|
1
|
Zhu Y, Li C, Sun A, Wang Y and Zhou S:
Quantification of microRNA-210 in the cerebrospinal fluid and
serum: Implications for Alzheimer's disease. Exp Ther Med.
9:1013–1017. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Chambers JK, Uchida K, Harada T, Tsuboi M,
Sato M, Kubo M, Kawaguchi H, Miyoshi N, Tsujimoto H and Nakayama H:
Neurofibrillary tangles and the deposition of a beta amyloid
peptide with a novel-N-terminal epitope in the brains of wild
Tsushima leopard cats. PLoS One. 7:e464522012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Guo J, Chang L, Zhang X, Pei S, Yu M and
Gao J: Ginsenoside compound K promotes β-amyloid peptide clearance
in primary astrocytes via autophagy enhancement. Exp Ther Med.
8:1271–1274. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Floyd RA and Hensley K: Oxidative stress
in brain aging. Implications for therapeutics of neurodegenerative
diseases. Neurobiol Aging. 23:795–807. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Mattson MP, Chan SL and Duan W:
Modification of brain aging and neurodegenerative disorders by
genes, diet, and behavior. Physiol Rev. 82:637–672. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Huang X, Atwood CS, Hartshorn MA, Multhaup
G, Goldstein LE, Scarpa RC, Cuajungco MP, Gray DN, Lim J, Moir RD,
et al: The A beta peptide of Alzheimer's disease directly produces
hydrogen peroxide through metal ion reduction. Biochemistry.
38:7609–7616. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Christen Y: Oxidative stress and Alzheimer
disease. Am J Clin Nutr. 71:621s–629s. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Sultana R, Perluigi M and Butterfield DA:
Oxidatively modified proteins in Alzheimer's disease (AD), mild
cognitive impairment and animal models of AD: Role of Abeta in
pathogenesis. Acta Neuropathol. 118:131–150. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Zhu X, Su B, Wang X, Smith MA and Perry G:
Causes of oxidative stress in Alzheimer disease. Cell Mol Life Sci.
64:2202–2210. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Mark RJ, Lovell MA, Markesbery WR, Uchida
K and Mattson MP: A role for 4-hydroxynonenal, an aldehydic product
of lipid peroxidation, in disruption of ion homeostasis and
neuronal death induced by amyloid beta-peptide. J Neurochem.
68:255–264. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Butterfield DA, Hensley K, Harris M,
Mattson M and Carney J: beta-amyloid peptide free radical fragments
initiates synaptosomal lipoperoxidation in a sequence-specific
fashion: Implications to Alzheimer's disease. Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 200:710–715. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
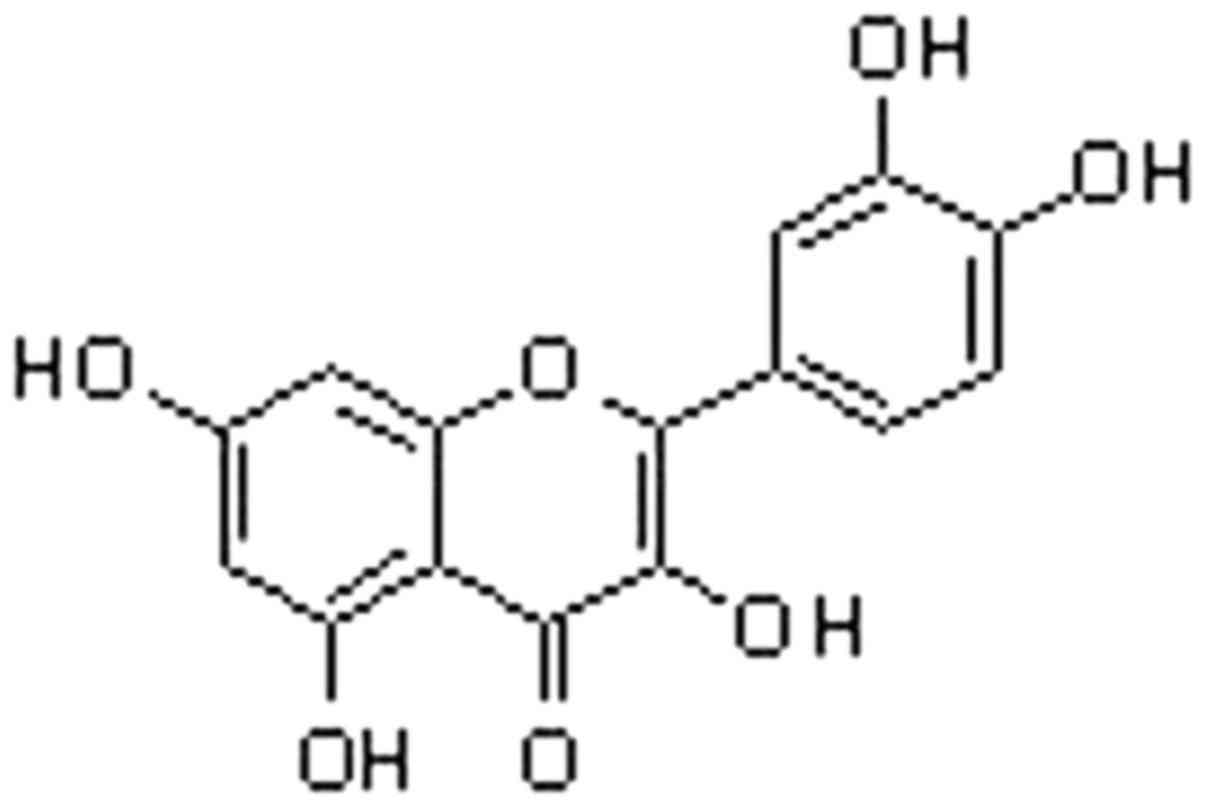
Kelly GS: Quercetin. Monograph. Altern Med
Rev. 16:172–194. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Heim KE, Tagliaferro AR and Bobilya DJ:
Flavonoid antioxidants: Chemistry, metabolism and
