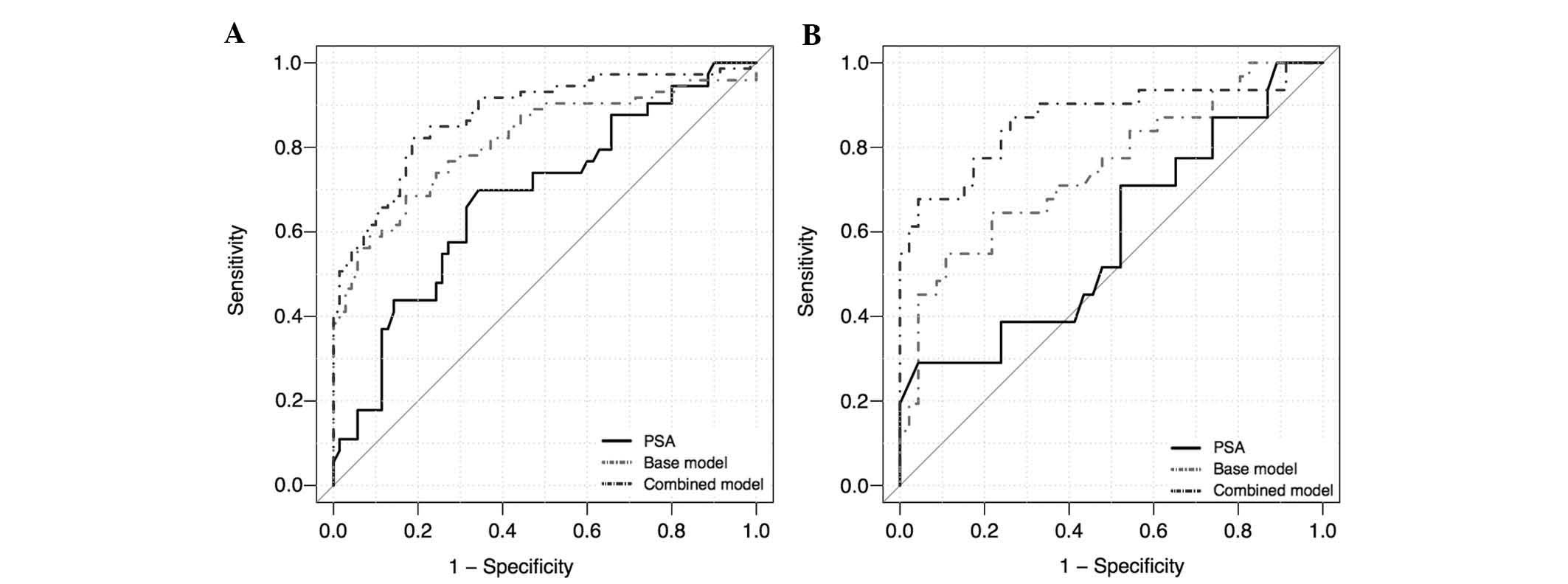
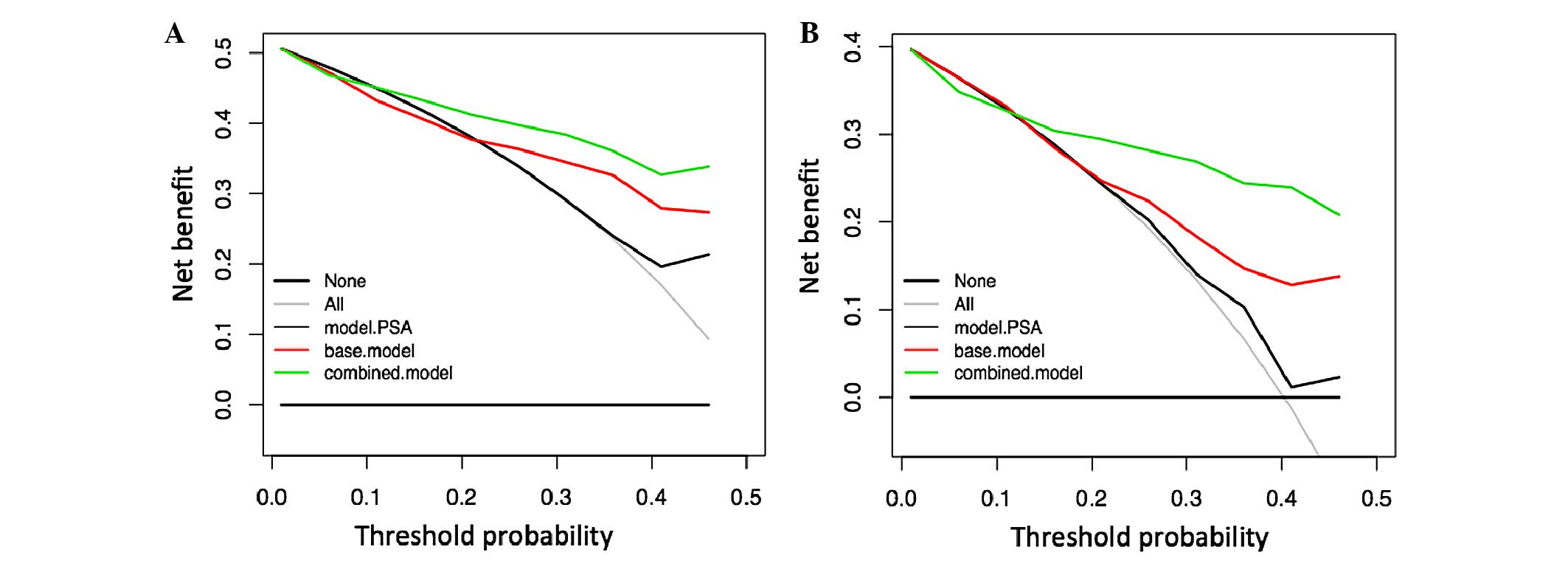
|
1
|
Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, Ferlay J,
Lortet-Tieulent J and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA
Cancer J Clin. 65:87–108. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
De Marzo AM, DeWeese TL, Platz EA, Meeker
AK, Nakayama M, Epstein JI, Isaacs WB and Nelson WG: Pathological
and molecular mechanisms of prostate carcinogenesis: Implications
for diagnosis, detection, prevention, and treatment. J Cell
Biochem. 91:459–477. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Schröder FH, Hugosson J, Roobol MJ,
Tammela TL, Ciatto S, Nelen V, Kwiatkowski M, Lujan M, Lilja H,
Zappa M, et al: Screening and prostate-cancer mortality in a
randomized European study. N Engl J Med. 360:1320–1328. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Shappell SB: Clinical utility of prostate
carcinoma molecular diagnostic tests. Rev Urol. 10:44–69.
2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Dall'Era MA, Albertsen PC, Bangma C,
Carroll PR, Carter HB, Cooperberg MR, Freedland SJ, Klotz LH,
Parker C and Soloway MS: Active surveillance for prostate cancer: A
systematic review of the literature. Eur Urol. 62:976–983. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Romero Otero J, Garcia Gomez B, Campos
