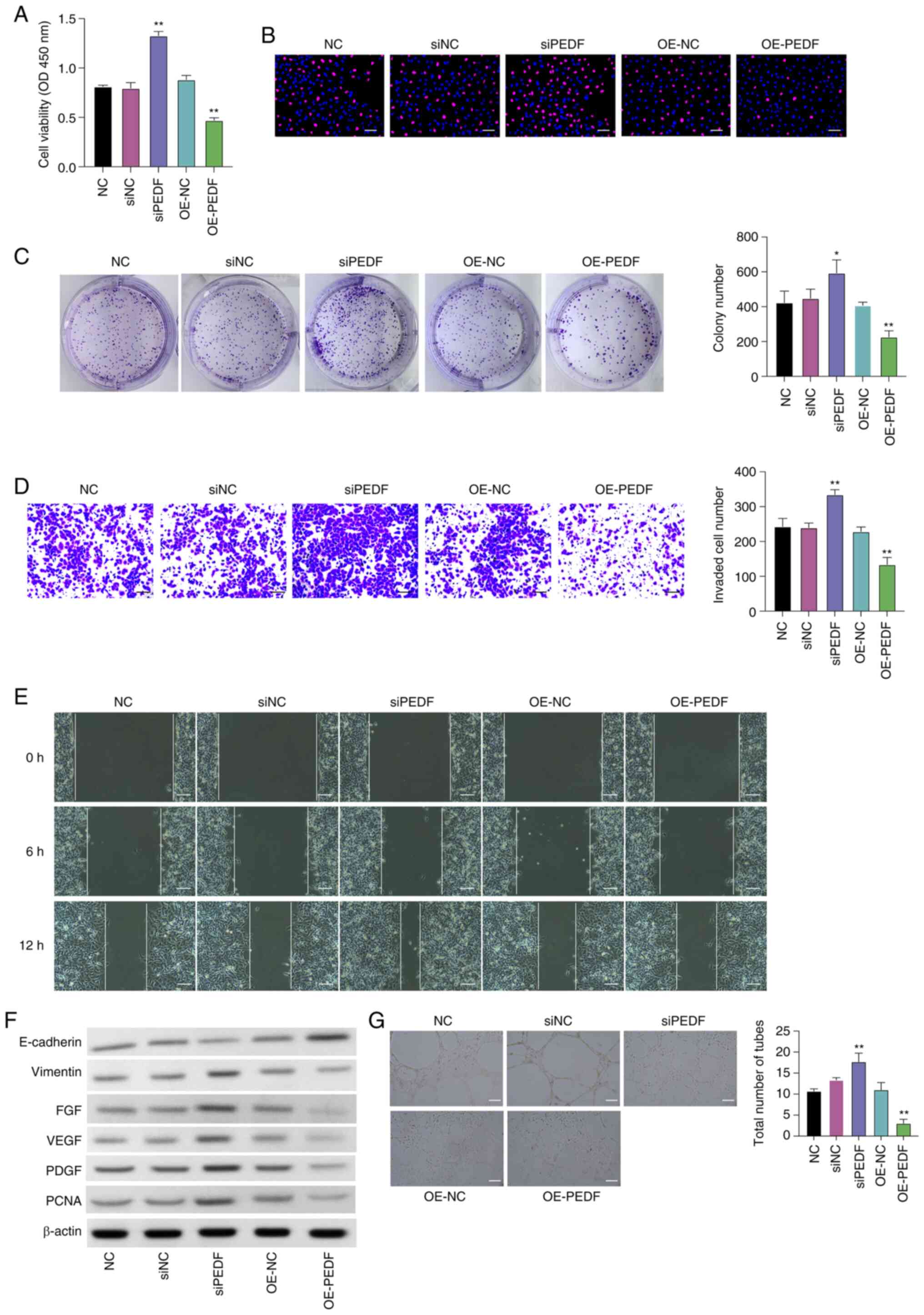
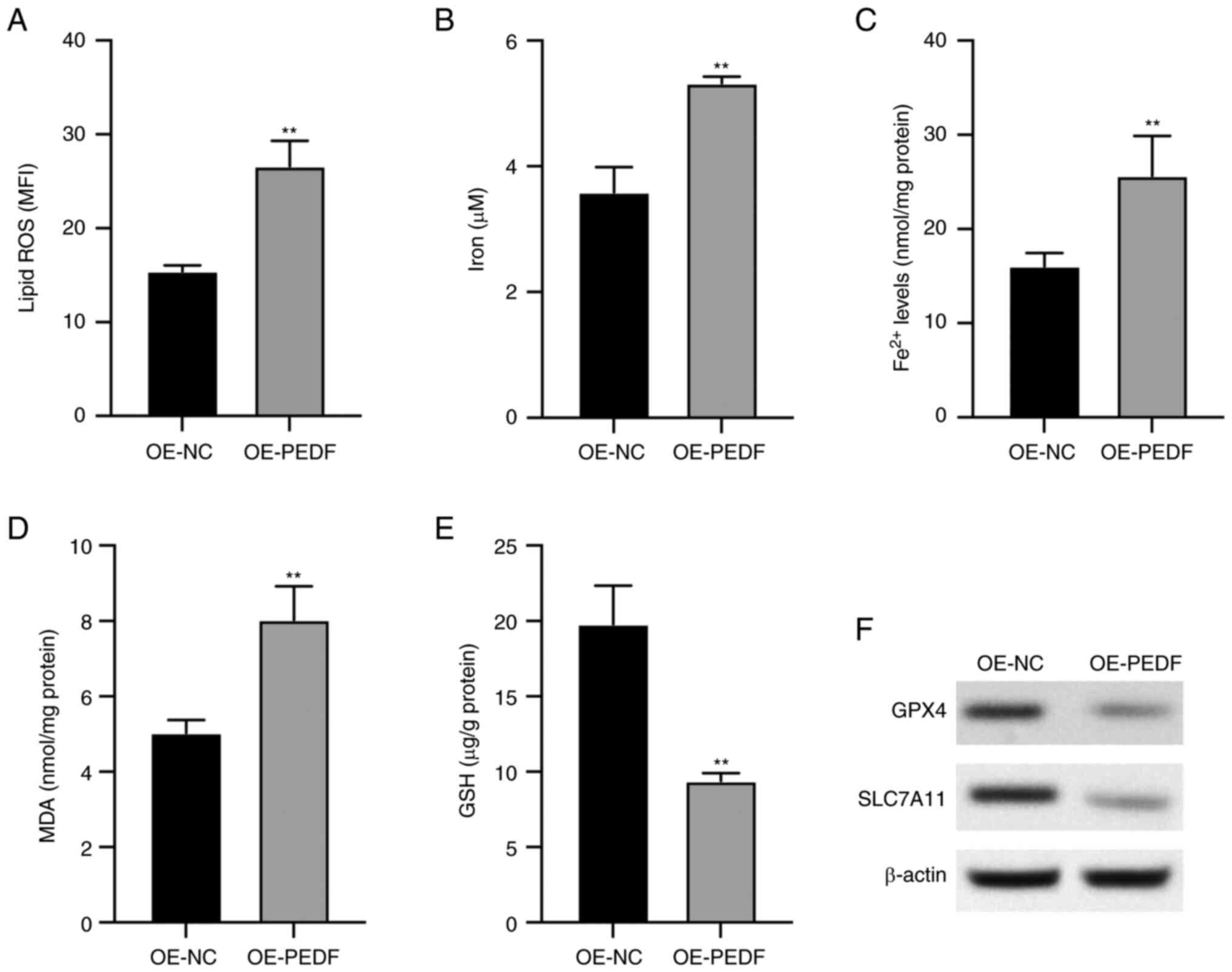
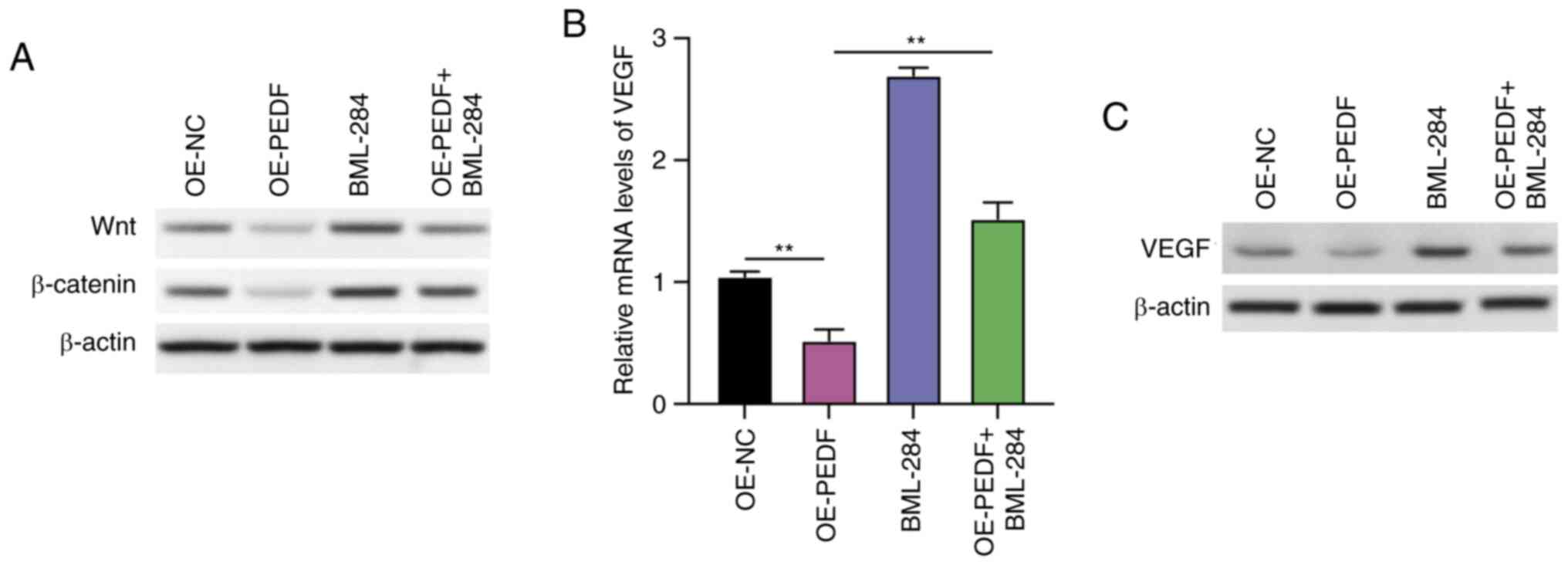
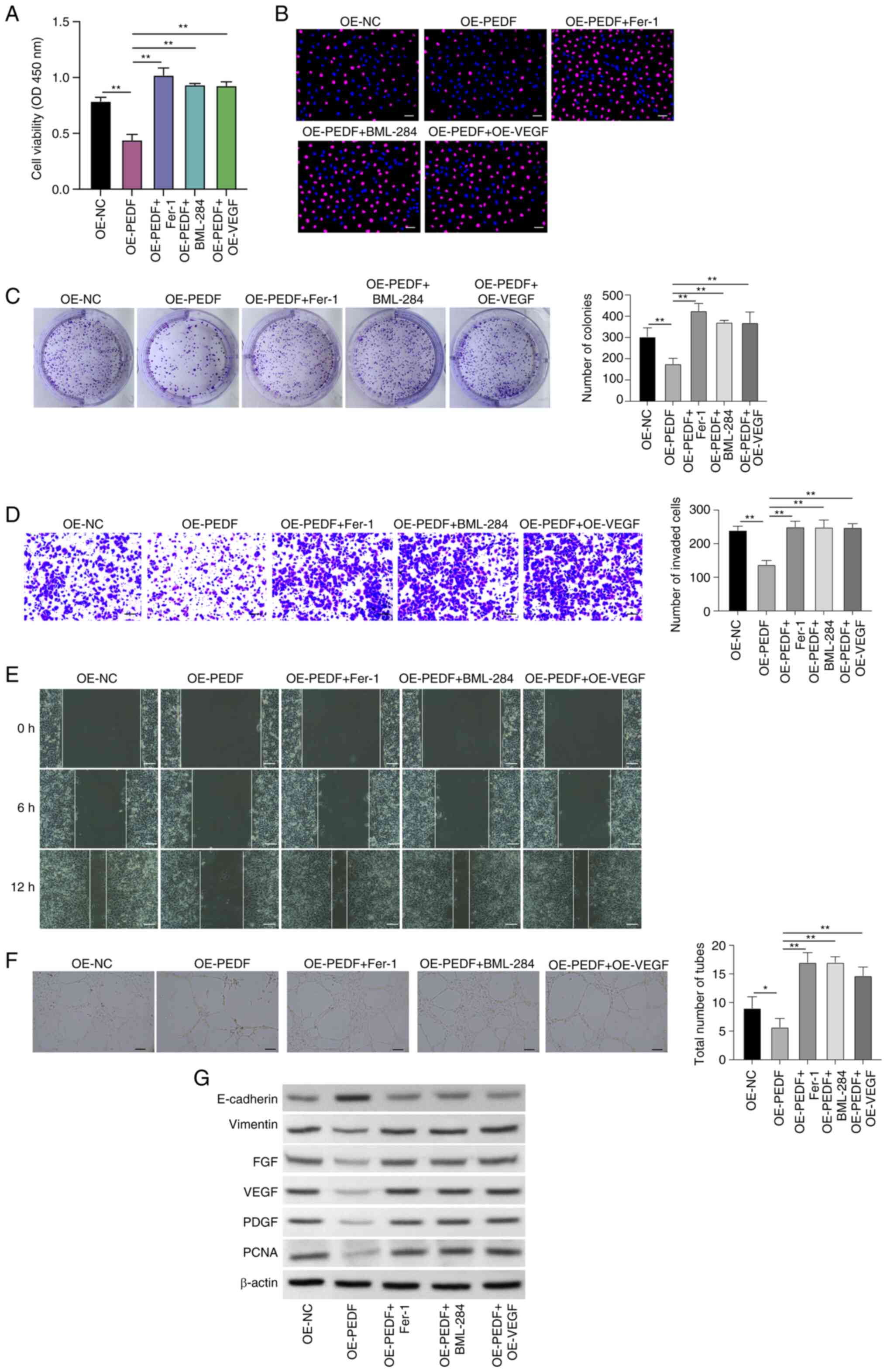
|
1
|
Moser G and Huppertz B: Implantation and
extravillous trophoblast invasion: From rare archival specimens to
modern biobanking. Placenta. 56:19–26. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Wei XW, Zhang YC, Wu F, Tian FJ and Lin Y:
The role of extravillous trophoblasts and uterine NK cells in
vascular remodeling during pregnancy. Front Immunol. 13:9514822022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Illsley NP, DaSilva-Arnold SC, Zamudio S,
Alvarez M and Al-Khan A: Trophoblast invasion: Lessons from
abnormally invasive placenta (placenta accreta). Placenta.
102:61–66. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Horgan R and Abuhamad A: Placenta accreta
spectrum: Prenatal diagnosis and management. Obstet Gynecol Clin
North Am. 49:423–438. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Sonderegger S, Haslinger P, Sabri A,
