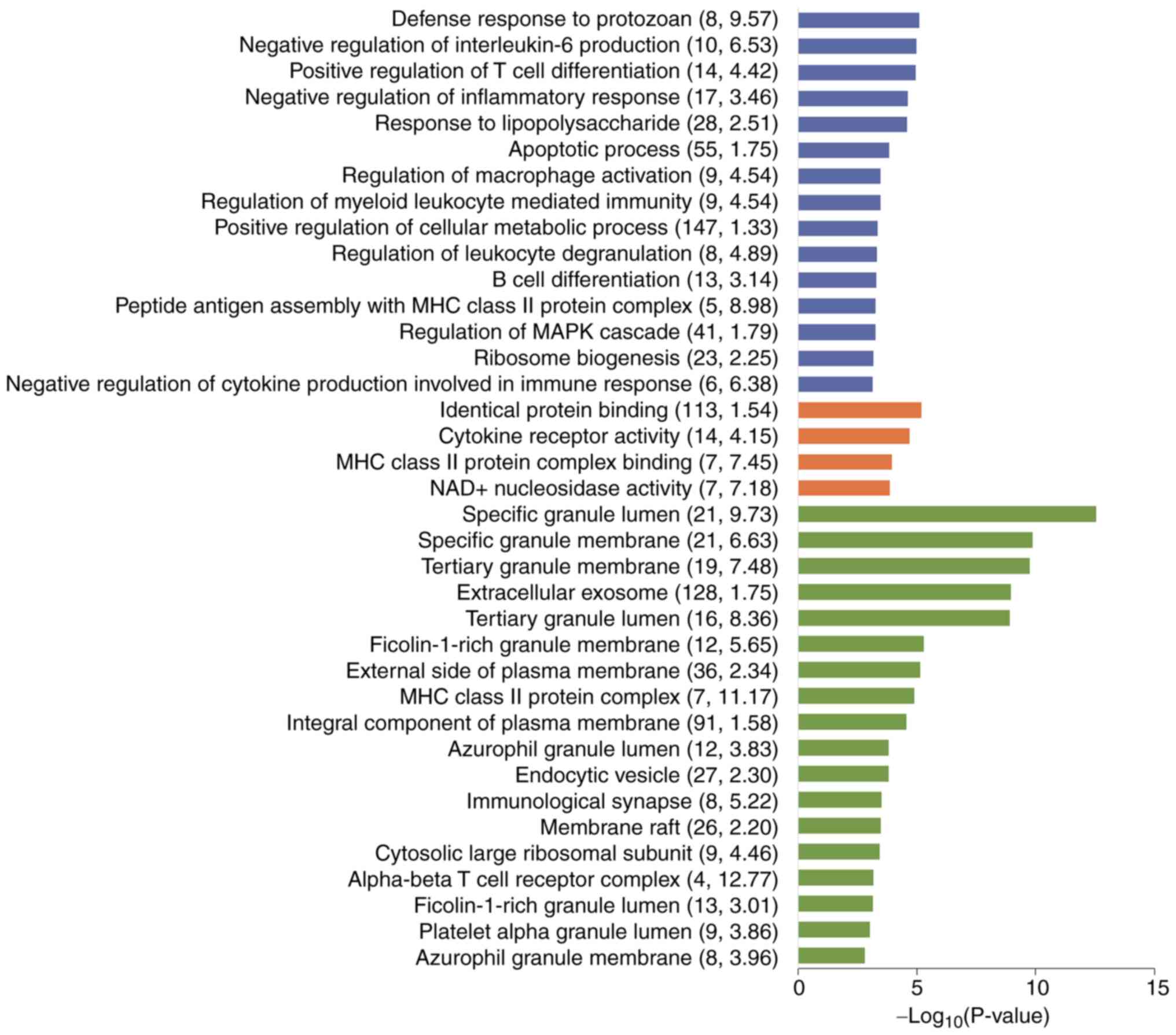
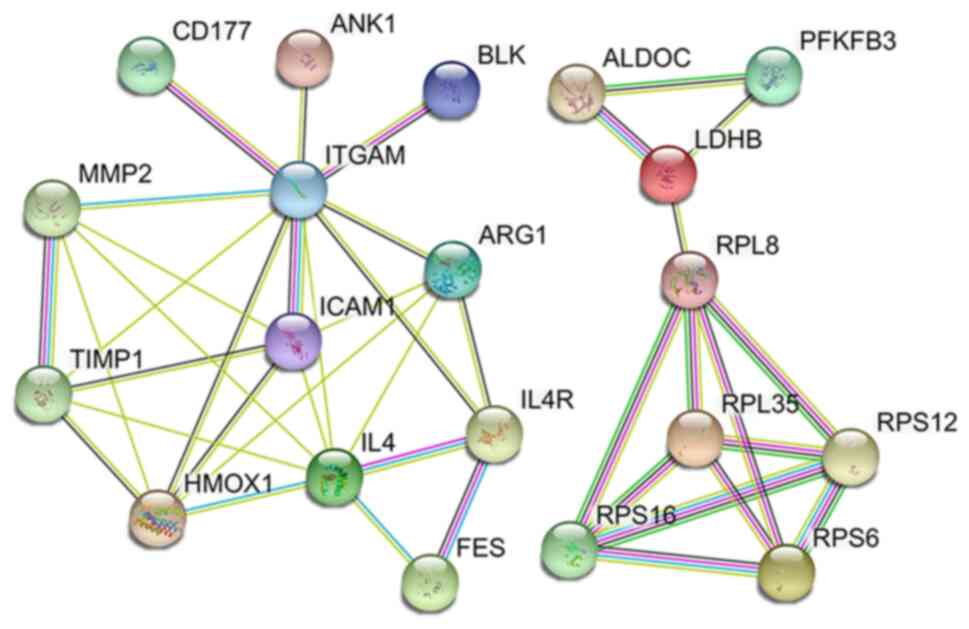
|
1
|
Park HS, Jun SC, Han KH, Hong SB and Yu
JH: Diversity, application, and synthetic biology of industrially
important aspergillus fungi. Adv Appl Microbiol. 100:161–202.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Becker KL, Ifrim DC, Quintin J, Netea MG
and van de Veerdonk FL: Antifungal innate immunity: Recognition and
inflammatory networks. Semin Immunopathol. 37:107–116.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Takakura S: Zygomycosis. Nihon Rinsho.
66:2356–2361. 2008.PubMed/NCBI(In Japanese).
|
|
4
|
Cadena J, Thompson GR III and Patterson
TF: Invasive aspergillosis: Current strategies for diagnosis and
management. Infect Dis Clin North Am. 30:125–142. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Cadena J, Thompson GR III and Patterson
TF: Aspergillosis: Epidemiology, diagnosis, and treatment. Infect
Dis Clin North Am. 35:415–434. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Latge JP and Chamilos G: Aspergillus
fumigatus and aspergillosis in 2019. Clin Microbiol Rev.
33:e00140–18. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Oren I and Goldstein N: Invasive pulmonary
aspergillosis. Curr Opin Pulm Med. 8:195–200. 2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Darling BA and Milder EA: Invasive
aspergillosis. Pediatr Rev. 39:476–478. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Verma N, Singh S, Syal A, Pradhan P and
Singh M and Singh M: Invasive aspergillosis is a critical
determinant of mortality in cirrhosis: A systematic review with
meta-analysis. Med Mycol. 59:1092–1100. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Arvanitis M and Mylonakis E: Diagnosis of