Juanatey F and Touijer KA: Prostate cancer biomarkers: An update.
Urol Oncol. 32:252–260. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Mao G, Liu Y, Fang X, Liu Y, Fang L, Lin
L, Liu X and Wang N: Tumor-derived microRNA-494 promotes
angiogenesis in non-small cell lung cancer. Angiogenesis.
18:373–382. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Kulshreshtha R, Ferracin M, Wojcik SE,
Garzon R, Alder H, Agosto-Perez FJ, Davuluri R, Liu CG, Croce CM,
Negrini M, et al: A microRNA signature of hypoxia. Mol Cell Biol.
27:1859–1867. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
9
|
Katz B, Reis ST, Viana NI, Morais DR,
Moura CM, Dip N, Silva IA, Iscaife A, Srougi M and Leite KR:
Comprehensive study of gene and microRNA expression related to
epithelial-mesenchymal transition in prostate cancer. PLoS One.
9:e1137002014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Wang Y, Kim S and Kim IM: Regulation of
Metastasis by microRNAs in Ovarian Cancer. Front Oncol. 4:1432014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Bouyssou JM, Manier S, Huynh D, Issa S,
Roccaro AM and Ghobrial IM: Regulation of microRNAs in cancer
metastasis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1845:255–265. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Fang YX and Gao WQ: Roles of microRNAs
during prostatic tumorigenesis and tumor progression. Oncogene.
