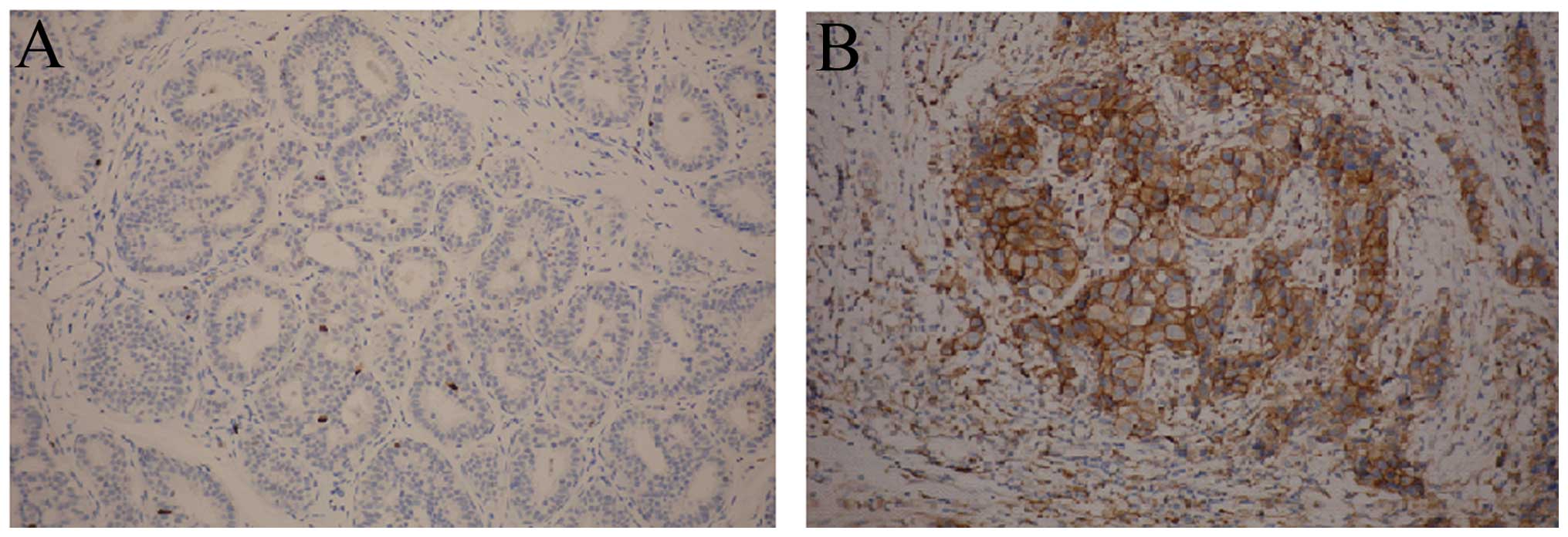
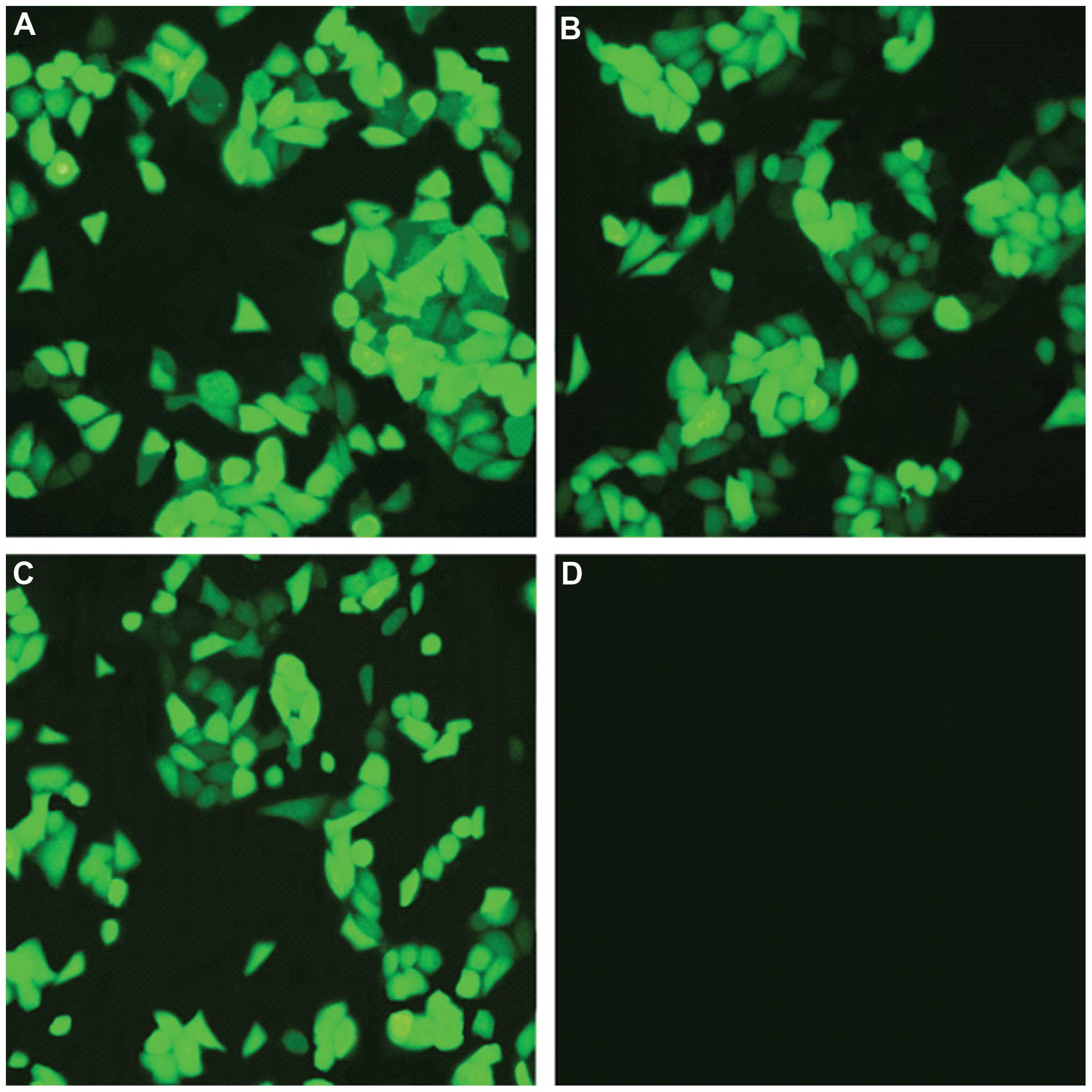
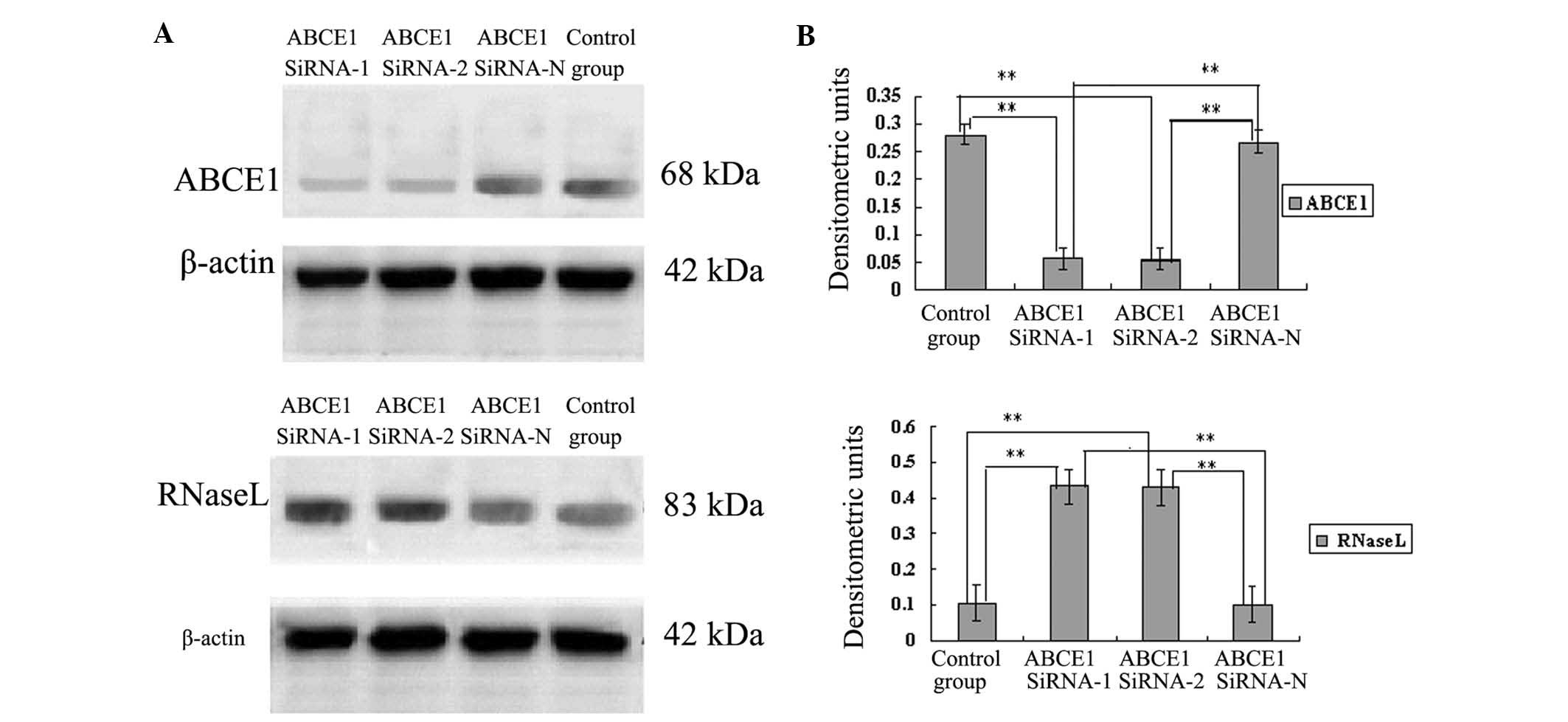
