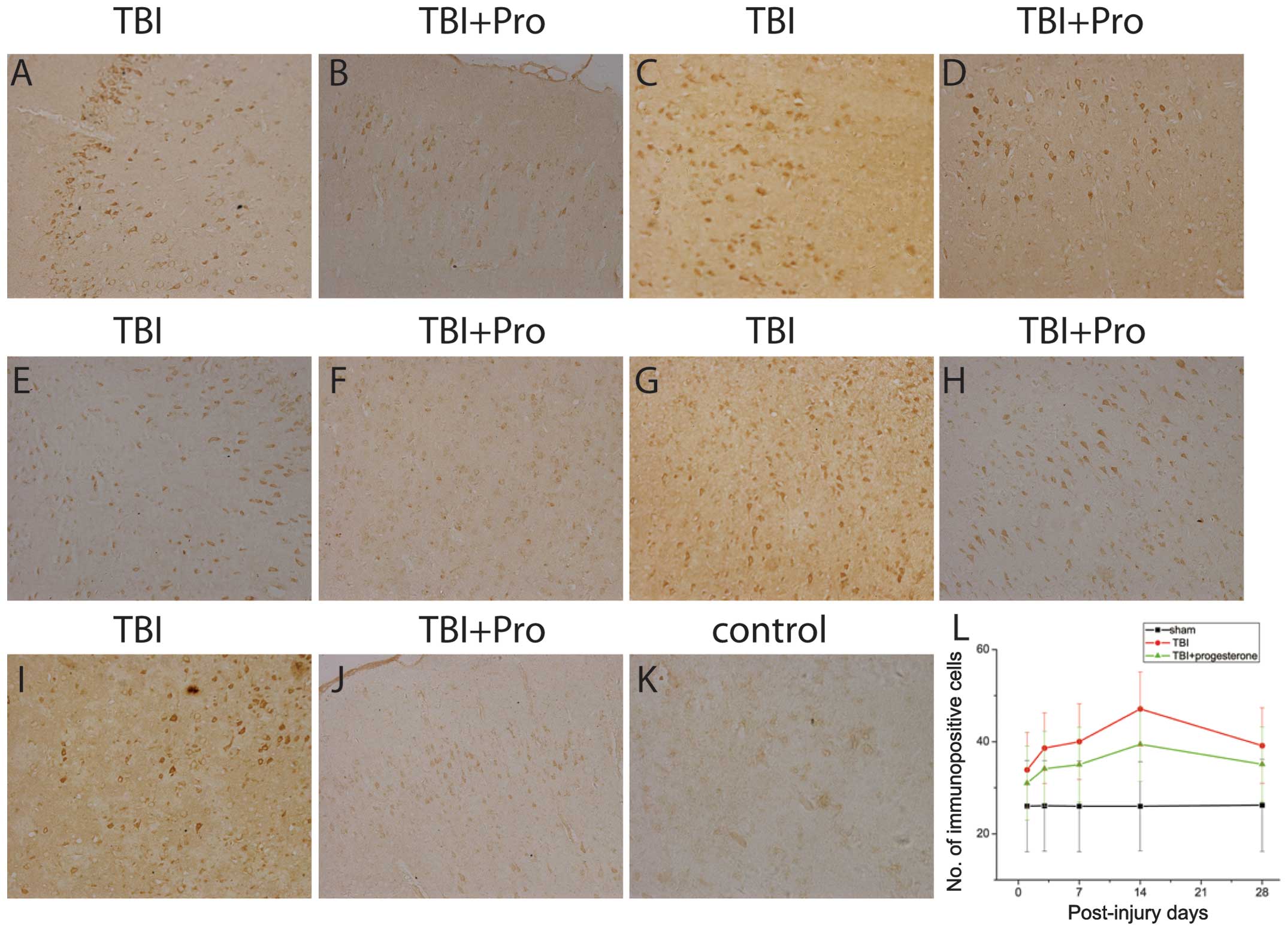
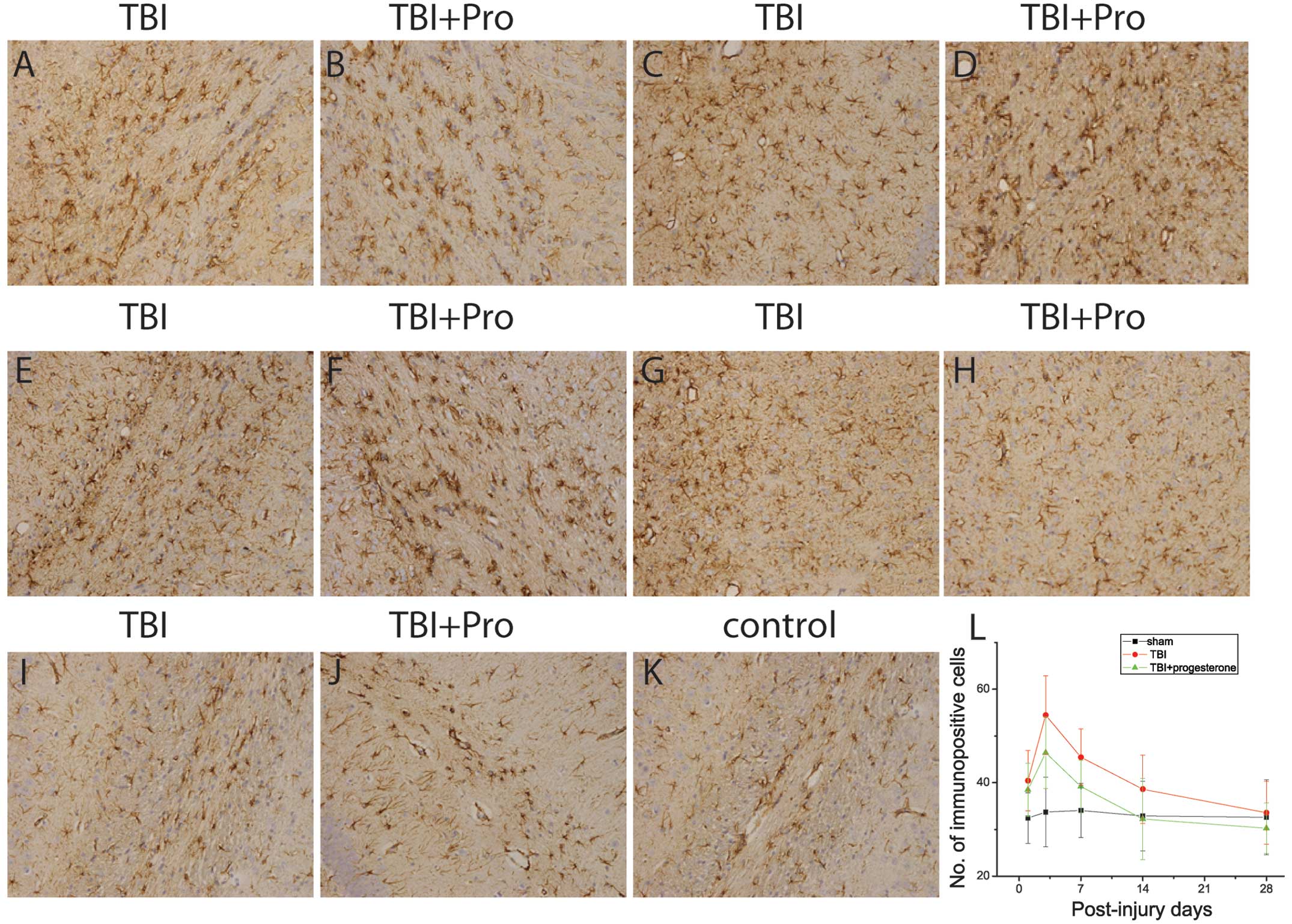
|
1
|
Asemota AO, George BP, Bowman SM, Haider
AH and Schneider EB: Causes and trends in traumatic brain injury
for United States adolescents. J Neurotrauma. 30:67–75. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Feeser VR and Loria RM: Modulation of
traumatic brain injury using progesterone and the role of glial
cells on its neuroprotective actions. J Neuroimmunol. 237:4–12.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Gibson CL, Gray LJ, Bath PM and Murphy SP:
Progesterone for the treatment of experimental brain injury; a
systematic review. Brain. 131:318–328. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Roof RL, Duvdevani R, Braswell L and Stein
DG: Progesterone facilitates cognitive recovery and reduces
secondary neuronal loss caused by cortical contusion injury in male
rats. Exp Neurol. 129:64–69. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Roof RL, Duvdevani R and Stein DG:
Progesterone treatment attenuates brain edema following contusion
injury in male and female rats. Restor Neurol Neurosci. 4:425–427.
1992.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Gibson CL, Constantin D, Prior MJ, Bath PM
and Murphy SP: Progesterone suppresses the inflammatory response
and nitric oxide synthase-2 expression following cerebral ischemia.
