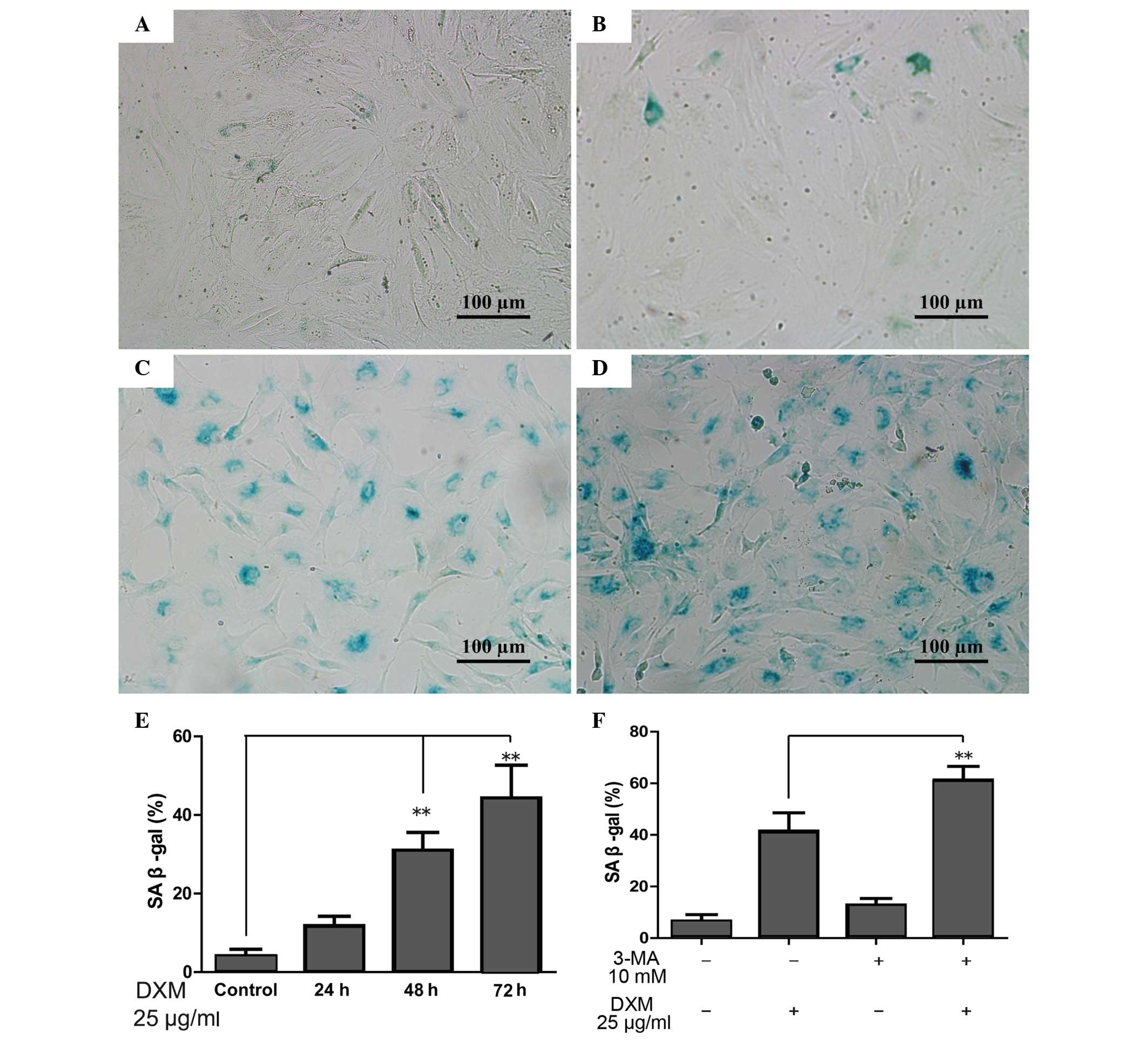
|
1
|
Reyes C, Garcia-Gil M, Elorza JM,
Mendez-Boo L, Hermosilla E, Javaid MK, Cooper C, Diez-Perez A,
Arden NK, Bolibar B, et al: Socio-economic status and the risk of
developing hand, hip or knee osteoarthritis: A region-wide
ecological study. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 23:1323–1329. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Takayama K, Kawakami Y, Kobayashi M, Greco
N, Cummins JH, Matsushita T, Kuroda R, Kurosaka M, Fu FH and Huard
J: Local intra-articular injection of rapamycin delays articular
cartilage degeneration in a murine model of osteoarthritis.
Arthritis Res Ther. 16:4822014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
López de Figueroa P, Lotz MK, Blanco FJ
and Caramés B: Autophagy activation and protection from
mitochondrial dysfunction in human chondrocytes. Arthritis
Rheumatol. 67:966–976. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Caramés B, Hasegawa A, Taniguchi N, Miyaki
S, Blanco FJ and Lotz M: Autophagy activation by rapamycin reduces
severity of experimental osteoarthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 71:575–581.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
5
|
Zhang M, Zhang J, Lu L, Qiu ZY, Zhang X,
Yu SB, Wu YP and Wang MQ: Enhancement of chondrocyte autophagy is
an early response in the degenerative cartilage of the
temporomandibular joint to biomechanical dental stimulation.