33:135–147. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Ambs S, Prueitt RL, Yi M, Hudson RS, Howe
TM, Petrocca F, Wallace TA, Liu CG, Volinia S, Calin GA, et al:
Genomic profiling of microRNA and messenger RNA reveals deregulated
microRNA expression in prostate cancer. Cancer Res. 68:6162–6170.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Porkka KP, Pfeiffer MJ, Waltering KK,
Vessella RL, Tammela TL and Visakorpi T: MicroRNA expression
profiling in prostate cancer. Cancer Res. 67:6130–6135. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Salido-Guadarrama I, Romero-Cordoba S,
Peralta-Zaragoza O, Hidalgo-Miranda A and Rodriguez-Dorantes M:
MicroRNAs transported by exosomes in body fluids as mediators of
intercellular communication in cancer. Onco Targets Ther.
7:1327–1338. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Moltzahn F, Olshen AB, Baehner L, Peek A,
Fong L, Stöppler H, Simko J, Hilton JF, Carroll P and Blelloch R:
Microfluidic-based multiplex qRT-PCR identifies diagnostic and
prognostic microRNA signatures in the sera of prostate cancer
patients. Cancer Res. 71:550–560. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
17
|
Brase JC, Johannes M, Schlomm T, Fälth M,
Haese A, Steuber T, Beissbarth T, Kuner R and Sültmann H:
Circulating miRNAs are correlated with tumor progression in
prostate cancer. Int J Cancer. 128:608–616. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Park NJ, Zhou H, Elashoff D, Henson BS,
Kastratovic DA, Abemayor E and Wong DT: Salivary microRNA:
Discovery, characterization, and clinical utility for oral cancer
detection. Clin Cancer Res. 15:5473–5477. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Srivastava A, Goldberger H, Dimtchev A,
Ramalinga M, Chijioke J, Marian C, Oermann EK, Uhm S, Kim JS, Chen
LN, et al: MicroRNA profiling in prostate cancer-the diagnostic
potential of urinary miR-205 and miR-214. PLoS One. 8:e769942013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Sapre N, Hong MK, Macintyre G, Lewis H,
Kowalczyk A, Costello AJ, Corcoran NM and Hovens CM: Curated
microRNAs in urine and blood fail to validate as predictive
biomarkers for high-risk prostate cancer. PLoS One. 9:e917292014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Eissa S, Habib H, Ali E and Kotb Y:
Evaluation of urinary miRNA-96 as a potential biomarker for bladder
cancer diagnosis. Med Oncol. 32:4132015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Haj-Ahmad TA, Abdalla MA and Haj-Ahmad Y:
Potential urinary miRNA biomarker candidates for the accurate
detection of prostate cancer among benign prostatic hyperplasia
patients. J Cancer. 5:182–191. 2014. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Groskopf J, Aubin SM, Deras IL, Blase A,
Bodrug S, Clark C, Brentano S, Mathis J, Pham J, Meyer T, et al:
APTIMA PCA3 molecular urine test: Development of a method to aid in
the diagnosis of prostate cancer. Clin Chem. 52:1089–1095. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Lewis H, Lance R, Troyer D, Beydoun H,
Hadley M, Orians J, Benzine T, Madric K, Semmes OJ, Drake R and
Esquela-Kerscher A: miR-888 is an expressed prostatic
secretions-derived microRNA that promotes prostate cell growth and
migration. Cell Cycle. 13:227–239. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
25
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Suyundikov A, Stevens JR, Corcoran C,
Herrick J, Wolff RK and Slattery ML: Incorporation of subject-level
covariates in quantile normalization of miRNA data. BMC Genomics.
16:10452015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Ukimura O, Coleman JA, de la Taille A,
Emberton M, Epstein JI, Freedland SJ, Giannarini G, Kibel AS,
Montironi R, Ploussard G, et al: Contemporary role of systematic
prostate biopsies: Indications, techniques, and implications for
patient care. Eur Urol. 63:214–230. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Loeb S, Han M, Roehl KA, Antenor JA and
Catalona WJ: Accuracy of prostate weight estimation by digital
rectal examination versus transrectal ultrasonography. J Urol.
