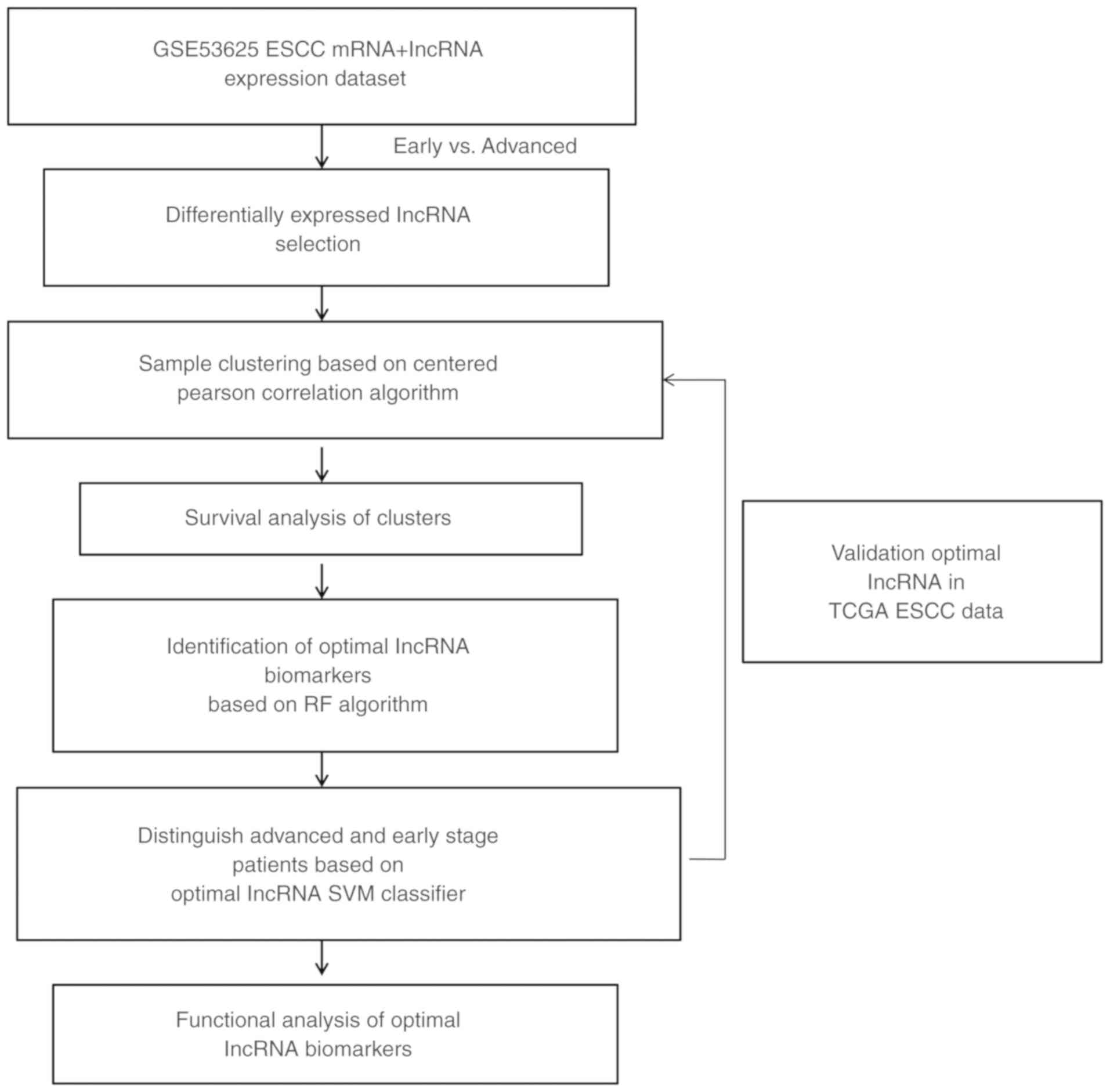
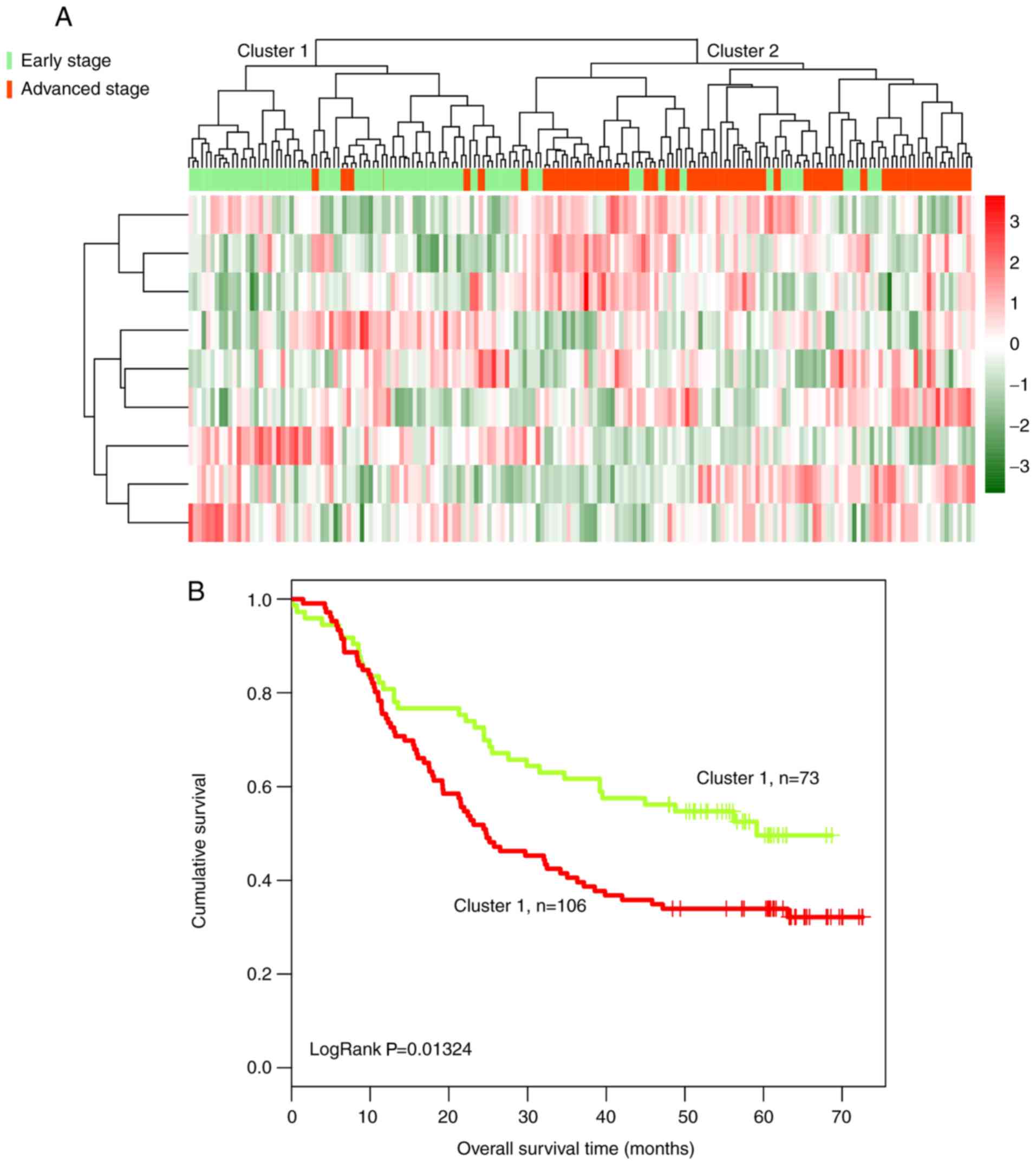
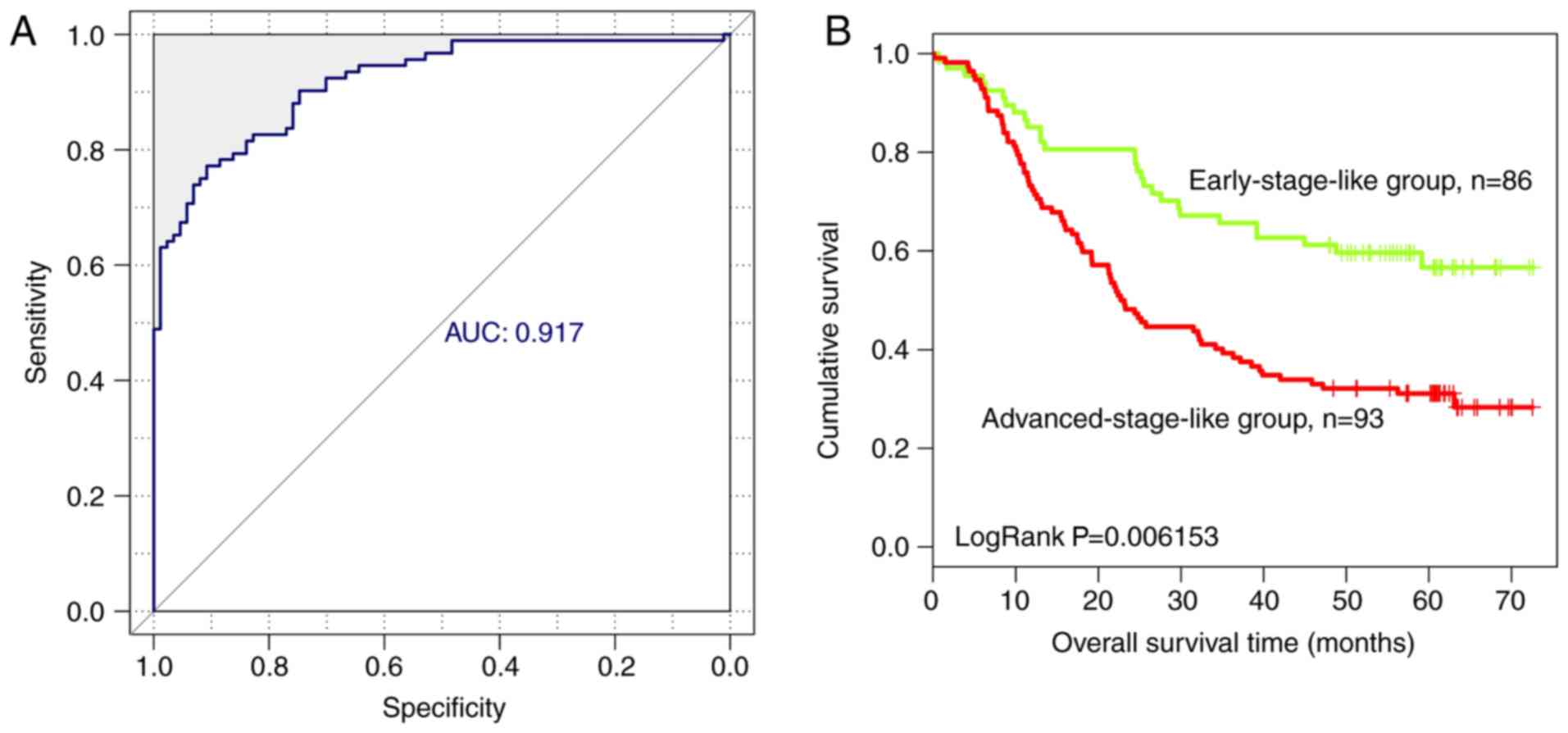
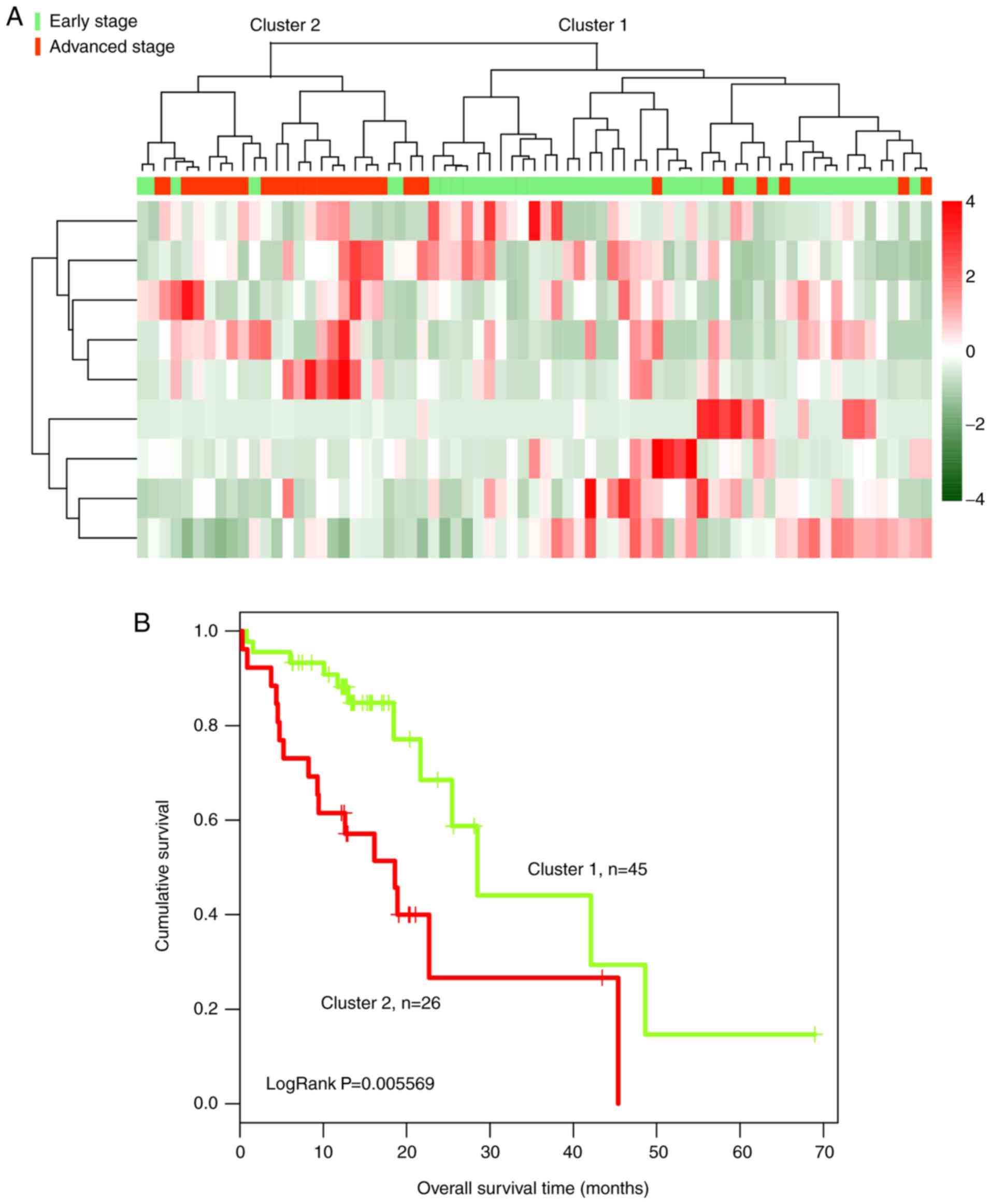
|
1
|
Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, Ferlay J,
Lortet-Tieulent J and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA
Cancer J Clin. 65:87–108. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
van Hagen P, Hulshof M, van Lanschot J,
Steyerberg EW, van Berge Henegouwen MI, Wijnhoven BP, Richel DJ,
Nieuwenhuijzen GA, Hospers GA, Bonenkamp JJ, et al: Preoperative
chemoradiotherapy for esophageal or junctional cancer. N Engl J
Med. 366:2074–2084. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Matsushima K, Isomoto H, Yamaguchi N,
Inoue N, Machida H, Nakayama T, Hayashi T, Kunizaki M, Hidaka S,
Nagayasu T, et al: MiRNA-205 modulates cellular invasion and
migration via regulating zinc finger E-box binding homeobox 2
expression in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma cells. J Transl
Med. 9:302011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Ohashi S, Miyamoto S, Kikuchi O, Goto T,
Amanuma Y and Muto M: Recent advances from basic and clinical
studies of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Gastroenterology.