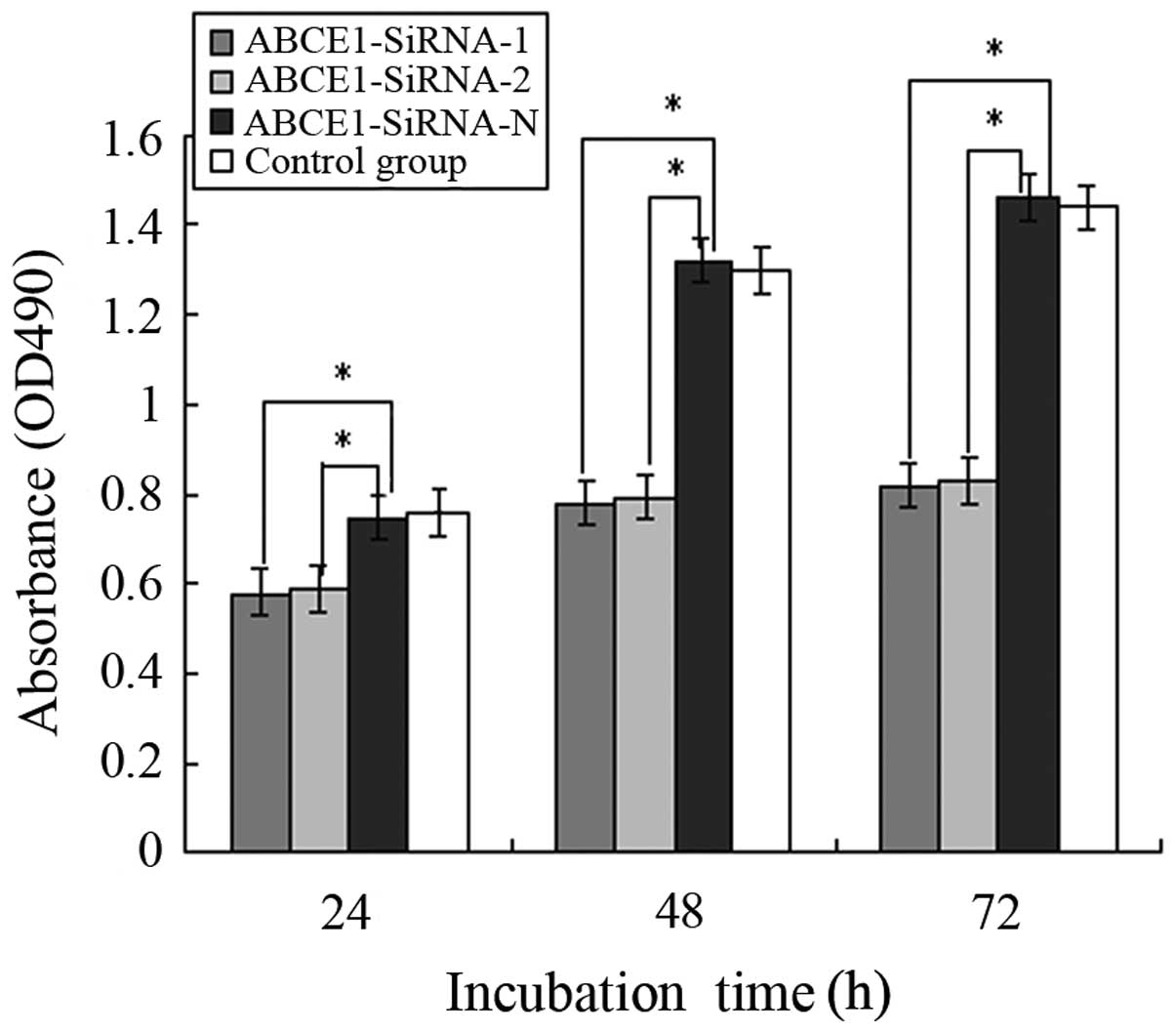
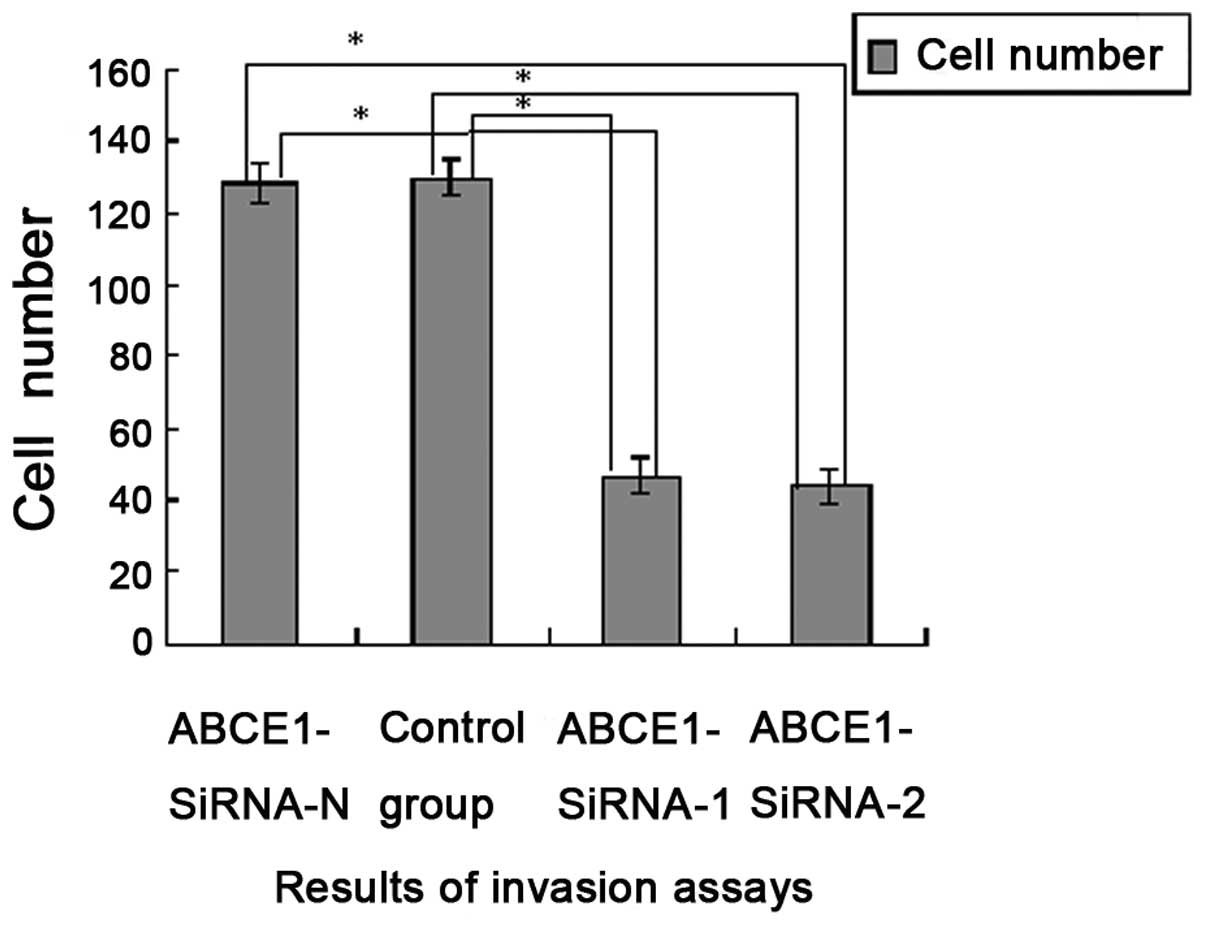
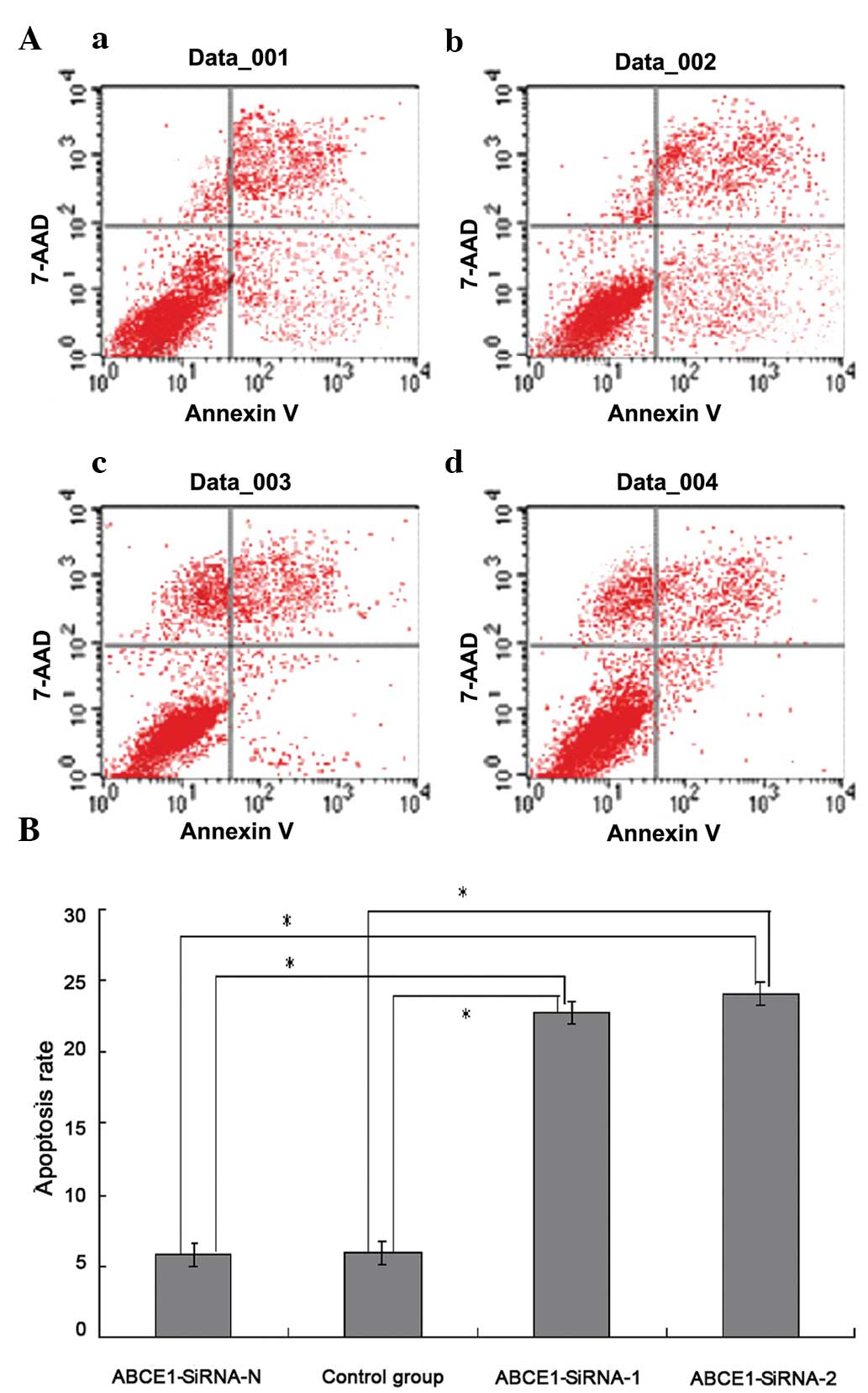
|
1
|
Jemal A, Siegel R, Ward E, Hao Y, Xu J and
Thun MJ: Cancer statistics, 2009. CA Cancer J Clin. 59:225–249.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Barthelme D, Scheele U, Dinkelaker S,
Janoschka A, Macmillan F, Albers SV, Driessen AJ, Stagni MS, Bill
E, Meyer-Klaucke W, Schünemann V and Tampé R: Structural
organization of essential iron-sulfur clusters in the
evolutionarily highly conserved ATP-binding cassette protein ABCE1.
