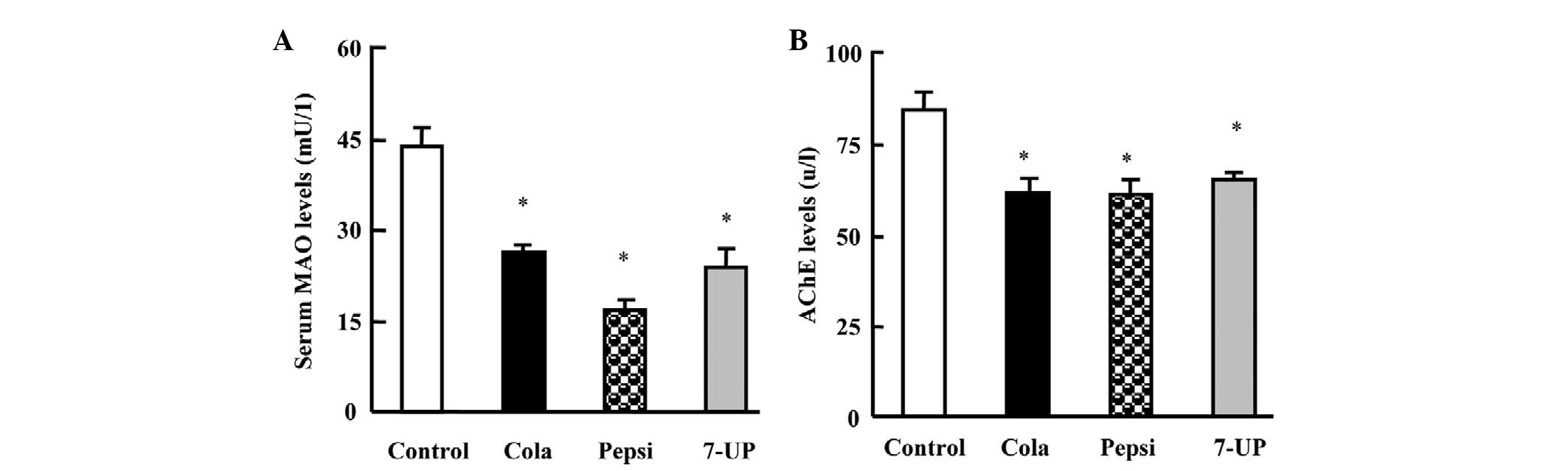
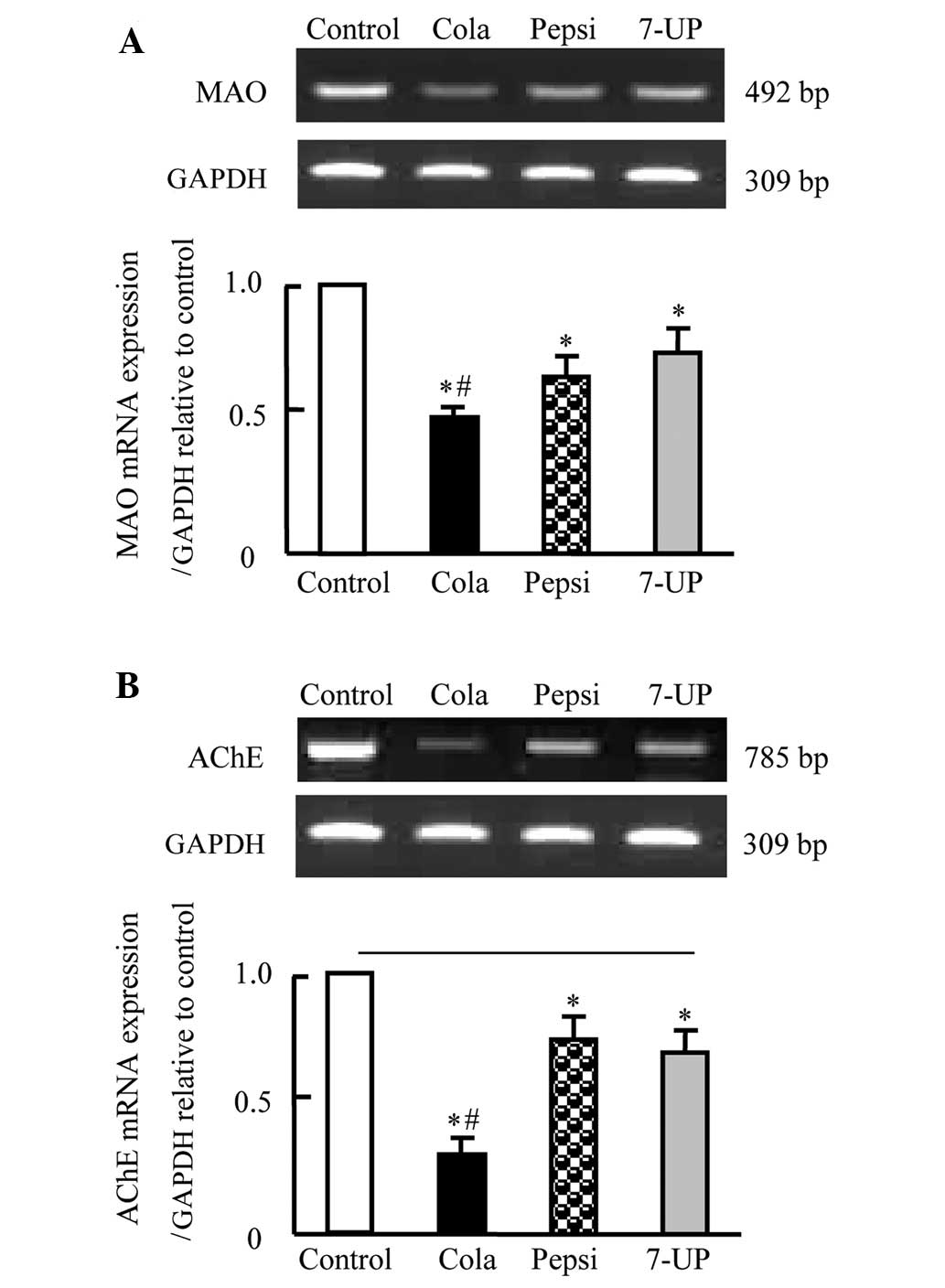
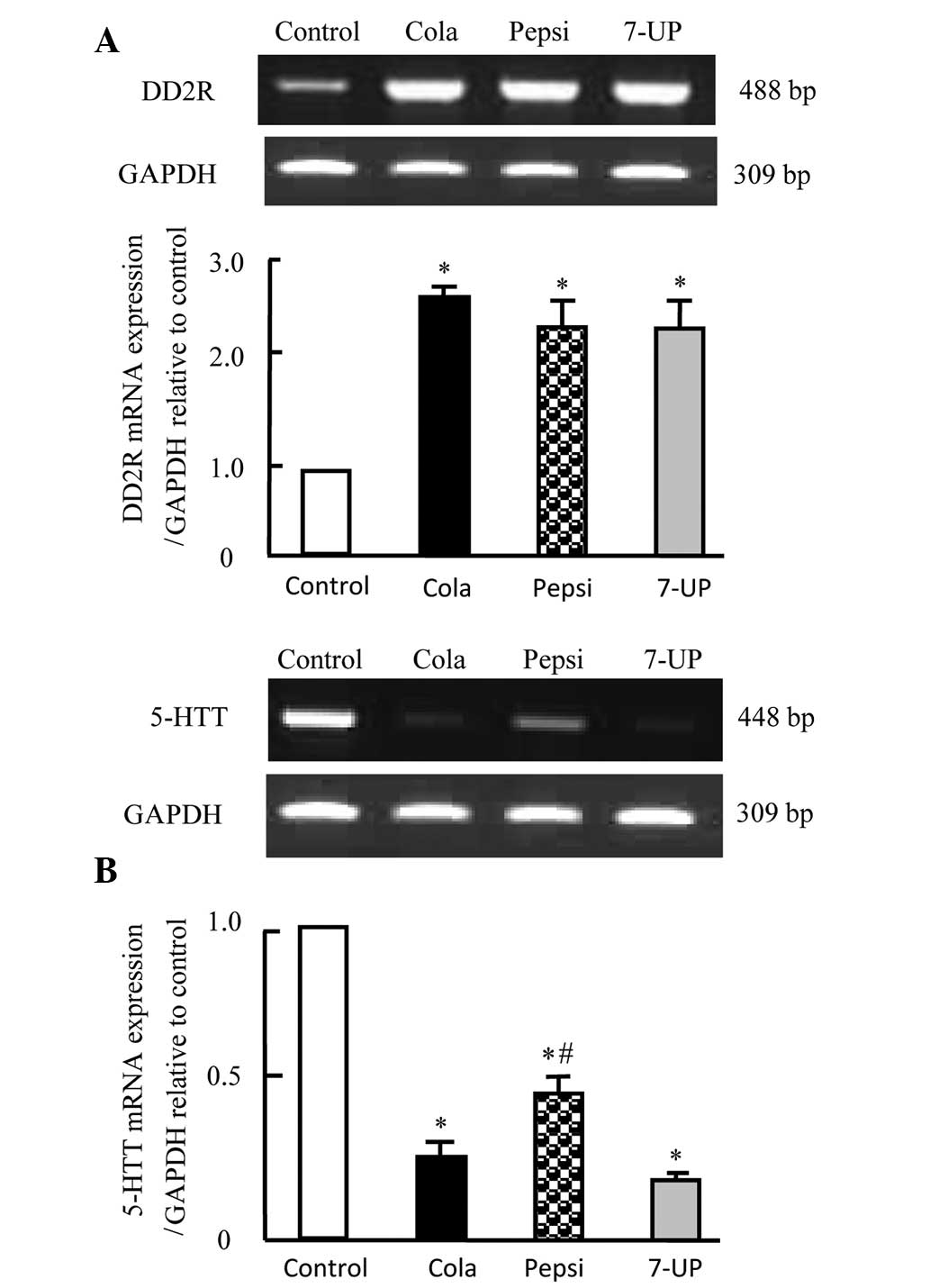
