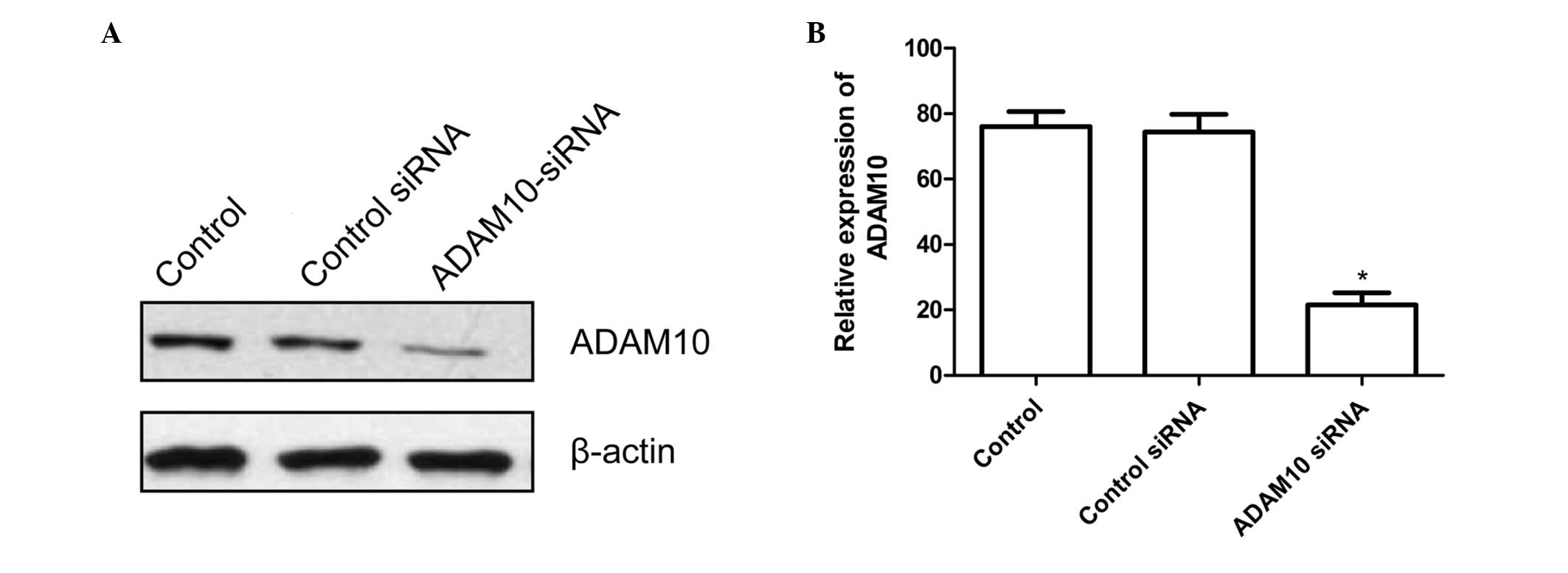
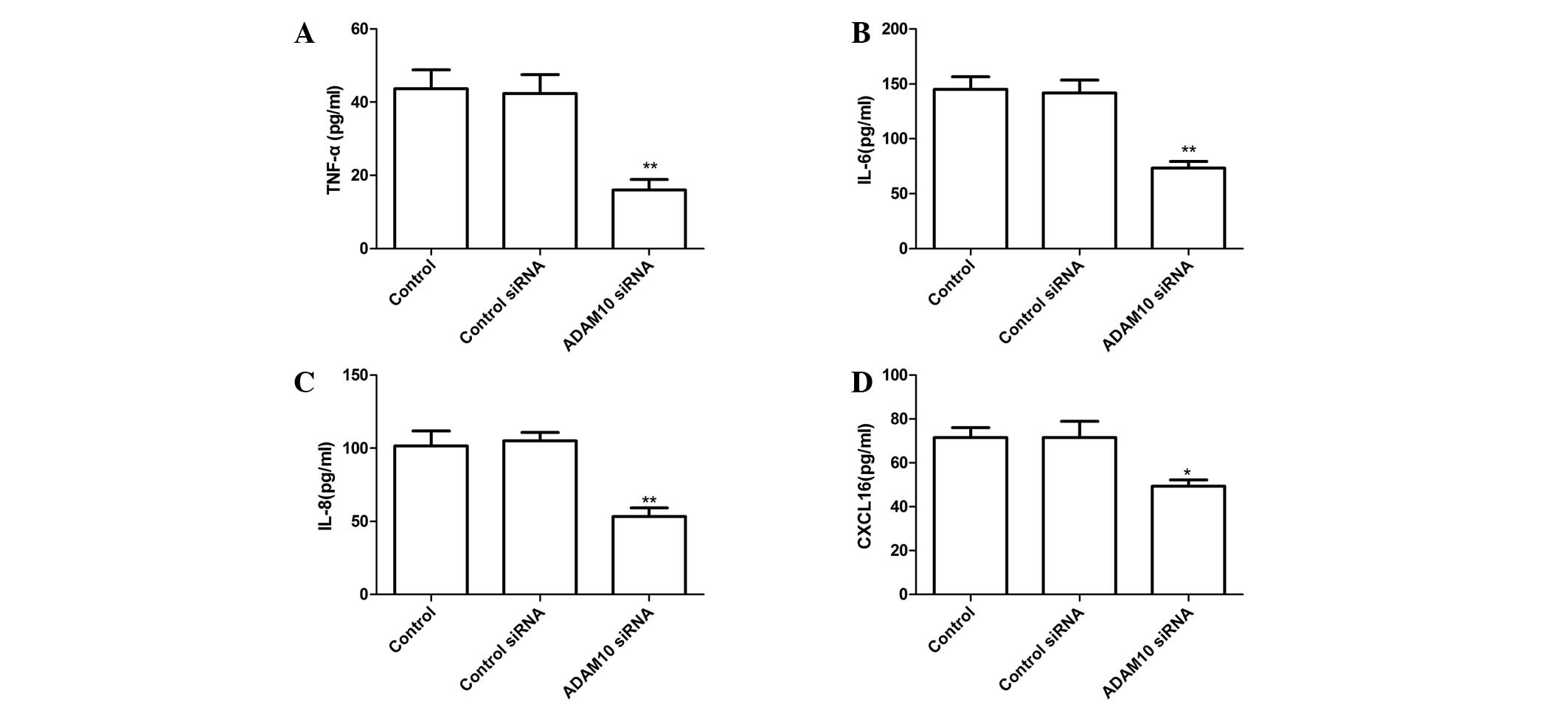
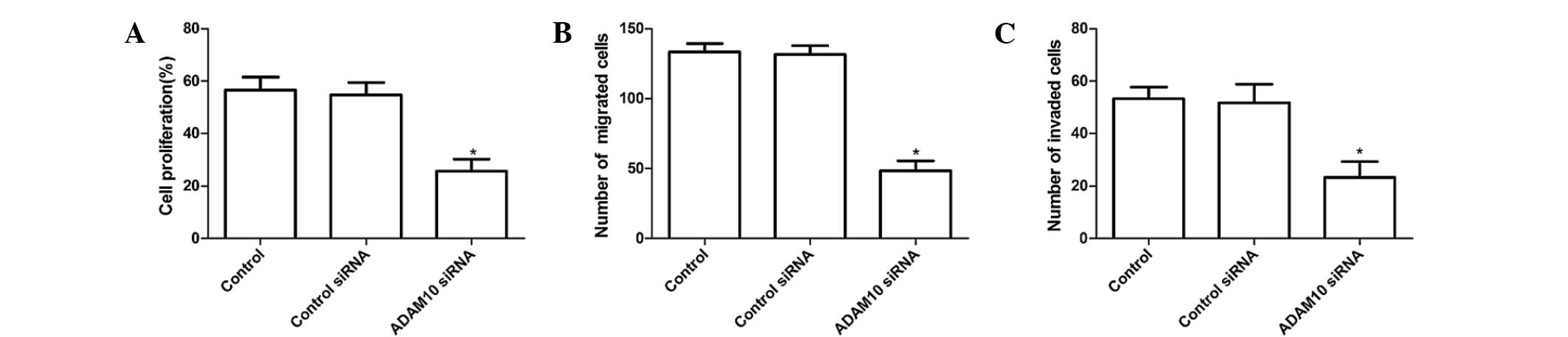
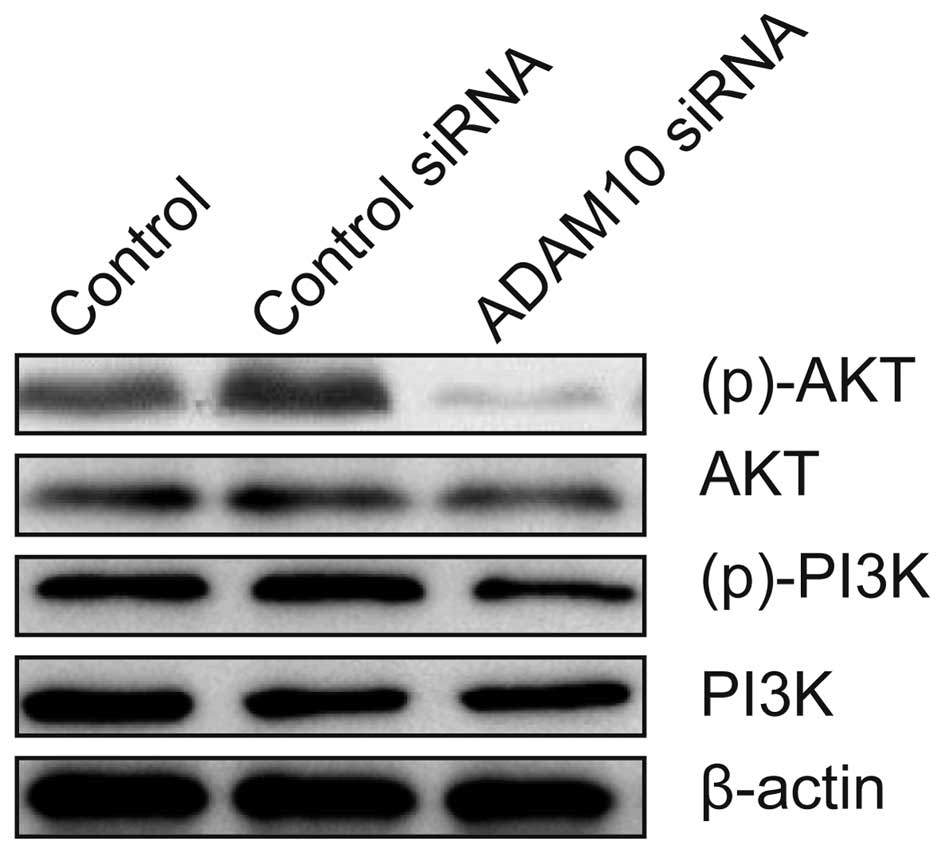
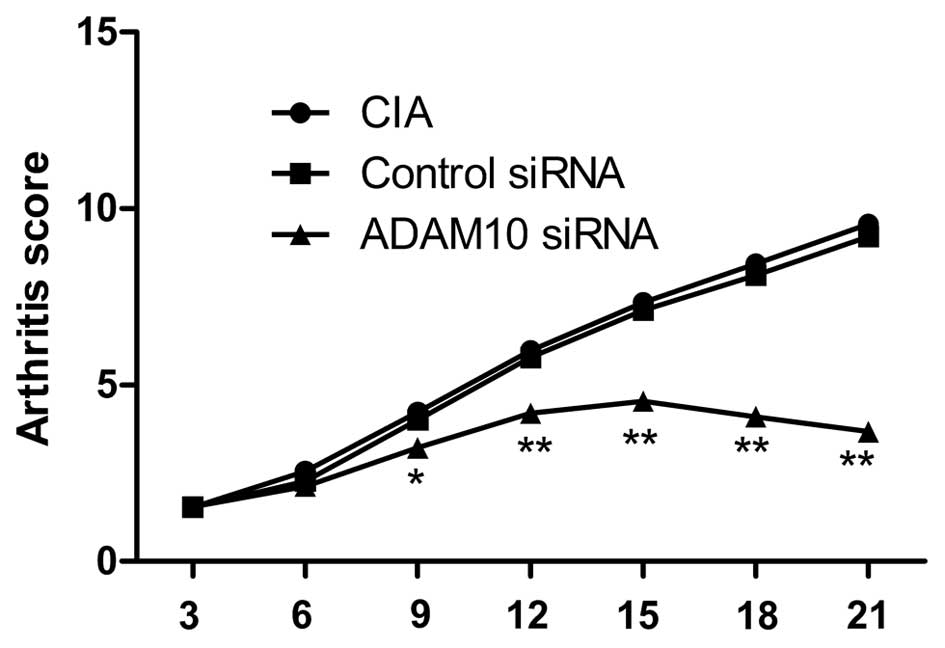
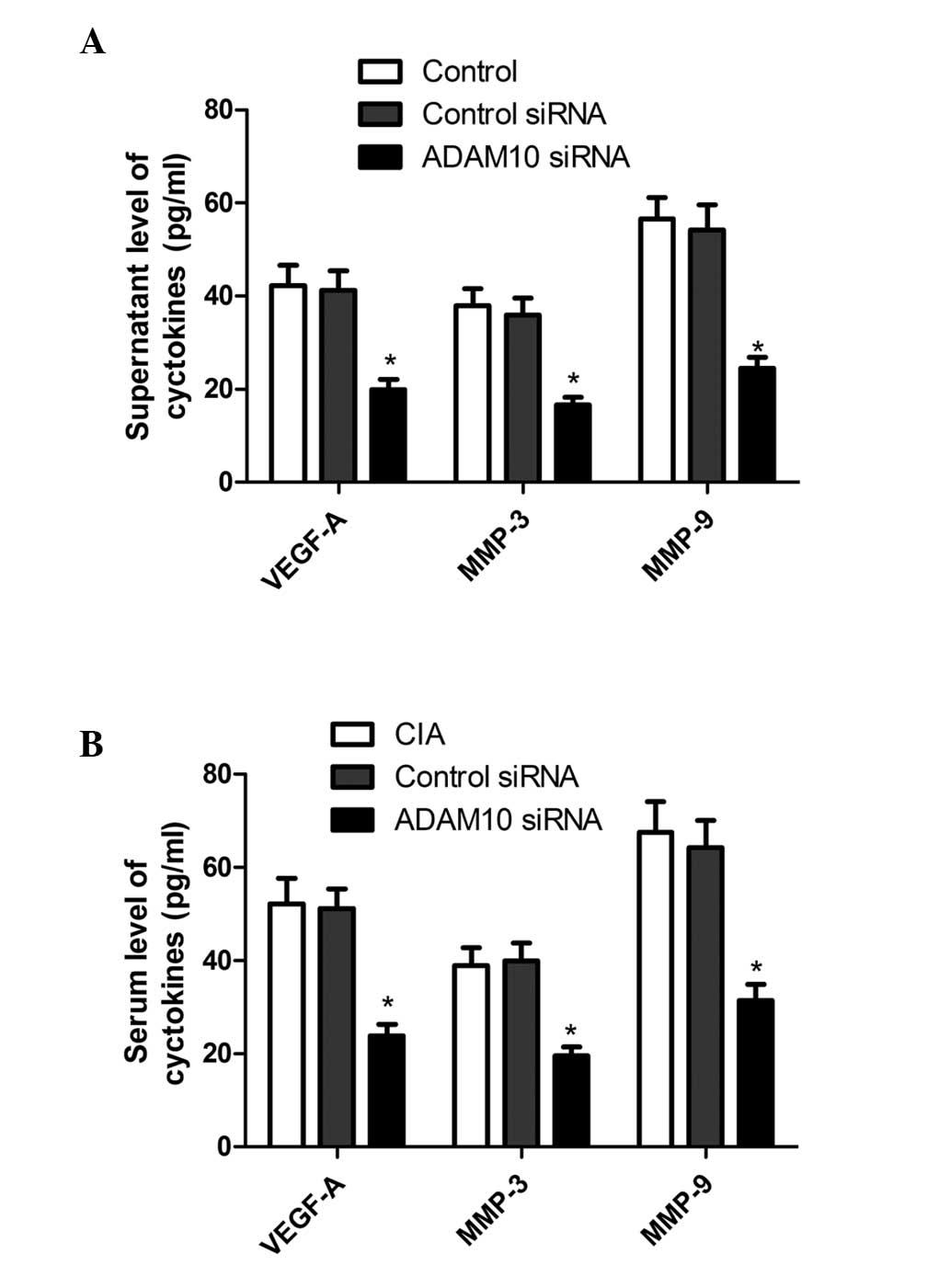
|
1
|
Firestein GS: Evolving concepts of
rheumatoid arthritis. Nature. 423:356–361. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Miossec P: Rheumatoid arthritis: Still a
chronic disease. Lancet. 381:884–886. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Bottini N and Firestein GS: Duality of
fibroblast-like synoviocytes in RA: Passive responders and
imprinted aggressors. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 9:24–33. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Li F, Li X, Kou L, Li Y, Meng F and Ma F:
SUMO-conjugating enzyme UBC9 promotes proliferation and migration
of fibroblast-like synoviocytes in rheumatoid arthritis.
