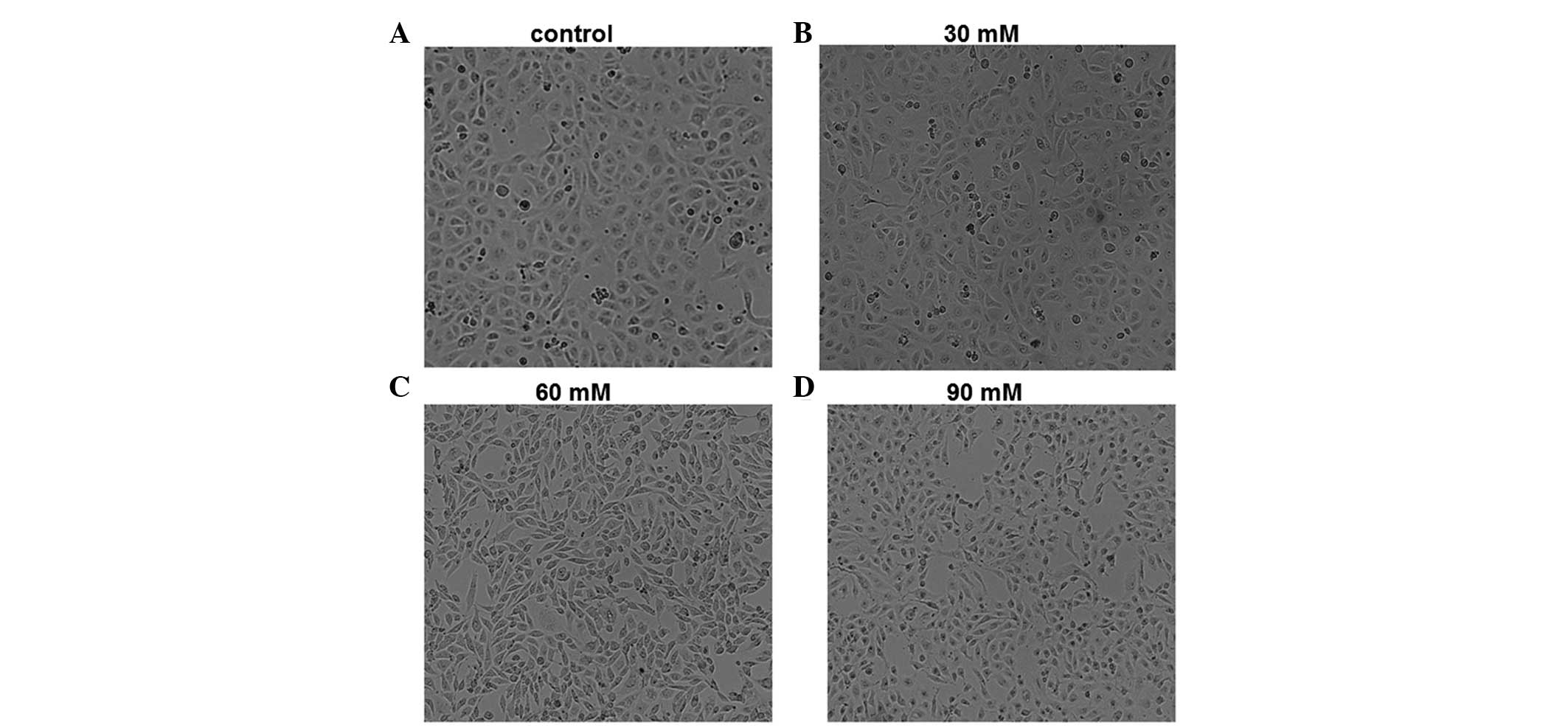
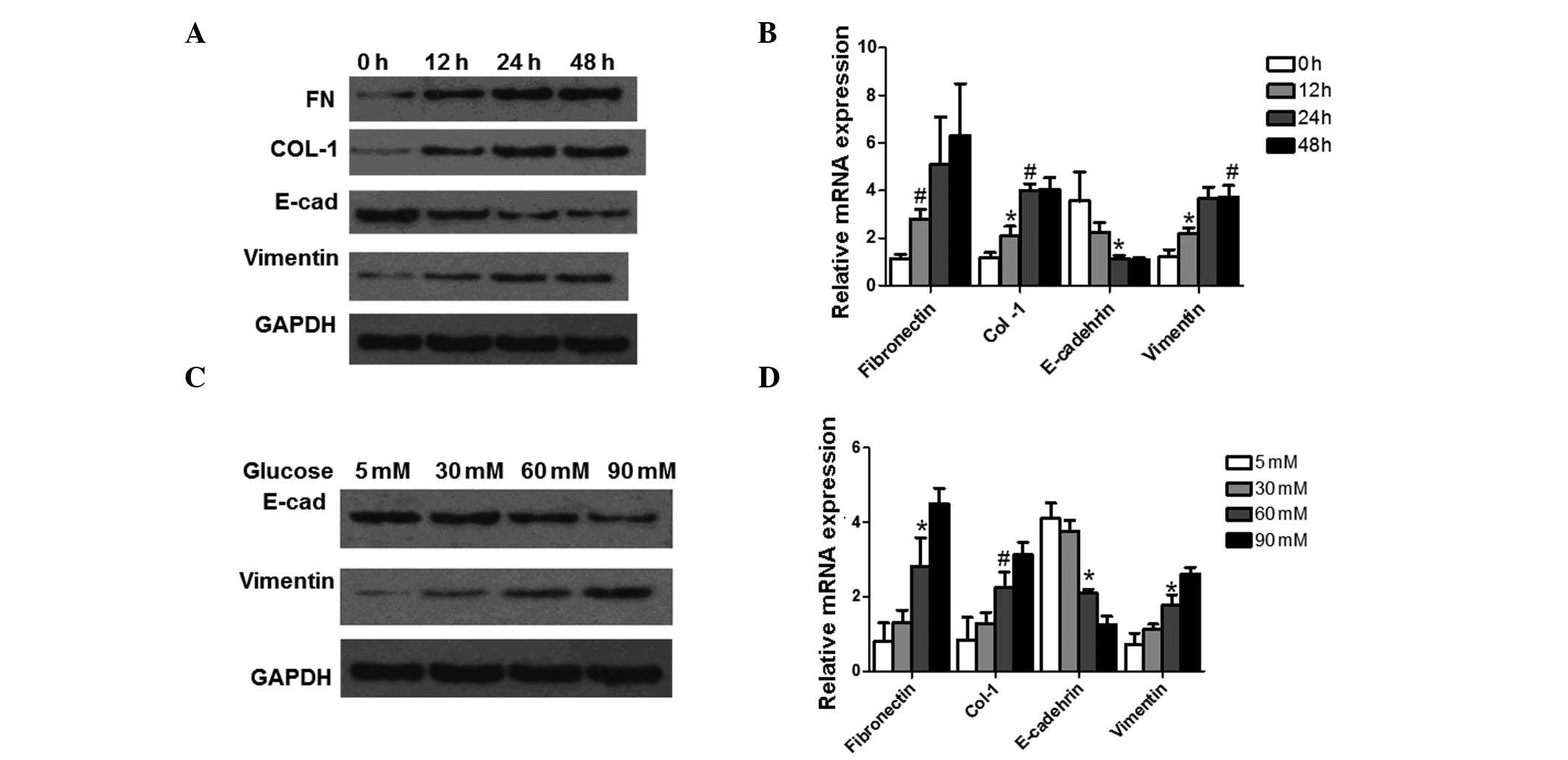
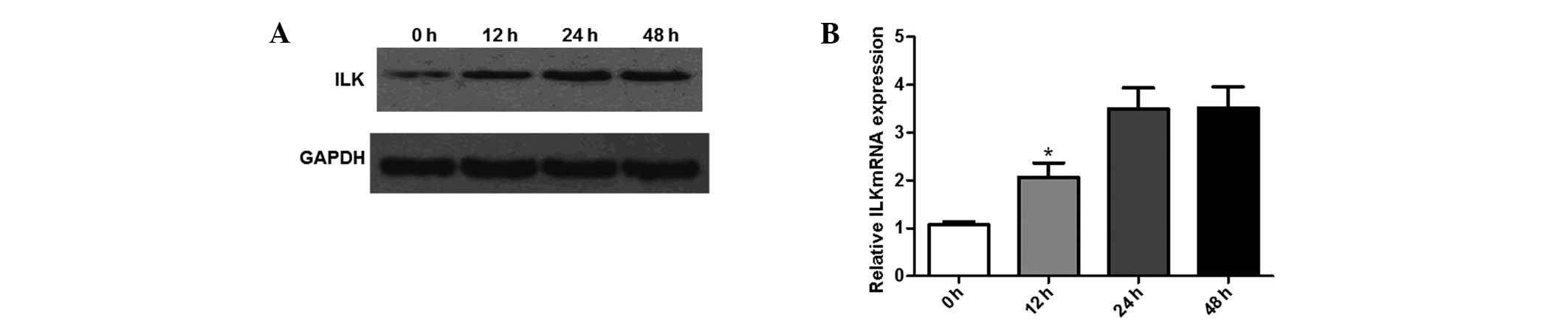
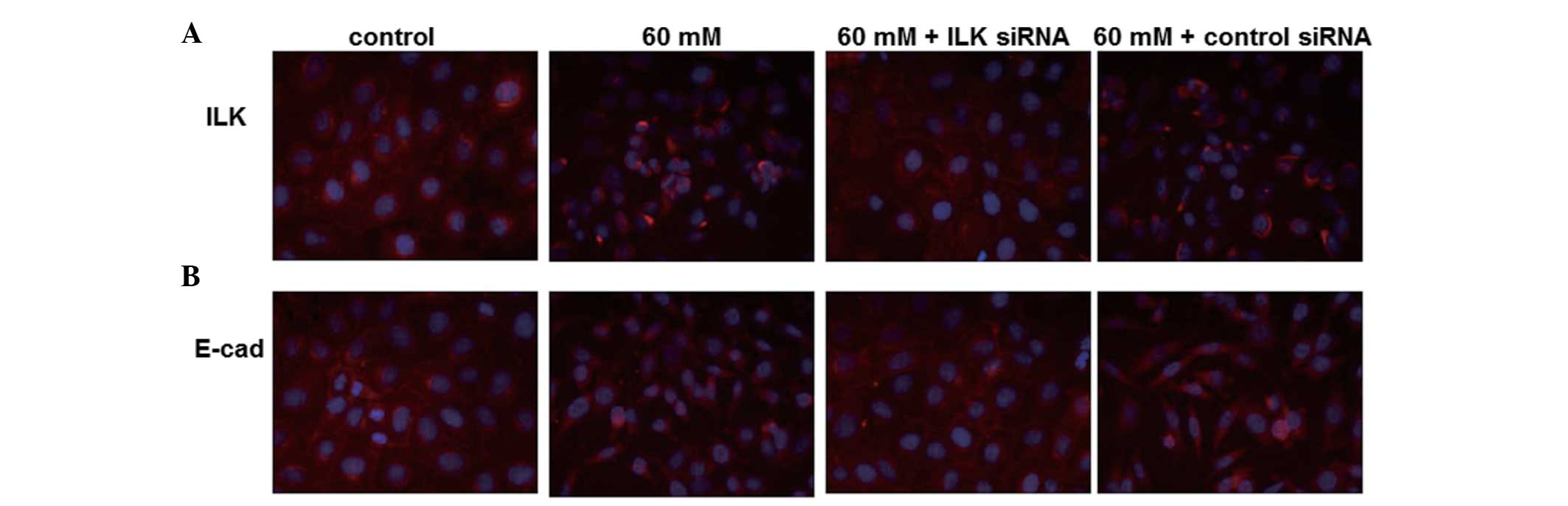
|
1
|
Aroeira LS, Aguilera A, Selgas R, et al:
Mesenchymal conversion of mesothelial cells as a mechanism
responsible for high solute transport rate in peritoneal dialysis:
role of vascular endothelial growth factor. Am J Kidney Dis.
46:938–948. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Yáñez-Mó M, Lara-Pezzi E, Selgas R, et al:
Peritoneal dialysis and epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition of
mesothelial cells. N Engl J Med. 348:403–413. 2003.
|
|
3
|
Kim YL: Update on mechanisms of
ultrafiltration failure. Perit Dial Int. 29(Suppl 2): S123–S127.
