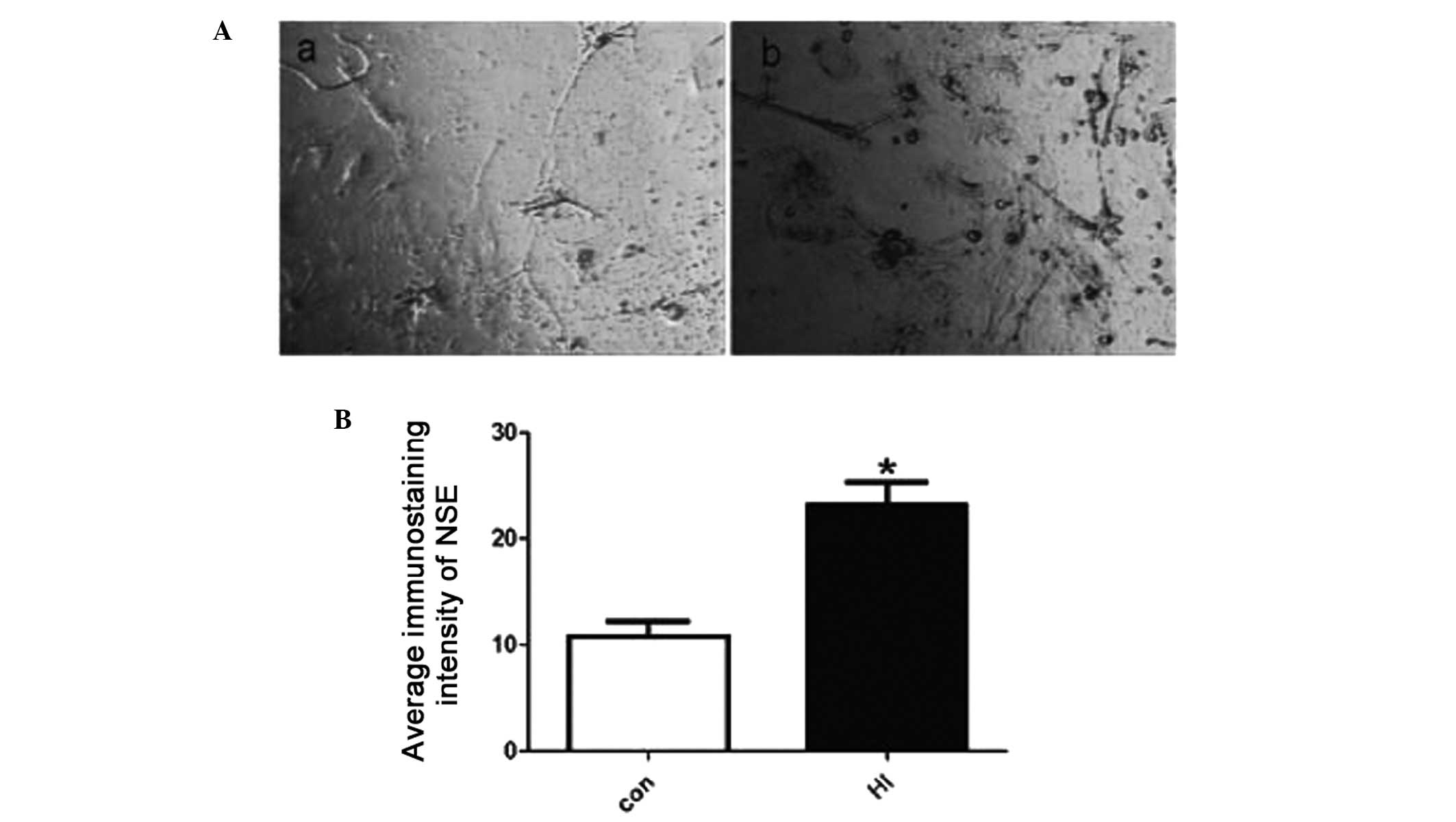
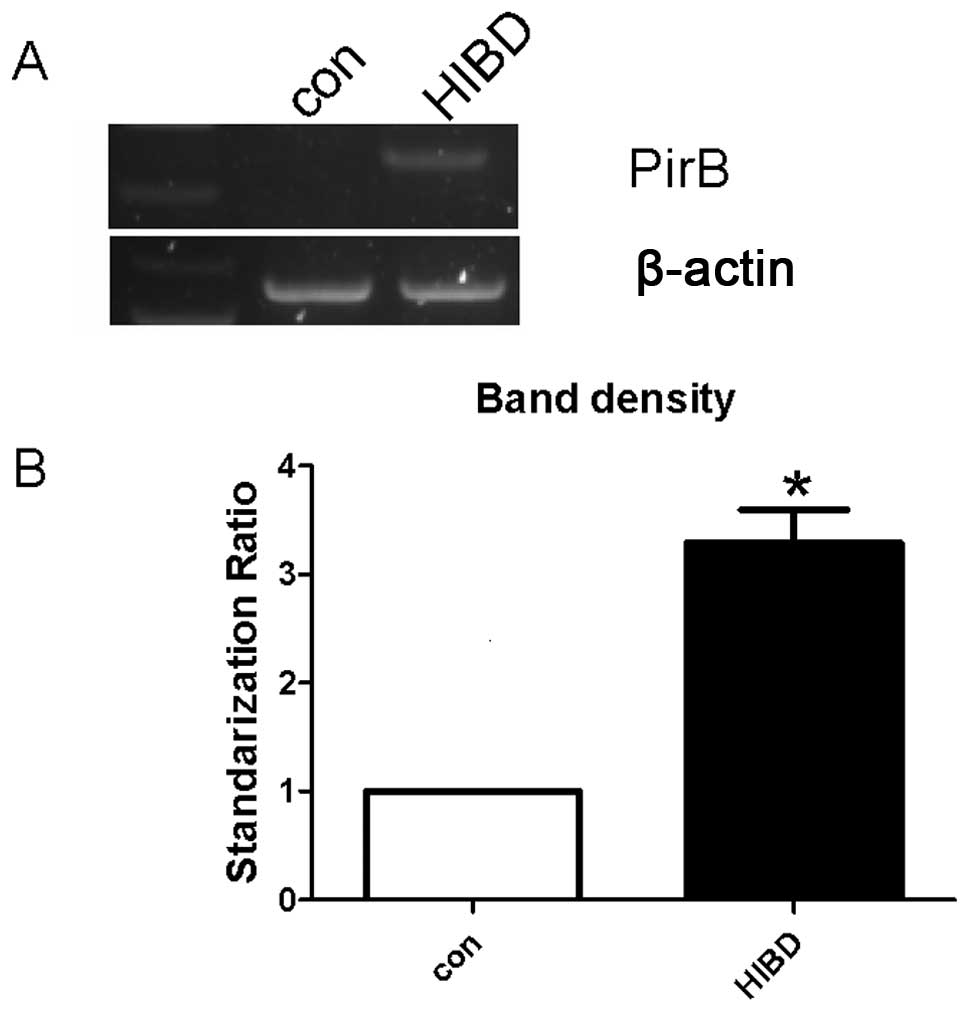