Inflammation. 37:1134–1141. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Juarez M, Filer A and Buckley CD:
Fibroblasts as therapeutic targets in rheumatoid arthritis and
cancer. Swiss Med Wkly. 142:w135292012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Bartok B and Firestein GS: Fibroblast-like
synoviocytes: Key effector cells in rheumatoid arthritis. Immunol
Rev. 233:233–255. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Muller-Ladner U, Kriegsmann J, Franklin
BN, Matsumoto S, Geiler T, Gay RE and Gay S: Synovial fibroblasts
of patients with rheumatoid arthritis attach to and invade normal
human cartilage when engrafted into SCID mice. Am J Pathol.
149:1607–1615. 1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Huber LC, Distler O, Tarner I, Gay RE, Gay
S and Pap T: Synovial fibroblasts: Key players in rheumatoid
arthritis. Rheumatology (Oxford). 45:669–675. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Pruessmeyer J and Ludwig A: The good, the
bad and the ugly substrates for ADAM10 and ADAM17 in brain
pathology, inflammation and cancer. Semin Cell Dev Biol.
20:164–174. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Schulz B, Pruessmeyer J, Maretzky T,
Ludwig A, Blobel CP, Saftig P and Reiss K: ADAM10 regulates
endothelial permeability and T-Cell transmigration by proteolysis
of vascular endothelial cadherin. Circ Res. 102:1192–1201. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Eichenauer DA, Simhadri VL, von Strandmann
EP, Ludwig A, Matthews V, Reiners KS, von Tresckow B, Saftig P,
Rose-John S, Engert A, et al: ADAM10 inhibition of human CD30
shedding increases specificity of targeted immunotherapy in vitro.
Cancer Res. 67:332–338. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Weskamp G, Ford JW, Sturgill J, Martin S,
Docherty AJ, Swendeman S, Broadway N, Hartmann D, Saftig P, Umland
S, et al: ADAM10 is a principal 'sheddase' of the low-affinity
immunoglobulin E receptor CD23. Nat Immunol. 7:1293–1298. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
McCulloch DR, Akl P, Samaratunga H,
Herington AC and Odorico DM: Expression of the disintegrin
metalloprotease, ADAM-10, in prostate cancer and its regulation by
dihydrotes-tosterone, insulin-like growth factor I and epidermal
growth factor in the prostate cancer cell model LNCaP. Clin Cancer
Res. 10:314–323. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Gough PJ, Garton KJ, Wille PT, Rychlewski
M, Dempsey PJ and Raines EW: A disintegrin and metalloproteinase
10-mediated cleavage and shedding regulates the cell surface
expression of CXC chemokine ligand 16. J Immunol. 172:3678–3685.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Hundhausen C, Misztela D, Berkhout TA,
Broadway N, Saftig P, Reiss K, Hartmann D, Fahrenholz F, Postina R
and Matthews V: The disintegrin-like metalloproteinase ADAM10 is
involved in constitutive cleavage of CX3CL1 (fractalkine) and
regulates CX3CL1-mediated cell-cell adhesion. Blood. 102:1186–1195.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Isozaki T, Rabquer BJ, Ruth JH, Haines GK
III and Koch AE: ADAM-10 is overexpressed in rheumatoid arthritis
synovial tissue and mediates angiogenesis. Arthritis Rheum.
65:98–108. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Chen SY, Wu CL, Lai MD, Lin CC, Yo YT, Jou
IM, Lee CH, Weng CT, Shiau AL and Wang CR: Amelioration of rat
collagen-induced arthritis through CD4+T cells apoptosis and
synovial interleukin-17 reduction by indoleamine 2,3-dioxy-genase
gene therapy. Hum Gene Ther. 22:145–154. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Minakuchi Y, Takeshita F, Kosaka N, Sasaki
H, Yamamoto Y, Kouno M, Honma K, Nagahara S, Hanai K, Sano A, et
al: Atelocollagen-mediated synthetic small interfering RNA delivery
for effective gene silencing in vitro and in vivo. Nucleic Acids
Res. 32:e1092004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Li F, Li X, Kou L, Li Y, Meng F and Ma F:
SUMO-conjugating enzyme UBC9 promotes proliferation and migration
of fibroblast-like synoviocytes in rheumatoid arthritis.