2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Loureiro J, Aguilera A, Selgas R, et al:
Blocking TGF-β1 protects the peritoneal membrane from
dialysate-induced damage. J Am Soc Nephrol. 22:1682–1695. 2011.
|
|
5
|
Margetts PJ, Bonniaud P, Liu L, et al:
Transient overexpression of TGF-{beta}1 induces epithelial
mesenchymal transition in the rodent peritoneum. J Am Soc Nephrol.
16:425–436. 2005.
|
|
6
|
Vargha R, Endemann M, Kratochwill K, et
al: Ex vivo reversal of in vivo transdifferentiation in mesothelial
cells grown from peritoneal dialysate effluents. Nephrol Dial
Transplant. 21:2943–2947. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Wang X, Nie J, Jia Z, et al: Impaired
TGF-beta signalling enhances peritoneal inflammation induced by
E. coli in rats. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 25:399–412. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Lee HB and Ha H: Mechanisms of
epithelial-mesenchymal transition of peritoneal mesothelial cells
during peritoneal dialysis. J Korean Med Sci. 22:943–945. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Zeisberg M and Duffield JS: Resolved: EMT
produces fibroblasts in the kidney. J Am Soc Nephrol. 21:1247–1253.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Liu Y: New insights into
epithelial-mesenchymal transition in kidney fibrosis. J Am Soc
Nephrol. 21:212–222. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Hannigan GE, Leung-Hagesteijn C,
Fitz-Gibbon L, Coppolino MG, Radeva G, Filmus J, Bell JC and Dedhar
S: Regulation of cell adhesion and anchorage-dependent growth by a
new beta 1-integrin-linked protein kinase. Nature. 379:91–96. 1996.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Legate KR, Montañez E, Kudlacek O and
Fässler R: ILK, PINCH and parvin: the tIPP of integrin signaling.
Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 7:20–31. 2006. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Dai HY, Zheng M, Lv LL, Tang RN, Ma KL,
Liu D, Wu M and Liu BC: The roles of connective tissue growth
factor and integrin-linked kinase in high glucose-induced
phenotypic alterations of podocytes. J Cell Biochem. 113:293–301.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Li Y, Tan X, Dai C, Stolz DB, Wang D and
Liu Y: Inhibition of integrin-linked kinase attenuates renal
interstitial fibrosis. J Am Soc Nephrol. 20:1907–1918. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
de Teixeira VP, Blattner SM, Li M, et al:
Functional consequences of integrin-linked kinase activation in
podocyte damage. Kidney Int. 67:514–523. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Kretzler M, Teixeira VP, Unschuld PG, et
al: Integrin-linked kinase as a candidate downstream effector in
proteinuria. FASEB J. 15:1843–1845. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Guo L, Sanders PW, Woods A and Wu C: The
distribution and regulation of integrin-linked kinase in normal and
diabetic kidneys. Am J Pathol. 159:1735–1742. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Li Y, Yang J, Dai C, et al: Role for
integrin-linked kinase in mediating tubular epithelial to
mesenchymal transition and renal interstitial fibrogenesis. J Clin
Invest. 112:503–516. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Persad S, Attwell S, Gray V, Mawji N, Deng
JT, Leung D, et al: Regulation of protein kinase B/Akt-serine 473
phosphorylation by integrin-linked kinase: critical roles for
kinaseactivity and amino acids arginine 211 and serine 343. J Biol
Chem. 276:27462–27469. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Delcommenne M, Tan C, Gray V, Rue L,
Woodgett J and Dedhar S: Phosphoinositide-3-OH kinase-dependent
regulation of glycogen synthase kinase 3 and protein kinase B/AKT
by the integrin-linked kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
95:11211–11216. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Vi L, de Lasa C, DiGuglielmo GM, et al:
Integrin-linked kinase is required for TGF-β1 induction of dermal
myofibroblast differentiation. J Invest Dermatol. 131:586–593.
