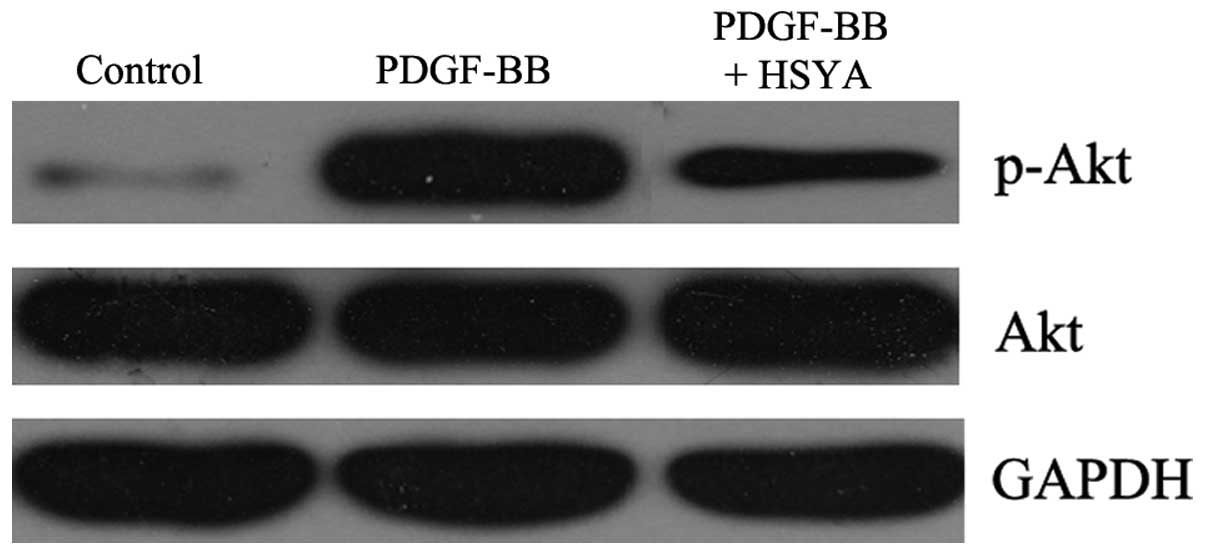
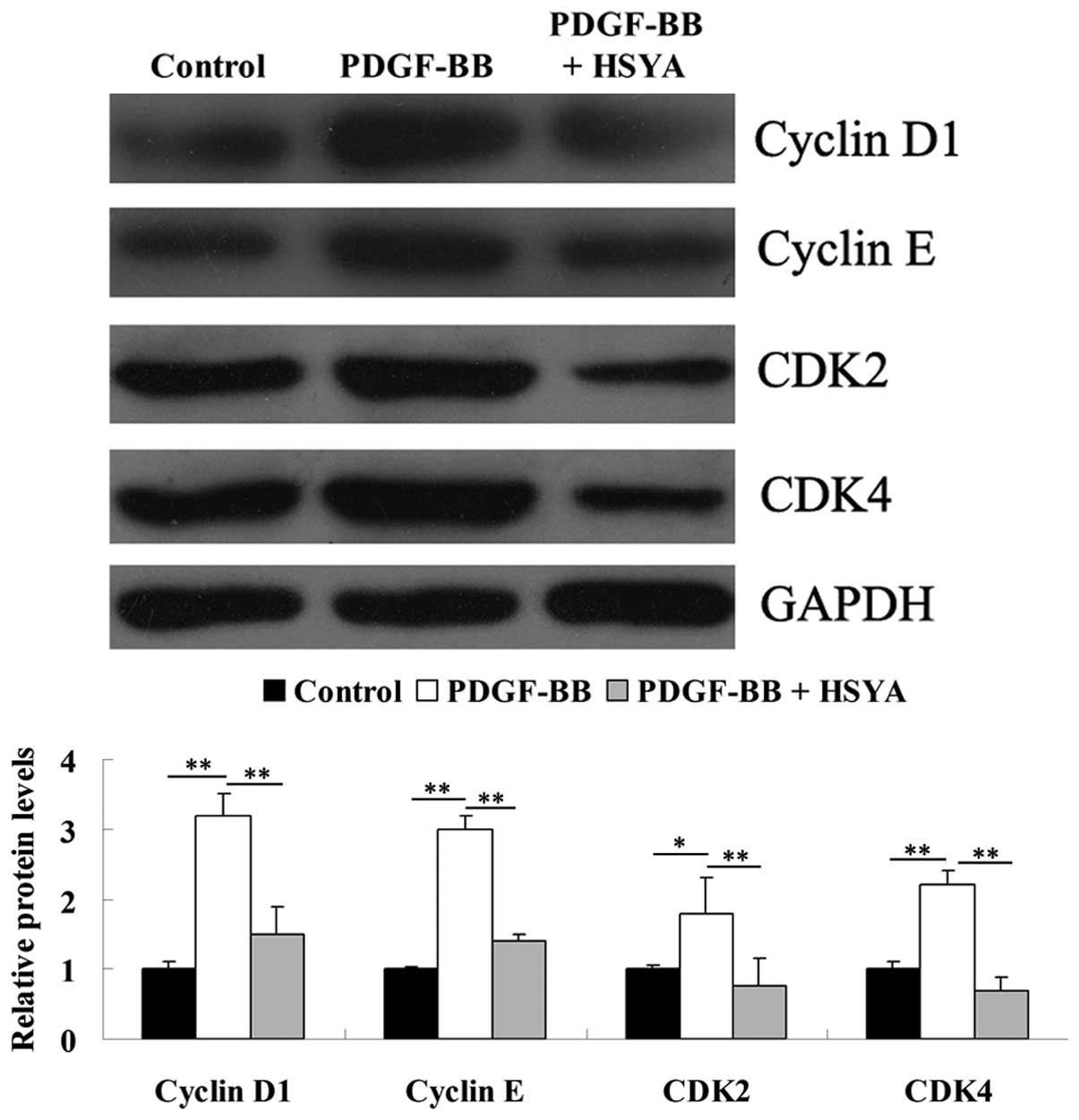
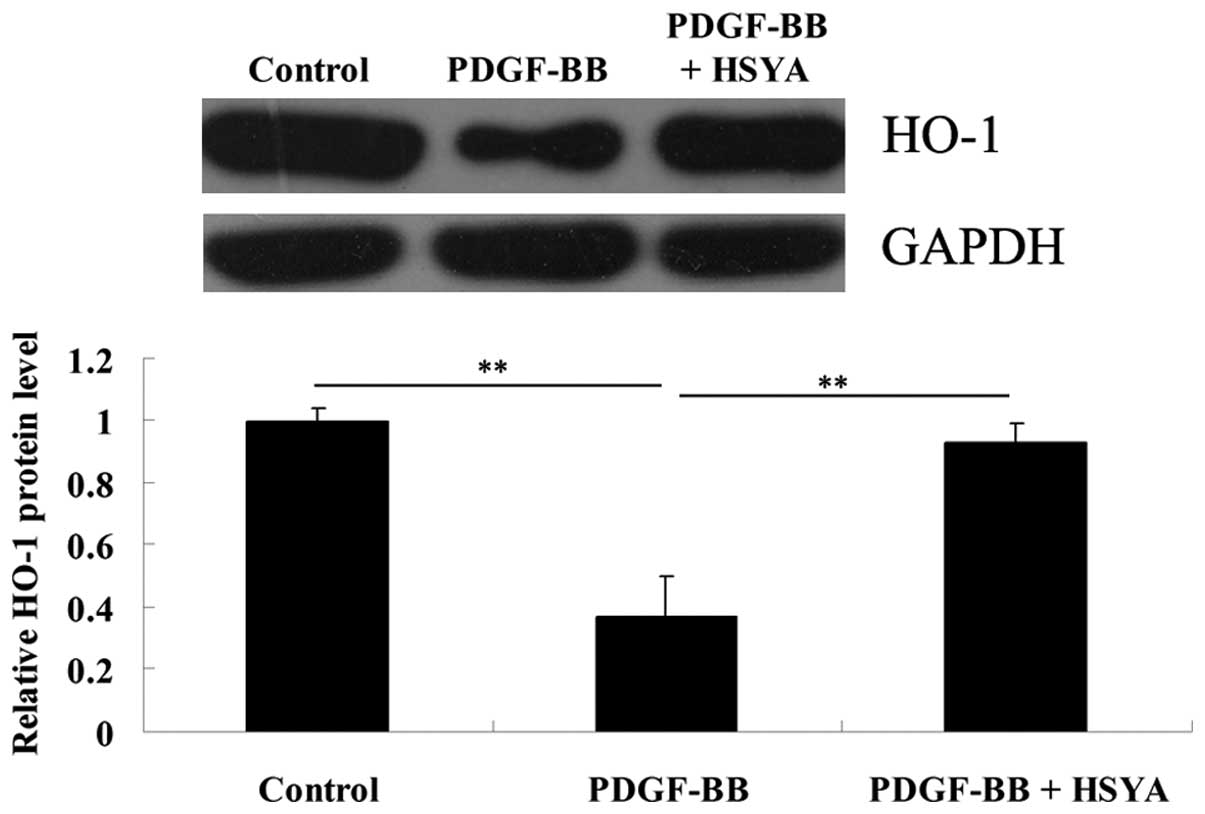
|
1
|
Gan J, Li P, Wang Z, et al: Rosuvastatin
suppresses platelet-derived growth factor-BB-induced vascular
smooth muscle cell proliferation and migration via the MAPK
signaling pathway. Exp Ther Med. 6:899–903. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Chen YC, Chu LY, Yang SF, et al:
Prostacyclin and PPARalpha agonists control vascular smooth muscle
cell apoptosis and phenotypic switch through distinct 14-3-3
isoforms. PLoS One. 8:e697022013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Hakimi M, Peters A, Becker A, Bockler D
and Dihlmann S: Inflammation-related induction of absent in
melanoma 2 (AIM2) in vascular cells and atherosclerotic lesions
suggests a role in vascular pathogenesis. J Vasc Surg. 5:794–803.
2013.
|
|
4
|
Li P, Liu Y, Yi B, et al: MicroRNA-638 is
highly expressed in human vascular smooth muscle cells and inhibits
PDGF-BB-induced cell proliferation and migration through targeting
