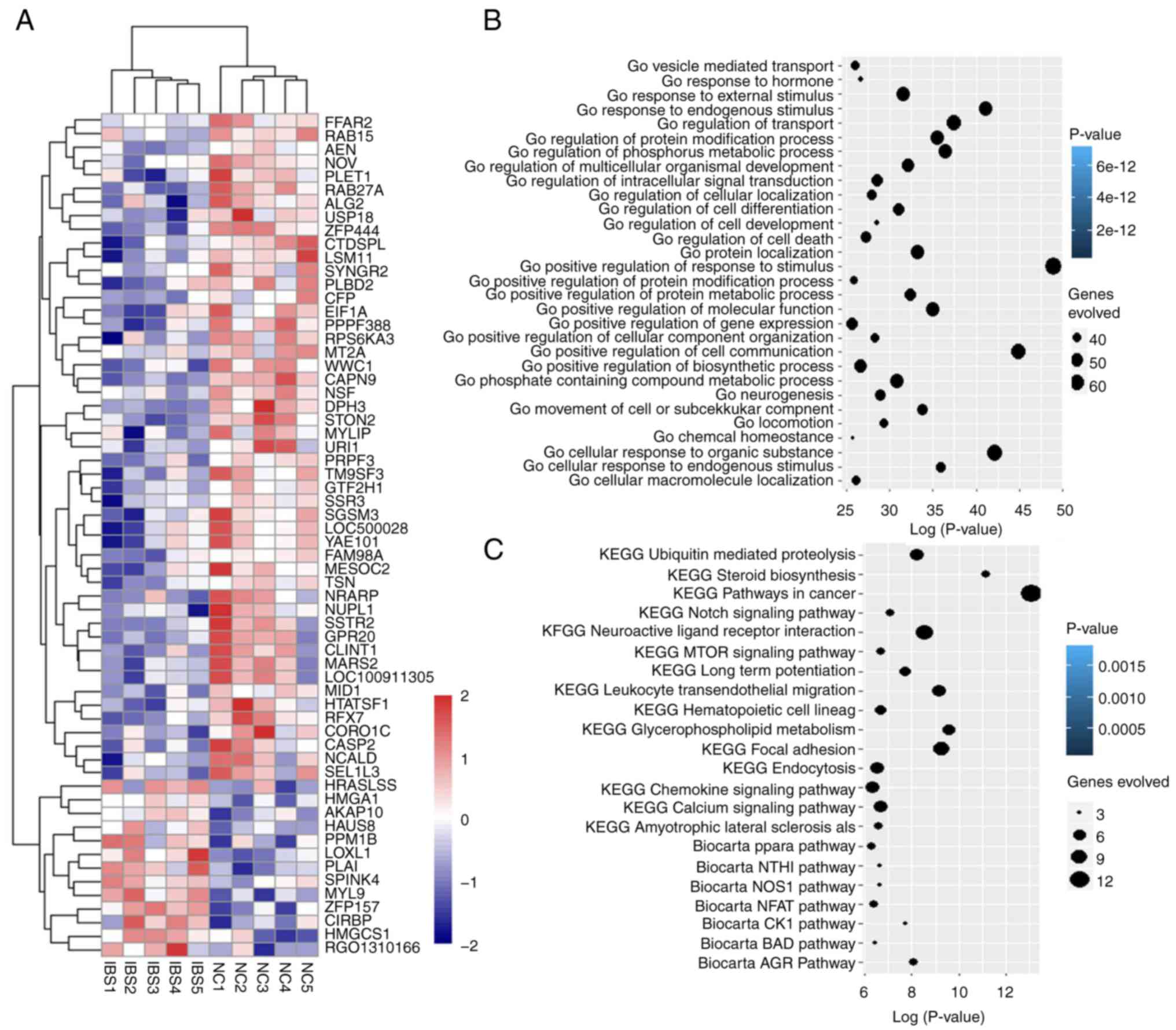
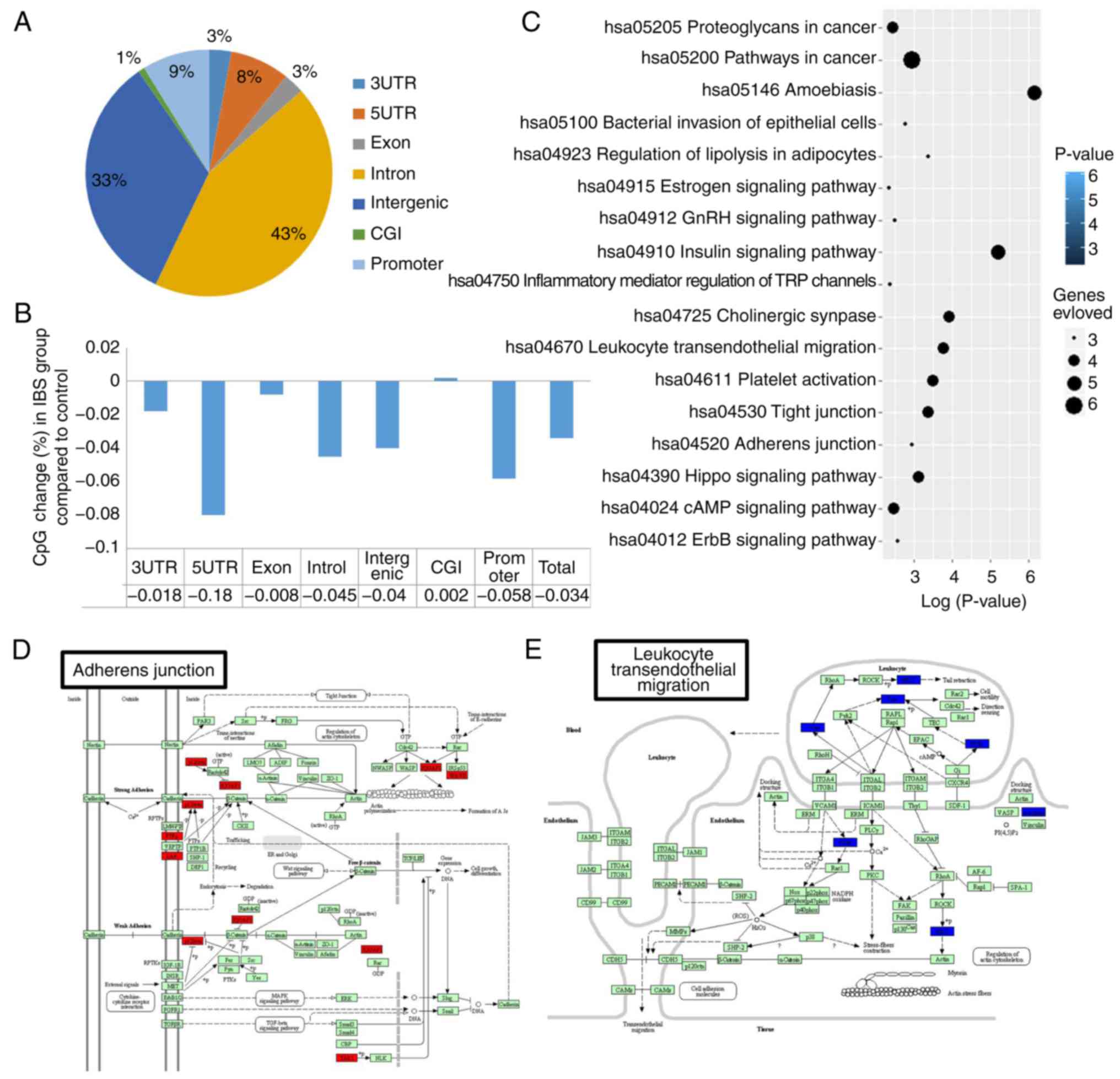
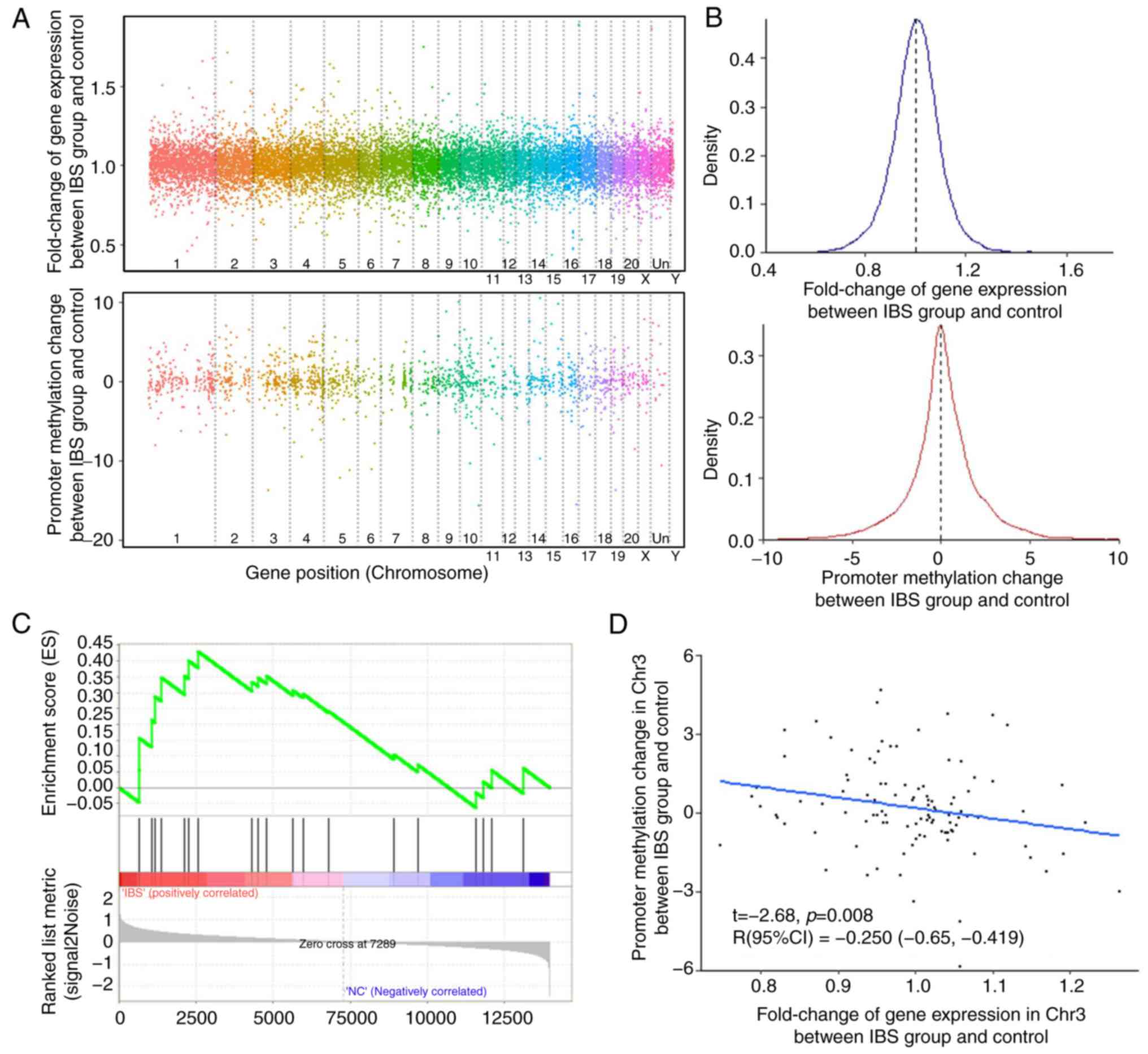
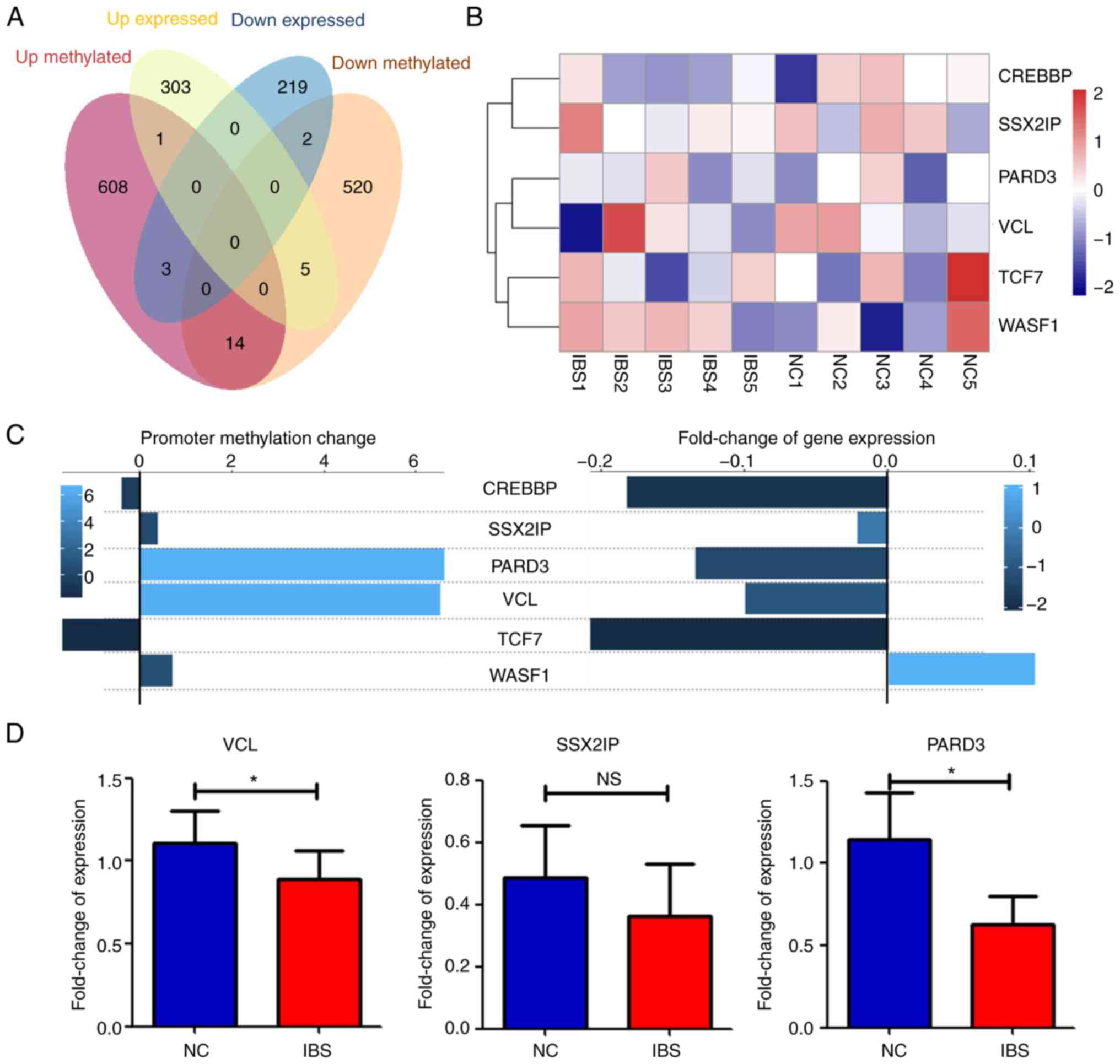
|
1
|
Sperber AD, Dumitrascu D, Fukudo S, Gerson
C, Ghoshal UC, Gwee KA, Hungin AP, Kang JY, Minhu C, Schmulson M,
et al: The global prevalence of IBS in adults remains elusive due
to the heterogeneity of studies: A Rome Foundation working team
literature review. Gut. 66:1075–1082. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Schoenfeld PS: Advances in IBS 2016: A
review of current and emerging data. Gastroenterol Hepatol (NY).
12:1–11. 2016.
|
|
3
|
Atluri DK, Chandar AK, Bharucha AE and
Falck-Ytter Y: Effect of linaclotide in irritable bowel syndrome
with constipation (IBS-C): A systematic review and meta-analysis.