2011.
|
|
22
|
Li Y, Yang J, Luo JH, et al: Tubular
epithelial cell dedifferentiation is driven by the helix-loop-helix
transcriptional inhibitor Id1. J Am Soc Nephrol. 18:449–460. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Smeeton J, Zhang X, Bulus N, et al:
Integrin-linked kinase regulates p38 MAPK-dependent cell cycle
arrest in ureteric bud development. Development. 137:3233–3243.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Liu XC, Liu BC, Zhang XL, et al: Role of
ERK1/2 and PI3-K in the regulation of CTGF-induced ILK expression
in HK-2 cells. Clin Chim Acta. 382:89–94. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Stylianou E, Jenner LA, Davies M, Coles GA
and Williams JD: Isolation, culture and characterization of human
peritoneal mesothelial cells. Kidney Int. 37:1563–1570. 1990.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Rougier JP, Moullier P, Piedagnel R and
Ronco PM: Hyperosmolality suppresses but TGF beta 1 increases MMP9
in human peritoneal mesothelial cells. Kidney Int. 51:337–347.
1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Blattner SM and Kretzler M:
Integrin-linked kinase in renal disease: connecting cell-matrix
interaction to the cytoskeleton. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens.
14:404–410. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Dai C, Stolz DB, Bastacky SI, St-Arnaud R,
Wu C, Dedhar S and Liu Y: Essential role of integrin-linked kinase
in podocyte biology: Bridging the integrin and slit diaphragm
signaling. J Am Soc Nephrol. 17:2164–2175. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Kang YS, Li Y, Dai C, Kiss LP, Wu C and
Liu Y: Inhibition of integrin-linked kinase blocks podocyte
epithelial-mesenchymal transition and ameliorates proteinuria.
Kidney Int. 78:363–373. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Li Y, Dai C, Wu C and Liu Y: PINCH-1
promotes tubular epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition by
interacting with integrin-linked kinase. J Am Soc Nephrol.
18:2534–2543. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Hu K, Wu C, Mars WM and Liu Y: Tissue-type
plasminogen activator promotes murine myofibroblast activation
through LDL receptor-related protein 1-mediated integrin signaling.
J Clin Invest. 117:3821–3832. 2007.
|
|
32
|
Guo L and Wu C: Regulation of fibronectin
matrix deposition and cell proliferation by the PINCH-ILK-CH-ILKBP
complex. FASEB J. 16:1298–1300. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Tu Y, Huang Y, Zhang Y, Hua Y and Wu C: A
new focal adhesion protein that interacts with integrin-linked
kinase and regulates cell adhesion and spreading. J Cell Biol.
153:585–598. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Nikolopoulos SN and Turner CE: Molecular
dissection of actopaxin-integrin-linked kinase-Paxillin
interactions and their role in subcellular localization. J Biol
Chem. 277:1568–1575. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Troussard AA, Costello P, Yoganathan TN,
Kumagai S, Roskelley CD and Dedhar S: The integrin linked kinase
(ILK) induces an invasive phenotype via AP-1 transcription
factor-dependent upregulation of matrix metalloproteinase 9
(MMP-9). Oncogene. 19:5444–5452. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
D’Amico M, Hulit J, Amanatullah DF, et al:
The integrin-linked kinase regulates the cyclin D1 gene through
glycogen synthase kinase 3beta and cAMP-responsive element-binding
protein-dependent pathways. J Biol Chem. 275:32649–32657.
2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Joshi MB, Ivanov D, Philippova M, Erne P
and Resink TJ: Integrin-linked kinase is an essential mediator for
T-cadherin-dependent signaling via Akt and GSK3beta in endothelial
cells. FASEB J. 21:3083–3095. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Sellin JH, Umar S, Xiao J and Morris AP:
Increased beta-catenin expression and nuclear translocation
accompany cellular hyperproliferation in vivo. Cancer Res.
61:2899–2906. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Yang Y, Guo L, Blattner SM, Mundel P,
Kretzler M and Wu C: Formation and phosphorylation of the
PINCH-1-integrin linked kinase-alpha-parvin complex are important
for regulation of renal glomerular podocyte adhesion, architecture,
and survival. J Am Soc Nephrol. 16:1966–1976. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Cortés JC, Montalvo EA, Muñiz J, Mornet D,
Garrido E, Centeno F and Cisneros B: Dp71f modulates GSK3-beta
recruitment to the beta1-integrin adhesion complex. Neurochem Res.
