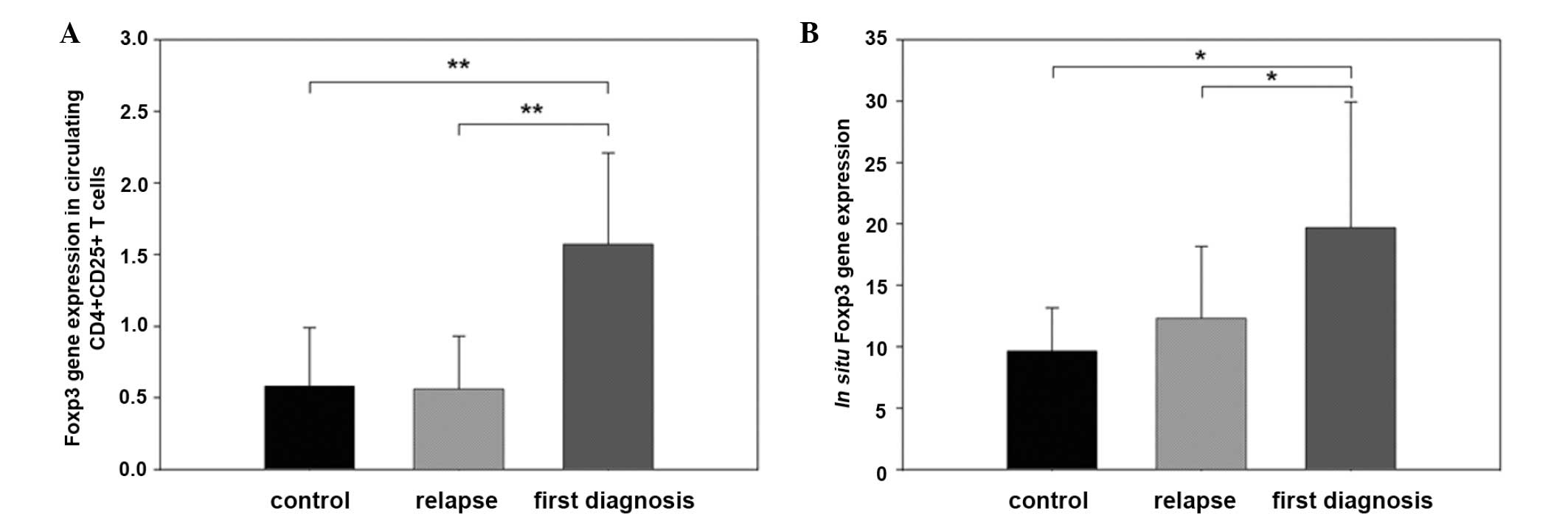
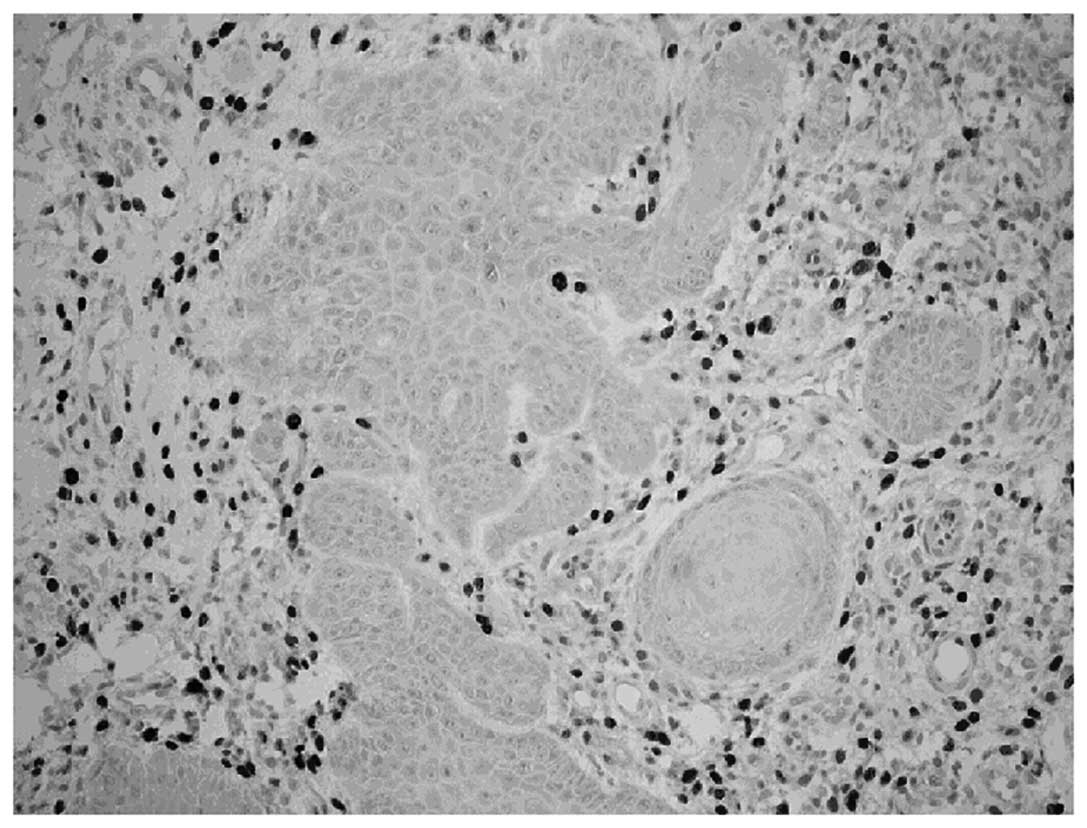
|
1
|
de Moura Castro Jacques C, Cardozo Pereira
AL, Cabral MG, Cardoso AS and Ramos-e-Silva M: Oral lichen planus
part I: epidemiology, clinics, etiology, immunopathogeny, and
diagnosis. Skinmed. 2:342–347. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Sugerman PB, Savage NW, Walsh LJ, et al:
The pathogenesis of oral lichen planus. Crit Rev Oral Biol Med.
