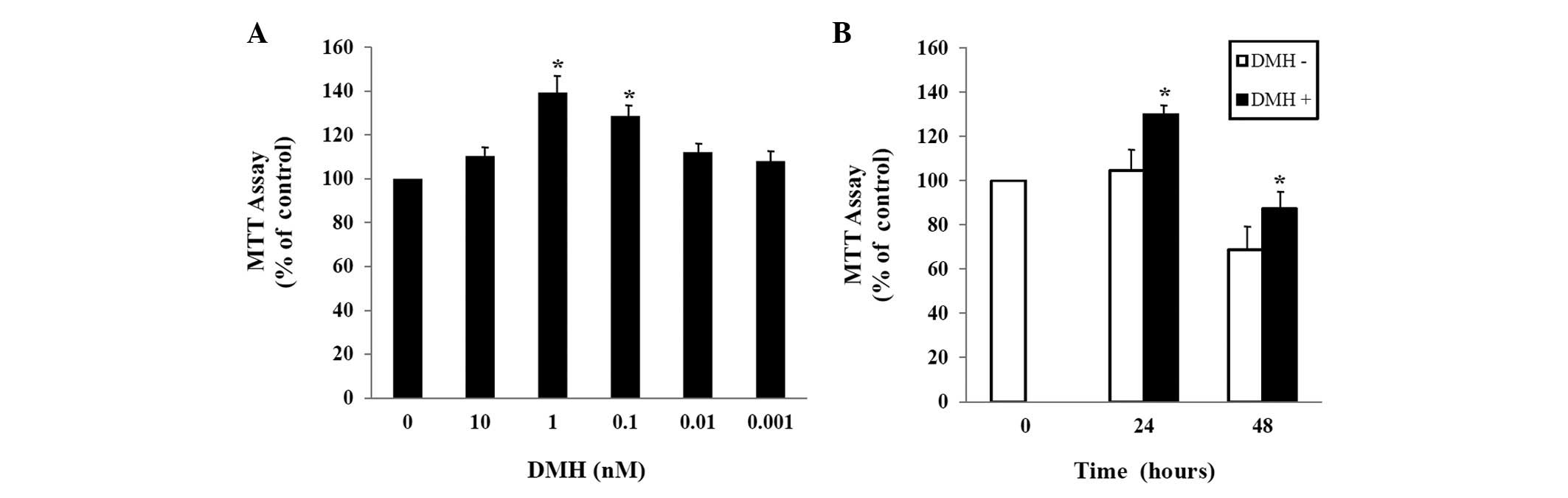
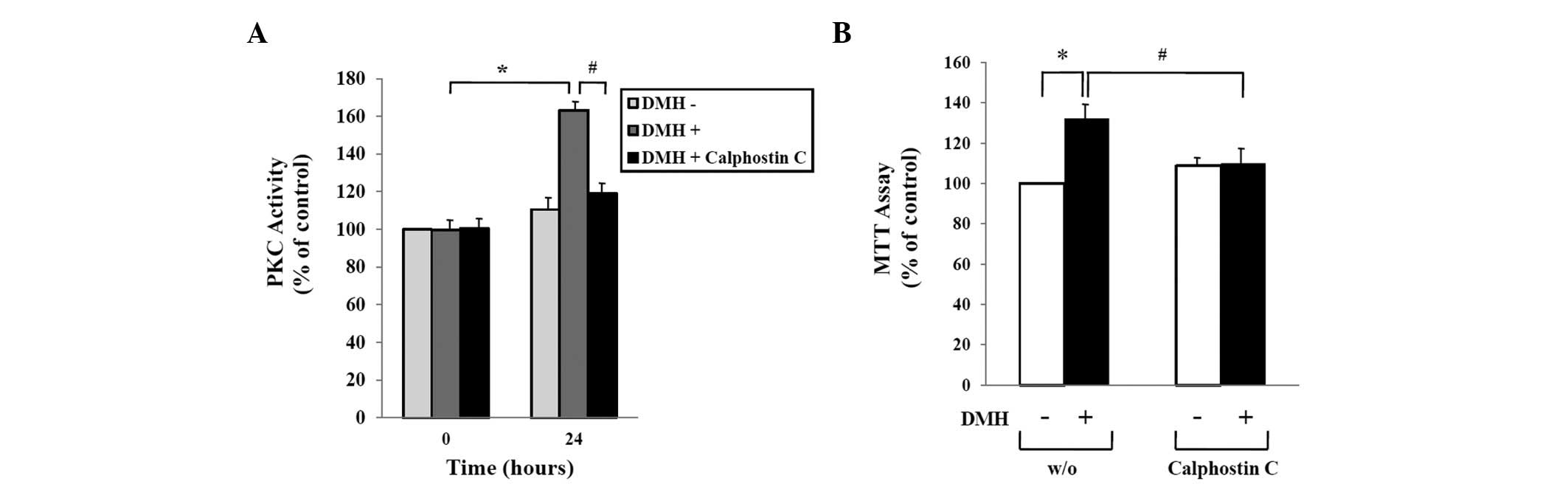
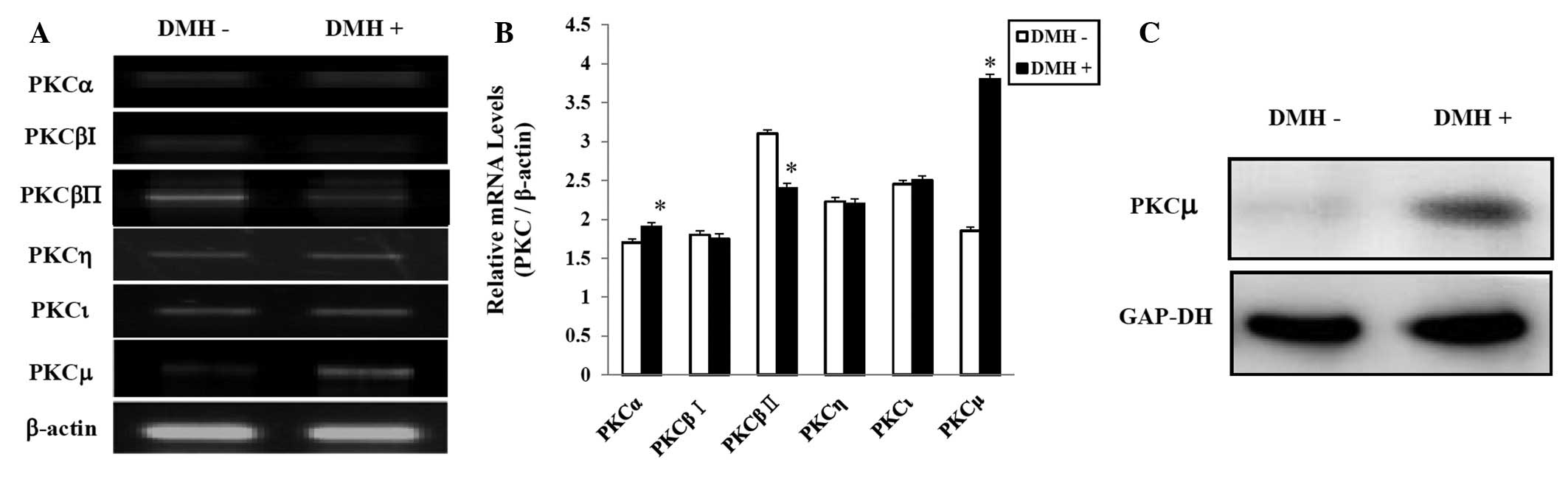
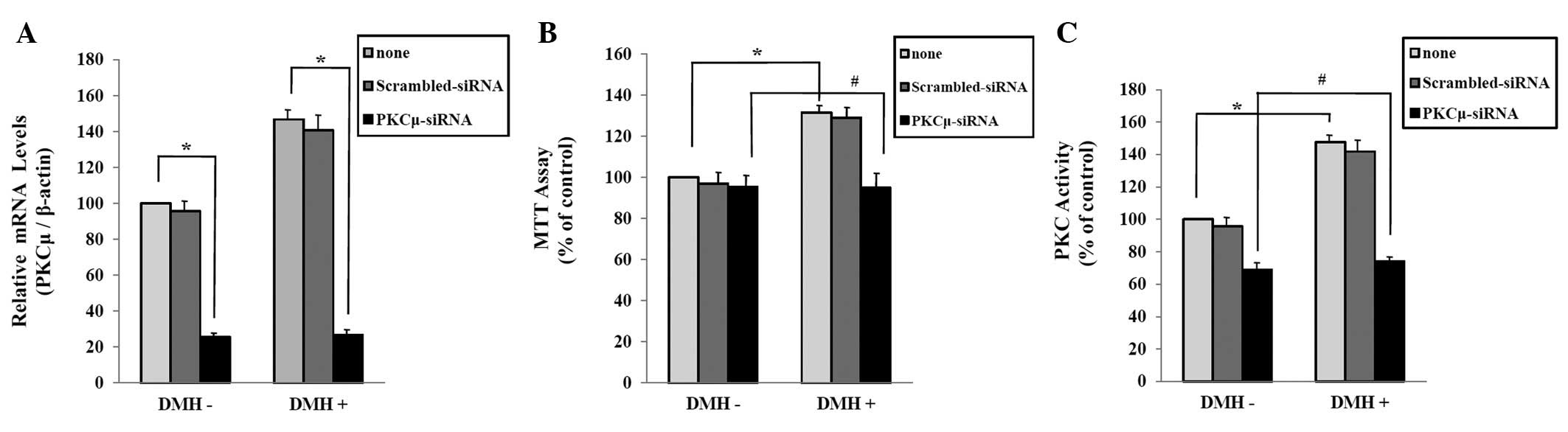
|
1
|
Klagsbrun M and D’Amore PA: Regulators of
angiogenesis. Annu Rev Physiol. 53:217–239. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Folkman J and Shing Y: Angiogenesis. J
Biol Chem. 267:10931–11934. 1992.
|
|
3
|
Folkman J: What is the evidence that
tumors are angiogenesis dependent? J Natl Cancer Inst. 82:4–6.
1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Ingber D, Fujita T, Kishimoto S, Sudo K,
Kanamaru T, Brem H and Folkman J: Synthetic analogues of fumagillin
that inhibit angiogenesis and suppress tumour growth. Nature.
348:555–557. 1990. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Weidner N, Semple JP, Welch WR and Folkman
J: Tumor angiogenesis and metastasis-correlation in invasive breast
carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 324:1–8. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Mulliken JB: Pathogenesis of hemangiomas.
Vascular Birthmarks: Hemangiomas and Malformations. Mulliken JB and
Young AE: Saunders; Philadelphia: pp. 63–76. 1988
|
|
7
|
Druckrey H: Production of colonic
carcinomas by 1,2-dialkylhydrazines and azoalkanes. Carcinoma of
the Colon and Antecedent Epithelium. Burdette WJ: Sprinpfield, III:
Charles C Thomas; pp. 267–279. 1970
|
|
8
|
Druckrey H, Preussmann R, Matzkies F and
Ivankovic S: Selective production of intestinal cancer in rats by
1,2-dimethylhydrazine. Naturwissenschaften. 54:285–286.
1967.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Wiebecke B, Löhrs U, Gimmy J and Eder M:
Production of tumors in the intestines of mice by
1,2-dimethylhydrazine. Z Gesamte Exp Med. 149:277–278.
1969.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Kim HO, Kang YS, Bae YC, Park SY, Hwang SM
and Nam SB: Gene expression profiling of
1,2-Dimethylhydrazine-stimulated human umbilical vein endothelial
cells. J Korean Soc Plast Reconstr Surg. 31:858–864. 2004.
|
|
11
|
Kim SH, Kang YS, Bae YC, Park SY and Nam
SB: RT-PCR of Up-Regulated Factors in Abnormally Proliferated
Vascular Endothelial Cells by 1,2-Dimethylhydrazine. J Korean Soc
Plast Reconstr Surg. 32:689–698. 2005.
|
|
12
|
Bae YC, Park SY, Nam SB, Herh JY and Kang
YS: A study for the mechanism of abnormal proliferation in vascular
endothelial cells using inhibitors to the signal transduction
pathway. J Korean Soc Plast Reconstr Surg. 33:5–12. 2006.
|
|
13
|
Lee J, Bae YC, Park SY, Moon JS and Nam
SB: Role of protein kinase C in abnormal proliferation of vascular
endothelial cell induced by 1,2-dimethylhydrazine; analysis of
isoform. J Korean Soc Plast Reconstr Surg. 34:8–12. 2007.(In
Korean).
