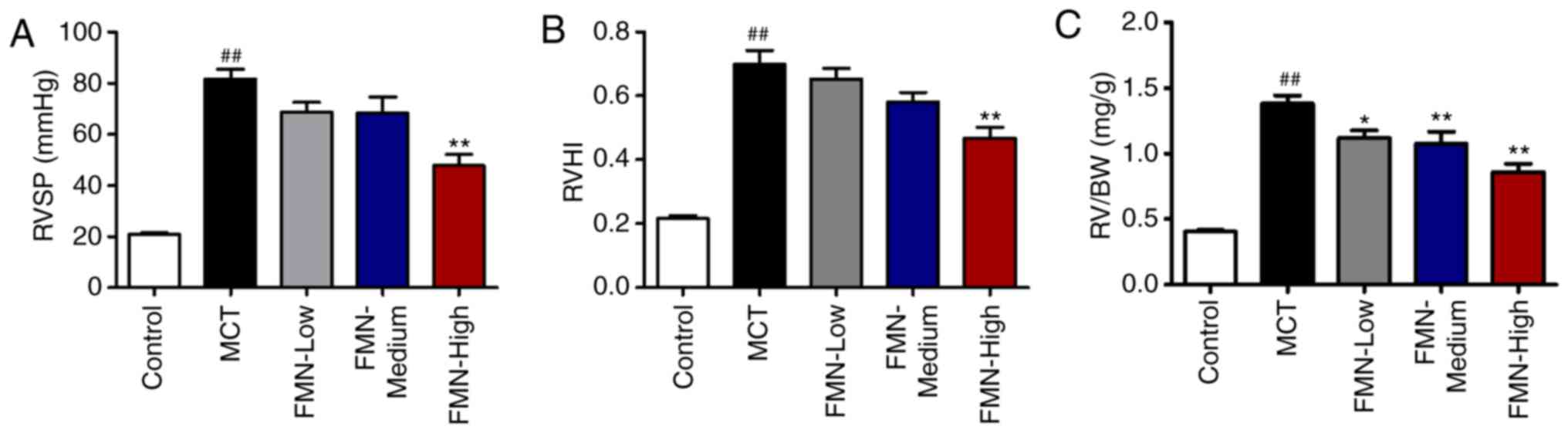
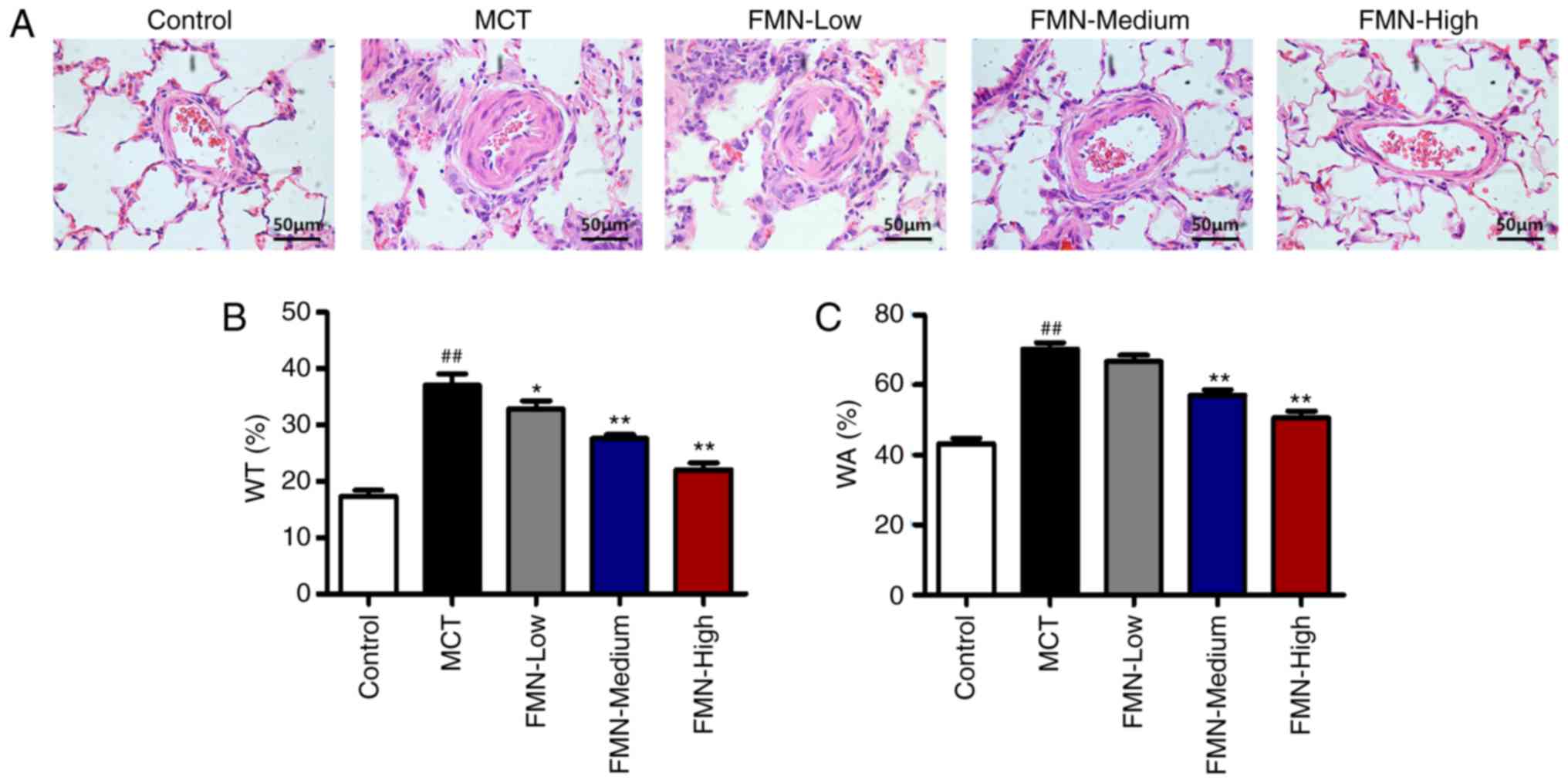
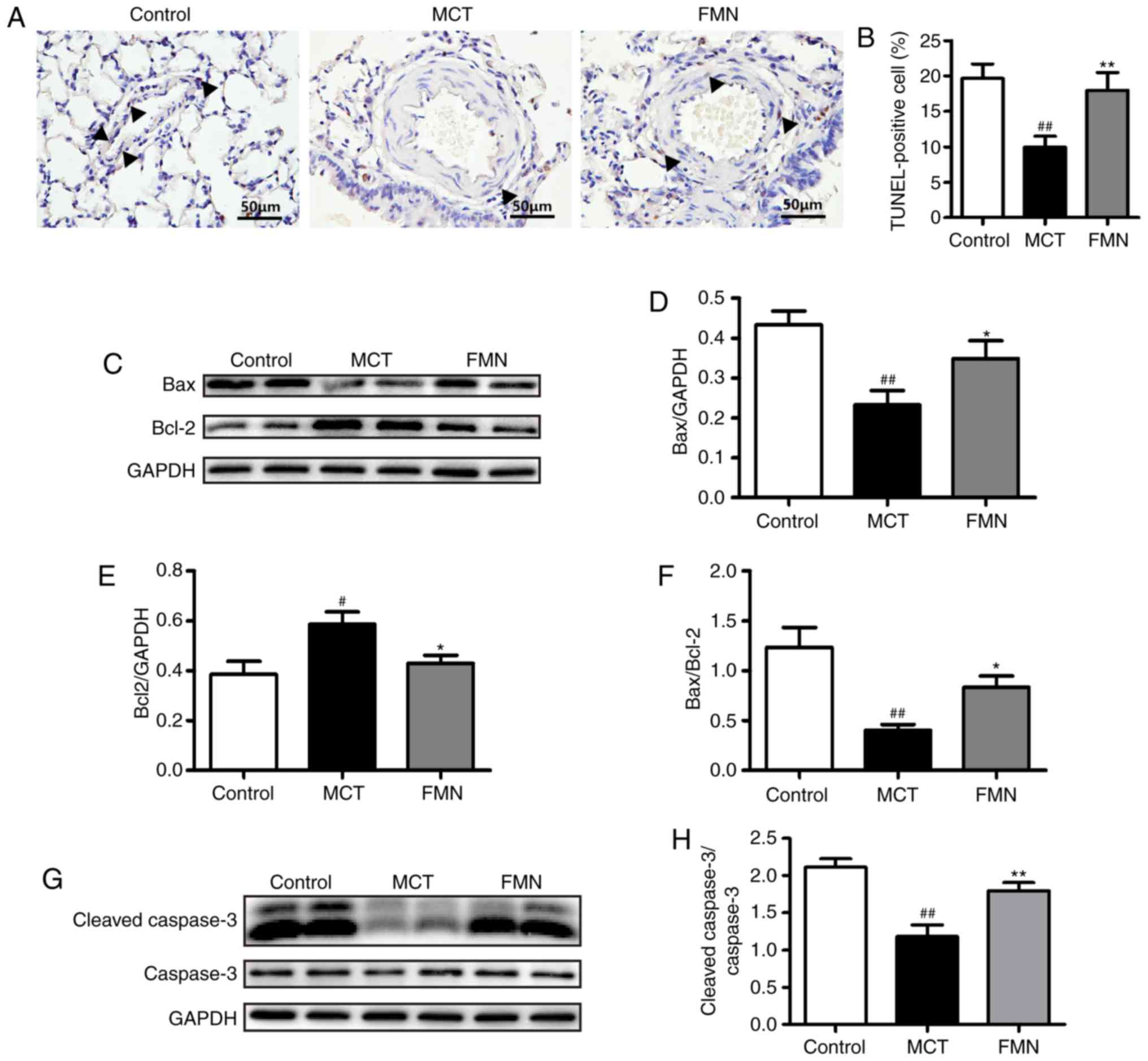
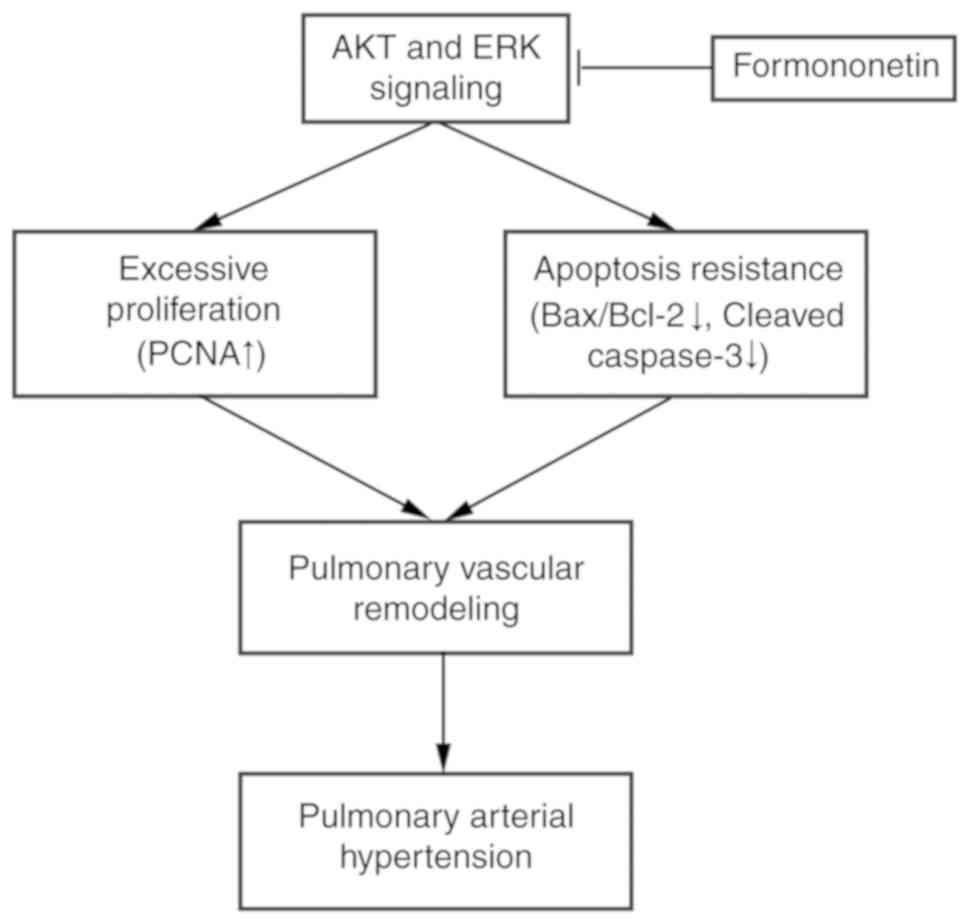
|
1
|
Maron BA and Leopold JA: Emerging concepts
in the molecular basis of pulmonary arterial hypertension: Part II:
Neurohormonal signaling contributes to the pulmonary vascular and
right ventricular pathophenotype of pulmonary arterial
hypertension. Circulation. 131:2079–2091. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Simonneau G, Gatzoulis MA, Adatia I,
Celermajer D, Denton C, Ghofrani A, Gomez Sanchez MA, Krishna Kumar
R, Landzberg M, Machado RF, et al: Updated clinical classification
of pulmonary hypertension. J Am Coll Cardiol. 62 (25
Suppl):D34–D41. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Lai YC, Potoka KC, Champion HC, Mora AL
and Gladwin MT: Pulmonary arterial hypertension: The clinical
syndrome. Cir Res. 115:115–130. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Guignabert C, Tu L, Girerd B, Ricard N,