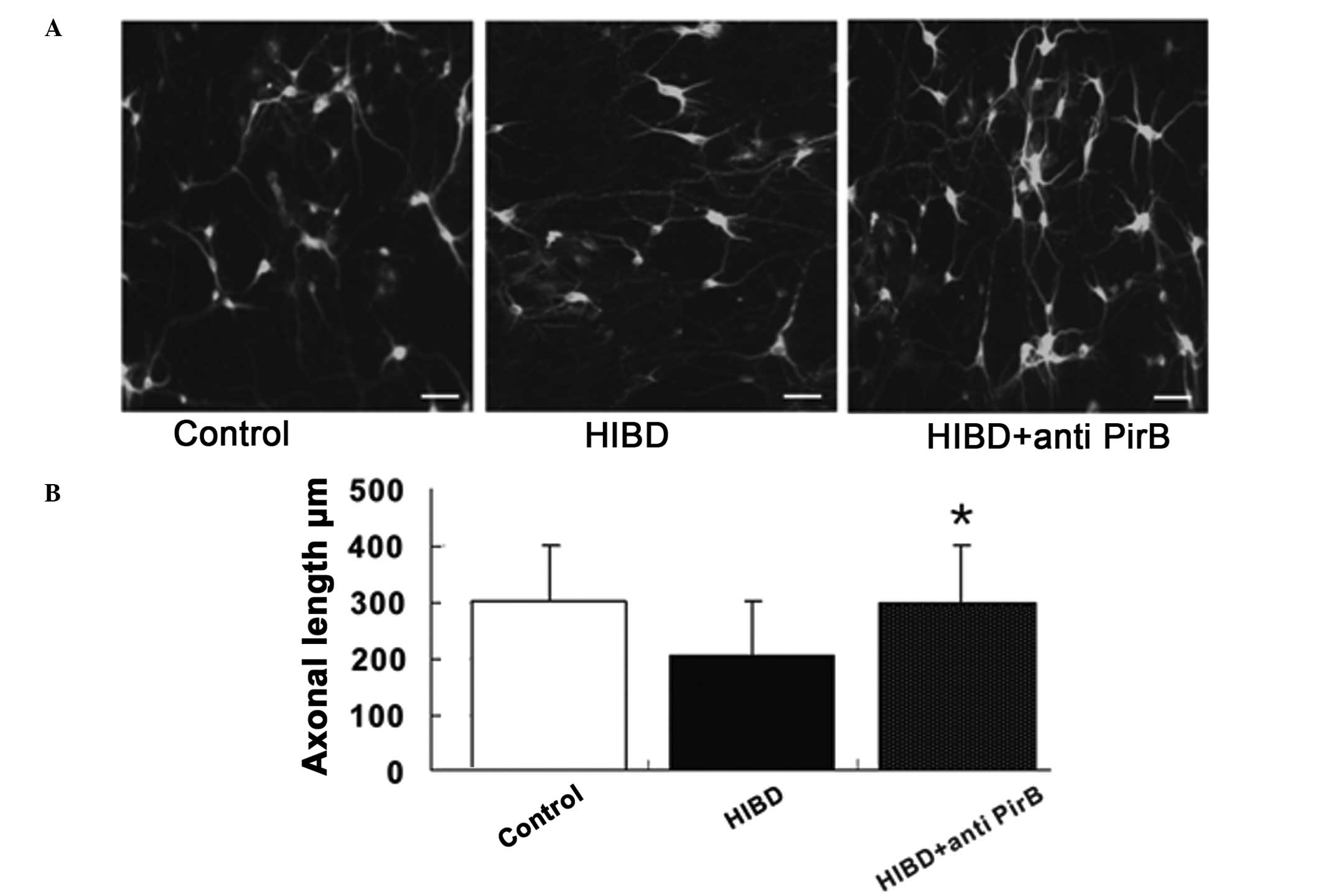
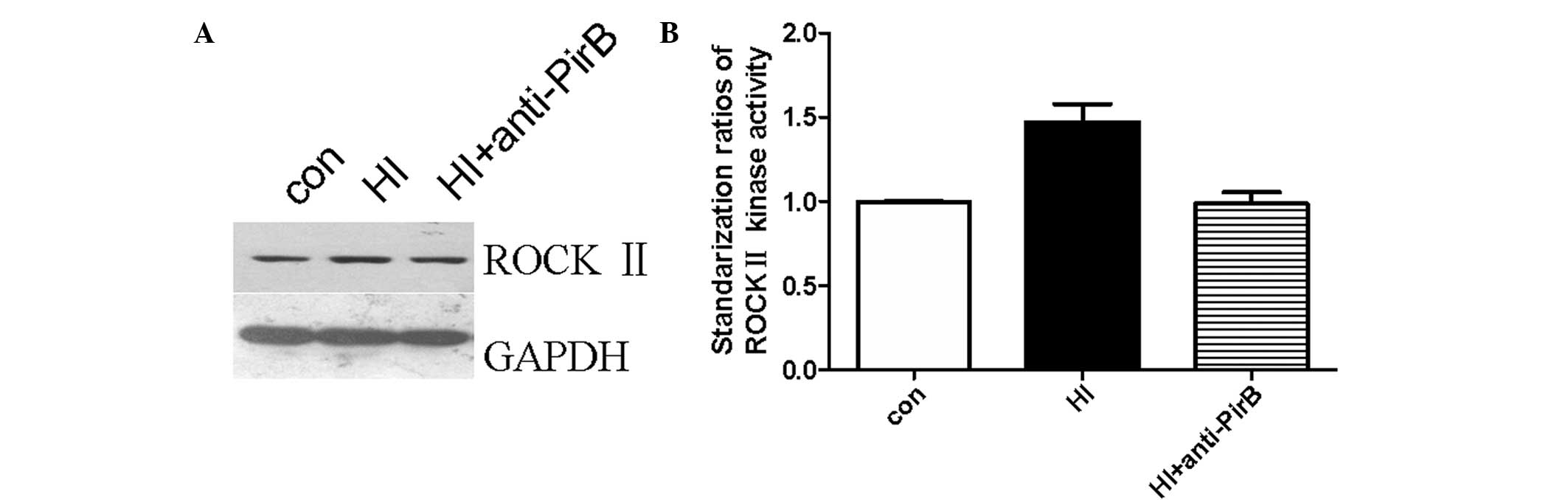
|
1
|
Roland EH and Hill A: Clinical aspects of
perinatal hypoxic-ischemic brain injury. Semin Pediatr Neurol.
2:57–71. 1995.
|
|
2
|
Lai MC and Yang SN: Perinatal
hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy. J Biomed Biotechnol.
2011:6098132011.
|
|
3
|
Schwab ME: Nogo and axon regeneration.
Curr Opin Neurobiol. 14:118–124. 2004.
|
|
4
|
Fournier AE, GrandPre T and Strittmatter
SM: Identification of a receptor mediating Nogo-66 inhibition of
axonal regeneration. Nature. 409:341–346. 2001.
|
|
5
|
Wang KC, Koprivica V, Kim JA, Sivasankaran
R, Guo Y, Neve RL and He Z: Oligodendrocyte-myelin glycoprotein is
a Nogo receptor ligand that inhibits neurite outgrowth. Nature.
417:941–944. 2002.
|
|
6
|
Domeniconi M, Cao Z, Spencer T, et al:
Myelin-associated glycoprotein interacts with the Nogo66 receptor
to inhibit neurite outgrowth. Neuron. 35:283–290. 2002.
|
|
7
|
Shao Z, Browning JL, Lee X, et al:
TAJ/TROY, an orphan TNF receptor family member, binds Nogo-66
receptor 1 and regulates axonal regeneration. Neuron. 45:353–359.
2005.
|
|
8
|
Wang H, Yao YJ and Mu DZ: Expression of
Nogo-A and NgR in the developing rat brain after hypoxia-ischemia.
Brain Res. 1114:212–220. 2006.
|
|
9
|
GrandPré T, Li S and Strittmatter SM:
Nogo-66 receptor antagonist peptide promotes axonal regeneration.
Nature. 417:547–551. 2002.
|
|
10
|
Zheng B, Atwal J, Ho C, He XL, Garcia KC,
Steward O and Tessier-Lavigne M: Genetic deletion of the Nogo
receptor does not reduce neurite inhibition in vitro or promote
corticospinal tract regeneration in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
102:1205–1210. 2005.
|
|
11
|
Syken J, GrandPre T, Kanold PO and Shatz
CJ: PirB restricts ocular-dominance plasticity in visual cortex.
Science. 313:1795–1800. 2006.
|
|
12
|
Atwal JK, Pinkston-Gosse J, Syken J,
Stawicki S, Wu Y, Shatz C and Tessier-Lavigne M: PirB is a
functional receptor for myelin inhibitors of axonal regeneration.
Science. 322:867–870. 2008.
|
|
13
|
Nakamura Y, Fujita Y, Ueno M, Takai T and
Yamashita T: Paired immunoglobulin-like receptor B knockout does
not enhance axonal regeneration or locomotor recovery after spinal
cord injury. J Biol Chem. 286:1876–1883. 2011.
|
|
14
|
Omoto S, Ueno M, Mochio S, Takai T and
Yamashita T: Genetic deletion of paired immunoglobulin-like
receptor B does not promote axonal plasticity or functional
recovery after traumatic brain injury. J Neurosci. 30:13045–13052.
2010.
|
|
15
|
Cohen-Cory S and Fraser SE: Effects of
brain-derived neurotrophic factor on optic axon branching and
remodelling in vivo. Nature. 378:192–196. 1995.
|
|
16
|
Cohen-Cory S and Fraser SE: Effects of
brain-derived neurotrophic factor on optic axon branching and
remodelling in vivo. Nature. 378:192–196. 1995.
|
|
17
|
Hashimoto R, Nakamura Y, Kosako H, Amano
M, Kaibuchi K, Inagaki M and Takeda M: Distribution of Rho-kinase
in the bovine brain. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 263:575–579.
1999.
|