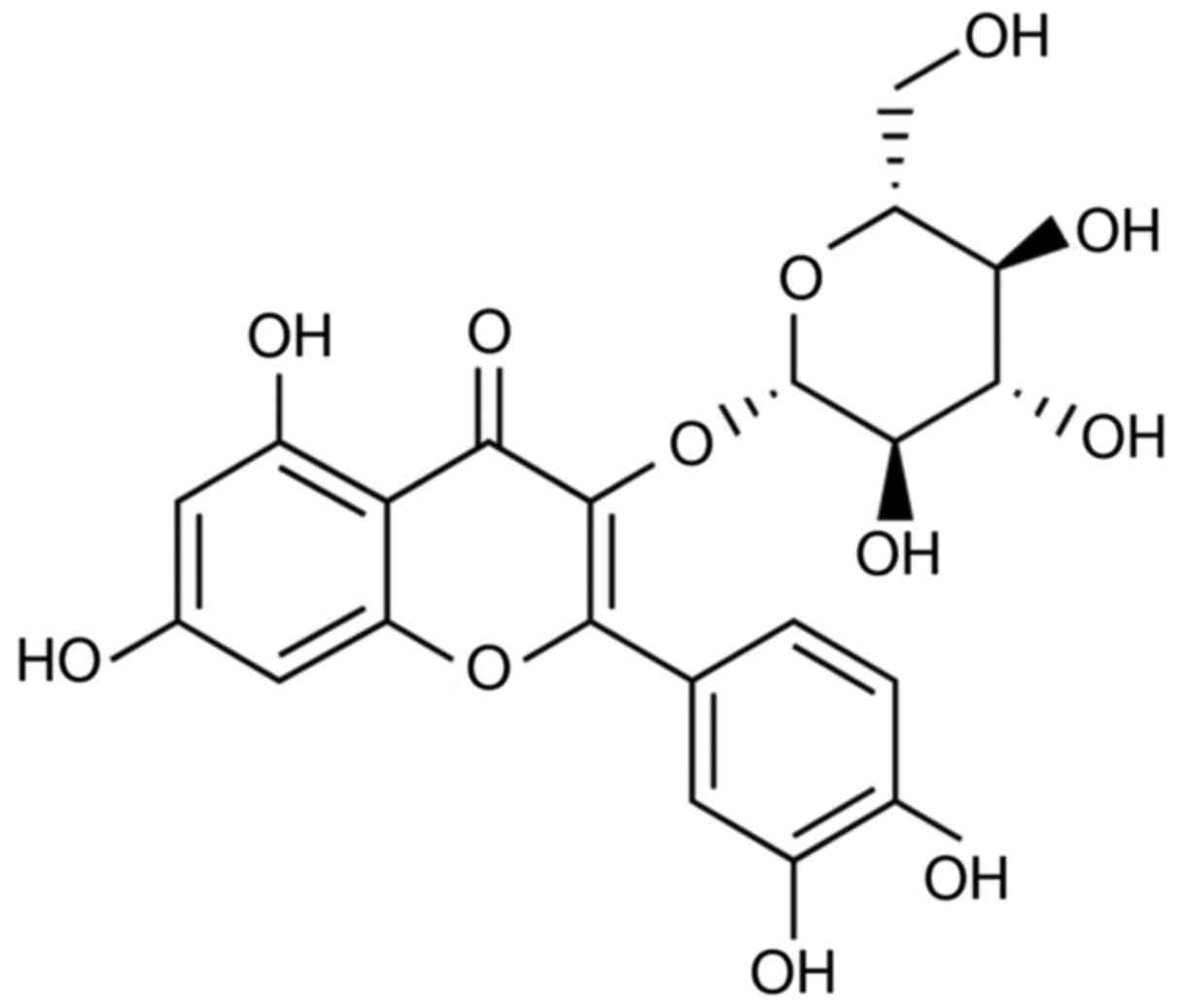
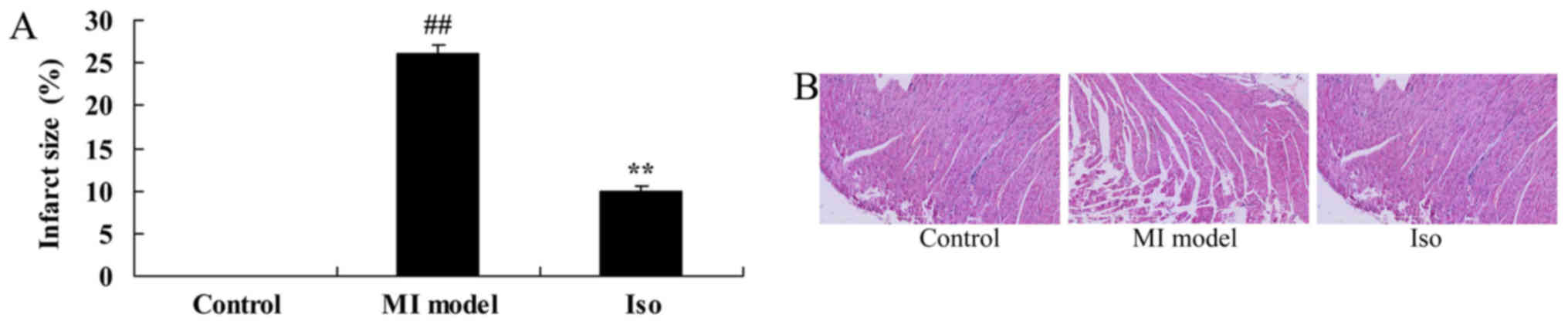
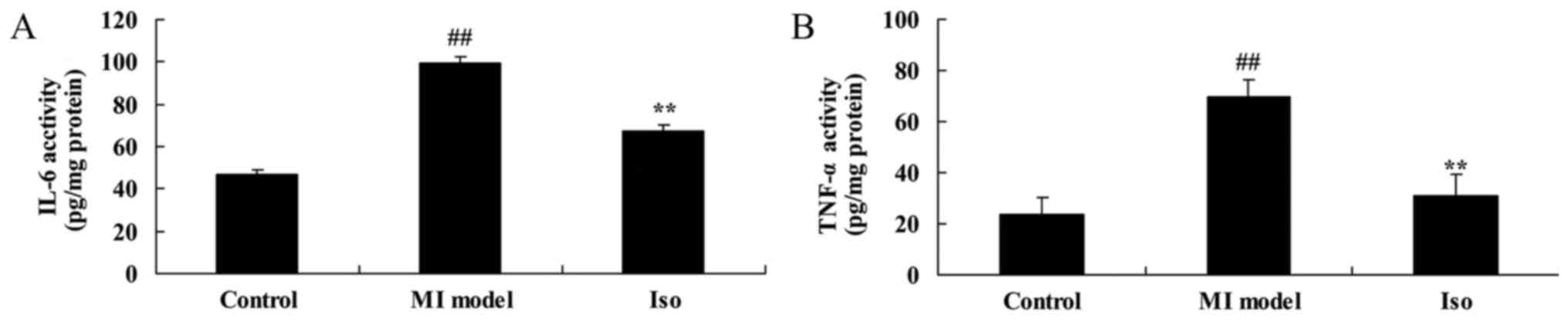
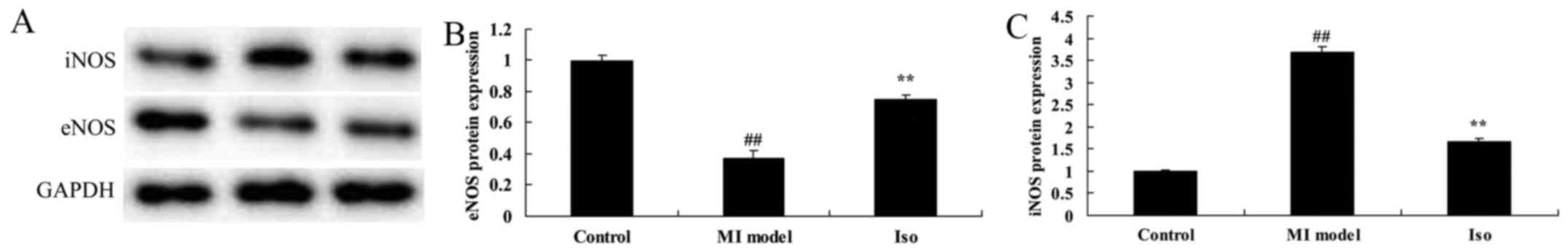
|
1
|
Morita Y, Maeda K, Kondo T, Ishii H,
Matsudaira K, Okumura N, Mitsuhashi H, Shibata R and Murohara T:
Nagoya Acute Myocardial Infarction Study (NAMIS) Group: Impact of
adiponectin and leptin on long-term adverse events in Japanese
patients with acute myocardial infarction. Results from the Nagoya
Acute Myocardial Infarction Study (NAMIS). Circ J. 77:2778–2785.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Jensen LJ, Munk K, Flyvbjerg A, Bøtker HE
and Bjerre M: Soluble receptor of advanced glycation end-products
in patients with acute myocardial infarction treated with remote
ischaemic conditioning. Clin Lab. 61:323–328. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Tanaka S, Masuda T, Kamiya K, Hamazaki N,
Akiyama A, Kamada Y, Maekawa E, Noda C, Yamaoka-Tojo M and Ako J: A
Single session of neuromuscular electrical stimulation enhances
vascular endothelial function and peripheral blood circulation in
patients with acute myocardial infarction. Int Heart J. 57:676–681.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Høfsten DE, Kelbæk H, Helqvist S,
Kløvgaard L, Holmvang L, Clemmensen P, Torp-Pedersen C, Tilsted HH,
Bøtker HE, Jensen LO, et al: The third DANish study of optimal
acute treatment of patients with ST-segment elevation myocardial
infarction: Ischemic postconditioning or deferred stent
implantation versus conventional primary angioplasty and complete
revascularization versus treatment of culprit lesion only:
Rationale and design of the DANAMI 3 trial program. Am Heart J.