Huertas A, Montani D and Humbert M: New molecular targets of
pulmonary vascular remodeling in pulmonary arterial hypertension:
Importance of endothelial communication. Chest. 147:529–537. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Schermuly RT, Ghofrani HA, Wilkins MR and
Grimminger F: Mechanisms of disease: Pulmonary arterial
hypertension. Nat Rev Cardiol. 8:443–455. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Sakao S and Tatsumi K: Vascular remodeling
in pulmonary arterial hypertension: Multiple cancer-like pathways
and possible treatment modalities. Int J Cardiol. 147:4–12. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Dumas de la Roque E, Savineau JP and
Bonnet S: Dehydroepiandrosterone: A new treatment for vascular
remodeling diseases including pulmonary arterial hypertension.
Pharmacol Ther. 126:186–199. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Michelakis ED: Pulmonary arterial
hypertension: Yesterday, today, tomorrow. Circ Res. 115:109–114.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Montani D, Chaumais MC, Guignabert C,
Günther S, Girerd B, Jaïs X, Algalarrondo V, Price LC, Savale L,
Sitbon O, et al: Targeted therapies in pulmonary arterial
hypertension. Pharmacol Ther. 141:172–191. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Archer SL, Weir EK and Wilkins MR: Basic
science of pulmonary arterial hypertension for clinicians: New
concepts and experimental therapies. Circulation. 121:2045–2066.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Zhang Q, Cao Y, Luo Q, Wang P, Shi P, Song
C, E M, Ren J, Fu B and Sun H: The transient receptor potential
vanilloid-3 regulates hypoxia-mediated pulmonary artery smooth
muscle cells proliferation via PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. Cell
Prolif. 51:e124362018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Wu J, Yu Z and Su D: BMP4 protects rat
pulmonary arterial smooth muscle cells from apoptosis by
PI3K/AKT/Smad1/5/8 signaling. Int J Mol Sci. 15:13738–13754. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Wang W, Prince CZ, Mou Y and Pollman MJ:
Notch3 signaling in vascular smooth muscle cells induces c-FLIP
expression via ERK/MAPK activation. J Biol Chem. 277:21723–21729.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Wu F, Hao Y, Yang J, Yao W, Xu Y, Yan L,
Niu Y, Sun T, Yu J and Zhou R: Protective effects of aloperine on
monocrotaline-induced pulmonary hypertension in rats. Biomed
Pharmacother. 89:632–641. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Krenn L and Paper DH: Inhibition of
angiogenesis and inflammation by an extract of red clover
(Trifolium pratense L.). Phytomedicine. 16:1083–1088. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Mu H, Bai YH, Wang ST, Zhu ZM and Zhang
YW: Research on antioxidant effects and estrogenic effect of
formononetin from Trifolium pratense (red clover). Phytomedicine.
