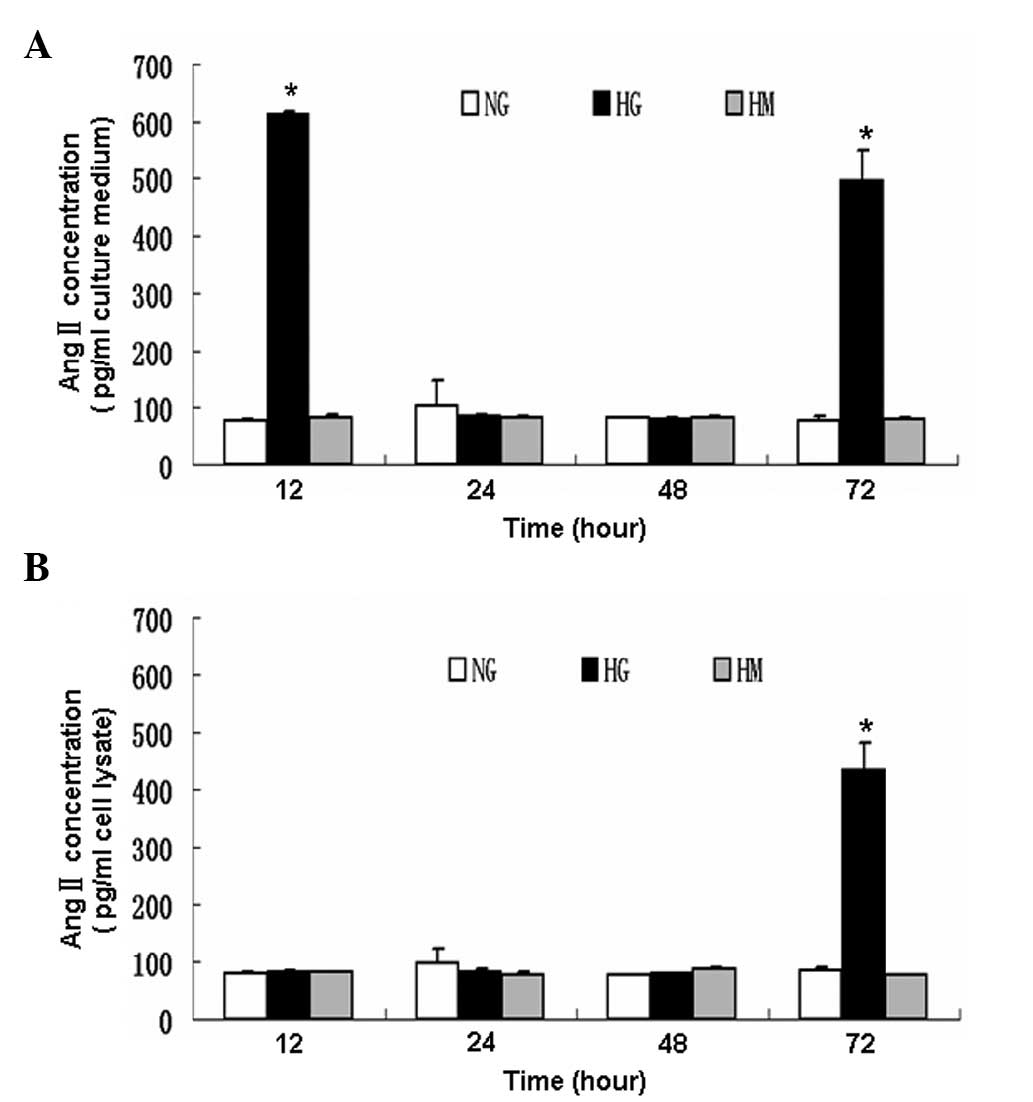
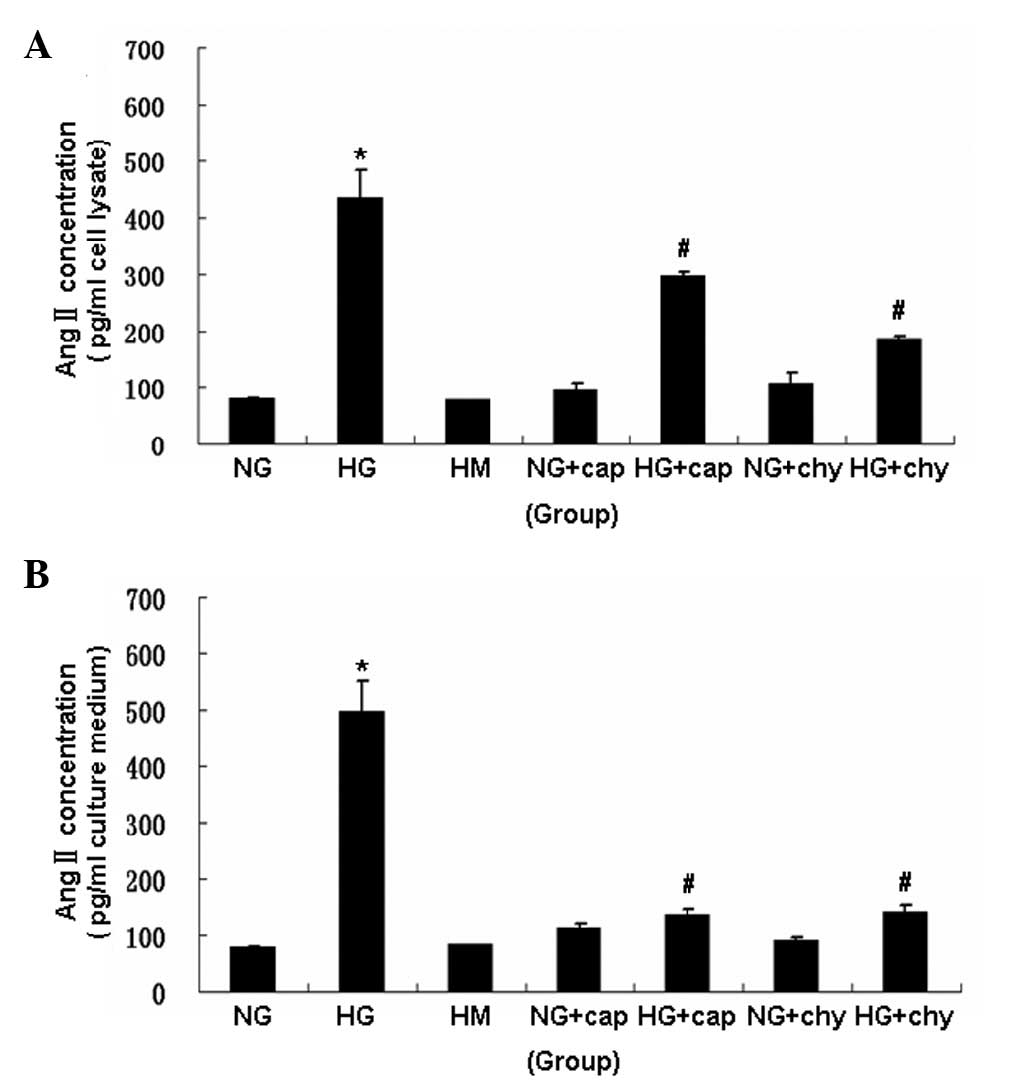
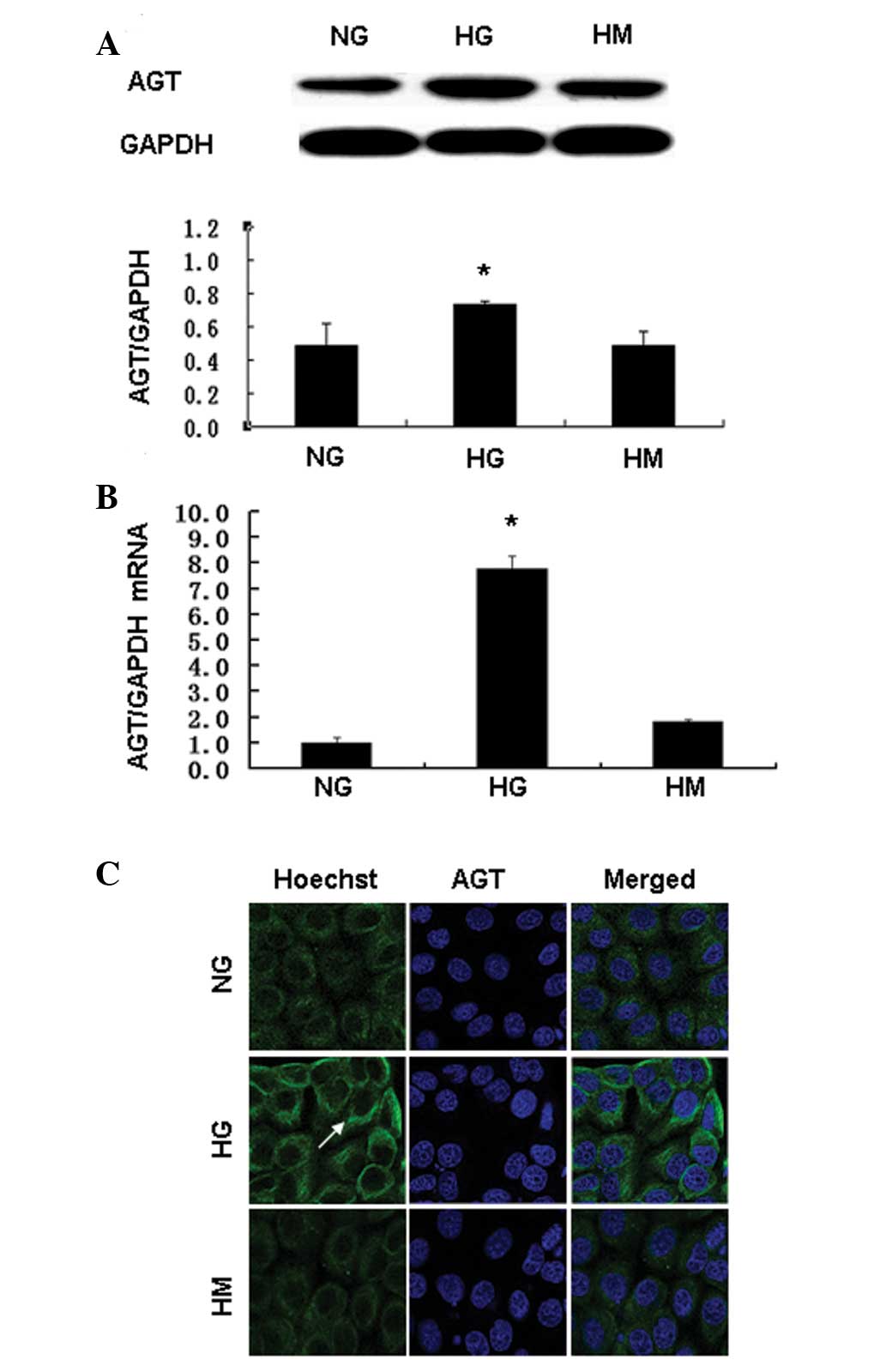
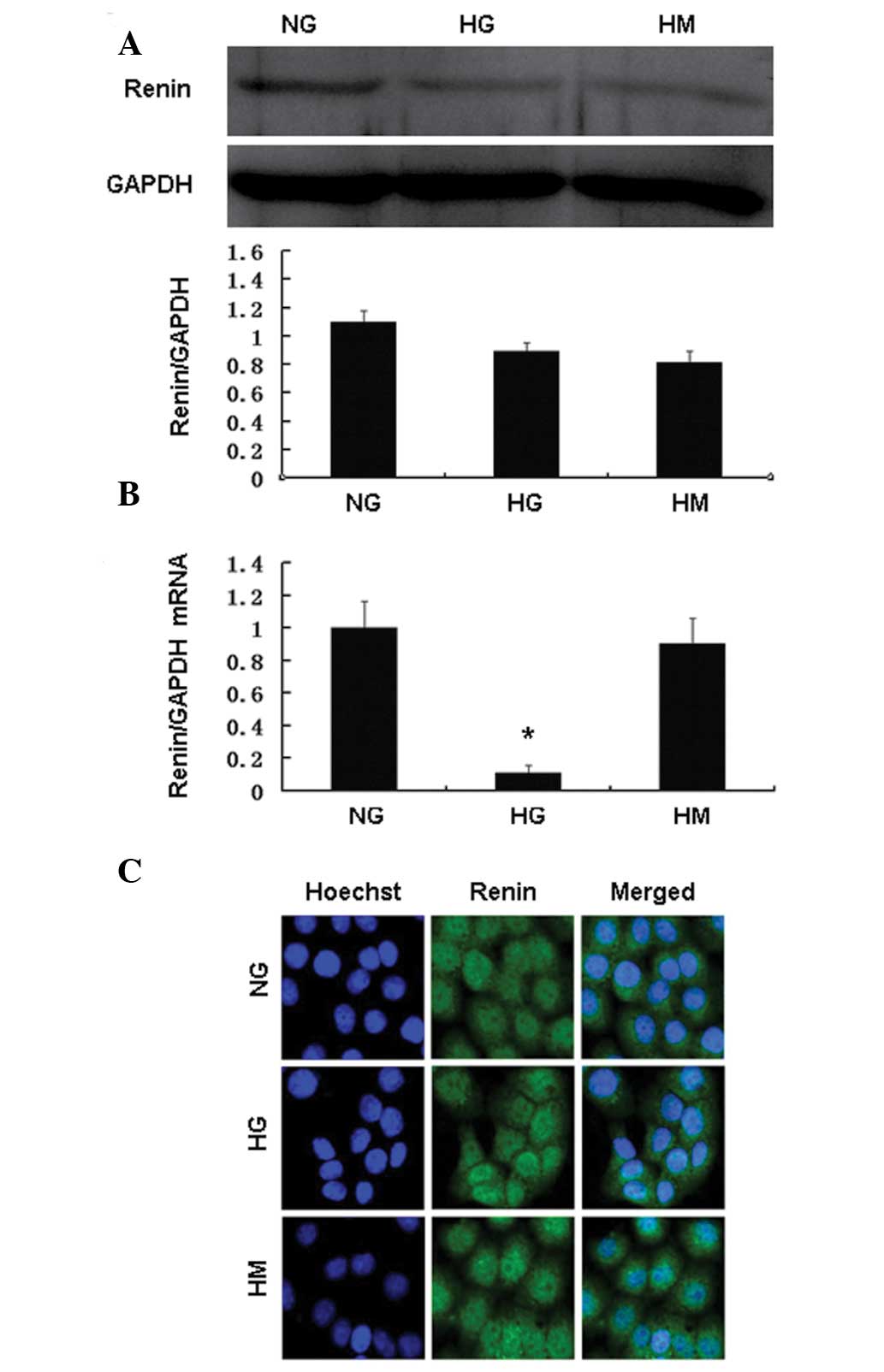
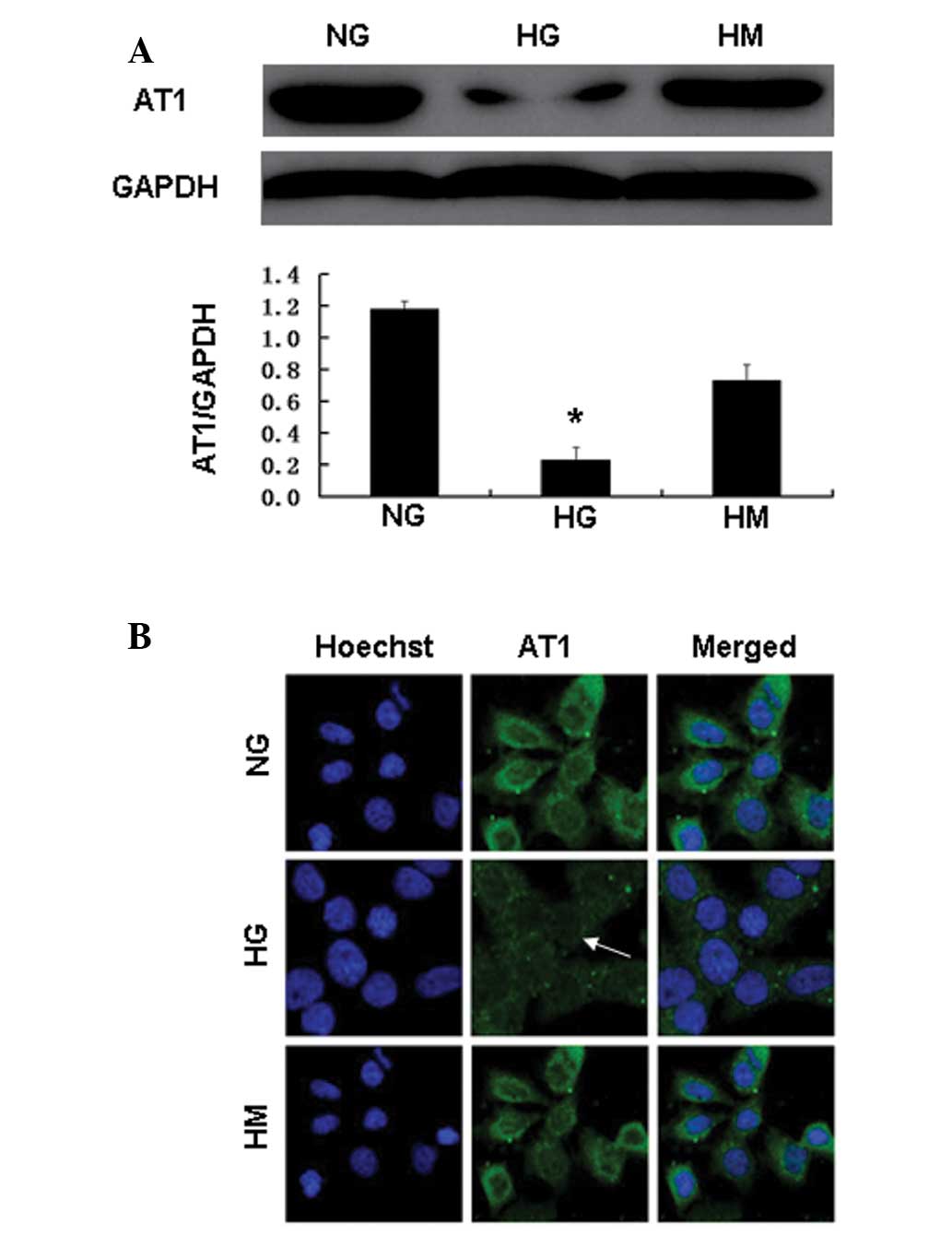
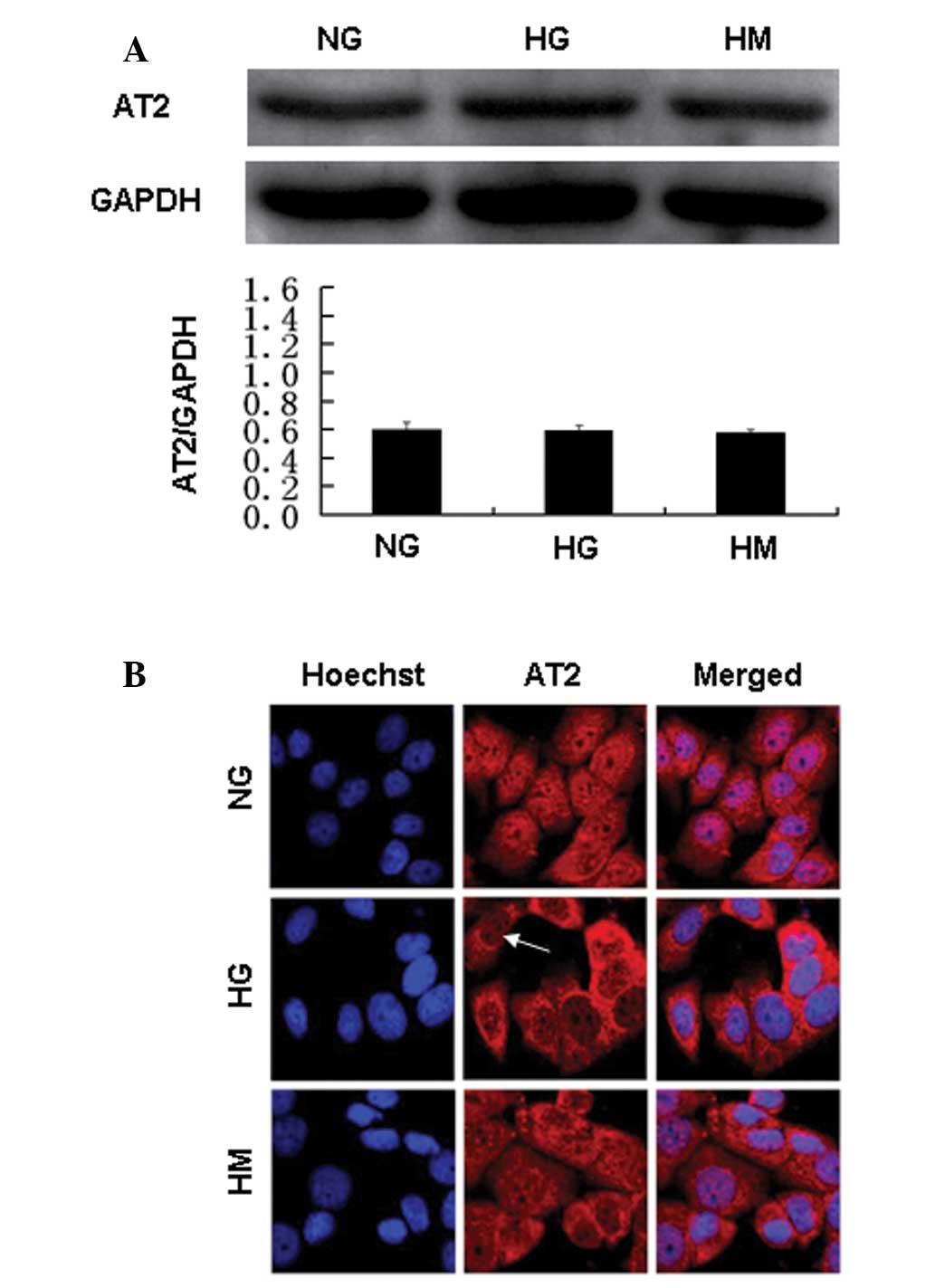
|
1
|
Wolf G: Molecular mechanisms of
angiotensin II in the kidney: emerging role in the progression of
renal disease: beyond haemodynamics. Nephrol Dial Transplant.
13:1131–1142. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Suzuki Y, Ruiz-Ortega M, Lorenzo O,