invasive aspergillosis: Recent developments and ongoing challenges.
Eur J Clin Invest. 45:646–652. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Dhesi Z, Herbst S and Armstrong-James D:
Transcript profiling of the murine immune response to invasive
aspergillosis. Methods Mol Biol. 845:435–444. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Wang M, Zhang M, Qiu J, Liu C, Lou Y, Wang
T, Zhang Y and Mao Y: PU.1-CD23 signaling mediates pulmonary innate
immunity against Aspergillus fumigatus infection by driving
inflammatory response. BMC Immunol. 24(4)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Fliesser M, Morton CO, Bonin M, Ebel F,
Hünniger K, Kurzai O, Einsele H and Löffler J: Hypoxia-inducible
factor 1α modulates metabolic activity and cytokine release in
anti-Aspergillus fumigatus immune responses initiated by human
dendritic cells. Int J Med Microbiol. 305:865–873. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Morris NL, Michael DN, Crotty KM, Chang SS
and Yeligar SM: Alcohol-Induced glycolytic shift in alveolar
macrophages is mediated by hypoxia-inducible factor-1 Alpha. Front
Immunol. 13(865492)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Dix A, Czakai K, Springer J, Fliesser M,
Bonin M, Guthke R, Schmitt AL, Einsele H, Linde J and Löffler J:
Genome-Wide expression profiling reveals S100B as biomarker for
invasive aspergillosis. Front Microbiol. 7(320)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Wang Y, Sun FZ, Lin W and Zhang SQ:
AC-PCoA: Adjustment for confounding factors using principal
coordinate analysis. PLoS Comput Biol. 18(e1010184)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Delbeke H, Casteels I and Joossens M: DNA
extraction protocol impacts ocular surface microbiome profile.