16:314–319. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Zhang S, Tang X, Tian J, Li C, Zhang G,
Jiang W and Zhang Z: Cardioprotective effect of sulphonated
formononetin on acute myocardial infarction in rats. Basic Clin
Pharmacol Toxicol. 108:390–395. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Sun T, Wang J, Huang LH and Cao YX:
Antihypertensive effect of formononetin through regulating the
expressions of eNOS, 5-HT2A/1B receptors and α1-adrenoceptors in
spontaneously rat arteries. Eur J Pharmacol. 699:241–249. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Li T, Zhao X, Mo Z, Huang W, Yan H, Ling Z
and Ye Y: Formononetin promotes cell cycle arrest via
downregulation of Akt/Cyclin D1/CDK4 in human prostate cancer
cells. Cell Physiol Biochem. 34:1351–1358. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Qi C, Xie M, Liang J, Li H, Li Z, Shi S,
Yang X, Wang Z, Tang J and Tang A: Formononetin targets the MAPK
and PI3K/AKT pathways to induce apoptosis in human nasopharyngeal
carcinoma cells in vitro and in vivo. Int J Clin Exp Med.
9:1180–1189. 2016.
|
|
21
|
Jin YM, Xu TM, Zhao YH, Wang YC and Cui
MH: In vitro and in vivo anti-cancer activity of formononetin on
human cervical cancer cell line HeLa. Tumor Biol. 35:2279–2284.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Zhang X, Bi L, Ye Y and Chen J:
Formononetin induces apoptosis in PC-3 prostate cancer cells
through enhancing the Bax/Bcl-2 ratios and regulating the p38/Akt
pathway. Nutr Cancer. 66:656–661. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Yang Y, Zhao Y, Ai X, Cheng B and Lu S:
Formononetin suppresses the proliferation of human non-small cell
lung cancer through induction of cell cycle arrest and apoptosis.
Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 7:8453–8461. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Chen Z, Liu S, Cai Y, Xie K, Zhang W, Dong
L, Liu Y, Zheng F, Dun Y and Li N: Suppressive effect of
formononetin on platelet-derived growth factor-BB-stimulated
proliferation and migration of vascular smooth muscle cells. Exp
Ther Med. 12:1901–1907. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Liu Y, He J, Chen X, Li J, Shen M, Yu W,
Yang Y and Xiao Z: The proapoptotic effect of formononetin in human
osteosarcoma cells: Involvement of inactivation of ERK and Akt
pathways. Cell Physiol Biochem. 34:637–645. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Isoda K, Akita K, Kitamura K,
Sato-Okabayashi Y, Kadoguchi T, Isobe S, Ohtomo F, Sano M, Shimada
K, Iwakura Y and Daida H: Inhibition of interleukin-1 suppresses
angiotensin II-induced aortic inflammation and aneurysm formation.
