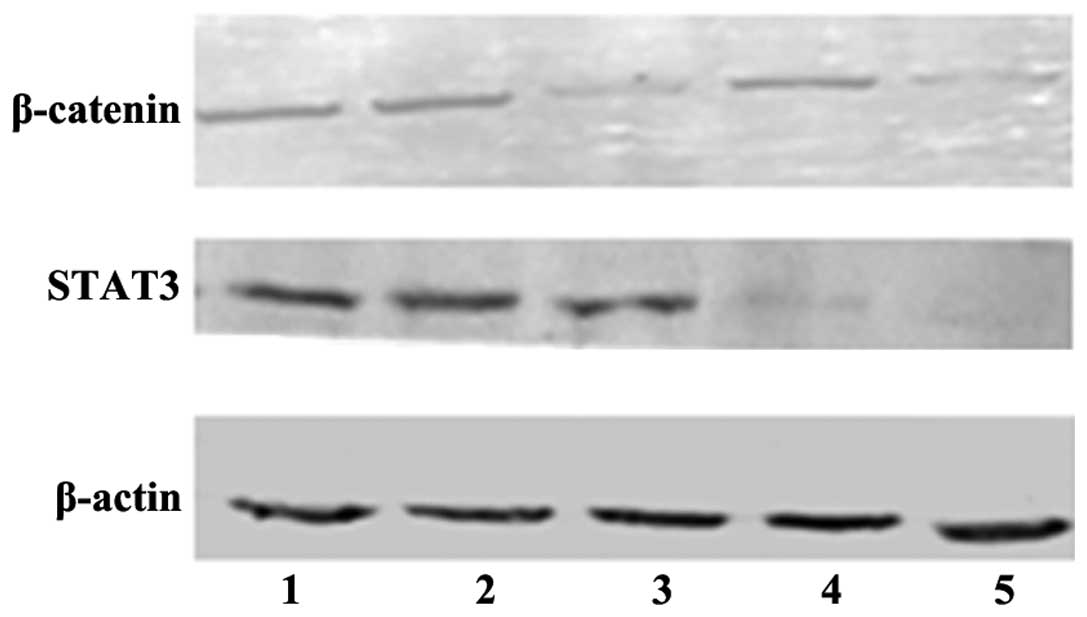
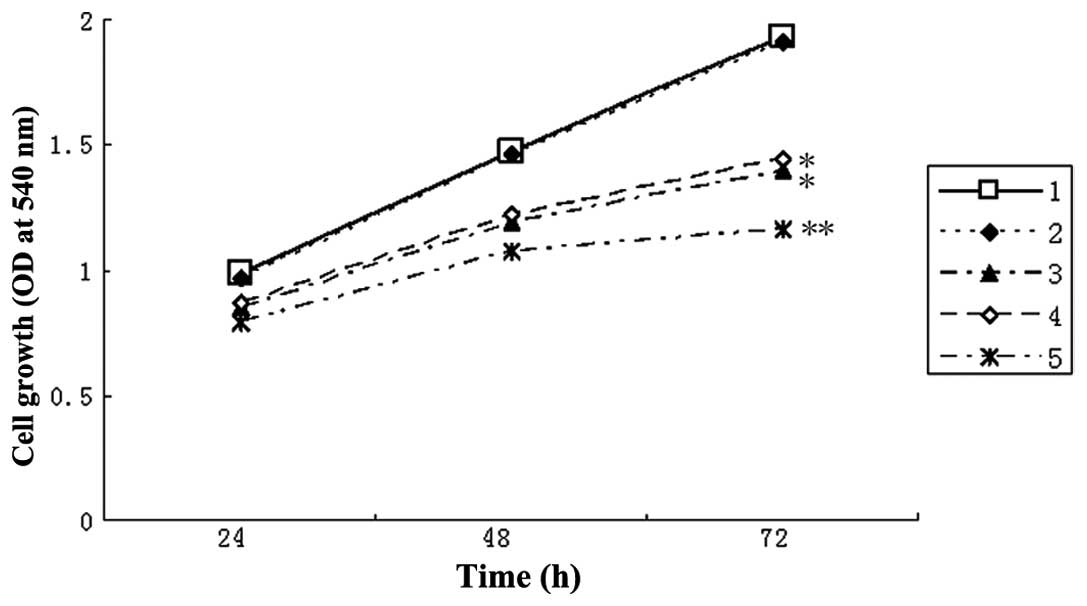
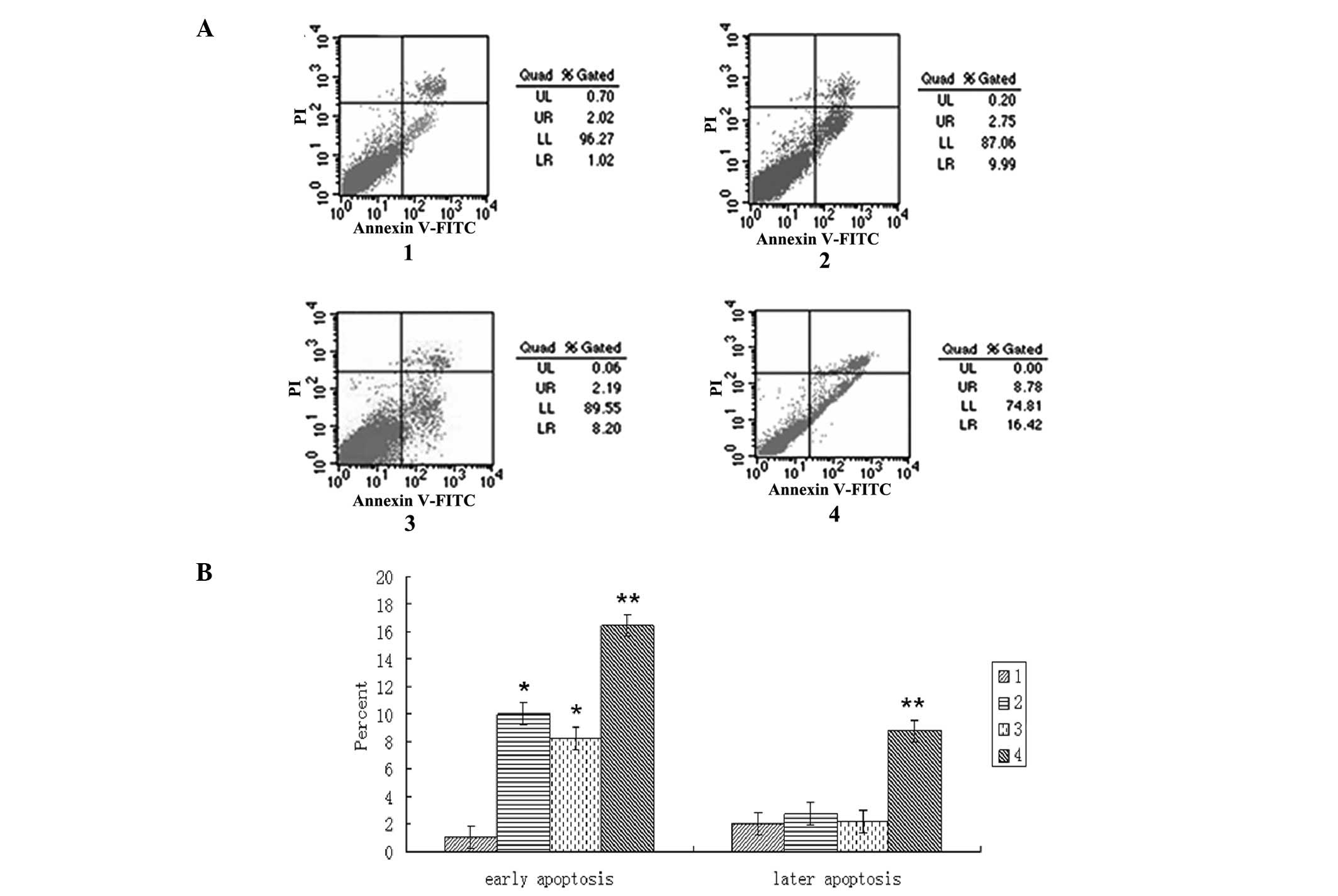
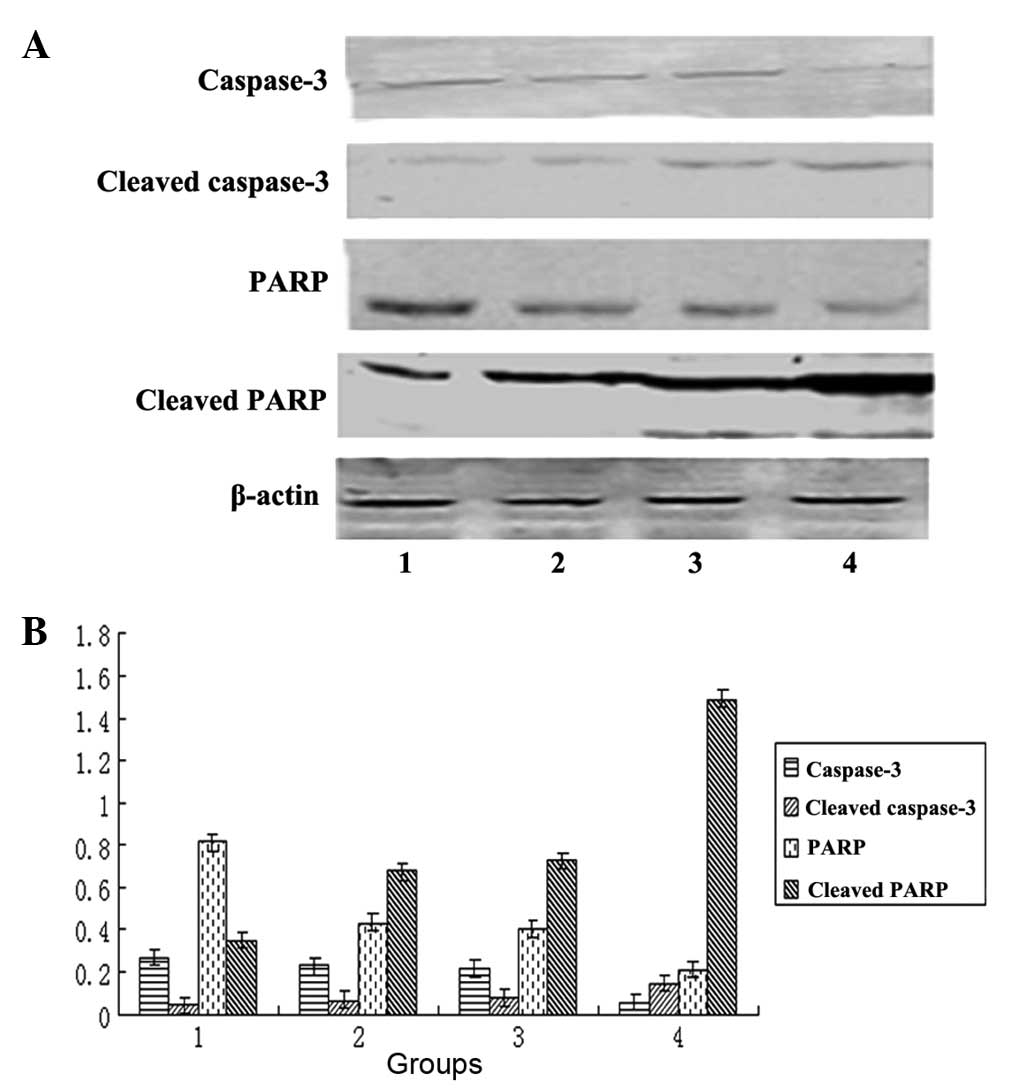
|
1
|
Yamakado K and Kudo M: Treatment
strategies of intermediate-stage hepatocellular carcinomas in Japan
(Barcelona Clinic Liver Cancer stage B). Oncology. 87(Suppl 1):
78–81. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Chan LH, Luk ST and Ma S: Turning hepatic
cancer stem cells inside out - a deeper understanding through
multiple perspectives. Mol Cells. Feb 4–2015.Epub ahead of print.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Wang XH, Sun X, Meng XW, et al: β-catenin
siRNA regulation of apoptosis- and angiogenesis-related gene
expression in hepatocellular carcinoma cells: potential uses for
gene therapy. Oncol Rep. 24:1093–1099. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Zulehner G, Mikula M, Schneller D, et al:
Nuclear beta-catenin induces an early liver progenitor phenotype in
hepatocellular carcinoma and promotes tumor recurrence. Am J
Pathol. 176:472–481. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
5
|
Li W, Tong H, Huang X, et al: High levels
of β-catenin promote IFNγ-induced apoptosis in hepatocellular
carcinoma cells. Oncol Lett. 4:1092–1096. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Guturi KK, Mandal T, Chatterjee A, et al:
Mechanism of β-catenin-mediated transcriptional regulation of
epidermal growth factor receptor expression in glycogen synthase
kinase 3 β-inactivated prostate cancer cells. J Biol Chem.
287:18287–18296. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Wang XH, Meng XW, Sun X, et al:
Wnt/β-catenin signaling regulates MAPK and Akt1 expression and
growth of hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Neoplasma. 58:239–244.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Tian XH, Hou WJ, Fang Y, et al: XAV939, a
tankyrase 1 inhibitior, promotes cell apoptosis in neuroblastoma
cell lines by inhibiting Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. J Exp
Clin Cancer Res. 32:1002013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Liu YZ, Wu K, Huang J, et al: The
PTEN/PI3K/Akt and Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathways are involved in
the inhibitory effect of resveratrol on human colon cancer cell
proliferation. Int J Oncol. 45:104–112. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Fletcher S, Turkson J and Gunning PT:
Molecular approaches towards the inhibition of the signal
transducer and activator of transcription 3 (Stat3) protein.