Front Microbiol. 14(1128917)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Zhan Z, Chen Y, Duan Y, Li L, Mew K, Hu P,
Ren H and Peng M: Identification of key genes, pathways and
potential therapeutic agents for liver fibrosis using an integrated
bioinformatics analysis. PeerJ. 7(e6645)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Haldermans P, Shkedy Z, Van Sanden S,
Burzykowski T and Aerts M: Using linear mixed models for
normalization of cDNA microarrays. Stat Appl Genet Mol Biol.
6(Article 19)2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Ding J and Zhang Y: Analysis of key GO
terms and KEGG pathways associated with carcinogenic chemicals.
Comb Chem High Throughput Screen: Dec 18, 2017 (Epub ahead of
print).
|
|
21
|
Chen L, Zhang YH, Lu G, Huang T and Cai
YD: Analysis of cancer-related lncRNAs using gene ontology and KEGG
pathways. Artif Intell Med. 76:27–36. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Dennis G Jr, Sherman BT, Hosack DA, Yang
J, Gao W, Lane HC and Lempicki RA: DAVID: Database for annotation,
visualization, and integrated discovery. Genome Biol.
4(P3)2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Goutzelas Y, Kontou P, Mamuris Z, Bagos P
and Sarafidou T: Meta-analysis of gene expression data in adipose
tissue reveals new obesity associated genes. Gene.
818(146223)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Wallach T, Schellenberg K, Maier B,
Kalathur RK, Porras P, Wanker EE, Futschik ME and Kramer A: Dynamic
circadian protein-protein interaction networks predict temporal
organization of cellular functions. PLoS Genet.
9(e1003398)2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Szklarczyk D, Gable AL, Nastou KC, Lyon D,
Kirsch R, Pyysalo S, Doncheva NT, Legeay M, Fang T, Bork P, et al:
The STRING database in 2021: Customizable protein-protein networks,
and functional characterization of user-uploaded gene/measurement
sets. Nucleic Acids Res. 49(D1):D605–D612. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Liu J, Zhou S, Li S, Jiang Y, Wan Y, Ma X
and Cheng W: Eleven genes associated with progression and prognosis
of endometrial cancer (EC) identified by comprehensive
bioinformatics analysis. Cancer Cell Int. 19(136)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Chen Y, Li H, Lai L, Feng Q and Shen J:
Identification of common differentially expressed genes and
potential therapeutic targets in ulcerative colitis and rheumatoid
arthritis. Front Genet. 11(572194)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408.
2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Johnson G, Ferrini A, Dolan SK, Nolan T,
Agrawal S, Doyle S and Bustin SA: Biomarkers for invasive
aspergillosis: The challenges continue. Biomark Med. 8:429–451.
2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Margalit A and Kavanagh K: The innate
immune response to aspergillus fumigatus at the alveolar surface.
FEMS Microbiol Rev. 39:670–687. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Seifert M, Nairz M, Schroll A, Schrettl M,
Haas H and Weiss G: Effects of the aspergillus fumigatus
siderophore systems on the regulation of macrophage immune effector
pathways and iron homeostasis. Immunobiology. 213:767–778.
2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Heinekamp T, Schmidt H, Lapp K, Pahtz V,
Shopova I, Koster-Eiserfunke N, Kruger T, Kniemeyer O and Brakhage
AA: Interference of aspergillus fumigatus with the immune response.
Semin Immunopathol. 37:141–152. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Tan HY, Wang N, Zhang C, Chan YT, Yuen MF
and Feng Y: Lysyl Oxidase-Like 4 Fosters an immunosuppressive
microenvironment during hepatocarcinogenesis. Hepatology.
73:2326–2341. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Fecher RA, Horwath MC, Friedrich D, Rupp J
and Deepe GS Jr: Inverse correlation between IL-10 and HIF-1alpha
in macrophages infected with histoplasma capsulatum. J Immunol.
197:565–579. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Goncalves SM, Duarte-Oliveira C, Campos
CF, Aimanianda V, Ter Horst R, Leite L, Mercier T, Pereira P,
Fernandez-Garcia M, Antunes D, et al: Phagosomal removal of fungal
melanin reprograms macrophage metabolism to promote antifungal
immunity. Nat Commun. 11(2282)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Cheng Y, Feng Y, Xia Z, Li X and Rong J:
ω-Alkynyl arachidonic acid promotes anti-inflammatory macrophage M2
polarization against acute myocardial infarction via regulating the
cross-talk between PKM2, HIF-1α and iNOS. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol
Cell Biol Lipids. 1862:1595–1605. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|