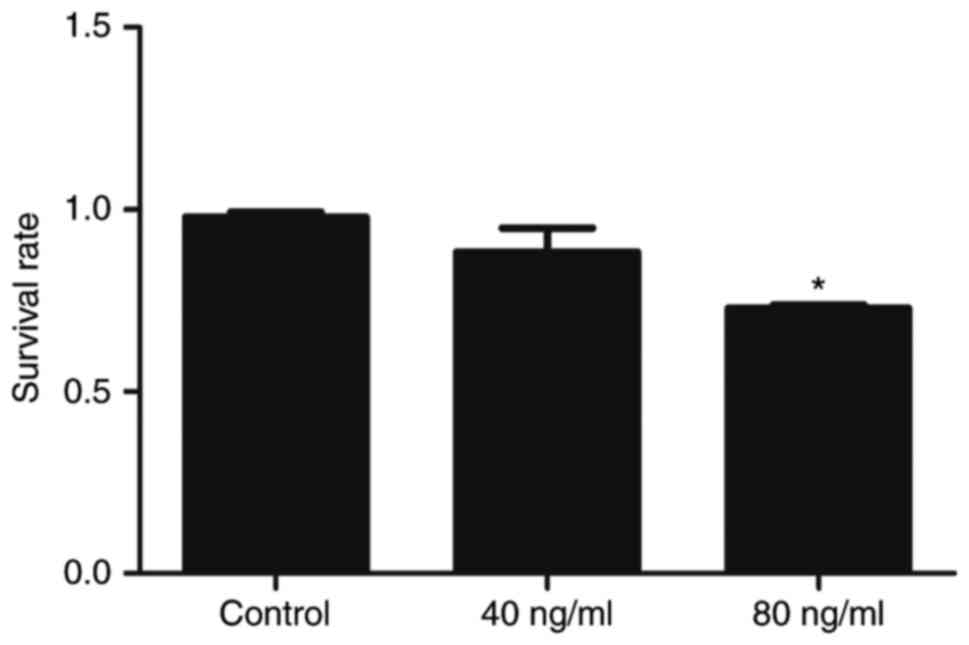
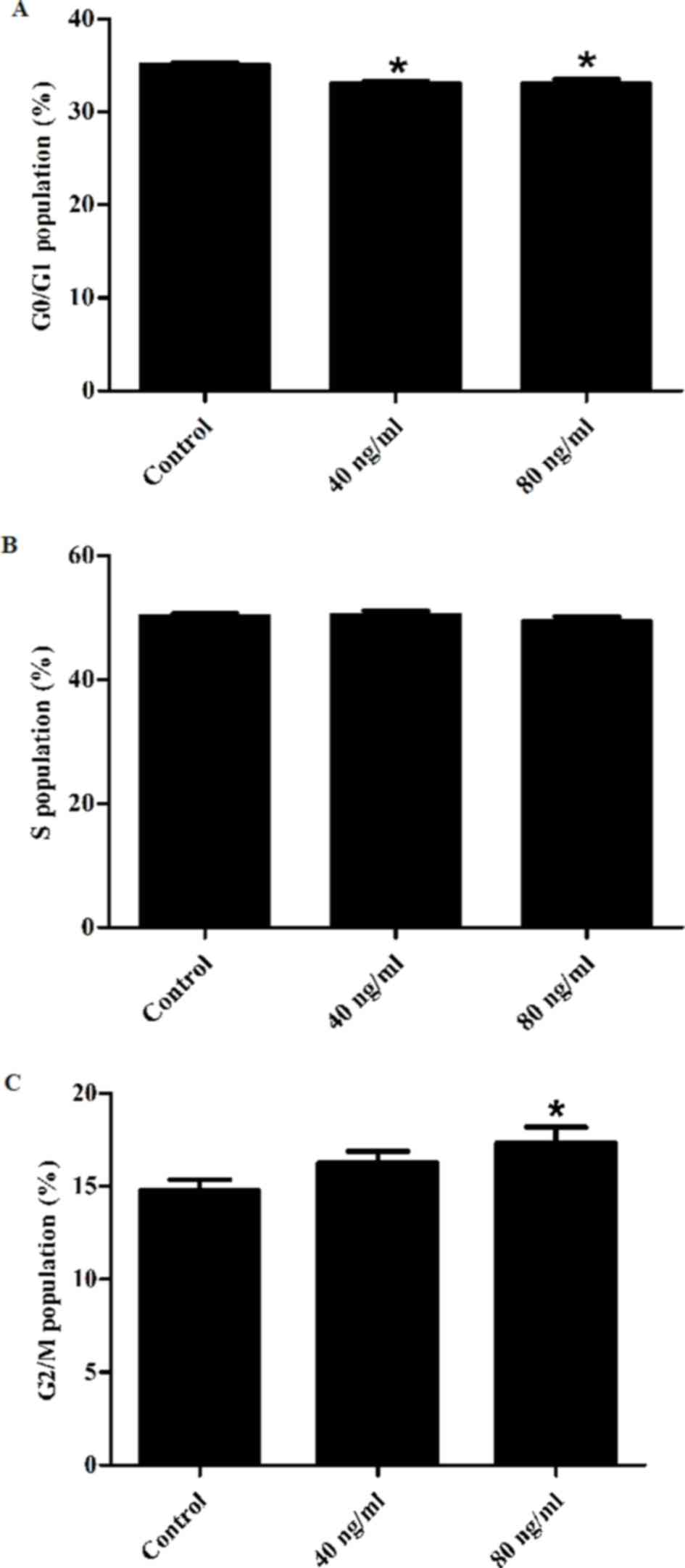
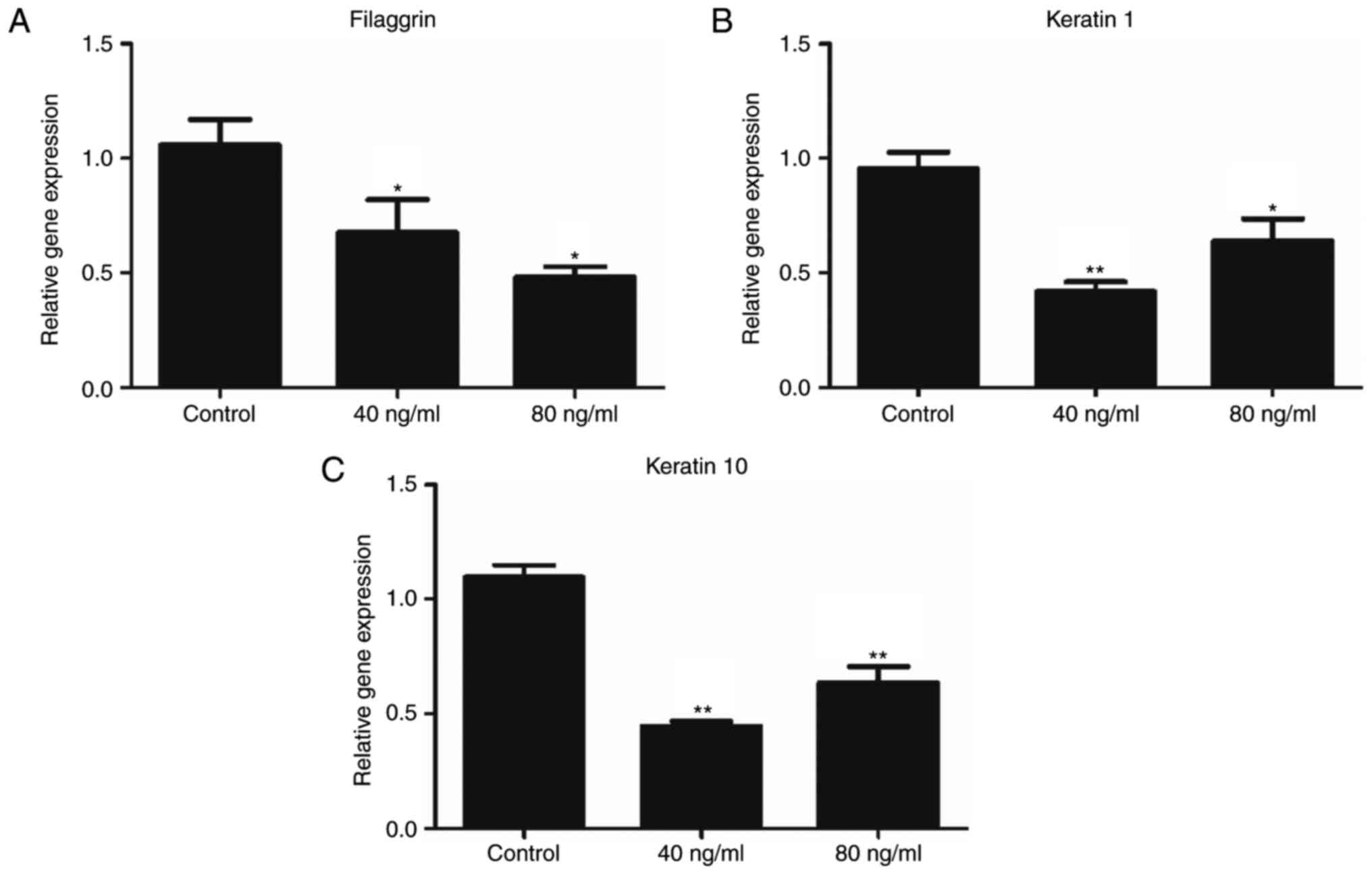
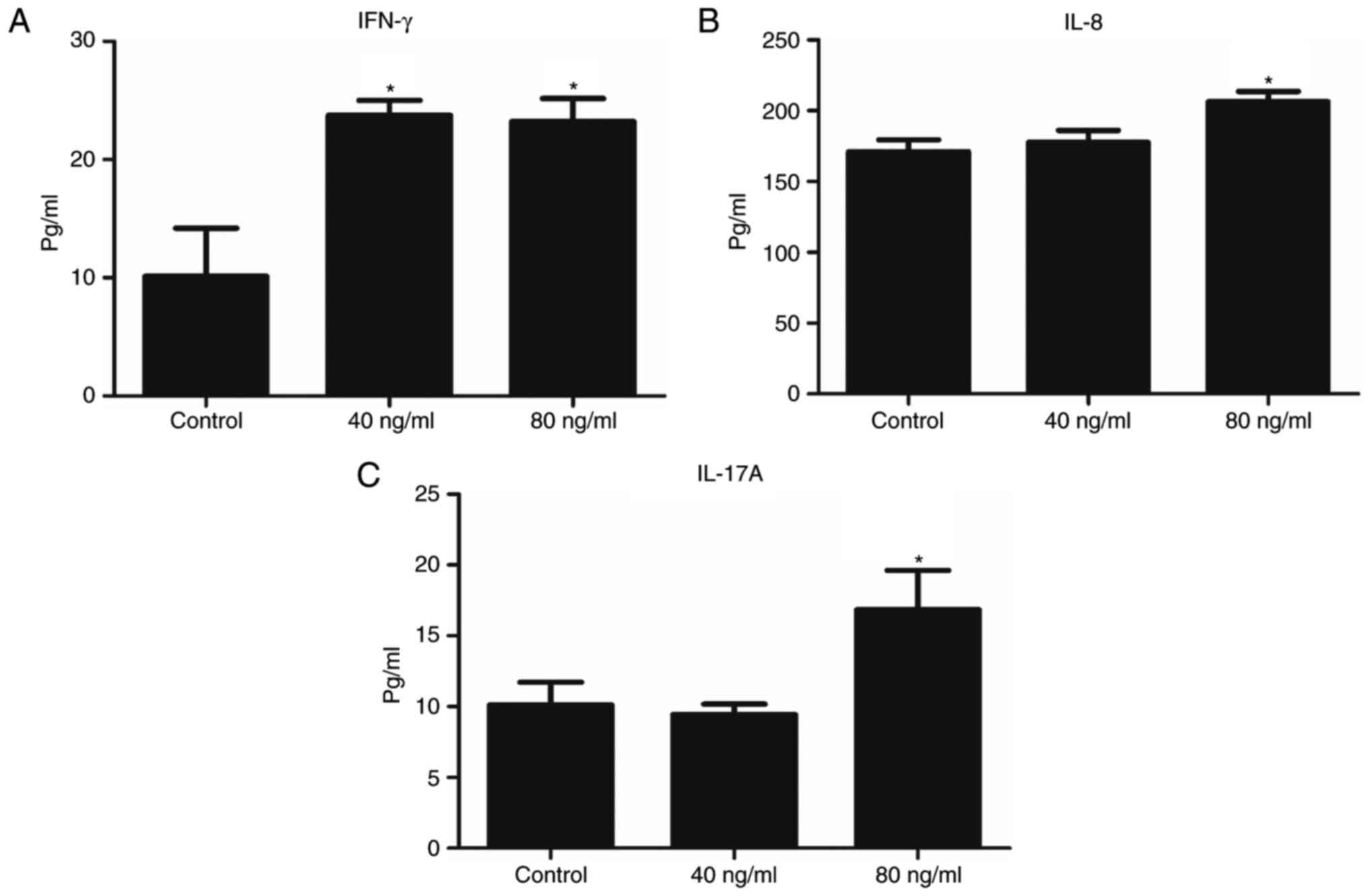
|
1
|
Baliwag J, Barnes DH and Johnston A:
Cytokines in psoriasis. Cytokine. 73:342–350. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Raychaudhuri SK, Maverakis E and
Raychaudhuri SP: Diagnosis and classification of psoriasis.
Autoimmun Rev. 13:490–495. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Gudjonsson JE, Johnston A, Stoll SW,
Riblett MB, Xing X, Kochkodan JJ, Ding J, Nair RP, Aphale A,
Voorhees JJ and Elder JT: Evidence for altered Wnt signaling in
psoriatic skin. J Invest Dermatol. 130:1849–1859. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Weinstein GD, McCullough JL and Ross PA:
Cell kinetic basis for pathophysiology of psoriasis. J Invest
Dermatol. 85:579–583. 1985. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Rabeony H, Petit-Paris I, Garnier J,
