|
1
|
Foulkes WD, Smith IE and Reis-Filho JS:
Triple-negative breast cancer. N Engl J Med. 363:1938–1948. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Sun S, Zhao Y and Xu K: Post-adjuvant
chemotherapy for triple-negative breast cancer. Med Hypotheses.
90:74–75. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Wang X, Crowe PJ, Goldstein D and Yang JL:
STAT3 inhibition, a novel approach to enhancing targeted therapy in
human cancers (review). Int J Oncol. 41:1181–1191. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Kim MS, Lee WS, Jeong J, Kim SJ and Jin W:
Induction of metastatic potential by TrkB via activation of
IL6/JAK2/STAT3 and PI3K/AKT signaling in the breast cancer.
Oncotarget. 6:40158–40171. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Wu L, Guo L, Liang Y, Liu X, Jiang L and
Wang L: Curcumin suppresses stem-like traits of lung cancer cells
via inhibiting the JAK2/STAT3 signaling pathway. Oncol Rep.
34:3311–3317. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Zhao H, Guo Y, Li S, Han R, Ying J, Zhu H,
Wang Y, Yin L, Han Y, Sun L, et al: A novel anti-cancer agent
Icaritin suppresses hepatocellular carcinoma initiation and
malignant growth through the IL-6/Jak2/Stat3 pathway. Oncotarget.
6:31927–31943. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Liu X, Wang J, Wang H, Yin G, Liu Y, Lei X
and Xiang M: REG3A accelerates pancreatic cancer cell growth under
IL-6-associated inflammatory condition: Involvement of a
REG3A-JAK2/STAT3 positive feedback loop. Cancer Lett. 362:45–60.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Wang SW, Hu J, Guo QH, Zhao Y, Cheng JJ,
Zhang DS, Fei Q, Li J and Sun YM: AZD1480, a JAK inhibitor,
inhibits cell growth and survival of colorectal cancer via
modulating the JAK2/STAT3 signaling pathway. Oncol Rep.
32:1991–1998. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Jorvig JE and Chakraborty A: Zerumbone
inhibits growth of hormone refractory prostate cancer cells by
inhibiting JAK2/STAT3 pathway and increases paclitaxel sensitivity.
Anticancer Drugs. 26:160–166. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Gritsina G, Xiao F, O'Brien SW, Gabbasov
R, Maglaty MA, Xu RH, Thapa RJ, Zhou Y, Nicolas E, Litwin S, et al:
Targeted blockade of JAK/STAT3 signaling inhibits ovarian carcinoma
Growth. Mol Cancer Ther. 14:1035–1047. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Judd LM, Menheniott TR, Ling H, Jackson
CB, Howlett M, Kalantzis A, Priebe W and Giraud AS: Inhibition of
the JAK2/STAT3 pathway reduce gastric cancer growth in vitro and in
vivo. PLoS One. 9:e959932014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Liu Y, Wang L, Wu Y, Lv C, Li X, Cao X,
Yang M, Feng D and Luo Z: Pterostilbene exerts antitumor activity
against human osteosarcoma cells by inhibiting the JAK2/STAT3
signaling pathway. Toxicology. 304:120–131. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
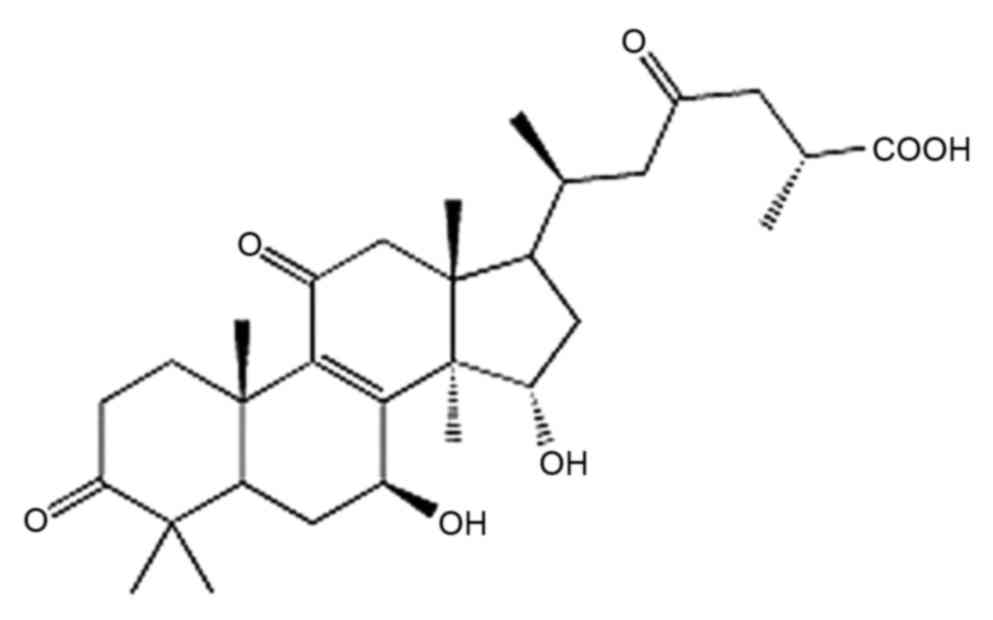
Ruan W, Wei Y and Popovich DG: Distinct
responses of cytotoxic Ganoderma lucidum trierpenoids in human
carcinoma cells. Phytother Res. 29:1744–1752. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Radwan FF, Hossain A, God JM, Leaphart N,
Elvington M, Nagarkatti M, Tomlinson S and Haque A: Reduction of
myeloid-derived suppressor cells and lymphoma growth by a natural
triterpenoid. J Cell Biochem. 116:102–114. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Yao X, Li G, Xu H and Lü C: Inhibition of
the JAK-STAT3 signaling pathway by ganoderic acid A enhances
chemosensitivity of HepG2 cells to cisplatin. Planta Med.
78:1740–1748. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Shao J, Li Z, Jiao G, Sun G and Zhou Z:
Ganoderic acid A suppresses proliferation and invasion and induces
apoptosis in human osteosarcoma cells. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue
Bao. 35:619–624. 2015.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Quintás-Cardama A and Verstovsek S:
Molecular pathways: JAK/STAT pathway: Mutations, inhibitors, and
resistance. Clin Cancer Res. 19:1933–1940. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Buchert M, Burns CJ and Ernst M: Targeting
JAK kinase in solid tumors: Emerging opportunities and challenges.
Oncogene. 35:939–951. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Khanna P, Chua PJ, Bay BH and Baeg GH: The
JAK/STAT signaling cascade in gastric carcinoma (Review). Int J
Oncol. 47:1617–1626. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
O'Shea JJ, Holland SM and Staudt LM: JAKs
and STATs in immunity, immunodeficiency, and cancer. N Engl J Med.
368:161–170. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Bowman T, Garcia R, Turkson J and Jove R:
STATs in oncogenesis. Oncogene. 19:2474–2488. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Yu H, Pardoll D and Jove R: STATs in
cancer inflammation and immunity: A leading role for STAT3. Nat Rev
Cancer. 9:798–809. 2009. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Walker SR, Xiang M and Frank DA: STAT3
activity and function in cancer: Modulation by STAT5 and miR-146b.
Cancers (Basel). 6:958–968. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
He G and Karin M: NF-κB and STAT3-key
players in liver inflammation and cancer. Cell Res. 21:159–168.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Frank DA: STAT3 as a central mediator of
neoplastic cellular transformation. Cancer Lett. 251:199–210. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Schroeder A, Herrmann A, Cherryholmes G,
Kowolik C, Buettner R, Pal S, Yu H, Müller-Newen G and Jove R: Loss
of androgen receptor expression promotes a stem-like cell phenotype
in prostate cancer through STAT3 signaling. Cancer Res.
74:1227–1237. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Lin L, Liu A, Peng Z, Lin HJ, Li PK, Li C
and Lin J: STAT3 is necessary for proliferation and survival in
colon cancer-initiating cells. Cancer Res. 71:7226–7237. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Kim DY, Cha ST, Ahn DH, Kang HY, Kwon CI,
Ko KH, Hwang SG, Park PW, Rim KS and Hong SP: STAT3 expression in
gastric cancer indicates a poor prognosis. J Gastroenterol Hepatol.
24:646–651. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Wei D, Le X, Zheng L, Wang L, Frey JA, Gao
AC, Peng Z, Huang S, Xiong HQ, Abbruzzese JL and Xie K: Stat3
activation regulates the expression of vascular endothelial growth
factor and human pancreatic cancer angiogenesis and metastasis.
Oncogene. 22:319–329. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Kamran MZ, Patil P and Gude RP: Role of
STAT3 in cancer metastasis and translational advance. Biomed Res
Int. 2013:4218212013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Li Y, Yang F, Zheng W, Hu M, Wang J, Ma S,
Deng Y, Luo Y, Ye T and Yin W: Punica granatum (pomegranate) leaves
extract induces apoptosis through mitochondrial intrinsic pathway
and inhibits migration and invasion in non-small cell lung cancer
in vitro. Biomed Pharmacother. 80:227–235. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Li X, Zhang Q, Cai L, Wang Y, Wang Q,
Huang X, Fu S, Bai J, Liu J, Zhang G and Qi J: Inhibitor of growth
4 induces apoptosis in human lung adenocarcinoma cell line A549 via
Bcl-2 family proteins and mitochondria apoptosis pathway. J Cancer
Res Clin Oncol. 135:829–835. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Su JC, Lin KL, Chien CM, Chuang PW, Chang
LS and Lin SR: Concomitant inactivation of the epidermal growth
factor receptor, phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt and Janus
tyrosine kinase 2/signal transducer and activator of transcription
3 signalling pathways in cardiotoxin III-treated A549 cells. Clin
Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 37:833–840. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Du W, Hong J, Wang YC, Zhang YJ, Wang P,
Su WY, Lin YW, Lu R, Zou WP, Xiong H and Fang JY: Inhibition of
JAK2/STAT3 signalling induces colorectal cancer cell apoptosis via
mitochondrial pathway. J Cell Mol Med. 16:1878–1888. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Bhardwaj M, Kim NH, Paul S, Jakhar R, Han
J and Kang SC: 5-Hydroxy-7-methoxyflavone triggers
mitochondrial-associated cell death via reactive oxygen species
signaling in human colon carcinoma cells. PLoS One.
11:e01545252016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Zhang F, Wang Z, Yuan J, Wei X, Tian R and
Niu R: RNAi-mediated silencing of Anxa2 inhibits breast cancer cell
proliferation by downregulating cyclin D1 in STAT3-dependent
pathway. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 153:263–275. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Cai Q, Lin J, Wei L, Zhang L, Wang L, Zhan
Y, Zeng J, Xu W, Shen A, Hong Z and Peng J: Hedyotis diffusa Willd
inhibits colorectal cancer growth in vivo via inhibition of STAT3
signaling pathway. Int J Mol Sci. 13:6117–6128. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Zhou Y, Zeng Z, Zhang W, Xiong W, Wu M,
Tan Y, Yi W, Xiao L, Li X, Huang C, et al: Lactotransferrin: A
candidate tumor suppressor-deficient expression in human
nasopharyngeal carcinoma and inhibition of NPC cell proliferation
by modulating the mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway. Int J
Cancer. 123:2065–2072. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Sai K, Wang S, Balasubramaniyan V, Conrad
C, Lang FF, Aldape K, