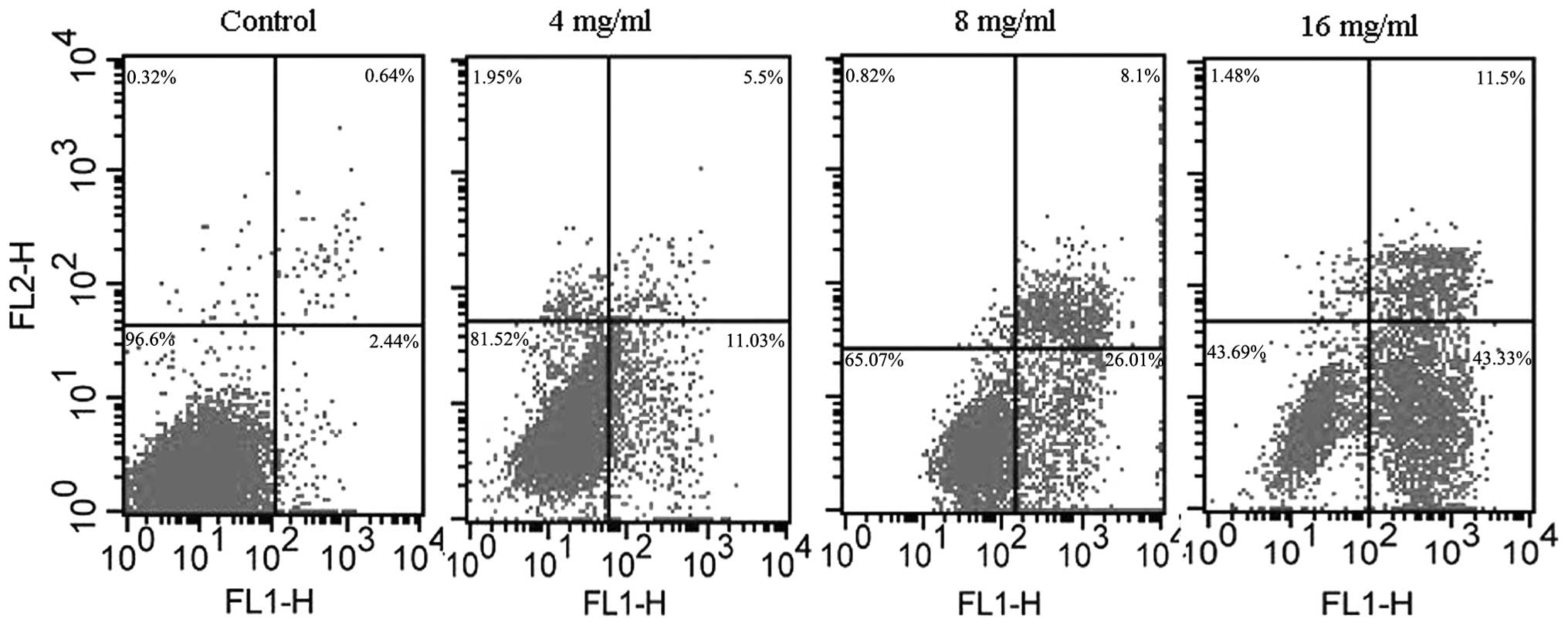
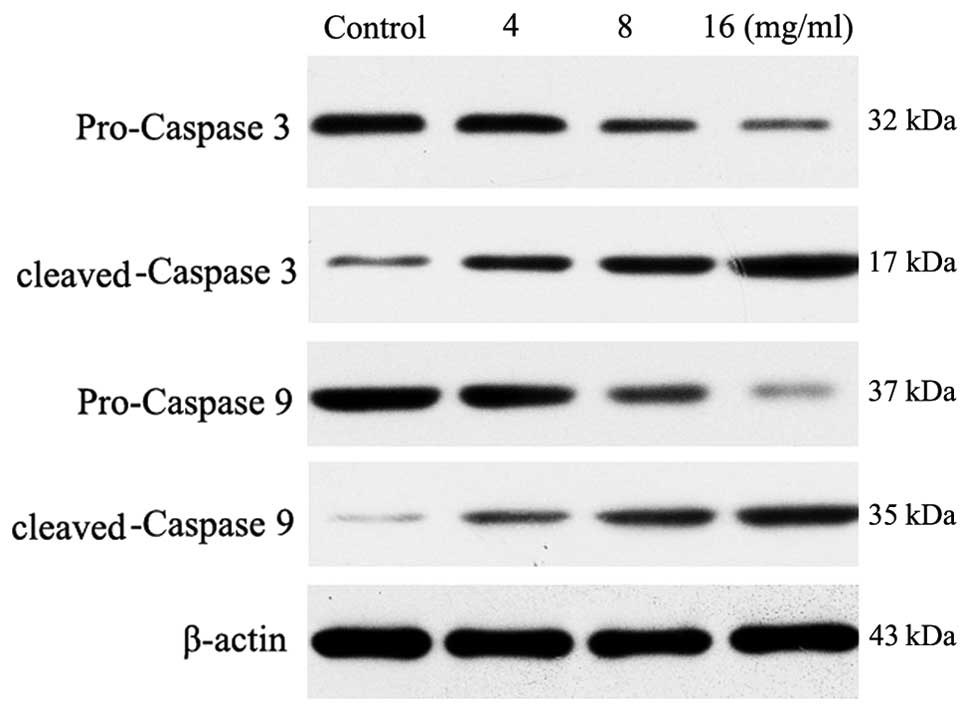
|
1
|
Siegel R, Naishadham D and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J Clin. 62:10–29. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Siegel R, DeSantis C, Virgo K, Stein K,
Mariotto A, Smith T, et al: Cancer treatment and survivorship
statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J Clin. 62:220–241. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward
E and Forman D: Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin.
61:69–90. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Bosetti C, Levi F, Rosato V, et al: Recent
trends in colorectal cancer mortality in Europe. Int J Cancer.
129:180–191. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Møller H, Sandin F, Robinson D, et al:
Colorectal cancer survival in socioeconomic groups in England:
variation is mainly in the short term after diagnosis. Eur J
Cancer. 48:46–53. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Malvezzi M, Arfé A, Bertuccio P, et al:
European cancer mortality predictions for the year 2011. Ann Oncol.
22:947–956. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Kopetz S, Chang GJ, Overman MJ, et al:
Improved survival in metastatic colorectal cancer is associated
with adoption of hepatic resection and improved chemotherapy. J