149:1700–1715. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Hirajima S, Komatsu S, Ichikawa D,
Takeshita H, Konishi H, Shiozaki A, Morimura R, Tsujiura M, Nagata
H, Kawaguchi T, et al: Clinical impact of circulating miR-18a in
plasma of patients with oesophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Br J
Cancer. 108:1822–1829. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Kosugi S, Nishimaki T, Kanda T, Nakagawa
S, Ohashi M and Hatakeyama K: Clinical significance of serum
carcinoembryonic antigen, carbohydrate antigen 19-9, and squamous
cell carcinoma antigen levels in esophageal cancer patients. World
J Surg. 28:680–685. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Jones PA and Baylin SB: The fundamental
role of epigenetic events in cancer. Nat Rev Genet. 3:415–428.
2002. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Evans JR, Feng FY and Chinnaiyan AM: The
bright side of dark matter: lncRNAs in cancer. J Clin Invest.
126:2775–2782. 2016. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Schmitt AM and Chang HY: Long noncoding
RNAs in cancer pathways. Cancer Cell. 29:452–463. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Clark MB, Johnston RL, Inostroza-Ponta M,
Fox AH, Fortini E, Moscato P, Dinger ME and Mattick JS: Genome-wide
analysis of long noncoding RNA stability. Genome Res. 22:885–898.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Rinn JL and Chang HY: Genome regulation by
long noncoding RNAs. Annu Rev Biochem. 81:145–166. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
ENCODE Project Consortium, ; Birney E,
Stamatoyannopoulos JA, Dutta A, Guigó R, Gingeras TR, Margulies EH,
Weng Z, Snyder M, Dermitzakis ET, et al: Identification and
analysis of functional elements in 1% of the human genome by the
ENCODE pilot project. Nature. 447:799–816. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Nagano T and Fraser P: No-nonsense
functions for long noncoding RNAs. Cell. 145:178–181. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Yoon JH, Abdelmohsen K, Srikantan S, Yang
X, Martindale JL, De S, Huarte M, Zhan M, Becker KG and Gorospe M:
LincRNA-p21 suppresses target mRNA translation. Mol Cell.
47:648–655. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Guttman M and Rinn JL: Modular regulatory
principles of large non-coding RNAs. Nature. 482:339–346. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Gupta RA, Shah N, Wang KC, Kim J, Horlings
HM, Wong DJ, Tsai MC, Hung T, Argani P, Rinn JL, et al: Long
non-coding RNA HOTAIR reprograms chromatin state to promote cancer
metastasis. Nature. 464:1071–1076. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Yu W, Gius D, Onyango P, Muldoon-Jacobs K,
Karp J, Feinberg AP and Cui H: Epigenetic silencing of tumour
suppressor gene p15 by its antisense RNA. Nature. 451:202–206.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Ren S, Wang F, Shen J, Sun Y, Xu W, Lu J,
Wei M, Xu C, Wu C, Zhang Z, et al: Long non-coding RNA metastasis
associated in lung adenocarcinoma transcript 1 derived miniRNA as a
novel plasma-based biomarker for diagnosing prostate cancer. Eur J
Cancer. 49:2949–2959. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Ji P, Diederichs S, Wang W, Böing S,
Metzger R, Schneider PM, Tidow N, Brandt B, Buerger H, Bulk E, et
al: MALAT-1, a novel noncoding RNA, and thymosin beta4 predict
metastasis and survival in early-stage non-small cell lung cancer.