169:613–621. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Uysal H and Ozcan Ş: The effect of
individual education on patients' physical activity capacity after
myocardial infarction. Int J Nurs Pract. 21:18–28. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Li Z, Li Y, Zhang T, Miao W and Su G:
Comparison of the influence of ticagrelor and clopidogrel on
inflammatory biomarkers and vascular endothelial function for
patients with ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction receiving
emergency percutaneous coronary intervention: Study protocol for a
randomized controlled trial. Trials. 17:752016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Stefanadi E, Tousoulis D, Antoniades C,
Katsi V, Bosinakou E, Vavuranakis E, Triantafyllou G, Marinou K,
Tsioufis C, Papageorgiou N, et al: Early initiation of low-dose
atorvastatin treatment after an acute ST-elevated myocardial
infarction, decreases inflammatory process and prevents endothelial
injury and activation. Int J Cardiol. 133:266–268. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Cheng L, Jin Z, Zhao R, Ren K, Deng C and
Yu S: Resveratrol attenuates inflammation and oxidative stress
induced by myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury: Role of Nrf2/ARE
pathway. Int J Clin Exp Med. 8:10420–10428. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Cheng XY, Gu XY, Gao Q, Zong QF, Li XH and
Zhang Y: Effects of dexmedetomidine postconditioning on myocardial
ischemia and the role of the PI3K/Akt-dependent signaling pathway
in reperfusion injury. Mol Med Rep. 14:797–803. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Börekçi A, Gür M, Türkoğlu C, Selek Ş,
Baykan AO, Şeker T, Harbalıoğlu H, Özaltun B, Makça İ, Aksoy N, et
al: Oxidative stress and spontaneous reperfusion of infarct-related
artery in patients with ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction.
Clin Appl Thromb Hemost. 22:171–177. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Elmas E, Ahmad-Nejad P, Weiss C, Neumaier
M and Borggrefe M: Plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 (PAI-1),
toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4), factor II (FII), FXIII and fibrinogen
polymorphisms are not associated with the prevalence of sudden
death due to ventricular fibrillation during myocardial infarction.
Clin Chem Lab Med. 46:1329–1331. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Liu Q, Zhang J, Xu Y, Huang Y and Wu C:
Effect of carvedilol on cardiomyocyte apoptosis in a rat model of
myocardial infarction: A role for toll-like receptor 4. Indian J
Pharmacol. 45:458–463. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Yang Y, Lv J, Jiang S, Ma Z, Wang D, Hu W,
Deng C, Fan C, Di S, Sun Y and Yi W: The emerging role of Toll-like
receptor 4 in myocardial inflammation. Cell Death Dis. 7:e22342016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Wang CP, Shi YW, Tang M, Zhang XC, Gu Y,
Liang XM, Wang ZW and Ding F: Isoquercetin ameliorates cerebral
impairment in focal ischemia through anti-oxidative,
anti-inflammatory and anti-apoptotic effects in primary culture of
rat hippocampal neurons and hippocampal CA1 region of rats. Mol
Neurobiol. 54:2126–2142. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Bhatia N, Kaur G, Soni V, Kataria J and
Dhawan RK: Evaluation of the wound healing potential of
isoquercetin-based cream on scald burn injury in rats. Burns
Trauma. 4:72016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Vongsak B, Sithisarn P and Gritsanapan W:
Simultaneous determination of crypto-chlorogenic acid,
isoquercetin, and astragalin contents in moringa oleifera leaf
extracts by TLC-densitometric method. Evid Based Complement
Alternat Med. 2013:9176092013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Zhang R, Yao Y, Wang Y and Ren G:
Antidiabetic activity of isoquercetin in diabetic KK-Ay mice. Nutr
Metab (Lond). 8:852011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Lu T, Zhang C, Chai M and An Y:
Isoquercetin ameliorates tunicamycin-induced apoptosis in rat
dorsal root ganglion neurons via suppressing ROS-dependent
endoplasmic reticulum stress. Biomed Pharmacother. 80:343–351.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Mao S, Wang L, Ouyang W, Zhou Y, Qi J, Guo
L, Zhang M and Hinek A: Traditional Chinese medicine, Danlou
tablets alleviate adverse left ventricular remodeling after
myocardial infarction: Results of a double-blind, randomized,
placebo-controlled, pilot study. BMC Complement Altern Med.