Clin Oncol. 27:3677–3683. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Coleman MP, Quaresma M, Berrino F, Lutz
JM, De Angelis R, et al; CONCORD Working Group. Cancer survival in
five continents: a worldwide population-based study (CONCORD).
Lancet Oncol. 9:730–756. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Jayne DG, Thorpe HC, Copeland J, et al:
Five-year follow-up of the Medical Research Council CLASICC trial
of laparoscopically assisted versus open surgery for colorectal
cancer. Br J Surg. 97:1638–1645. 2010.
|
|
10
|
Puls R, Langner S, Rosenberg C, et al:
Laser ablation of liver metastases from colorectal cancer with MR
thermometry: 5-year survival. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 20:225–234.
2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Jung KW, Park S, Kong HJ, et al: Cancer
statistics in Korea: incidence, mortality, survival, and prevalence
in 2008. Cancer Res Treat. 43:1–11. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Li DR and Lin HS: Safety and effectiveness
of large dose compound Sophora flavescens Ait injection in
the treatment of advanced malignant tumors. Zhonghua Zhong Liu Za
Zhi. 33:291–294. 2011.(In Chinese).
|
|
13
|
Lin Z, Huang CF, Liu XS and Jiang J: In
vitro anti-tumour activities of quinolizidine alkaloids derived
from Sophora flavescens Ait. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol.