|
|
14
|
Livneh E and Fishman DD: Linking protein
kinase C to cell-cycle control. Eur J Biochem. 248:1–9. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Nishi K, Schnier JB and Bradbury EM: The
accumulation of cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p27kip1 is a
primary response to staurosporine and independent of G1 cell cycle
arrest. Exp Cell Res. 243:222–231. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Fukumoto S, Nishizawa Y, Hosoi M, Koyama
H, Yamakawa K, Ohno S and Morii H: Protein kinase C delta inhibits
the proliferation of vascular smooth muscle cells by suppressing G1
cyclin expression. J Biol Chem. 272:13816–13822. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Ways DK, Kukoly CA, DeVente J, Hooker JL,
Bryant WO, Posekany KJ, Fletcher DJ, Cook PP and Parker PJ: MCF-7
breast cancer cells transfected with protein kinase C-alpha exhibit
altered expression of other protein kinase C isoforms and display a
more aggressive neoplastic phenotype. J Clin Invest. 95:1906–1915.
1995. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Dean N, McKay R, Miraglia L, Howard R,
Cooper S, Giddings J, Nicklin P, Meister L, Ziel R, Geiger T,
Muller M and Fabbro D: Inhibition of growth of human tumor cell
lines in nude mice by an antisense of oligonucleotide inhibitor of
protein kinase C-alpha expression. Cancer Res. 56:3499–3507.
1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
O’Brian C, Vogel VG, Singletary SE and
Ward NE: Elevated protein kinase C expression in human breast tumor
biopsies relative to normal breast tissue. Cancer Res.
49:3215–3217. 1989.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Schwartz GK, Redwood SM, Ohnuma T, Holland
JF, Droller MJ and Liu BC: Inhibition of invasion of invasive human
bladder carcinoma cells by protein kinase C inhibitor
staurosporine. J Natl Cancer Inst. 82:1753–1756. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Newton AC: Protein kinase C: structure,
function, and regulation. J Biol Chem. 270:28495–28498. 1995.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Gampper TJ and Morgan RF: Vascular
anomaly: Hemangiomas. Plast Reconstr Surg. 110:572–585. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Mulliken JB and Glowacki J: Hemangiomas
and vascular malformations in infants and children: A
classification based on endothelial characteristics. Plast Reconstr
Surg. 69:412–422. 1982. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Clemens MJ, Trayner I and Menaya J: The
role of protein kinase C isoenzymes in regulation of cell
proliferation and differentiation. J Cell Sci. 103:881–887.
1992.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Bischoff J: Perspectives series; cell
adhesion in vascular biology. J Clin Invest. 99:373–376. 1997.
|
|
26
|
Lee OH, Kim YM, Lee YM, Moon EJ, Lee DJ,
Kim JH, Kim KW and Kwon YG: Sphingosine1-phosphat induces
angiogenesis: its angiogenic action and signaling mechanism in
human umbilical vein endothelial cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
264:743–750. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Lutz MP, Esser IB, Flossmann-Kast BB,
Vogelmann R, Luhrs H, Friess H, Buchler MW and Adler G:
Overexpression and activation of the tyrosine kinase Src in human
pancreatic carcinoma. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 243:503–508.
1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Hug H: Protein kinase C isoenzymes
divergence in signal transduction? Biochem J. 291:329–343.
1993.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Yang JH and Kodavinti PR: Possible
molecular targets of halogenated aromatic hydrobons in neural
cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 280:1372–1377. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Mischak H, Goodnight JA, Kolch W,
Martiny-Baron G, Schaechtle C, Kazanietz MG, Blumberg PM, Pierce JH
and Mushinski JF: Overexpression of prtein kinase C-δ and -ɛ in NIH
3T3 cells induces opposite effects on growth, morphology, anchorage
dependence, and tumorigeniccity. J Biol Chem. 268:6090–6096.
1993.
|
|
31
|
Grabam MA, Rawe I, Dartt DA and Joyce NC:
Protein kinase C refulation of corneal endothelial cell
proliferation and cell cycle. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci.
41:4124–4132. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Farivar RS, Gardner-Thorpe J, Ito H,
Arshad H, Zinner MJ, Ashley SW and Whang EE: The efficacy of
tyrosine kinase inhibitors on human pancreatic cancer cell lines. J
Surg Res. 115:219–225. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|