173:63–65. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Levy DA and Jones JS: Management of rising
prostate-specific antigen after a negative biopsy. Curr Urol Rep.
12:197–202. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Jamaspishvili T, Kral M, Khomeriki I,
Student V, Kolar Z and Bouchal J: Urine markers in monitoring for
prostate cancer. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis. 13:12–19. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Korzeniewski N, Tosev G, Pahernik S,
Hadaschik B, Hohenfellner M and Duensing S: Identification of
cell-free microRNAs in the urine of patients with prostate cancer.
Urol Oncol. 33:16.e17–e22. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Stephan C, Jung M, Rabenhorst S, Kilic E
and Jung K: Urinary miR-183 and miR-205 do not surpass PCA3 in
urine as predictive markers for prostate biopsy outcome despite
their highly dysregulated expression in prostate cancer tissue.
Clin Chem Lab Med. 53:1109–1118. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Kim J, Morley S, Le M, Bedoret D, Umetsu
DT, Di Vizio D and Freeman MR: Enhanced shedding of extracellular
vesicles from amoeboid prostate cancer cells: Potential effects on
the tumor microenvironment. Cancer Biol Ther. 15:409–418. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Hessvik NP, Phuyal S, Brech A, Sandvig K
and Llorente A: Profiling of microRNAs in exosomes released from
PC-3 prostate cancer cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1819:1154–1163.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Schröder FH, Raaijmakers R, Postma R, van
der Kwast TH and Roobol MJ: 4-year prostate specific antigen
progression and diagnosis of prostate cancer in the European
randomized study of screening for prostate cancer, section
Rotterdam. J Urol. 174:489–494; discussion 493–494. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Fitzgerald M, Saville BR and Lewis RJ:
Decision curve analysis. JAMA. 313:409–410. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Tomlins SA: Urine PCA3 and TMPRSS2: ERG
using cancer-specific markers to detect cancer. Eur Urol.
65:543–545. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Cornu JN, Cancel-Tassin G, Egrot C,
Gaffory C, Haab F and Cussenot O: Urine TMPRSS2: ERG fusion
transcript integrated with PCA3 score, genotyping, and biological
features are correlated to the results of prostatic biopsies in men
at risk of prostate cancer. Prostate. 73:242–249. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Roobol MJ, Schröder FH, van Leeuwen P,
Wolters T, van den Bergh RC, van Leenders GJ and Hessels D:
Performance of the prostate cancer antigen 3 (PCA3) gene and
prostate-specific antigen in prescreened men: Exploring the value
of PCA3 for a first-line diagnostic test. Eur Urol. 58:475–481.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Leite KR, Tomiyama A, Reis ST,
Sousa-Canavez JM, Sañudo A, Camara-Lopes LH and Srougi M: MicroRNA
expression profiles in the progression of prostate cancer - from
high-grade prostate intraepithelial neoplasia to metastasis. Urol
Oncol. 31:796–801. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Leite KR, Tomiyama A, Reis ST,
Sousa-Canavez JM, Sañudo A, Dall'Oglio MF, Camara-Lopes LH and
Srougi M: MicroRNA-100 expression is independently related to
biochemical recurrence of prostate cancer. J Urol. 185:1118–1122.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Cheng HH, Mitchell PS, Kroh EM, Dowell AE,
Chéry L, Siddiqui J, Nelson PS, Vessella RL, Knudsen BS, Chinnaiyan
AM, et al: Circulating microRNA profiling identifies a subset of
metastatic prostate cancer patients with evidence of
cancer-associated hypoxia. PLoS One. 8:e692392013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Mitchell PS, Parkin RK, Kroh EM, Fritz BR,
Wyman SK, Pogosova-Agadjanyan EL, Peterson A, Noteboom J, O'Briant
KC, Allen A, et al: Circulating microRNAs as stable blood-based
markers for cancer detection. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
105:10513–10518. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Mueller AC, Sun D and Dutta A: The miR-99
family regulates the DNA damage response through its target SNF2H.
Oncogene. 32:1164–1172. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|