Exp Neurol. 193:522–530. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Horner PJ and Gage FH: Regenerating the
damaged central nervous system. Nature. 407:963–970. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Xiong NX, Zhao HY, Zhang FC and He ZQ:
Negative correlation of Nogo-A with the malignancy of
oligodendroglial tumor. Neurosci Bull. 23:41–45. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Hsieh SH, Ferraro GB and Fournier AE:
Myelin-associated inhibitors regulate cofilin phosphorylation and
neuronal inhibition through LIM kinase and Slingshot phosphatase. J
Neurosci. 26:1006–1015. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Wang KC, Koprivica V, Kim JA, Sivasankaran
R, Guo Y, Neve RL and He Z: Oligodendrocyte-myelin glycoprotein is
a Nogo receptor ligand that inhibits neurite outgrowth. Nature.
417:941–944. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Yiu G and He Z: Glial inhibition of CNS
axon regeneration. Nat Rev Neurosci. 7:617–627. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Fitch MT and Silver J: CNS injury, glial
scars, and inflammation: Inhibitory extracellular matrices and
regeneration failure. Exp Neurol. 209:294–301. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Brenneman MM, Wagner SJ, Cheatwood JL,
Heldt SA, Corwin JV, Reep RL, Kartje GL, Mir AK and Schwab ME:
Nogo-A inhibition induces recovery from neglect in rats. Behav
Brain Res. 187:262–272. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Wang H, Yao YJ and Chen DP: Expression of
Nogo-A mRNA and Nogo-A protein in brain tissue of neonatal mice
with ischemic-hypoxic brain damage. Zhonghua Er Ke Za Zhi.
44:792–793. 2006.(In Chinese).
|
|
15
|
Stichel CC and Müller HW: The CNS lesion
scar: new vistas on an old regeneration barrier. Cell Tissue Res.
294:1–9. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Clayton GH, Mahalik TJ and Finger TE:
Expression of GAP43 mRNA in normally developing and transplanted
neurons from the rat ventral mesencephalon. J Comp Neurol.
347:470–480. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Denny JB: Molecular mechanisms, biological
actions, and neuropharmacology of the growth-associated protein
GAP-43. Curr Neuropharmacol. 4:293–304. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Benowitz LI and Routtenberg A: GAP-43: an
intrinsic determinant of neuronal development and plasticity.
Trends Neurosci. 20:84–91. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Donovan SL and McCasland JS: GAP-43 is
critical for normal targeting of thalamocortical and
corticothalamic, but not trigeminothalamic axons in the whisker
barrel system. Somatosens Mot Res. 25:33–47. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Hughes-Davis EJ, Cogen JP, Jakowec MW,
Cheng HW, Grenningloh G, Meshul CK and McNeill TH: Differential
regulation of the growth-associated proteins GAP-43 and superior
cervical ganglion 10 in response to lesions of the cortex and
substantia nigra in the adult rat. Neuroscience. 135:1231–1239.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Nagamoto-Combs K, Morecraft RJ, Darling WG
and Combs CK: Long-term gliosis and molecular changes in the
cervical spinal cord of the rhesus monkey after traumatic brain
injury. J Neurotrauma. 27:565–585. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Schmidt-Kastner R, Bedard A and Hakim A:
Transient expression of GAP-43 within the hippocampus after global
brain ischemia in rat. Cell Tissue Res. 288:225–238. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Labombarda F, González Deniselle MC, De
Nicola AF and González SL: Progesterone and the spinal cord: good
friends in bad times. Neuroimmunomodulation. 17:146–149. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Garay L, Deniselle MC, Meyer M, Costa JJ,
Lima A, Roig P and De nicola AF: Protective effects of progesterone
administration on axonal pathology in mice with experimental
autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Brain Res. 1283:177–185. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
De Nicola AF, Labombarda F, Deniselle MC,
Gonzalez SL, Garay L, Meyer M, Gargiulo G, Guennoun R and
Schumacher M: Progesterone neuroprotection in traumatic CNS injury
and motoneuron degeneration. Front Neuroendocrinol. 30:173–187.
2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Feeney DM, Boyeson MG, Linn RT, Murray HM
and Dail WG: Responses to cortical injury: I. Methodology and local
effects of contusions in the rat. Brain Res. 211:67–77. 1981.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Goss CW, Hoffman SW and Stein DG:
Behavioral effects and anatomic correlates after brain injury: a
progesterone dose-response study. Pharmacol Biochem Behav.