Ruperez M, Esteban V and Egido J: Inflammation and angiotensin II.
Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 35:881–900. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Seikaly MG, Arant BS Jr and Seney FD Jr:
Endogenous angiotensin concentrations in specific intrarenal fluid
compartments of the rat. J Clin Invest. 86:1352–1357. 1990.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Zhang SL, To C, Chen X, et al: Effect of
renin-angiotensin system blockade on the expression of the
angiotensinogen gene and induction of hypertrophy in rat kidney
proximal tubular cells. Exp Nephrol. 9:109–117. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Cristovam PC, Arnoni CP, de Andrade MC, et
al: ACE-dependent and chymase-dependent angiotensin II generation
in normal and glucose-stimulated human mesangial cells. Exp Biol
Med (Maywood). 233:1035–1043. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Durvasula RV and Shankland SJ: Activation
of a local renin angiotensin system in podocytes by glucose. Am J
Physiol Renal Physiol. 294:F830–F839. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Lee LK, Meyer TW, Pollock AS and Lovett
DH: Endothelial cell injury initiates glomerular sclerosis in the
rat remnant kidney. J Clin Invest. 96:953–964. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Satchell SC and Tooke JE: What is the
mechanism of microalbuminuria in diabetes: a role for the
glomerular endothelium? Diabetologia. 51:714–725. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Ballermann BJ: Contribution of the
endothelium to the glomerular permselectivity barrier in health and
disease. Nephron Physiol. 106:19–25. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Zanatta CM, Canani LH, Silveiro SP,
Burttet L, Nabinger G and Gross JL: Endothelin system function in
diabetic nephropathy. Arq Bras Endocrinol Metabol. 52:581–588.
2008.(In Portuguese).
|
|
11
|
Jefferson JA, Shankland SJ and Pichler RH:
Proteinuria in diabetic kidney disease: a mechanistic viewpoint.
Kidney Int. 74:22–36. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Jaimes EA, Hua P, Tian RX and Raij L:
Human glomerular endothelium: interplay among glucose, free fatty
acids, angiotensin II, and oxidative stress. Am J Physiol Renal
Physiol. 298:F125–F132. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Adler S: Integrin receptors in the
glomerulus: potential role in glomerular injury. Am J Physiol.