Oncogene. 22:8031–8041. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Li CQ, Huang GW, Wu ZY, Xu YJ, Li XC, Xue
YJ, Zhu Y, Zhao JM, Li M, Zhang J, et al: Integrative analyses of
transcriptome sequencing identify novel functional lncRNAs in
esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Oncogenesis. 6:e2972017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Cao W, Wu W, Shi F, Chen X, Wu L, Yang K,
Tian F, Zhu M, Chen G, Wang W, et al: Integrated analysis of long
noncoding RNA and coding RNA expression in esophageal squamous cell
carcinoma. Int J Genomics. 2013:4805342013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Pan Z, Mao W, Bao Y, Zhang M, Su X and Xu
X: The long noncoding RNA CASC9 regulates migration and invasion in
esophageal cancer. Cancer Med. 5:2442–2447. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Yao J, Huang JX, Lin M, Wu ZD, Yu H, Wang
PC, Ye J, Chen P, Wu J and Zhao GJ: Microarray expression profile
analysis of aberrant long non-coding RNAs in esophageal squamous
cell carcinoma. Int J Oncol. 48:2543–2557. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Wang W, Wei C, Li P, Wang L, Li W, Chen K,
Zhang J, Zhang W and Jiang G: Integrative analysis of mRNA and
lncRNA profiles identified pathogenetic lncRNAs in esophageal
squamous cell carcinoma. Gene. 661:169–175. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Mathé EA, Nguyen GH, Bowman ED, Zhao Y,
Budhu A, Schetter AJ, Braun R, Reimers M, Kumamoto K, Hughes D, et
al: MicroRNA expression in squamous cell carcinoma and
adenocarcinoma of the esophagus: Associations with survival. Clin
Cancer Res. 15:6192–6200. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Clough E and Barrett T: The gene
expression omnibus database. Methods Mol Biol. 1418:93–110. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Tomczak K, Czerwinska P and Wiznerowicz M:
The cancer genome atlas (TCGA): An immeasurable source of
knowledge. Contemp Oncol (Pozn). 19:A68–A77. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Huang Y, Guo W, Shi S and He J: Evaluation
of the 7(th) edition of the UICC-AJCC tumor, node, metastasis
classification for esophageal cancer in a Chinese cohort. J Thorac
Dis. 8:1672–1680. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Li J, Chen Z, Tian L, Zhou C, He MY, Gao
Y, Wang S, Zhou F, Shi S, Feng X, et al: LncRNA profile study
reveals a three-lncRNA signature associated with the survival of
patients with oesophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Gut.
63:1700–1710. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Moon TK: The expectation maximization
algorithm. IEEE Signal Process Mag. 13:47–60. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Ritchie ME, Phipson B, Wu D, Hu Y, Law CW,
Shi W and Smyth GK: Limma powers differential expression analyses
for RNA-sequencing and microarray studies. Nucleic Acids Res.
43:e472015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Jiao S and Zhang S: On correcting the
overestimation of the permutation-based false discovery rate
estimator. Bioinformatics. 24:1655–1661. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Eisen MB, Spellman PT, Brown PO and
Botstein D: Cluster analysis and display of genome-wide expression
patterns. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 95:14863–14868. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Wang L, Cao C, Ma Q, Zeng Q, Wang H, Cheng
Z, Zhu G, Qi J, Ma H, Nian H and Wang Y: RNA-seq analyses of
multiple meristems of soybean: Novel and alternative transcripts,
evolutionary and functional implications. BMC Plant Biol.