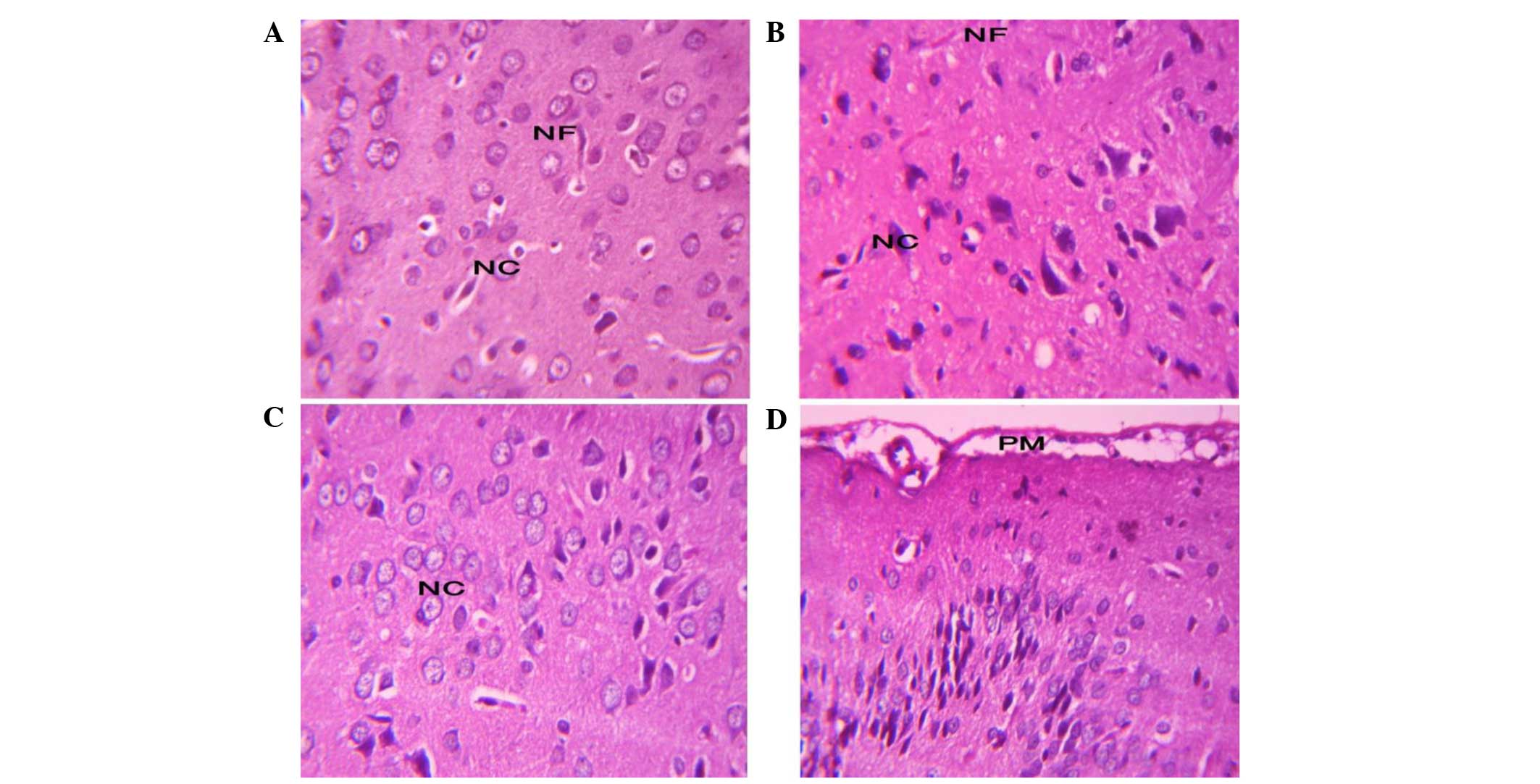
|
1
|
Adjene JO, Ezeoke JC and Nwose EU:
Histological effects of chronic consumption of soda pop drinks on
kidney of adult Wister rats. N Am J Med Sci. 2:215–217.