34:438–444. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Kalra J, Sutherland BW, Stratford AL, et
al: Suppression of Her2/neu expression through ILK inhibition is
regulated by a pathway involving TWIST and YB-1. Oncogene.
29:6343–6356. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
del Nogal M, Luengo A, Olmos G, Lasa M,
Rodriguez-Puyol D, Rodriguez-Puyol M and Calleros L: Balance
between apoptosis or survival induced by changes in
extracellular-matrix composition in human mesangial cells: a key
role for ILK-NfκB pathway. Apoptosis. 17:1261–1274. 2012.
|
|
43
|
Papachristou DJ, Gkretsi V, Rao UN, et al:
Expression of integrin-linked kinase and its binding partners in
chondrosarcoma: association with prognostic significance. Eur J
Cancer. 44:2518–2525. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
McDonald PC, Fielding AB and Dedhar S:
Integrin-linked kinase - essential roles in physiology and cancer
biology. J Cell Sci. 121:3121–3132. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Fielding AB, Dobreva I, McDonald PC,
Foster LJ and Dedhar S: Integrin-linked kinase localizes to the
centrosome and regulates mitotic spindle organization. J Cell Biol.
180:681–689. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Shin SY, Rath O, Zebisch A, Choo SM, Kolch
W and Cho KH: Functional roles of multiple feedback loops in
extracellular signal-regulated kinase and Wnt signaling pathways
that reg-ulate epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Cancer Res.
70:6715–6724. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Acloque H, Thiery JP and Nieto MA: The
physiology and pathology of the EMT. Meeting on the
epithelial-mesenchymal transition. EMBO Rep. 9:322–326. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Xing Y, Qi J, Deng S, Wang C, Zhang L and
Chen J: Small interfering RNA targeting ILK inhibits metastasis in
human tongue cancer cells through repression of
epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition. Exp Cell Res. 319:2058–2072.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
McDonald PC, Oloumi A, Mills J, et al:
Rictor and integrin-linked kinase interact and regulate Akt
phosphorylation and cancer cell survival. Cancer Res. 68:1618–1624.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Doble BW and Woodgett JR: Role of glycogen
synthase kinase-3 in cell fate and epithelial-mesenchymal
transitions. Cells Tissues Organs. 185:73–84. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
McPhee TR, McDonald PC, Oloumi A and
Dedhar S: Integrin-linked kinase regulates E-cadherin expression
through PARP-1. Dev Dyn. 237:2737–2747. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Maseki S, Ijichi K, Tanaka H, et al:
Acquisition of EMT phenotype in the gefitinib-resistant cells of a
head and neck squamous cell carcinoma cell line through
Akt/GSK-3β/snail signalling pathway. Br J Cancer. 106:1196–1204.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Wu C and Dedhar S: Integrin-linked kinase
(ILK) and its interactors: a new paradigm for the coupling of
extracellular matrix to actin cytoskeleton and signaling complexes.
J Cell Biol. 155:505–510. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Radeva G, Petrocelli T, Behrend E,
Leung-Hagesteijn C, Filmus J, Slingerland J and Dedhar S:
Overexpression of the integrin-linked kinase promotes
anchorage-independent cell cycle progression. J Biol Chem.
272:13937–13944. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Tan C, Costello P, Sanghera J, Dominguez
D, Baulida J, de Herreros AG and Dedhar S: Inhibition of integrin
linked kinase (ILK) suppresses beta-catenin-Lef/Tcf-dependent
transcription and expression of the E-cadherin repressor, snail, in
APC−/− human colon carcinoma cells. Oncogene. 20:133–140.
2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Barisoni L, Mokrzycki M, Sablay L, Nagata
M, Yamase H and Mundel P: Podocyte cell cycle regulation and
proliferation in collapsing glomerulopathies. Kidney Int.
58:137–143. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Petermann AT, Pippin J, Hiromura K, et al:
Mitotic cell cycle proteins increase in podocytes despite lack of
proliferation. Kidney Int. 63:113–122. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|