Leisser C, Otten JV, Fiala C and Knöfler M: Wingless (Wnt)-3A
induces trophoblast migration and matrix metalloproteinase-2
secretion through canonical Wnt signaling and protein kinase B/AKT
activation. Endocrinology. 151:211–220. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Knöfler M and Pollheimer J: Human
placental trophoblast invasion and differentiation: A particular
focus on Wnt signaling. Front Genet. 4:1902013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Dietrich B, Haider S, Meinhardt G,
Pollheimer J and Knöfler M: WNT and NOTCH signaling in human
trophoblast development and differentiation. Cell Mol Life Sci.
79:2922022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Pollheimer J, Vondra S, Baltayeva J,
Beristain AG and Knöfler M: Regulation of placental extravillous
trophoblasts by the maternal uterine environment. Front Immunol.
9:25972018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Abbas Y, Turco MY, Burton GJ and Moffett
A: Investigation of human trophoblast invasion in vitro. Hum Reprod
Update. 26:501–513. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Shang Z, Li C, Liu X, Xu M, Zhang X, Li X,
Barnstable CJ, Zhao S and Tombran-Tink J: PEDF gene deletion
disrupts corneal innervation and ocular surface function. Invest
Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 62:182021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Ma B, Zhou Y, Liu R, Zhang K, Yang T, Hu
C, Gao Y, Lan Q, Liu Y, Yang X and Qi H: Pigment epithelium-derived
factor (PEDF) plays anti-inflammatory roles in the pathogenesis of
dry eye disease. Ocul Surf. 20:70–85. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Ansari D, Althini C, Ohlsson H, Bauden M
and Andersson R: The role of PEDF in pancreatic cancer. Anticancer
Res. 39:3311–3315. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Bao X, Zeng J, Huang H, Ma C, Wang L, Wang
F, Liao X and Song X: Cancer-targeted PEDF-DNA therapy for
metastatic colorectal cancer. Int J Pharm. 576:1189992020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Loegl J, Nussbaumer E, Hiden U,
Majali-Martinez A, Ghaffari-Tabrizi-Wizy N, Cvitic S, Lang I,
Desoye G and Huppertz B: Pigment epithelium-derived factor (PEDF):
A novel trophoblast-derived factor limiting feto-placental
angiogenesis in late pregnancy. Angiogenesis. 19:373–388. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Li J, Cao F, Yin HL, Huang ZJ, Lin ZT, Mao
N, Sun B and Wang G: Ferroptosis: Past, present and future. Cell
Death Dis. 11:882020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Wei X, Yi X, Zhu XH and Jiang DS:
Posttranslational modifications in ferroptosis. Oxid Med Cell
Longev. 2020:88320432020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Wu X, Li Y, Zhang S and Zhou X:
Ferroptosis as a novel therapeutic target for cardiovascular
disease. Theranostics. 11:3052–3059. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Chen X, Kang R, Kroemer G and Tang D:
Ferroptosis in infection, inflammation immunity. J Exp Med.