Barrault C, Pedretti N, Guilloteau K, Jegou JF, Guillet G, Huguier
V, Lecron JC, et al: Inhibition of keratinocyte differentiation by
the synergistic effect of IL-17A, IL-22, IL-1α, TNFα and oncostatin
M. PLoS One. 9:e1019372014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Nestle FO, Kaplan DH and Barker J:
Psoriasis. N Engl J Med. 361:496–509. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Endo M, Nishita M, Fujii M and Minami Y:
Insight into the role of Wnt5a-induced signaling in normal and
cancer cells. Int Rev Cell Mol Biol. 314:117–148. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Asem MS, Buechler S, Wates RB, Miller DL
and Stack MS: Wnt5a Signaling in Cancer. Cancers. 8:E792016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Liang H, Chen Q, Coles AH, Anderson SJ,
Pihan G, Bradley A, Gerstein R, Jurecic R and Jones SN: Wnt5a
inhibits B cell proliferation and functions as a tumor suppressor
in hematopoietic tissue. Cancer cell. 4:349–360. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Cheng R, Sun B, Liu Z, Zhao X, Qi L, Li Y
and Gu Q: Wnt5a suppresses colon cancer by inhibiting cell
proliferation and epithelial-mesenchymal transition. J Cell
Physiol. 229:1908–1917. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Kumawat K and Gosens R: WNT-5A: Signaling
and functions in health and disease. Cell Mol Life Sci. 73:567–587.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Zhang Y, Tu C, Zhang D, Zheng Y, Peng Z,
Feng Y, Xiao S and Li Z: Wnt/β-Catenin and Wnt5a/Ca pathways
regulate proliferation and apoptosis of keratinocytes in psoriasis
lesions. Cell Physiol Biochem. 36:1890–1902. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Bhatt PM and Malgor R: Wnt5a: A player in
the pathogenesis of atherosclerosis and other inflammatory
disorders. Atherosclerosis. 237:155–162. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Kikuchi A, Yamamoto H, Sato A and
Matsumoto S: Wnt5a: Its signalling, functions and implication in
diseases. Acta physiol(Oxf). 204:17–33. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Malgor R, Bhatt PM, Connolly BA, Jacoby
DL, Feldmann KJ, Silver MJ, Nakazawa M, McCall KD and Goetz DJ:
Wnt5a, TLR2 and TLR4 are elevated in advanced human atherosclerotic
lesions. Inflamm Res. 63:277–285. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Sen M, Chamorro M, Reifert J, Corr M and
Carson DA: Blockade of Wnt-5A/frizzled 5 signaling inhibits
rheumatoid synoviocyte activation. Arthritis Rheum. 44:772–781.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Suarez-Farinas M, Fuentes-Duculan J, Lowes
MA and Krueger JG: Resolved psoriasis lesions retain expression of
a subset of disease-related genes. J Invest Dermatol. 131:391–400.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Wright M, Aikawa M, Szeto W and Papkoff J:
Identification of a Wnt-responsive signal transduction pathway in
primary endothelial cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 263:384–388.