108:304–309. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Meng XH, Lu CF, Zang GH, et al:
Spermicidal effect of alcohol extracts from different ratios of
Sophora flavescens Ait/Chinese Bulbul in vitro. Zhonghua Nan
Ke Xue. 18:83–87. 2012.(In Chinese).
|
|
15
|
Chen S, Peng X and Liu J: Effect of
Sophora flavescens Ait on cultured beating myocardial cells
of Coxsackie B3 virus infected newborn rat. Zhonghua Shi Yan He Lin
Chuang Bing Du Xue Za Zhi. 14:137–140. 2000.(In Chinese).
|
|
16
|
Sun M, Cao H, Sun L, Dong S, et al:
Antitumor activities of kushen: literature review. Evid Based
Complement Alternat Med. 2012:3732192012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Liu T, Song Y, Chen H, et al: Matrine
inhibits proliferation and induces apoptosis of pancreatic cancer
cells in vitro and in vivo. Biol Pharm Bull. 33:1740–1745. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Yu HB, Zhang HF, Li DY, et al: Matrine
inhibits matrix metalloproteinase-9 expression and invasion of
human hepatocellular carcinoma cells. J Asian Nat Prod Res.
13:242–250. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Li H, Tan G, Jiang X, et al: Therapeutic
effects of matrine on primary and metastatic breast cancer. Am J
Chin Med. 38:1115–1130. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Taylor LA, Pletschen L, Arends J, et al:
Marine phospholipids - a promising new dietary approach to
tumor-associated weight loss. Support Care Cancer. 18:159–170.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Xu R, Zhang Y, Ye X, et al: Inhibition
effects and induction of apoptosis of flavonoids on the prostate
cancer cell line PC-3 in vitro. Food Chem. 138:48–53. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Thomas S, Quinn BA, Das SK, et al:
Targeting the Bcl-2 family for cancer therapy. Expert Opin Ther
Targets. 17:61–75. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Low IC, Kang J and Pervaiz S: Bcl-2: a
prime regulator of mitochondrial redox metabolism in cancer cells.
Antioxid Redox Signal. 15:2975–2987. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Mukhtar H: Chemoprevention: making it a
success story for controlling human cancer. Cancer Lett.
326:123–127. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Adhami VM and Mukhtar H: Human cancer
chemoprevention: hurdles and challenges. Top Curr Chem.
329:203–220. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Naviglio S, Caraglia M, Abbruzzese A, et
al: Protein kinase A as a biological target in cancer therapy.
Expert Opin Ther Targets. 13:83–92. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Rasheva VI and Domingos PM: Cellular
responses to endoplasmic reticulum stress and apoptosis. Apoptosis.
14:996–1007. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Ghobrial IM, Witzig TE and Adjei AA:
Targeting apoptosis pathways in cancer therapy. CA Cancer J Clin.
55:178–194. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Circu ML and Aw TY: Reactive oxygen
species, cellular redox systems, and apoptosis. Free Radic Biol
Med. 48:749–762. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Eisenberg-Lerner A, Bialik S, Simon HU and
Kimchi A: Life and death partners: apoptosis, autophagy and the
cross-talk between them. Cell Death Differ. 16:966–775. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Brunelle JK and Letai A: Control of
mitochondrial apoptosis by the Bcl-2 family. J Cell Sci.
122:437–441. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Cotter TG: Apoptosis and cancer: the
genesis of a research field. Nat Rev Cancer. 9:501–507. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Chen HW and Huang HC: Effect of curcumin
on cell cycle progression and apoptosis in vascular smooth muscle
cells. Br J Pharmacol. 124:1029–1040. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Wang C and Youle RJ: The role of
mitochondria in apoptosis. Annu Rev Genet. 43:95–118. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Kang MH and Reynolds CP: Bcl-2 inhibitors:
targeting mitochondrial apoptotic pathways in cancer therapy. Clin
Cancer Res. 15:1126–1132. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Chipuk JE, Moldoveanu T, Llambi F, et al:
The BCL-2 family reunion. Mol Cell. 37:299–310. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Autret A and Martin SJ: Emerging role for
members of the Bcl-2 family in mitochondrial morphogenesis. Mol
Cell. 36:355–363. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Shamas-Din A, Kale J, Leber B and Andrews
DW: Mechanisms of Action of Bcl-2 Family Proteins. Cold Spring Harb
Perspect Biol. 5:a0087142013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Weyhenmeyer B, Murphy AC, Prehn JH and
Murphy BM: Targeting the anti-apoptotic Bcl-2 family members for
the treatment of cancer. Exp Oncol. 34:192–199. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|