13:350–365. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Sugerman PB and Savage NW: Oral lichen
planus: causes, diagnosis and management. Aust Dent J. 47:290–297.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Gadenne AS, Strucke R, Dunn D, Wagner M,
Bleichner P and Bigby M: T-cell lines derived from lesional skin of
lichen planus patients contain a distinctive population of T-cell
receptor gamma delta-bearing cells. J Invest Dermatol. 103:347–351.
1994. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Sugerman PB, Savage NW and Seymour GJ:
Phenotype and suppressor activity of T-lymphocyte clones extracted
from lesions of oral lichen planus. Br J Dermatol. 131:319–324.
1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Roopashree MR, Gondhalekar RV, Shashikanth
MC, et al: Pathogenesis of oral lichen planus - a review. J Oral
Pathol Med. 39:729–734. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Khan A, Farah CS, Savage NW, et al: Th1
cytokines in oral lichen planus. J Oral Pathol Med. 32:77–83. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Lu R, Zhou G, Du G, Xu X, Yang J and Hu J:
Expression of T-bet and GATA-3 in peripheral blood mononuclear
cells of patients with oral lichen planus. Arch Oral Biol.
56:499–505. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Pindborg JJ, Reichart PA, Smith CJ, et al:
Histological typing of cancer and precancer of the oral mucosa.
World Health Organization International histological classification
of tumours. 2nd edition. Springer; 25. Berlin, Germany: pp. 29–30.
1997
|
|
10
|
Sakaguchi S, Sakaguchi N, Asano M, Itoh M
and Toda M: Immunologic self-tolerance maintained by activated T
cells expressing IL-2 receptor alpha-chains (CD25). Breakdown of a
single mechanism of self-tolerance causes various autoimmune
diseases. J Immunol. 155:1151–1164. 1995.
|
|
11
|
Josefowicz SZ, Lu LF and Rudensky AY:
Regulatory T cells: mechanisms of differentiation and function.
Annu Rev Immunol. 30:531–564. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Wing K and Sakaguchi S: Regulatory T cells
exert checks and balances on self-tolerance and autoimmunity. Nat
Immunol. 11:7–13. 2010. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Taams LS, Palmer DB, Akbar AN, Robinson
DS, Brown Z and Hawrylowicz CM: Regulatory T cells in human disease
and their potential for therapeutic manipulation. Immunology.
118:1–9. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Hori S, Nomura T and Sakaguchi S: Control
of regulatory T cell development by the transcription factor Foxp3.
Science. 299:1057–1061. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Gavin MA, Rasmussen JP, Fontenot JD, et
al: Foxp3-dependent programme of regulatory T-cell differentiation.
Nature. 445:771–775. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Yagi H, Takashi Nomura T, Nakamura K, et
al: Crucial role of Foxp3 in the development and function of human
CD25+CD4+ regulatory T cells. Int Immunol.
16:1643–1656. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Bignone PA and Banham AH: Foxp3+
regulatory T cells as biomarkers in human malignancies. Expert Opin
Biol Ther. 8:1897–1920. 2008.
|
|
18
|
Chen S, Yang L, Lu X, et al: Gene
expression profiling of CD3gamma, delta, epsilon, and zeta chains
in CD4(+) and CD8(+) T cells from human umbilical cord blood.
Hematology. 15:230–235. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
|
|
20
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
|
|
21
|
Zhou XJ, Sugerman PB, Savage NW, Walsh LJ
and Seymour GJ: Intra-epithelial CD8+ T cells and
basement membrane disruption in oral lichen planus. J Oral Pathol
Med. 31:23–27. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Sugerman PB, Satterwhite K and Bigby M:
Autocytotoxic T-cell clones in lichen planus. Br J Dermatol.
142:449–456. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Bascones-Ilundain C, Gonzalez-Moles MA,
Esparza-Gómez G, Gil-Montoya JA and Bascones-Martínez A: Importance
of apoptotic mechanisms in inflammatory infiltrate of oral lichen
planus lesions. Anticancer Res. 26:357–362. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Lei L, Tan WX, Zhou XL and Zheng PE:
Expression of Fas and Fas ligand in infiltrating lymphocytes in
patients with oral lichen planus. Zhonghua Kou Qiang Yi Xue Za Zhi.