Int J Cardiol. 270:221–227. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Zhu N, Zhao X, Xiang Y, Ye S, Huang J, Hu
W, Lv L and Zeng C: Thymoquinone attenuates monocrotaline-induced
pulmonary artery hypertension via inhibiting pulmonary arterial
remodeling in rats. Int J Cardiol. 221:587–596. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Huang Z, Liu Z, Luo Q, Zhao Z, Zhao Q,
Zheng Y, Xi Q and Tang Y: Glycoprotein 130 inhibitor ameliorates
monocrotaline-induced pulmonary hypertension in rats. Can J
Cardiol. 32:1356.e1–1356.e10. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Xia S, Tai X, Wang Y, An X, Qian G, Dong
J, Wang X, Sha B, Wang D, Murthi P, et al: Involvement of Gax gene
in hypoxia-induced pulmonary hypertension, proliferation, and
apoptosis of arterial smooth muscle cells. Am J Respir Cell Mol
Biol. 44:66–73. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Liang K, Ye Y, Wang Y, Zhang J and Li C:
Formononetin mediates neuroprotection against cerebral
ischemia/reperfusion in rats via downregulation of the Bax/Bcl-2
ratio and upregulation PI3K/Akt signaling pathway. J Neurol Sci.
344:100–104. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Li XL, Guan RJ and Li JJ: Attenuation of
monocrotaline-induced pulmonary arterial hypertension in rats by
rosuvastatin. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 60:219–226. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Wilcox SR, Kabrhel C and Channick RN:
Pulmonary hypertension and right ventricular failure in emergency
medicine. Ann Emerg Med. 66:619–628. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Tang B, Chen GX, Liang MY, Yao JP and Wu
ZK: Ellagic acid prevents monocrotaline-induced pulmonary artery
hypertension via inhibiting NLRP3 inflammasome activation in rats.
Int J Cardiol. 180:134–141. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Thenappan T, Ormiston ML, Ryan JJ and
Archer SL: Pulmonary arterial hypertension: Pathogenesis and
clinical management. BMJ. 360:j54922018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Ryan JJ and Archer SL: The right ventricle
in pulmonary arterial hypertension: Disorders of metabolism,
angiogenesis and adrenergic signaling in right ventricular failure.
Circ Res. 115:176–188. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Guignabert C, Tu L, Le Hiress M, Ricard N,
Sattler C, Seferian A, Huertas A, Humbert M and Montani D:
Pathogenesis of pulmonary arterial hypertension: Lessons from
cancer. Eur Respir Rev. 22:543–551. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Rabinovitch M: Molecular pathogenesis of
pulmonary arterial hypertension. J Clin Invest. 122:4306–4313.
2012. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Falcetti E, Hall SM, Phillips PG, Patel J,
Morrell NW, Haworth SG and Clapp LH: Smooth muscle proliferation
and role of the prostacyclin (IP) receptor in idiopathic pulmonary
arterial hypertension. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 182:1161–1170.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Bishopric NH, Andreka P, Slepak T and
Webster KA: Molecular mechanisms of apoptosis in the cardiac
myocyte. Curr Opin Pharmacol. 1:141–150. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Huang X, Zou L, Yu X, Chen M, Guo R, Cai
H, Yao D, Xu X, Chen Y, Ding C, et al: Salidroside attenuates
chronic hypoxia-induced pulmonary hypertension via adenosine A 2a
receptor related mitochondria-dependent apoptosis pathway. J Mol
Cell Cardiol. 82:153–166. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Rahmani M, Aust MM, Attkisson E, Williams
DC Jr, Ferreira-Gonzalez A and Grant S: Dual inhibition of Bcl-2
and Bcl-xL strikingly enhances PI3K inhibition-induced apoptosis in
human myeloid leukemia cells through a GSK3- and Bim-dependent
mechanism. Cancer Res. 73:1340–1351. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Diab S, Kumarasiri M, Yu M, Teo T, Proud
C, Milne R and Wang S: MAP kinase-interacting kinases-emerging
targets against cancer. Chem Biol. 21:441–452. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|