Inflammation. 37:1134–1141. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Tarrant TK, Liu P, Rampersad RR, Esserman
D, Rothlein LR, Timoshchenko RG, McGinnis MW, Fitzhugh DJ, Patel DD
and Fong AM: Decreased Th17 and antigen-specific humoral responses
in CX3 CR1-deficient mice in the collagen-induced arthritis model.
Arthritis Rheum. 64:1379–1387. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Afuwape AO, Kiriakidis S and Paleolog EM:
The role of the angiogenic molecule VEGF in the pathogenesis of
rheumatoid arthritis. Histol Histopathol. 17:961–972.
2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Muller-Ladner U, Pap T, Gay RE, Neidhart M
and Gay S: Mechanisms of disease: The molecular and cellular basis
of joint destruction in rheumatoid arthritis. Nat Clin Pract
Rheumatol. 1:102–110. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Huber LC, Distler O, Tarner I, Gay RE, Gay
S and Pap T: Synovial fibroblasts: Key players in rheumatoid
arthritis. Rheumatology (Oxford). 45:669–675. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Buchan G, Barrett K, Turner M, Chantry D,
Maini RN and Feldmann M: Interleukin-1 and tumour necrosis factor
mRNA expression in rheumatoid arthritis: Prolonged production of
IL-1 alpha. Clin Exp Immunol. 73:449–455. 1988.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Choy EH and Panayi GS: Cytokine pathways
and joint inflammation in rheumatoid arthritis. N Engl J Med.
344:907–916. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Feldmann M: Development of anti-TNF
therapy for rheumatoid arthritis. Nat Rev Immunol. 2:364–371. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Ehrenstein MR, Evans JG, Singh A, Moore S,
Warnes G, Isenberg DA and Mauri C: Compromised function of
regulatory T cells in rheumatoid arthritis and reversal by
anti-TNFalpha therapy. J Exp Med. 200:277–285. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Hashizume M and Mihara M: The roles of
interleukin-6 in the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis.
Arthritis. 2011:7656242011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
de Benedetti F, Massa M, Robbioni P,
Ravelli A, Burgio GR and Martini A: Correlation of serum
interleukin-6 levels with joint involvement and thrombocytosis in
systemic juvenile rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum.
34:1158–1163. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Saftig P and Reiss K: The 'A Disintegrin
And Metalloproteases' ADAM10 and ADAM17: Novel drug targets with
therapeutic potential? Eur J Cell Biol. 90:527–535. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Zhao H, Zhu J, Cui K, Xu X, O'Brien M,
Wong KK, Kesari S, Xia W and Wong ST: Bioluminescence imaging
reveals inhibition of tumor cell proliferation by Alzheimer's
amyloid beta protein. Cancer Cell Int. 9:152009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Murai T, Miyazaki Y, Nishinakamura H,
Sugahara KN, Miyauchi T, Sako Y, Yanagida T and Miyasaka M:
Engagement of CD44 promotes Rac activation and CD44 cleavage during
tumor cell migration. J Biol Chem. 279:4541–4550. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Zhang W, Liu S, Liu K, Ji B, Wang Y and
Liu Y: Knockout of ADAM10 enhances sorafenib antitumor activity of
hepatocellular carcinoma in vitro and in vivo. Oncol Rep.
32:1913–1922. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Yuan Q, Cai S, Zhang X, Liu Z, Li Z, Luo
X, Xiong C, Wang J, Hu J and Ruan J: A new protoapigenone analog
RY10–4 induces apoptosis and suppresses invasion through the
PI3K/Akt pathway in human breast cancer. Cancer Lett. 324:210–220.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Yuan H, Yang P, Zhou D, Gao W, Qiu Z, Fang
F, Ding S and Xiao W: Knockdown of sphingosine kinase 1 inhibits
the migration and invasion of human rheumatoid arthritis
fibroblast-like synoviocytes by down-regulating the PI3K/AKT
activation and MMP-2/9 production in vitro. Mol Biol Rep.
41:5157–5165. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Xue M, McKelvey K, Shen K, Minhas N, March
L, Park SY and Jackson CJ: Endogenous MMP-9 and not MMP-2 promotes
rheumatoid synovial fibroblast survival, inflammation and cartilage
degradation. Rheumatology (Oxford). 53:2270–2279. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Li F, Li X, Kou L, Li Y, Meng F and Ma F:
SUMO-conjugating enzyme UBC9 promotes proliferation and migration
of fibroblast-like synoviocytes in rheumatoid arthritis.
Inflammation. 37:1134–1141. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|