76:231–242. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Anderson GD, Farin FM, Bammler TK, Beyer
RP, Swan AA, Wilkerson HW, Kantor ED and Hoane MR: The effect of
progesterone dose on gene expression after traumatic brain injury.
J Neurotrauma. 28:1827–1843. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Pajović SB, Saicić ZS, Spasić MB, Petrović
VM and Martinović JV: Effects of progesterone and estradiol
benzoate on glutathione dependent antioxidant enzyme activities in
the brain of female rats. Gen Physiol Biophys. 18:35–44.
1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Pierson RC, Lyons AM and Greenfield LJ Jr:
Gonadal steroids regulate GABAA receptor subunit mRNA expression in
NT2-N neurons. Brain Res Mol Brain Res. 138:105–115. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
GrandPré T, Nakamura F, Vartanian T and
Strittmatter SM: Identification of the Nogo inhibitor of axon
regeneration as a Reticulon protein. Nature. 403:439–444.
2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Oertle T, van der Haar ME, Bandtlow CE, et
al: Nogo-A inhibits neurite outgrowth and cell spreading with three
discrete regions. J Neurosci. 23:5393–5406. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Marklund N, Bareyre FM, Royo NC, Thompson
HJ, Mir AK, Grady MS, Schwab ME and McIntosh TK: Cognitive outcome
following brain injury and treatment with an inhibitor of Nogo-A in
association with an attenuated downregulation of hippocampal
growth-associated protein-43 expression. J Neurosurg. 107:844–853.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Lenzlinger PM, Shimizu S, Marklund N, et
al: Delayed inhibition of Nogo-A does not alter injury-induced
axonal sprouting but enhances recovery of cognitive function
following experimental traumatic brain injury in rats.
Neuroscience. 134:1047–1056. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Mueller BK, Mueller R and Schoemaker H:
Stimulating neuroregeneration as a therapeutic drug approach for
traumatic brain injury. Br J Pharmacol. 157:675–685. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Gonzalez Deniselle MC, Lopez Costa JJ,
Gonzalez SL, Labombarda F, Garay L, Guennoun R, Schumacher M and De
Nicola AF: Basis of progesterone protection in spinal cord
neurodegeneration. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 83:199–209.
2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Schreyer DJ and Skene JH:
Injury-associated induction of GAP-43 expression displays axon
branch specificity in rat dorsal root ganglion neurons. J
Neurobiol. 24:959–970. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Hulsebosch CE, DeWitt DS, Jenkins LW and
Prough DS: Traumatic brain injury in rats results in increased
expression of Gap-43 that correlates with behavioral recovery.
Neurosci Lett. 255:83–86. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Santoro B, Bigini P, Levandis G, Nobile V,
Biggiogera M, Botti F, Mennini T and Curti D: Evidence for chronic
mitochondrial impairment in the cervical spinal cord of a murine
model of motor neuron disease. Neurobiol Dis. 17:349–357. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
González Deniselle MC, González SL and De
Nicola AF: Cellular basis of steroid neuroprotection in the wobbler
mouse, a genetic model of motoneuron disease. Cell Mol Neurobiol.
21:237–254. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Udvadia AJ, Köster RW and Skene JH: GAP-43
promoter elements in transgenic zebrafish reveal a difference in
signals for axon growth during CNS development and regeneration.
Development. 128:1175–1182. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Nguyen L, He Q and Meiri KF: Regulation of
GAP-43 at serine 41 acts as a switch to modulate both intrinsic and
extrinsic behaviors of growing neurons, via altered membrane
distribution. Mol Cell Neurosci. 41:62–73. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Cutler SM, VanLandingham JW, Murphy AZ and
Stein DG: Slow-release and injected progesterone treatments enhance
acute recovery after traumatic brain injury. Pharmacol Biochem
Behav. 84:420–428. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Wali B, Sayeed I and Stein DG: Improved
behavioral outcomes after progesterone administration in aged male
rats with traumatic brain injury. Restor Neurol Neurosci. 29:61–71.
2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Wright DW, Kellermann AL, Hertzberg VS, et
al: ProTECT: a randomized clinical trial of progesterone for acute
traumatic brain injury. Ann Emerg Med. 49:391–402. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Xiao G, Wei J, Yan W, Wang W and Lu Z:
Improved outcomes from the administration of progesterone for
patients with acute severe traumatic brain injury: a randomized
controlled trial. Crit Care. 12:R612008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|