|
|
14
|
Peng H, Luo P, Li Y, Wang C, Liu X, et al:
Simvastatin Alleviates Hyperpermeability of Glomerular Endothelial
Cells in Early-Stage Diabetic Nephropathy by Inhibition of
RhoA/ROCK1. PLoS One. 8:e800092013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Peng H, Wang C, Ye ZC, et al: How
increased VEGF induces glomerular hyperpermeability: a potential
signaling pathway of Rac1 activation. Acta Diabetol. 47(Suppl 1):
57–63. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Durvasula RV, Petermann AT, Hiromura K, et
al: Activation of a local tissue angiotensin system in podocytes by
mechanical strain. Kidney Int. 65:30–39. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Li M, Liu K, Michalicek J, et al:
Involvement of chymase-mediated angiotensin II generation in blood
pressure regulation. J Clin Invest. 114:112–120. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Sadjadi J, Kramer GL, Yu CH, Burress
Welborn M III, Chappell MC and Gregory Modrall J: Angiotensin
converting enzyme-independent angiotensin ii production by chymase
is up-regulated in the ischemic kidney in renovascular
hypertension. J Surg Res. 127:65–69. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Homma T, Sonoda H, Manabe K, et al:
Activation of renal angiotensin type 1 receptor contributes to the
pathogenesis of progressive renal injury in a rat model for chronic
cardiorenal syndrome. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 302:F750–F761.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Filipeanu CM, Henning RH, de Zeeuw D and
Nelemans A: Intracellular Angiotensin II and cell growth of
vascular smooth muscle cells. Br J Pharmacol. 132:1590–1596. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Cook JL, Zhang Z and Re RN: In vitro
evidence for an intracellular site of angiotensin action. Circ Res.
89:1138–1146. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Kumar R, Singh VP and Baker KM: The
intracellular renin-angiotensin system: a new paradigm. Trends
Endocrinol Metab. 18:208–214. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Singh R, Singh AK, Alavi N and Leehey DJ:
Mechanism of increased angiotensin II levels in glomerular
mesangial cells cultured in high glucose. J Am Soc Nephrol.
14:873–880. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Vidotti DB, Casarini DE, Cristovam PC,
Leite CA, Schor N and Boim MA: High glucose concentration
stimulates intracellular renin activity and angiotensin II
generation in rat mesangial cells. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol.
286:F1039–F1045. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Singh VP, Le B, Bhat VB, Baker KM and
Kumar R: High-glucose-induced regulation of intracellular Ang II
synthesis and nuclear redistribution in cardiac myocytes. Am J
Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 293:H939–H948. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Heikkila HM, Latti S, Leskinen MJ, Hakala
JK, Kovanen PT and Lindstedt KA: Activated mast cells induce
endothelial cell apoptosis by a combined action of chymase and
tumor necrosis factor-alpha. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol.
28:309–314. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Kumar R, Singh VP and Baker KM: The
intracellular renin-angiotensin system: implications in
cardiovascular remodeling. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens. 17:168–173.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Singh VP, Baker KM and Kumar R: Activation
of the intracellular renin-angiotensin system in cardiac
fibroblasts by high glucose: role in extracellular matrix
production. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 294:H1675–H1684. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Takahashi H, Ichihara A, Kaneshiro Y, et
al: Regression of nephropathy developed in diabetes by (Pro)renin
receptor blockade. J Am Soc Nephrol. 18:2054–2061. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Matsusaka T, Nishimura H, Utsunomiya H, et
al: Chimeric mice carrying ‘regional’ targeted deletion of the
angiotensin type 1A receptor gene. Evidence against the role for
local angiotensin in the in vivo feedback regulation of renin
synthesis in juxtaglomerular cells. J Clin Invest. 98:1867–1877.
1996.
|
|
31
|
Schunkert H, Ingelfinger JR, Jacob H,
Jackson B, Bouyounes B and Dzau VJ: Reciprocal feedback regulation
of kidney angiotensinogen and renin mRNA expressions by angiotensin
II. Am J Physiol. 263:E863–E869. 1992.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Muller MW, Todorov V, Kramer BK and Kurtz
A: Angiotensin II inhibits renin gene transcription via the protein
kinase C pathway. Pflugers Arch. 444:499–505. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Wasse H, Rivera AA, Huang R, et al:
Increased plasma chymase concentration and mast cell chymase
expression in venous neointimal lesions of patients with CKD and
ESRD. Semin Dial. 24:688–693. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Huang XR, Chen WY, Truong LD and Lan HY:
Chymase is upregulated in diabetic nephropathy: implications for an
alternative pathway of angiotensin II-mediated diabetic renal and
vascular disease. J Am Soc Nephrol. 14:1738–1747. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Amiri F and Garcia R: Regulation of
angiotensin II receptors and PKC isoforms by glucose in rat
mesangial cells. Am J Physiol. 276:F691–F699. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|