45:219–222. 2010.(In Chinese).
|
|
25
|
Santoro A, Majorana A, Bardellini E, Festa
S, Sapelli P and Facchetti F: NF-kappaB expression in oral and
cutaneous lichen planus. J Pathol. 201:466–472. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Lei L, Yu M, Gao XY, Zhou XL and Zhan LH:
Expression of TGF-beta receptors in CD8+T cells of oral lichen
planus. Zhonghua Kou Qiang Yi Xue Za Zhi. 43:99–100. 2008.(In
Chinese).
|
|
27
|
Apostolou I, Sarukhan A, Klein L and von
Boehmer H: Origin of regulatory T cells with known specificity for
antigen. Nat Immunol. 3:756–763. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Wildin RS, Ramsdell F, Peake J, et al:
X-linked neonatal diabetes mellitus, enteropathy and endocrinopathy
syndrome is the human equivalent of mouse scurfy. Nat Genet.
27:18–20. 2001. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Lourenço EV and La Cava A: Natural
regulatory T cells in autoimmunity. Autoimmunity. 44:33–42.
2011.
|
|
30
|
Tao XA, Xia J, Chen XB, et al: Foxp3 T
regulatory cells in lesions of oral lichen planus correlated with
disease activity. Oral Dis. 16:76–82. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Vargas-Rojas MI, Crispín JC, Richaud-Patin
Y and Alcocer-Varela J: Quantitative and qualitative normal
regulatory T cells are not capable of inducing suppression in SLE
patients due to T-cell resistance. Lupus. 17:289–294. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Beavis PA, Gregory B, Green P, et al:
Resistance to regulatory T cell-mediated suppression in rheumatoid
arthritis can be bypassed by ectopic foxp3 expression in pathogenic
synovial T cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 108:16717–16722. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Buckner JH: Mechanisms of impaired
regulation by CD4(+)CD25(+)FOXP3(+) regulatory T cells in human
autoimmune diseases. Nat Rev Immunol. 10:849–859. 2010.
|
|
34
|
Jungell P, Malmström M, Wartiovaara J,
Konttinen Y and Sane J: Ultrastructure of oral leukoplakia and
lichen planus I. Basal region and inflammatory cells. J Oral
Pathol. 16:170–178. 1987. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Brant JMC, Vasconcelos AC and Rodrigues
LV: Role of apoptosis in erosive and reticular oral lichen planus
exhibiting variable epithelial thickness. Braz Dent J. 19:179–185.
2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Karatsaidis A, Schreurs O, Helgeland K,
Axéll T and Schenck K: Erythematous and reticular forms of oral
lichen planus and oral lichenoid reactions differ in pathological
features related to disease activity. J Oral Pathol Med.
32:275–281. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Wan YY and Flavell RA: The roles for
cytokines in the generation and maintenance of regulatory T cells.
Immunological Rev. 212:114–130. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
van Amelsfort JM, van Roon JA, Noordegraaf
M, et al: Proinflammatory mediator-induced reversal of CD4+, CD25+
regulatory T cell-mediated suppression in rheumatoid arthritis.
Arthritis Rheum. 56:732–742. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Simark-Mattsson C, Bergenholtz G, Jontell
M, et al: Distribution of interleukin-2, -4, -10, tumour necrosis
factor-alpha and transforming growth factor-beta mRNAs in oral
lichen planus. Arch Oral Biol. 44:499–507. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Prime SS, Pring M, Davies M and Paterson
IC: TGF-beta signal transduction in oro-facial health and
non-malignant disease (part I). Crit Rev Oral Biol Med. 15:324–336.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Valencia X, Stephens G, Goldbach-Mansky R,
Wilson M, Shevach EM and Lipsky PE: TNF downmodulates the function
of human CD4+CD25hi T-regulatory cells. Blood. 108:253–261.
2006.
|
|
42
|
O’Sullivan BJ, Thomas HE, Pai S, et al:
IL-1 beta breaks tolerance through expansion of CD25+ effector T
cells. J Immunol. 176:7278–7287. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Wan S, Xia C and Morel L: IL-6 produced by
dendritic cells from lupus-prone mice inhibits
CD4+CD25+ T cell regulatory functions. J
Immunol. 178:271–279. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Marie JC, Letterio JJ, Gavin M and
Rudensky AY: TGF-beta1 maintains suppressor function and Foxp3
expression in CD4+CD25+ regulatory T cells. J
Exp Med. 201:1061–1067. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Wan YY and Flavell RA: Regulatory T-cell
functions are subverted and converted owing to attenuated Foxp3
expression. Nature. 445:766–770. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Williams LM and Rudensky AY: Maintenance
of the Foxp3-dependent developmental program in mature regulatory T
cells requires continued expression of Foxp3. Nat Immunol.
8:277–284. 2007. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Frisullo G, Nociti V, Iorio R, et al:
Regulatory T cells fail to suppress CD4T+-bet+ T cells in relapsing
multiple sclerosis patients. Immunology. 127:418–428.
2009.PubMed/NCBI
|