orphan nuclear receptor NOR1. Cardiovasc Res. 99:185–193. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Li QL, Gu FM, Wang Z, et al: Activation of
PI3K/AKT and MAPK pathway through a PDGFRbeta-dependent feedback
loop is involved in rapamycin resistance in hepatocellular
carcinoma. PLoS One. 7:e333792012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Wang J, Zhang Q, Mei X and Zhang X:
Hydroxysafflor yellow A attenuates left ventricular remodeling
after pressure overload-induced cardiac hypertrophy in rats. Pharm
Biol. 52:31–35. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Zang BX, Jin M, Si N, et al: Antagonistic
effect of hydroxysafflor yellow A on the platelet activating factor
receptor. Yao Xue Xue Bao. 37:696–699. 2002.(In Chinese).
|
|
8
|
Liu L, Duan JA, Tang Y, et al:
Taoren-Honghua herb pair and its main components promoting blood
circulation through influencing on hemorheology, plasma coagulation
and platelet aggregation. J Ethnopharmacol. 139:381–387. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Zhu HB, Zhang L, Wang ZH, et al:
Therapeutic effects of hydroxysafflor yellow A on focal cerebral
ischemic injury in rats and its primary mechanisms. J Asian Nat
Prod Res. 7:607–613. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Park ES, Kang SI, Yoo KD, et al:
Camptothecin inhibits platelet-derived growth factor-BB-induced
proliferation of rat aortic vascular smooth muscle cells through
inhibition of PI3K/Akt signaling pathway. Exp Cell Res.
319:982–991. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Jin YJ, Lee JH, Kim YM, Oh GT and Lee H:
Macrophage inhibitory cytokine-1 stimulates proliferation of human
umbilical vein endothelial cells by up-regulating cyclins D1 and E
through the PI3K/Akt-, ERK-, and JNK-dependent AP-1 and E2F
activation signaling pathways. Cell Signal. 24:1485–1495. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Jiang F, Jiang R, Zhu X, Zhang X and Zhan
Z: Genipin inhibits TNF-alpha-induced vascular smooth muscle cell
proliferation and migration via induction of HO-1. PLoS One.