218:e202105182021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Hirschhorn T and Stockwell BR: The
development of the concept of ferroptosis. Free Radic Biol Med.
133:130–143. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Bloomfield V, Rogers S and Leyland N:
Placenta accreta spectrum. CMAJ. 192:E9802020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Zhang Q, Yu S, Huang X, Tan Y, Zhu C, Wang
YL and Wang H, Lin HY, Fu J and Wang H: New insights into the
function of Cullin 3 in trophoblast invasion and migration.
Reproduction. 150:139–149. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Scalise ML, Amaral MM, Reppetti J, Damiano
AE, Ibarra C and Sacerdoti F: Cytotoxic effects of Shiga toxin-2 on
human extravillous trophoblast cell lines. Reproduction.
157:297–304. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Jauniaux E, Jurkovic D, Hussein AM and
Burton GJ: New insights into the etiopathology of placenta accreta
spectrum. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 227:384–391. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Ma Y, Hu Y and Ma J: Animal models of the
placenta accreta spectrum: Current status and further perspectives.
Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 14:11181682023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Xia H, Ke SC, Qian RR, Lin JG, Li Y and
Zhang X: Comparison between abdominal ultrasound and nuclear
magnetic resonance imaging detection of placenta accreta in the
second and third trimester of pregnancy. Medicine (Baltimore).
99:e179082020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Burton GJ and Jauniaux E: Pathophysiology
of placental-derived fetal growth restriction. Am J Obstet Gynecol.
218:S745–S761. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Sun Y, Chen P, Zhai B, Zhang M, Xiang Y,
Fang J, Xu S, Gao Y, Chen X, Sui X and Li G: The emerging role of
ferroptosis in inflammation. Biomed Pharmacother. 127:1101082020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Pan Q, Luo Y, Xia Q and He K: Ferroptosis
and liver fibrosis. Int J Med Sci. 18:3361–3366. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Georgieff MK, Krebs NF and Cusick SE: The
benefits and risks of iron supplementation in pregnancy and
childhood. Annu Rev Nutr. 39:121–146. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Li Y, Zeng X, Lu D, Yin M, Shan M and Gao
Y: Erastin induces ferroptosis via ferroportin-mediated iron
accumulation in endometriosis. Hum Reprod. 36:951–964. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Tang D, Chen X, Kang R and Kroemer G:
Ferroptosis: Molecular mechanisms and health implications. Cell
Res. 31:107–125. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Ortega MA, Saez MÁ, Asúnsolo Á, Romero B,
Bravo C, Coca S, Sainz F, Álvarez-Mon M, Buján J and
García-Honduvilla N: Upregulation of VEGF and PEDF in placentas of
women with lower extremity venous insufficiency during pregnancy
and its implication in villous calcification. Biomed Res Int.
2019:53209022019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Duzyj CM, Buhimschi IA, Laky CA, Cozzini
G, Zhao G, Wehrum M and Buhimschi CS: Extravillous trophoblast
invasion in placenta accreta is associated with differential local
expression of angiogenic and growth factors: A cross-sectional
study. BJOG. 125:1441–1448. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Protiva P, Gong J, Sreekumar B, Torres R,
Zhang X, Belinsky GS, Cornwell M, Crawford SE, Iwakiri Y and Chung
C: Pigment epithelium-derived factor (PEDF) inhibits Wnt/β-catenin
signaling in the liver. Cell Mol Gastroenterol Hepatol.
1:535–549.e14. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Li Y, Baccouche B, Olayinka O, Serikbaeva
A and Kazlauskas A: The role of the Wnt pathway in
VEGF/anti-VEGF-dependent control of the endothelial cell barrier.
Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 62:172021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Jiang L, Yin M, Wei X, Liu J, Wang X, Niu
C, Kang X, Xu J, Zhou Z, Sun S, et al: Bach1 represses
Wnt/β-catenin signaling and angiogenesis. Circ Res. 117:364–375.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Kovács B, Vajda E and Nagy EE: Regulatory
effects and interactions of the Wnt and OPG-RANKL-RANK signaling at
the bone-cartilage interface in osteoarthritis. Int J Mol Sci.
20:46532019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|