Neurogastroenterol Motil. 26:499–509. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Fourie NH, Peace RM, Abey SK, Sherwin LB,
Rahim-Williams B, Smyser PA, Wiley JW and Henderson WA: Elevated
circulating miR-150 and miR-342 3pin patients with irritable bowel
syndrome. Exp Mol Pathol. 96:422–425. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Borghini R, Donato G, Alvaro D and
Picarelli A: New insights in IBS-like disorders: Pandora's box has
been opened; A review. Gastroenterol Hepatol Bed Bench. 10:79–89.
2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Chey WD: SYMPOSIUM REPORT: An
Evidence-based approach to IBS and CIC: Applying new advances to
daily practice: A review of an adjunct clinical symposium of the
American College of Gastroenterology Meeting October 16, 2016* Las
Vegas, Nevada. Gastroenterol Hepatol (NY). 13:1–16. 2017.
|
|
7
|
Levy RL, Von Korff M, Whitehead WE, Stang
P, Saunders K, Jhingran P, Barghout V and Feld AD: Costs of care
for irritable bowel syndrome patients in a health maintenance
organization. Am J Gastroenterol. 96:3122–3129. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Zheng G, Hong S, Hayes JM and Wiley JW:
Chronic stress and peripheral pain: Evidence for distinct,
region-specific changes in visceral and somatosensory pain
regulatory pathways. Exp Neurol. 273:301–311. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Sharkey KA and Wiley JW: The role of the
endocannabinoid system in the brain-gut axis. Gastroenterology.
151:252–266. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Jin Y, Ren X, Li G, Li Y, Zhang L, Wang H,
Qian W and Hou X: Rifaximin exerts beneficial effects in PI-IBS
mouse model beyond gut microbiota. J Gastroenterol Hepatol.
33:443–452. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Hong S, Zheng G and Wiley JW: Epigenetic
regulation of genes that modulate chronic stress-induced visceral
pain in the peripheral nervous system. Gastroenterology.
148:148–157.e147. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Taguchi R, Shikata K, Furuya Y, Hirakawa
T, Ino M, Shin K and Shibata H: Selective corticotropin-releasing
factor 1 receptor antagonist E2508 reduces restraint stress-induced
defecation and visceral pain in rat models.
Psychoneuroendocrinology. 75:110–115. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Zheng G, Victor Fon G, Meixner W,
Creekmore V, Zong Y, Dame MK, Colacino J, Dedhia PH, Hong S and
Wiley JW: Chronic stress and intestinal barrier dysfunction:
Glucocorticoid receptor and transcription repressor HES1 regulate
tight junction protein Claudin-1 promoter. Sci Rep. 7:45022017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Fond G, Loundou A, Hamdani N, Boukouaci W,
Dargel A, Oliveira J, Roger M, Tamouza R, Leboyer M and Boyer L:
Anxiety and depression comorbidities in irritable bowel syndrome
(IBS): A systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur Arch Psychiatry
Clin Neurosci. 264:651–660. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Chitkara DK, van Tilburg MA, Blois-Martin
N and Whitehead WE: Early life risk factors that contribute to
irritable bowel syndrome in adults: A systematic review. Am J
Gastroenterol. 103:765–774. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Videlock EJ, Adeyemo M, Licudine A, Hirano
M, Ohning G, Mayer M, Mayer EA and Chang L: Childhood trauma is
associated with hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis responsiveness
in irritable bowel syndrome. Gastroenterology. 137:1954–1962. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Funatsu T, Takeuchi A, Hirata T, Keto Y,
Akuzawa S and Sasamata M: Effect of ramosetron on conditioned
emotional stress-induced colonic dysfunction as a model of
irritable bowel syndrome in rats. Eur J Pharmacol. 573:190–195.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Bach DR, Erdmann G, Schmidtmann M and
Mönnikes H: Emotional stress reactivity in irritable bowel
syndrome. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 18:629–636. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Leserman J and Drossman DA: Relationship
of abuse history to functional gastrointestinal disorders and
symptoms: Some possible mediating mechanisms. Trauma Violence
Abuse. 8:331–343. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Moloney RD, O'Mahony SM, Dinan TG and
Cryan JF: Stress-induced visceral pain: Toward animal models of
irritable-bowel syndrome and associated comorbidities. Front
Psychiatry. 6:152015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Bonaz B and Tache Y: Water-avoidance
stress-induced c-fos expression in the rat brain and stimulation of
fecal output: Role of corticotropin-releasing factor. Brain Res.
641:21–28. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Tran L, Chaloner A, Sawalha AH and
Greenwood Van-Meerveld B: Importance of epigenetic mechanisms in
visceral pain induced by chronic water avoidance stress.
Psychoneuroendocrinology. 38:898–906. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Bian ZX, Qin HY, Tian SL and Qi SD:
Combined effect of early life stress and acute stress on colonic
sensory and motor responses through serotonin pathways: Differences
between proximal and distal colon in rats. Stress. 14:448–458.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Nozu T, Miyagishi S, Nozu R, Takakusaki K
and Okumura T: Water avoidance stress induces visceral
hyposensitivity through peripheral corticotropin releasing factor
receptor type 2 and central dopamine D2 receptor in rats.
Neurogastroenterol Motil. 28:522–531. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Fourie NH, Wang D, Abey SK, Creekmore AL,
Hong S, Martin CG, Wiley JW and Henderson WA: Structural and
functional alterations in the colonic microbiome of the rat in a
model of stress induced irritable bowel syndrome. Gut Microbes.
8:33–45. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Schwetz I, Bradesi S, McRoberts JA, Sablad
M, Miller JC, Zhou H, Ohning G and Mayer EA: Delayed stress-induced
colonic hypersensitivity in male Wistar rats: Role of neurokinin-1
and corticotropin-releasing factor-1 receptors. Am J Physiol
Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 286:G683–G691. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Camilleri M, Carlson P, Valentin N, Acosta
A, O'Neill J, Eckert D, Dyer R, Na J, Klee EW and Murray JA: Pilot
study of small bowel mucosal gene expression in patients with
irritable bowel syndrome with diarrhea. Am J Physiol Gastrointest
Liver Physiol. 311:G365–G376. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Dussik C, Grozić A, Hockley M, Zhang L,
Park J, Wang J, Nickerson C, Yale SH, Orenstein AF, Sandrin T and
Jurutka P: Characterization of Vitamin D and serotonin pathway
variations in patients with irritable bowel syndrome. FASEB J.
30:S8282016.
|
|
29
|
Bradesi S, Schwetz I, Ennes HS, Lamy CM,
Ohning G, Fanselow M, Pothoulakis C, McRoberts JA and Mayer EA:
Repeated exposure to water avoidance stress in rats: A new model
for sustained visceral hyperalgesia. Am J Physiol Gastrointest
Liver Physiol. 289:G42–G53. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2−ΔΔCT method. Methods.
25:402–408. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Drossman DA, Camilleri M, Mayer EA and
Whitehead WE: AGA technical review on irritable bowel syndrome.
Gastroenterology. 123:2108–2131. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Gonzalez-Castro AM, Martinez C,
Salvo-Romero E, Fortea M, Pardo-Camacho C, Pérez-Berezo T,
Alonso-Cotoner C, Santos J and Vicario M: Mucosal pathobiology and
molecular signature of epithelial barrier dysfunction in the small
intestine in irritable bowel syndrome. J Gastroenterol Hepatol.
32:53–63. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Fukudo S and Kanazawa M: Gene,
environment, and brain-gut interactions in irritable bowel
syndrome. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 26(Suppl 3): S110–S115. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Mahurkar S, Polytarchou C, Iliopoulos D,
Pothoulakis C, Mayer EA and Chang L: Genome-wide DNA methylation
profiling of peripheral blood mononuclear cells in irritable bowel
syndrome. Neurogastroenterol Motil. 28:410–422. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
35
|
Sayanjali B: Genome-wide transcriptome
analysis of prostate cancer tissue identified overexpression of
specific members of the human endogenous retrovirus-K family.
Cancer Transl Med. 3:1–12. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Wilson S, Fan L, Sahgal N, Qi J and Filipp
FV: The histone demethylase KDM3A regulates the transcriptional
program of the androgen receptor in prostate cancer cells.
Oncotarget. 8:30328–30343. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|