16:4472016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Eitel I, Pöss J, Jobs A, Eitel C, de Waha
S, Barkhausen J, Desch S and Thiele H: Left ventricular global
function index assessed by cardiovascular magnetic resonance for
the prediction of cardiovascular events in ST-elevation myocardial
infarction. J Cardiovasc Magn Reson. 17:622015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Ketchum ES, Dickstein K, Kjekshus J, Pitt
B, Wong MF, Linker DT and Levy WC: The Seattle Post Myocardial
Infarction Model (SPIM): Prediction of mortality after acute
myocardial infarction with left ventricular dysfunction. Eur Heart
J Acute Cardiovasc Care. 3:46–55. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Kohl LP, Leimberger JD, Chiswell K, Jones
WS, Thiele H, Smalling RW, Chandra P, Cohen M, Perera D, Chew DP,
et al: Clinical characteristics and outcomes after unplanned
intraaortic balloon counterpulsation in the counterpulsation to
reduce infarct size Pre-PCI acute myocardial infarction trial. Am
Heart J. 174:7–13. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Prondzinsky R, Unverzagt S, Lemm H,
Wegener N, Heinroth K, Buerke U, Fiedler M, Thiery J, Haerting J,
Werdan K and Buerke M: Acute myocardial infarction and cardiogenic
shock: Prognostic impact of cytokines: INF-γ, TNF-α, MIP-1β, G-CSF,
and MCP-1β. Med Klin Intensivmed Notfmed. 107:476–484. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Raish M: Momordica charantia
polysaccharides ameliorate oxidative stress, hyperlipidemia,
inflammation, and apoptosis during myocardial infarction by
inhibiting the NF-κB signaling pathway. Int J Biol Macromol.
97:544–551. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Basili S, Tanzilli G, Mangieri E,
Raparelli V, Di Santo S, Pignatelli P and Violi F: Intravenous
ascorbic acid infusion improves myocardial perfusion grade during
elective percutaneous coronary intervention: Relationship with
oxidative stress markers. JACC Cardiovasc Interv. 3:221–229. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Aldakkak M, Stowe DF, Heisner JS, Riess ML
and Camara AK: Adding ROS quenchers to cold K+ cardioplegia reduces
superoxide emission during 2-hour global cold cardiac ischemia. J
Cardiovasc Pharmacol Ther. 17:93–101. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Feng Q, Lu C, Wang L, Song L, Li C and
Uppada RC: Effects of renal denervation on cardiac oxidative stress
and local activity of the sympathetic nervous system and
renin-angiotensin system in acute myocardial infracted dogs. BMC
Cardiovasc Disord. 17:652017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Sedlic F, Muravyeva MY, Sepac A, Sedlic M,
Williams AM, Yang M, Bai X and Bosnjak ZJ: Targeted modification of
mitochondrial ROS production converts high glucose-induced
cytotoxicity to cytoprotection: Effects on anesthetic
preconditioning. J Cell Physiol. 232:216–224. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Lin J, Wang H, Li J, Wang Q, Zhang S, Feng
N, Fan R and Pei J: κ-Opioid receptor stimulation modulates
TLR4/NF-κB signaling in the rat heart subjected to
ischemia-reperfusion. Cytokine. 61:842–848. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Sun Y, Huang J and Song K: BET protein
inhibition mitigates acute myocardial infarction damage in rats via
the TLR4/TRAF6/NF-κB pathway. Exp Ther Med. 10:2319–2324. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Wang Y, Li C, Cheng K, Zhang R, Narsinh K,
Li S, Li X, Qin X, Zhang R, Li C, et al: Activation of liver X
receptor improves viability of adipose-derived mesenchymal stem
cells to attenuate myocardial ischemia injury through TLR4/NF-κB
and Keap-1/Nrf-2 signaling pathways. Antioxid Redox Signal.
21:2543–2557. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Wang CP, Li JL, Zhang LZ, Zhang XC, Yu S,
Liang XM, Ding F and Wang ZW: Isoquercetin protects cortical
neurons from oxygen-glucose deprivation-reperfusion induced injury
via suppression of TLR4-NF-κB, signal pathway. Neurochem Int.
63:741–749. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|