ChemMedChem. 3:1159–1168. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Morikawa T, Baba Y, Yamauchi M, et al:
STAT3 expression, molecular features, inflammation patterns and
prognosis in a database of 724 colorectal cancers. Clin Cancer Res.
17:1452–1462. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Park KW, Kundu J, Chae IG, Kim DH, Yu MH,
Kundu JK and Chun KS: Carnosol induces apoptosis through generation
of ROS and inactivation of STAT3 signaling in human colon cancer
HCT116 cells. Int J Oncol. 44:1309–1315. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Song X, Wang J, Zheng T, et al: LBH589
Inhibits proliferation and metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma
via inhibition of gankyrin/STAT3/Akt pathway. Mol Cancer.
12:1142013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Tsang CM, Cheung YC, Lui VW, et al:
Berberine suppresses tumorigenicity and growth of nasopharyngeal
carcinoma cells by inhibiting STAT3 activation induced by tumor
associated fibroblasts. BMC Cancer. 13:6192013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Li W, Huang X, Tong H, et al: Comparison
of the regulation of β-catenin signaling by type I, type II and
type III interferons in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. PLoS One.
7:e470402012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Zhang Y, Du XL, Wang CJ, et al: Reciprocal
activation between PLK1 and Stat3 contributes to survival and
proliferation of esophageal cancer cells. Gastroenterology.
142:521–530.e3. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Yang F, Jove V, Buettner R, et al:
Sorafenib inhibits endogenous and IL-6/S1P induced JAK2-STAT3
signaling in human neuroblastoma, associated with growth
suppression and apoptosis. Cancer Biol Ther. 13:534–541. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Wang XH, Liu BR, Qu B, et al: Silencing
STAT3 may inhibit cell growth through regulating signaling pathway,
telomerase, cell cycle, apoptosis and angiogenesis in
hepatocellular carcinoma: potential uses for gene therapy.
Neoplasma. 58:158–171. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Ogiwara H, Ui A, Shiotani B, et al:
Curcumin suppresses multiple DNA damage response pathways and has
potency as a sensitizer to PARP inhibitor. Carcinogenesis.
34:2486–2497. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Yuan K, Sun Y, Zhou T, McDonald J and Chen
Y: PARP-1 regulates resistance of pancreatic cancer to TRAIL
therapy. Clin Cancer Res. 19:4750–4759. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Booth L, Cruickshanks N, Ridder T, et al:
PARP and CHK inhibitors interact to cause DNA damage and cell death
in mammary carcinoma cells. Cancer Biol Ther. 14:458–465. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Dabir S, Kluge A, McColl K, et al: PIAS3
activates the intrinsic apoptotic pathway in non-small cell lung
cancer cells independent of p53 status. Int J Cancer.
134:1045–1054. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
23
|
Swiatek-Machado K, Mieczkowski J,
Ellert-Miklaszewska A, et al: Novel small molecular inhibitors
disrupt the JAK/STAT3 and FAK signaling pathways and exhibit a
potent antitumor activity in glioma cells. Cancer Biol Ther.
13:657–670. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Tierney BJ, McCann GA, Cohn DE, et al:
HO-3867, a STAT3 inhibitor induces apoptosis by inactivation of
STAT3 activity in BRCA1-mutated ovarian cancer cells. Cancer Biol
Ther. 13:766–775. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Lee NJ, Choi DY, Song JK, et al:
Deficiency of C-C chemokine receptor 5 suppresses tumor development
via inactivation of NF-κB and inhibition of monocyte
chemoattractant protein-1 in urethane-induced lung tumor model.
Carcinogenesis. 33:2520–2528. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Bill MA, Nicholas C, Mace TA, et al:
Structurally modified curcumin analogs inhibit STAT3
phosphorylation and promote apoptosis of human renal cell carcinoma
and melanoma cell lines. PLoS One. 7:e407242012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Xue M, Ge Y, Zhang J, et al: Fucoidan
inhibited 4T1 mouse breast cancer cell growth in vivo and in vitro
via downregulation of Wnt/β-catenin signaling. Nutr Cancer.
65:460–468. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Kundu J, Wahab SM, Kundu JK, et al: Tob1
induces apoptosis and inhibits proliferation, migration and
invasion of gastric cancer cells by activating Smad4 and inhibiting
β-catenin signaling. Int J Oncol. 41:839–848. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Jaeger A, Baake J, Weiss DG and Kriehuber
R: Glycogen synthase kinase-3beta regulates differentiation-induced
apoptosis of human neural progenitor cells. Int J Dev Neurosci.
31:61–68. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Wang Y, Tao ZZ, Chen SM, et al:
Application of combination of short hairpin RNA segments for
silencing VEGF, TERT and Bcl-xl expression in laryngeal squamous
carcinoma. Cancer Biol Ther. 7:896–901. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|