14:1692014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Zapf A, Brunner E and Konietschke F: A
wild bootstrap approach for the selection of biomarkers in early
diagnostic trials. BMC Med Res Methodol. 15:432015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Cutler A and Stevens JR: Random forests
for microarrays. Methods Enzymol. 411:422–432. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Wang Q and Liu X: Screening of feature
genes in distinguishing different types of breast cancer using
support vector machine. OncoTargets Ther. 8:2311–2317. 2015.
|
|
38
|
Fushiki T: Estimation of prediction error
by using K-fold cross-validation. Statistics Computing. 21:137–146.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Langfelder P and Horvath S: Fast R
functions for robust correlations and hierarchical clustering. J
Stat Softw. 46(pii): i112012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Szklarczyk D, Franceschini A, Wyder S,
Forslund K, Heller D, Huerta-Cepas J, Simonovic M, Roth A, Santos
A, Tsafou KP, et al: STRING v10: Protein-protein interaction
networks, integrated over the tree of life. Nucleic Acids Res 43
(Database Issue). D447–D452. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Kanehisa M and Goto S: KEGG: Kyoto
encyclopedia of genes and genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 28:27–30.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Huang da W, Sherman BT and Lempicki RA:
Systematic and integrative analysis of large gene lists using DAVID
bioinformatics resources. Nat Protoc. 4:44–57. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Enzinger PC and Mayer RJ: Esophageal
cancer. N Engl J Med. 349:2241–2252. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Dai L, Li JL, Liang XQ, Li L, Feng Y, Liu
HZ, Wei WE, Ning SF and Zhang LT: Flowers of Camellia nitidissima
cause growth inhibition, cell-cycle dysregulation and apoptosis in
a human esophageal squamous cell carcinoma cell line. Mol Med Rep.
14:1117–1122. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Dadkhah E, Naseh H, Farshchian M, Memar B,
Sankian M, Bagheri R, Forghanifard MM, Montazer M, Kazemi Noughabi
M, Hashemi M and Abbaszadegan MR: A cancer-array approach
elucidates the immune escape mechanism and defects in the DNA
repair system in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Arch Iran Med.
16:463–470. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Yang F, Zhang L, Huo XS, Yuan JH, Xu D,
Yuan SX, Zhu N, Zhou WP, Yang GS, Wang YZ, et al: Long noncoding
RNA high expression in hepatocellular carcinoma facilitates tumor
growth through enhancer of zeste homolog 2 in humans. Hepatology.
54:1679–1689. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Kogo R, Shimamura T, Mimori K, Kawahara K,
Imoto S, Sudo T, Tanaka F, Shibata K, Suzuki A, Komune S, et al:
Long non-coding RNA HOTAIR regulates Polycomb-dependent chromatin
modification and is associated with poor prognosis in colorectal
cancers. Cancer Res. 71:6320–6326. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Ito T, Shimada Y, Kan T, David S, Cheng Y,
Mori Y, Agarwal R, Paun B, Jin Z, Olaru A, et al: Pituitary
tumor-transforming 1 increases cell motility and promotes lymph
node metastasis in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer Res.
68:3214–3224. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Ma S, Bao JYJ, Kwan PS, Chan YP, Tong CM,
Fu L, Zhang N, Tong AHY, Qin YR, Tsao SW, et al: Identification of
PTK6, via RNA sequencing analysis, as a suppressor of esophageal
squamous cell carcinoma. Gastroenterology. 143:675–686.e12. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Sawada G, Niida A, Uchi R, Hirata H,
Shimamura T, Suzuki Y, Shiraishi Y, Chiba K, Imoto S, Takahashi Y,
et al: Genomic landscape of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma in a
Japanese population. Gastroenterology. 150:1171–1182. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|