2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Amato D, Maravilla A, García-Contreras F
and Paniagua R: Soft-drinks and health. Rev Invest Clin.
49:387–395. 1997.
|
|
3
|
Amato D, Maravilla A, Montoya C, Gaja O,
Revilla C, Guerra R and Paniagua R: Acute effects of soft drink
intake on calcium and phosphate metabolism in immature and adults
rats. Rev Invest Clin. 50:185–189. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Clauson KA, Shields KM, McQueen CE and
Persad N: Safety issues associated with commercially available
energy drinks. J Am Pharm Assoc (2003). 48:e55–e67. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Iyadurai SJ and Chung SS: New-onset
seizures in adults: Possible association with consumption of
popular energy drinks. Epilepsy Behav. 10:504–508. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
DiMeglio DP and Mattes RD: Liquid versus
solid carbohydrate: Effects on food intake and body weight. Int J
Obes Relat Metab Disord. 24:794–800. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Mattes RD: Fluid energy-Where's the
problem? J Am Diet Assoc. 106:1956–1961. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Frank GK, Oberndorfer TA, Simmons AN,
Paulus MP, Fudge JL, Yang TT and Kaye WH: Sucrose activates human
taste pathways differently from artificial sweetener. Neuroimage.
39:1559–1569. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Smeets PA, de Graaf C, Stafleu A, van Osch
MJ and van der Grond J: Functional magnetic resonance imaging of
human hypothalamic responses to sweet taste and calories. Am J Clin
Nutr. 82:1011–1016. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Eluwa MA, Inyangmme II, Akpantah AO,
Ekanem TB, Ekong MB, Asuquo OR and Nwakanma AA: A comparative study
of the effect of diet and soda carbonated drinks on the histology
of the cerebellum of adult female albino Wistar rats. Afr Health
Sci. 13:541–545. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Soliman MM, Abdo Nassan M and Ismail TA:
Immunohistochemical and molecular study on the protective effect of
curcumin against hepatic toxicity induced by paracetamol in Wistar
rats. BMC Complement Altern Med. 14:4572014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Bancroft JD and Gamble M: Theory and
practice of histological techniques. 6th ed. Churchill Livingstone
Elsevier; Philadelphia: pp. 126–127. 2008
|
|
13
|
Ceconi C, Boraso A, Cargnoni A and Ferrari
R: Oxidative stress in cardiovascular disease: Myth or fact? Arch
Biochem Biophys. 420:217–221. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Moldovan L and Moldovan NI: Oxygen free
radicals and redox biology of organelles. Histochem Cell Biol.
122:395–412. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Higgins JP, Tuttle TD and Higgins CL:
Energy beverages: Content and safety. Mayo Clin Proc. 85:1033–1041.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Usman A and Jawaid A: Hypertension in a
young boy: An energy drink effect. BMC Res Notes. 5:5912012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Hotamisligil GS and Breakefield XO: Human
monoamine oxidase A gene determines levels of enzyme activity. Am J
Hum Genet. 49:383–392. 1991.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
De Colibus L, Li M, Binda C, Lustig A,
Edmondson DE and Mattevi A: Three-dimensional structure of human
monoamine oxidase A (MAO A): Relation to the structures of rat MAO
A and human MAO B. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 102:12684–12689. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Meyer JH, Ginovart N, Boovariwala A,
Sagrati S, Hussey D, Garcia A, Young T, Praschak-Rieder N, Wilson
AA and Houle S: Elevated monoamine oxidase a levels in the brain:
An explanation for the monoamine imbalance of major depression.
Arch Gen Psychiatry. 63:1209–1216. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Cohen IL, Liu X, Lewis ME, Chudley A,
Forster-Gibson C, Gonzalez M, Jenkins EC, Brown WT and Holden JJ:
Autism severity is associated with child and maternal MAOA
genotypes. Clin Genet. 79:355–362. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Scott AL, Bortolato M, Chen K and Shih JC:
Novel monoamine oxidase A knock out mice with human-like
spontaneous mutation. Neuroreport. 19:739–743. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Vishnivetskaya GB, Skrinskaya JA, Seif I
and Popova NK: Effect of MAO A deficiency on different kinds of
aggression and social investigation in mice. Aggress Behav. 33:1–6.