J Biol Chem. 282:14598–14607. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Shichijo S, Ishihara Y, Azuma K, Komatsu
N, Higashimoto N, Ito M, Nakamura T, Ueno T, Harada M and Itoh K:
ABCE1, a member of ATP-binding cassette transporter gene, encodes
peptides capable of inducing HLA-A2-restricted and tumor-reactive
cytotoxic T lymphocytes in colon cancer patients. Oncol Rep.
13:907–913. 2005.
|
|
4
|
Pisarev AV, Skabkin MA, Pisareva VP,
Skabkina OV, Rakotondrafara AM, Hentze MW, Hellen CU and Pestova
TV: The role of ABCE1 in eukaryotic posttermination ribosomal
recycling. Mol Cell. 37:196–210. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Rodnina MV: Protein synthesis meets ABC
ATPases: new roles for Rli1/ABCE1. EMBO Rep. 11:143–144. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Huang B, Gao Y, Tian D and Zheng M: A
small interfering ABCE1-targeting RNA inhibits the proliferation
and invasiveness of small cell lung cancer. Int J Mol Med.
25:687–693. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Huang B, Zhou H, Wang X and Liu Z:
Silencing SATB1 with siRNA inhibits the proliferation and invasion
of small cell lung cancer cells. Cancer Cell Int. 13:82013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Cha Y, Kang Y and Moon A: HER2 induces
expression of leptin in human breast epithelial cells. BMB Rep.
45:719–723. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Tian Y, Han X and Tian DL: The biological
regulation of ABCE1. IUBMB Life. 64:795–800. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Barthelme D, Dinkelaker S, Albers SV,
Londei P, Ermler U and Tampé R: Ribosome recycling depends on a
mechanistic link between the FeS cluster domain and a
conformational switch of the twin-ATPase ABCE1. Proc Natl Acad Sci
USA. 108:3228–3233. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Langmann T, Mauerer R, Zahn A, Moehle C,
Probst M, Stremmel W and Schmitz G: Real-time reverse
transcription-PCR expression profiling of the complete human
ATP-binding cassette transporter superfamily in various tissues.
Clin Chem. 49:230–238. 2003. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Liang SL, Quirk D and Zhou A: RNase L: its
biological roles and regulation. IUBMB Life. 58:508–514. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Li G, Xiang Y, Sabapathy K and Silverman
RH: An apoptotic signaling pathway in the interferon antiviral
response mediated by RNase L and c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase. J Biol
Chem. 279:1123–1131. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Hlavata I, Mohelnikova-Duchonova B,
Vaclavikova R, Liska V, Pitule P, Novak P, Bruha J, Vycital O,
Holubec L, Treska V, Vodicka P and Soucek P: The role of ABC
transporters in progression and clinical outcome of colorectal
cancer. Mutagenesis. 27:187–196. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Ren Y, Li Y and Tian D: Role of the ABCE1
gene in human lung adenocarcinoma. Oncol Rep. 27:965–970.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Silverman RH: Implications for RNase L in
prostate cancer biology. Biochemistry. 42:1805–1812. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Shea PR, Ishwad CS, Bunker CH, Patrick AL,
Kuller LH and Ferrell RE: RNASEL and RNASEL-inhibitor variation and
prostate cancer risk in Afro-Caribbeans. Prostate. 68:354–359.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|