8:e748262013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Cheng C, Haasdijk RA, Tempel D, et al:
PDGF-induced migration of vascular smooth muscle cells is inhibited
by heme oxygenase-1 via VEGFR2 upregulation and subsequent assembly
of inactive VEGFR2/PDGFRbeta heterodimers. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc
Biol. 32:1289–1298. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Bai Y, Lu P, Han C, et al: Hydroxysafflor
yellow A (HSYA) from flowers of Carthamus inctorius L. and
its vasodilatation effects on pulmonary artery. Molecules.
17:14918–14927. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Han SY, Li HX, Ma X, et al: Evaluation of
the anti-myocardial ischemia effect of individual and combined
extracts of Panax notoginseng and Carthamus
tinctorius in rats. J Ethnopharmacol. 145:722–727. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Wan LH, Chen J, Li L, Xiong WB and Zhou
LM: Protective effects of Carthamus tinctorius injection on
isoprenaline-induced myocardial injury in rats. Pharm Biol.
49:1204–1209. 2011.
|
|
17
|
Nie PH, Zhang L, Zhang WH, Rong WF and Zhi
JM: The effects of hydroxysafflor yellow A on blood pressure and
cardiac function. J Ethnopharmacol. 139:746–750. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Jin Z, Zhang W, Chai W, Zheng Y and Zhi J:
Antibodies against AT1 receptors are associated with vascular
endothelial and smooth muscle function impairment: protective
effects of hydroxysafflor yellow A. PLoS One. 8:e670202013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Xiao Q, Zhang F, Grassia G, et al: Matrix
metalloproteinase-8 promotes vascular smooth muscle cell
proliferation and neointima formation. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc
Biol. 35:90–98. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Stansfield BK, Bessler WK, Mali R, et al:
Ras-Mek-Erk signaling regulates Nf1 heterozygous neointima
formation. Am J Pathol. 184:79–85. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
O’ Brien ER, Ma X, Simard T, Pourdjabbar A
and Hibbert B: Pathogenesis of neointima formation following
vascular injury. Cardiovasc Hematol Disord Drug Targets. 11:30–39.
2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Guo J, Li L, Wu YJ, et al: Inhibitory
effects of Brazilin on the vascular smooth muscle cell
proliferation and migration induced by PDGF-BB. Am J Chin Med.
41:1283–1296. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Hwang SM, Lee YJ, Lee YP, et al:
Anti-proliferative effect of an aqueous extract of Prunella
vulgaris in vascular smooth muscle cells. Evid Based Complement
Alternat Med. 2013:9364632013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Sartore S, Chiavegato A, Faggin E, et al:
Contribution of adventitial fibroblasts to neointima formation and
vascular remodeling: from innocent bystander to active participant.
Circ Res. 89:1111–1121. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Karki R, Kim SB and Kim DW: Magnolol
inhibits migration of vascular smooth muscle cells via cytoskeletal
remodeling pathway to attenuate neointima formation. Exp Cell Res.
319:3238–3250. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Lowe G, Woodward M, Hillis G, et al:
Circulating inflammatory markers and the risk of vascular
complications and mortality in people with Type 2 Diabetes mellitus
and cardiovascular disease or risk factors: The ADVANCE study.
Diabetes. 63:1115–1123. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Sedding DG, Widmer-Teske R, Mueller A, et
al: Role of the phosphatase PTEN in early vascular remodeling. PLoS
One. 8:e554452013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Son Y, Lee JH, Chung HT and Pae HO:
Therapeutic roles of heme oxygenase-1 in metabolic diseases:
curcumin and resveratrol analogues as possible inducers of heme
oxygenase-1. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2013:6395412013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Wu ML, Ho YC and Yet SF: A central role of
heme oxygenase-1 in cardiovascular protection. Antioxid Redox
Signal. 15:1835–1846. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Yang HL, Chang HC, Lin SW, et al: Antrodia
salmonea inhibits TNF-alpha-induced angiogenesis and atherogenesis
in human endothelial cells through the down-regulation of NF-kappaB
and up-regulation of Nrf2 signaling pathways. J Ethnopharmacol.
15:394–406. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|