2007. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Brunner HG, Nelen M, Breakefield XO,
Ropers HH and van Oost BA: Abnormal behavior associated with a
point mutation in the structural gene for monoamine oxidase A.
Science. 262:578–580. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Mohapel P, Leanza G, Kokaia M and Lindvall
O: Forebrain acetylcholine regulates adult hippocampal neurogenesis
and learning. Neurobiol Aging. 26:939–946. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Oda Y: Choline acetyltransferase: The
structure, distribution and pathologic changes in the central
nervous system. Pathol Int. 49:921–937. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Lam KS, Aman MG and Arnold LE:
Neurochemical correlates of autistic disorder: A review of the
literature. Res Dev Disabil. 27:254–289. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Eckenstein F and Sofroniew MV:
Identification of central cholinergic neurons containing both
choline acetyltransferase and acetylcholinesterase and of central
neurons containing only acetylcholinesterase. J Neurosci.
3:2286–2291. 1983.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Shytle RD, Silver AA, Lukas RJ, Newman MB,
Sheehan DV and Sanberg PR: Nicotinic acetylcholine receptors as
targets for antidepressants. Mol Psychiatry. 7:525–535. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Glazer WM and Dickson RA: Clozapine
reduces violence and persistent aggression in schizophrenia. J Clin
Psychiatry. 59(Suppl 3): 8–14. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Miczek KA, Covington HE III, Nikulina EM
Jr and Hammer RP: Aggression and defeat: Persistent effects on
cocaine self-administration and gene expression in peptidergic and
aminergic mesocorticolimbic circuits. Neurosci Biobehav Rev.
27:787–802. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
de Almeida RM, Ferrari PF, Parmigiani S
and Miczek KA: Escalated aggressive behavior: Dopamine, serotonin
and GABA. Eur J Pharmacol. 526:51–64. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Ferrari PF, van Erp AM, Tornatzky W and
Miczek KA: Accumbal dopamine and serotonin in anticipation of the
next aggressive episode in rats. Eur J Neurosci. 17:371–378. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Ferrari PF, Palanza P, Parmigiani S, de
Almeida RM and Miczek KA: Serotonin and aggressive behavior in
rodents and nonhuman primates: Predispositions and plasticity. Eur
J Pharmacol. 526:259–273. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Gogos JA, Morgan M, Luine V, Santha M,
Ogawa S, Pfaff D and Karayiorgou M:
Catechol-O-methyltransferase-deficient mice exhibit sexually
dimorphic changes in catecholamine levels and behavior. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 95:9991–9996. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Chiavegatto S and Nelson RJ: Interaction
of nitric oxide and serotonin in aggressive behavior. Horm Behav.
44:233–241. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Coccaro EF and Kavoussi RJ:
Neuropsychopharmacologic challenge in biological psychiatry. Clin
Chem. 40:319–327. 1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Barkan T, Peled A, Modai I, Barak P,
Weizman A and Rehavi M: Serotonin transporter characteristics in
lymphocytes and platelets of male aggressive schizophrenia patients
compared to non-aggressive schizophrenia patients. Eur
Neuropsychopharmacol. 16:572–579. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Blader JC: Pharmacotherapy and
postdischarge outcomes of child inpatients admitted for aggressive
behavior. J Clin Psychopharmacol. 26:419–425. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Bond AJ: Antidepressant treatments and
human aggression. Eur J Pharmacol. 526:218–225. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Carrillo M, Ricci LA, Coppersmith GA and
Melloni RH Jr: The effect of increased serotonergic
neurotransmission on aggression: A critical meta-analytical review
of preclinical studies. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 205:349–368.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Caldwell EE and Miczek KA: Long-term
citalopram maintenance in mice: Selective reduction of
alcohol-heightened aggression. Psychopharmacology (Berl).
196:407–416. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Deutch AY and Roth RH: Neurotransmitters.
Fundamental Neuroscience. Squire L, Berg S, Bloom F, du Lac S,
Ghosh A and Spitzer N: 3rd edition. Elsevier/Academic Press;
Amsterdam: pp. 1432008
|
|
43
|
Holmes A, Murphy DL and Crawley JN:
Reduced aggression in mice lacking the serotonin transporter.
Psychopharmacology (Berl). 161:160–167. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|