structure-activity relationships. J Nutr Biochem. 13:572–584. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Heijnen CG, Haenen GR, Oostveen RM,
Stalpers EM and Bast A: Protection of flavonoids against lipid
peroxidation: The structure activity relationship revisited. Free
Radic Res. 36:575–581. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Cai Q, Rahn RO and Zhang R: Dietary
flavonoids, quercetin, luteolin and genistein, reduce oxidative DNA
damage and lipid peroxidation and quench free radicals. Cancer
Lett. 119:99–107. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Meyers KJ, Rudolf JL and Mitchell AE:
Influence of dietary quercetin on glutathione redox status in mice.
J Agric Food Chem. 56:830–836. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Rivera L, Morón R, Sánchez M, Zarzuelo A
and Galisteo M: Quercetin ameliorates metabolic syndrome and
improves the inflammatory status in obese Zucker rats. Obesity
(Silver Spring). 16:2081–2087. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Phan TT, Lim IJ, Chan SY, Tan EK, Lee ST
and Longaker MT: Suppression of transforming growth factor
beta/smad signaling in keloid-derived fibroblasts by quercetin:
Implications for the treatment of excessive scars. J Trauma.
57:1032–1037. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Jung JC, Jang S, Lee Y, Min D, Lim E, Jung
H, Oh M, Oh S and Jung M: Efficient synthesis and neuroprotective
effect of substituted 1,3-diphenyl-2-propen-1-ones. J Med Chem.
51:4054–4058. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Heneka MT, O'Banion MK, Terwel D and
Kummer MP: Neuroinflammatory processes in Alzheimer's disease. J
Neural Transm (Vienna). 117:919–947. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Kim MJ, Seung AR, Yoo JY, Jin CH, Lee YH,
Kim YJ, Lee J, Jun WJ and Yoon HG: Gallic acid, a histone
acetyltransferase inhibitor, suppresses β-amyloid neurotoxicity by
inhibiting microglial-mediated neuroinflammation. Mol Nutr Food
Res. 55:1798–1808. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Varadarajan S, Yatin S, Aksenova M and
Butterfield DA: Review: Alzheimer's amyloid beta-peptide-associated
free radical oxidative stress and neurotoxicity. J Struct Biol.
130:184–208. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Kadowaki H, Nishitoh H, Urano F, Sadamitsu
C, Matsuzawa A, Takeda K, Masutani H, Yodoi J, Urano Y, Nagano T
and Ichijo H: Amyloid beta induces neuronal cell death through
ROS-mediated ASK1 activation. Cell Death Differ. 12:19–24. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Park SY, Kim HS, Cho EK, Kwon BY, Phark S,
Hwang KW and Sul D: Curcumin protected PC12 cells against
beta-amyloid-induced toxicity through the inhibition of oxidative
damage and tau hyperphosphorylation. Food Chem Toxicol.
46:2881–2887. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Bonda DJ, Wang X, Perry G, Numonura A,
Tabaton M, Zhu X and Smith MA: Oxidative stress in Alzheimer
disease: A possibility for prevention. Neuropharmacololgy.
59:290–294. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|