1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Shao Y, Zheng Q, Wang W, Xin N, Song X and
Zhao C: Biological functions of macrophage-derived Wnt5a and its
roles in human diseases. Oncotarget. 7:67674–67684. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Kim J, Chang W, Jung Y, Song K and Lee I:
Wnt5a activates THP-1 monocytic cells via a β-catenin-independent
pathway involving JNK and NF-κB activation. Cytokine. 60:242–248.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Tschachler E: Psoriasis: The epidermal
component. Clin Dermatol. 25:589–595. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Buchau AS and Gallo RL: Innate immunity
and antimicrobial defense systems in psoriasis. Clin Dermatol.
25:616–624. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Soleymani T, Hung T and Soung J: The role
of vitamin D in psoriasis: A review. Int J Dermatol. 54:383–392.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Hohl D: Expression patterns of loricrin in
dermatological disorders. Am J Dermatopathol. 15:20–27. 1993.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Bernard BA, Asselineau D,
Schaffar-Deshayes L and Darmon MY: Abnormal sequence of expression
of differentiation markers in psoriatic epidermis: Inversion of two
steps in the differentiation program? J Invest Dermatol.
90:801–805. 1988. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Gschwandtner M, Mildner M, Mlitz V, Gruber
F, Eckhart L, Werfel T, Gutzmer R, Elias PM and Tschachler E:
Histamine suppresses epidermal keratinocyte differentiation and
impairs skin barrier function in a human skin model. Allergy.
68:37–47. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Yu J, Chen L, Cui B, Widhopf GF II, Shen
Z, Wu R, Zhang L, Zhang S, Briggs SP and Kipps TJ: Wnt5a induces
ROR1/ROR2 heterooligomerization to enhance leukemia chemotaxis and
proliferation. J Clin Invest. 126:585–598. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Thiele S, Göbel A, Rachner TD, Fuessel S,
Froehner M, Muders MH, Baretton GB, Bernhardt R, Jakob F, Glüer CC,
et al: WNT5A has anti-prostate cancer effects in vitro and reduces
tumor growth in the skeleton in vivo. J Bone Miner Res. 30:471–480.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Xing Y, Ma X, Guo H, Deng F, Yang J and Li
Y: Wnt5a Suppresses β-catenin signaling during hair follicle
regeneration. Int J Med Sci. 13:603–610. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Tarapore RS, Siddiqui IA, Saleem M, Adhami
VM, Spiegelman VS and Mukhtar H: Specific targeting of
Wnt/β-catenin signaling in human melanoma cells by a dietary
triterpene lupeol. Carcinogenesis. 31:1844–1853. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Shi W, Hu J, Zhu S, Shen X, Zhang X, Yang
C, Gao H and Zhang H: Expression of MTA2 and Ki-67 in
hepatocellular carcinoma and their correlation with prognosis. Int
J Clin Exp Pathol. 8:13083–13089. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Hampton PJ, Ross OK and Reynolds NJ:
Increased nuclear beta-catenin in suprabasal involved psoriatic
epidermis. Br J Dermatol. 157:1168–1177. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Yamazaki F, Aragane Y, Kawada A and Tezuka
T: Immunohistochemical detection for nuclear beta-catenin in
sporadic basal cell carcinoma. Br J Dermatol. 145:771–777. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|