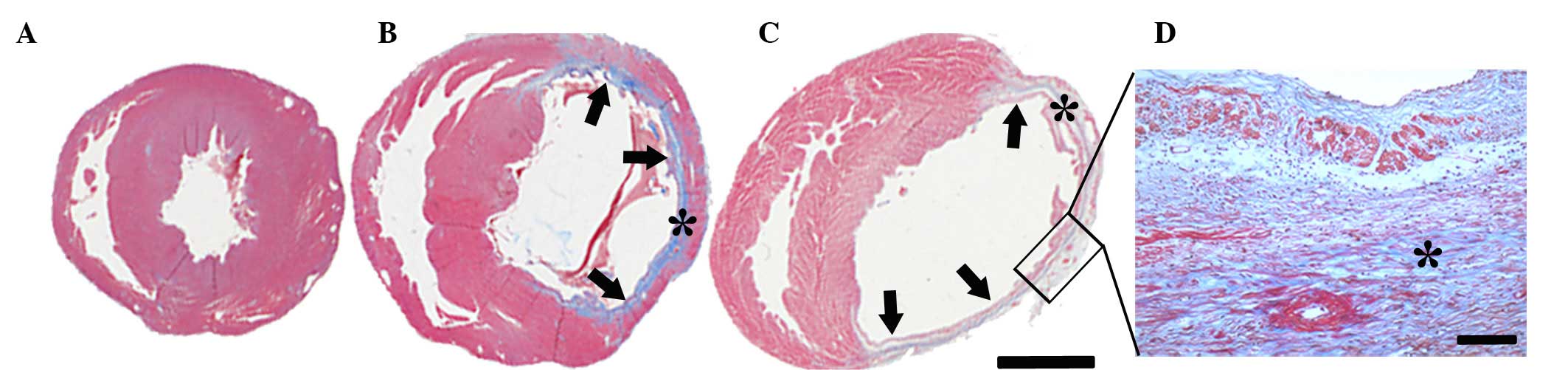
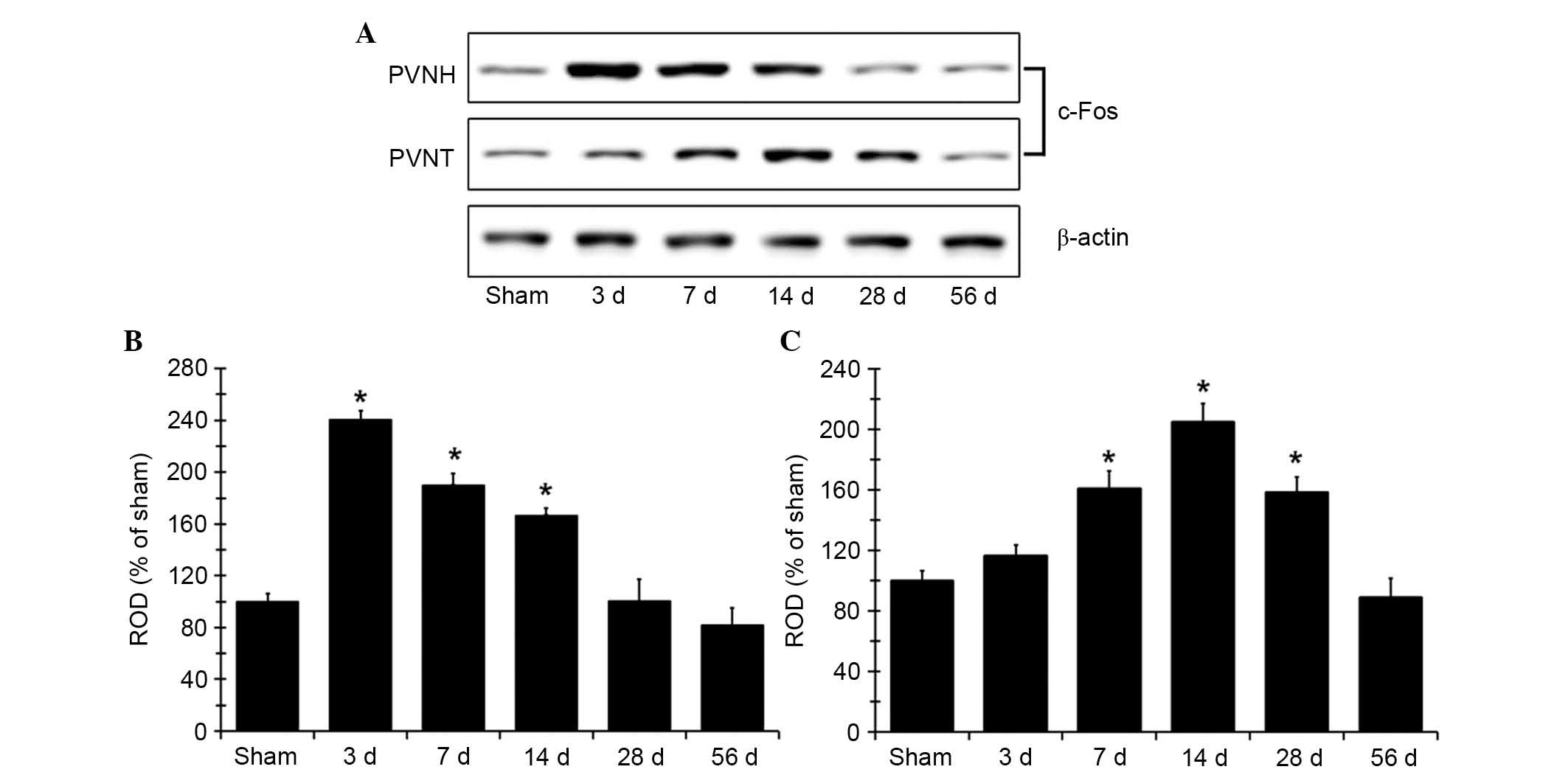
|
1
|
Van de Werf F, Bax J, Betriu A,
Blomstrom-Lundqvist C, Crea F, Falk V, Filippatos G, Fox K, Huber
K, Kastrati A, et al: ESC Committee for Practice Guidelines (CPG):
Management of acute myocardial infarction in patients presenting
with persistent ST-segment elevation: The Task Force on the
Management of ST-Segment Elevation Acute Myocardial Infarction of
the European Society of Cardiology. Eur Heart J. 29:2909–2945.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Kim MS and Kim JJ: Heart and brain
interconnection - clinical implications of changes in brain
function during heart failure. Circ J. 79:942–947. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Hodsman GP, Kohzuki M, Howes LG, Sumithran
E, Tsunoda K and Johnston CI: Neurohumoral responses to chronic
myocardial infarction in rats. Circulation. 78:376–381. 1988.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Frahm C, Haupt C and Witte OW: GABA
neurons survive focal ischemic injury. Neuroscience. 127:341–346.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Wann BP, Boucher M, Kaloustian S, Nim S,
Godbout R and Rousseau G: Apoptosis detected in the amygdala
following myocardial infarction in the rat. Biol Psychiatry.
59:430–433. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Schrier RW and Abraham WT: Hormones and
hemodynamics in heart failure. N Engl J Med. 341:577–585. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Patel KP, Zhang PL and Krukoff TL:
Alterations in brain hexokinase activity associated with heart
failure in rats. Am J Physiol. 265:R923–R928. 1993.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Sole MJ, Hussain MN and Lixfeld W:
Activation of brain catecholaminergic neurons by cardiac vagal
afferents during acute myocardial ischemia in the rat. Circ Res.
47:166–172. 1980. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Sole MJ, Hussain MN, Versteeg DH, de Kloet
ER, Adams D and Lixfeld W: The identification of specific brain
nuclei in which catecholamine turnover is increased by left
ventricular receptors during acute myocardial infarction in the
rat. Brain Res. 235:315–325. 1982. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Sole MJ, Versteeg DH, de Kloet ER, Hussain
N and Lixfeld W: The identification of specific serotonergic nuclei
inhibited by cardiac vagal afferents during acute myocardial
ischemia in the rat. Brain Res. 265:55–61. 1983. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Patel KP, Zhang K, Kenney MJ, Weiss M and
Mayhan WG: Neuronal expression of Fos protein in the hypothalamus
of rats with heart failure. Brain Res. 865:27–34. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Hoffman GE, Smith MS and Verbalis JG:
c-Fos and related immediate early gene products as markers of
activity in neuroendocrine systems. Front Neuroendocrinol.
14:173–213. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Sagar SM, Sharp FR and Curran T:
Expression of c-fos protein in brain: Metabolic mapping at the
cellular level. Science. 240:1328–1331. 1988. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Rockhold RW, Acuff CG and Clower BR:
Excitotoxic lesions of the paraventricular hypothalamus: Metabolic
and cardiac effects. Neuropharmacology. 29:663–673. 1990.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Ahmet I, Tae HJ, Brines M, Cerami A,
Lakatta EG and Talan MI: Chronic administration of small
nonerythropoietic peptide sequence of erythropoietin effectively
ameliorates the progression of postmyocardial infarction-dilated
cardiomyopathy. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 345:446–456. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Hwang IK, Yoo KY, Han TH, Lee CH, Choi JH,
Yi SS, Lee SY, Ryu PD, Yoon YS and Won MH: Enhanced cell
proliferation and neuroblast differentiation in the rat hippocampal
dentate gyrus following myocardial infarction. Neurosci Lett.
450:275–280. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Lee CH, Hwang IK, Choi JH, Yoo KY, Han TH,
Park OK, Lee SY, Ryu PD and Won MH: Calcium binding proteins
immunoreactivity in the rat basolateral amygdala following
myocardial infarction. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 30:333–338. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Lee CH, Park JH, Cho JH, Ahn JH, Yan BC,
Lee JC, Shin MC, Cheon SH, Cho YS, Cho JH, et al: Changes and
expressions of Redd1 in neurons and glial cells in the gerbil
hippocampus proper following transient global cerebral ischemia. J
Neurol Sci. 344:43–50. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Lee JC, Kim IH, Cho GS, Park JH, Ahn JH,
Yan BC, Kwon HM, Kim YM, Cheon SH, Cho JH, et al: Ischemic
preconditioning-induced neuroprotection against transient cerebral
ischemic damage via attenuating ubiquitin aggregation. J Neurol
Sci. 336:74–82. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Lindley TE, Doobay MF, Sharma RV and
Davisson RL: Superoxide is involved in the central nervous system
activation and sympathoexcitation of myocardial infarction-induced
heart failure. Circ Res. 94:402–409. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Sun Y, Zhang JQ, Zhang J and Lamparter S:
Cardiac remodeling by fibrous tissue after infarction in rats. J
Lab Clin Med. 135:316–323. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Fletcher PJ, Pfeffer JM, Pfeffer MA and
Braunwald E: Left ventricular diastolic pressure-volume relations
in rats with healed myocardial infarction. Effects on systolic
function. Circ Res. 49:618–626. 1981. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Kaloustian S, Wann BP, Bah TM, Girard SA,
Apostolakis A, Ishak S, Mathieu S, Ryvlin P, Godbout R and Rousseau
G: Apoptosis time course in the limbic system after myocardial
infarction in the rat. Brain Res. 1216:87–91. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Boucher M, Wann BP, Kaloustian S, Cardinal
R, Godbout R and Rousseau G: Reduction of apoptosis in the amygdala
by an A2A adenosine receptor agonist following
myocardial infarction. Apoptosis. 11:1067–1074. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Arseneault-Bréard J, Rondeau I, Gilbert K,
Girard SA, Tompkins TA, Godbout R and Rousseau G: Combination of
Lactobacillus helveticus R0052 and Bifidobacterium longum R0175
reduces post-myocardial infarction depression symptoms and restores
intestinal permeability in a rat model. Br J Nutr. 107:1793–1799.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Nillni EA: Regulation of the hypothalamic
thyrotropin releasing hormone (TRH) neuron by neuronal and
peripheral inputs. Front Neuroendocrinol. 31:134–156. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Li S and Kirouac GJ: Projections from the
paraventricular nucleus of the thalamus to the forebrain, with
special emphasis on the extended amygdala. J Comp Neurol.
506:263–287. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Fernandes GA, Perks P, Cox NK, Lightman
SL, Ingram CD and Shanks N: Habituation and cross-sensitization of
stress-induced hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal activity: Effect of
lesions in the paraventricular nucleus of the thalamus or bed
nuclei of the stria terminalis. J Neuroendocrinol. 14:593–602.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Penzo MA, Robert V, Tucciarone J, De
Bundel D, Wang M, Van Aelst L, Darvas M, Parada LF, Palmiter RD, He
M, et al: The paraventricular thalamus controls a central amygdala
fear circuit. Nature. 519:455–459. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Spencer SJ, Fox JC and Day TA: Thalamic
paraventricular nucleus lesions facilitate central amygdala
neuronal responses to acute psychological stress. Brain Res.
997:234–237. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Otake K, Kin K and Nakamura Y: Fos
expression in afferents to the rat midline thalamus following
immobilization stress. Neurosci Res. 43:269–282. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Radulovic J, Kammermeier J and Spiess J:
Relationship between fos production and classical fear
conditioning: Effects of novelty, latent inhibition, and
unconditioned stimulus preexposure. J Neurosci. 18:7452–7461.
1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Tischmeyer W and Grimm R: Activation of
immediate early genes and memory formation. Cell Mol Life Sci.
55:564–574. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Vanelzakker MB, Zoladz PR, Thompson VM,
Park CR, Halonen JD, Spencer RL and Diamond DM: Influence of
Pre-Training Predator Stress on the Expression of c-fos mRNA in the
Hippocampus, Amygdala, and Striatum Following Long-Term Spatial
Memory Retrieval. Front Behav Neurosci. 5:302011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Vann SD, Brown MW and Aggleton JP: Fos
expression in the rostral thalamic nuclei and associated cortical
regions in response to different spatial memory tests.
Neuroscience. 101:983–991. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Senba E, Matsunaga K, Tohyama M and
Noguchi K: Stress-induced c-fos expression in the rat brain:
Activation mechanism of sympathetic pathway. Brain Res Bull.
31:329–344. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|