Apoptosis. 18:423–434. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Martinet W, De Meyer GR, Herman AG and
Kockx MM: Amino acid deprivation induces both apoptosis and
autophagy in murine C2C12 muscle cells. Biotechnol Lett.
27:1157–1163. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Park EY and Park JB: High glucose-induced
oxidative stress promotes autophagy through mitochondrial damage in
rat notochordal cells. Int Orthop. 37:2507–2514. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Stevens DG, Beharry R, McKee MD, Waddell
JP and Schemitsch EH: The long-term functional outcome of
operatively treated tibial plateau fractures. J Orthop Trauma.
15:312–320. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Martin JA, Brown TD, Heiner AD and
Buckwalter JA: Chondrocyte senescence, joint loading and
osteoarthritis. Clin Orthop Relat Res. (427 Suppl): S96–S103. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Martin JA and Buckwalter JA: Telomere
erosion and senescence in human articular cartilage chondrocytes. J
Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 56:B172–B179. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Buckwalter JA, Martin J and Mankin HJ:
Synovial joint degeneration and the syndrome of osteoarthritis.
Instr Course Lect. 49:481–489. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Tu Y, Xue H, Francis W, Davies AP,
Pallister I, Kanamarlapudi V and Xia Z: Lactoferrin inhibits
dexamethasone-induced chondrocyte impairment from osteoarthritic
cartilage through up-regulation of extracellular signal-regulated
kinase 1/2 and suppression of FASL, FAS, and Caspase 3. Biochem
Biophys Res Commun. 441:249–255. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Zaman F, Chrysis D, Huntjens K, Chagin A,
Takigawa M, Fadeel B and Sävendahl L: Dexamethasone differentially
regulates Bcl-2 family proteins in human proliferative
chondrocytes: Role of pro-apoptotic Bid. Toxicol Lett. 224:196–200.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Hong D, Chen HX, Yu HQ, Wang C, Deng HT,
Lian QQ and Ge RS: Quantitative proteomic analysis of
dexamethasone-induced effects on osteoblast differentiation,
proliferation, and apoptosis in MC3T3-E1 cells using SILAC.
Osteoporos Int. 22:2175–2186. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Aigner T, Hemmel M, Neureiter D, Gebhard
PM, Zeiler G, Kirchner T and McKenna L: Apoptotic cell death is not
a widespread phenomenon in normal aging and osteoarthritis human
articular knee cartilage: A study of proliferation, programmed cell
death (apoptosis), and viability of chondrocytes in normal and
osteoarthritic human knee cartilage. Arthritis Rheum. 44:1304–1312.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Caramés B, Olmer M, Kiosses WB and Lotz
MK: The relationship of autophagy defects and cartilage damage
during joint aging in a mouse model. Arthritis Rheumatol.
67:1568–1576. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
17
|
Wu X, Won H and Rubinsztein DC: Autophagy
and mammalian development. Biochem Soc Trans. 41:1489–1494. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Levine B and Kroemer G: Autophagy in the
pathogenesis of disease. Cell. 132:27–42. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Sasaki H, Takayama K, Matsushita T, Ishida
K, Kubo S, Matsumoto T, Fujita N, Oka S, Kurosaka M and Kuroda R:
Autophagy modulates osteoarthritis-related gene expressions in
human chondrocytes. Arthritis Rheum. 64:1920–1928. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Alayev A and Holz MK: mTOR signaling for
biological control and cancer. J Cell Physiol. 228:1658–1664. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Caramés B, Kiosses WB, Akasaki Y, Brinson
DC, Eap W, Koziol J and Lotz MK: Glucosamine activates autophagy in
vitro and in vivo. Arthritis Rheum. 65:1843–1852. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Poulsen RC, Watts AC, Murphy RJ, Snelling
SJ, Carr AJ and Hulley PA: Glucocorticoids induce senescence in
primary human tenocytes by inhibition of sirtuin 1 and activation
of the p53/p21 pathway: In vivo and in vitro evidence. Ann Rheum
Dis. 73:1405–1413. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
23
|
Muller M: Cellular senescence: Molecular
mechanisms, in vivo, significance and redox considerations.
Antioxid Redox Signal. 11:59–98. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Kamalakannan V, Shiny A, Babu S and
Narayanan RB: Autophagy protects monocytes from wolbachia heat
shock protein 60-induced apoptosis and senescence. PLoS Negl Trop
Dis. 9:e00036752015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Ito S, Araya J, Kurita Y, Kobayashi K,
Takasaka N, Yoshida M, Hara H, Minagawa S, Wakui H, Fujii S, et al:
PARK2-mediated mitophagy is involved in regulation of HBEC
senescence in COPD pathogenesis. Autophagy. 11:547–559. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|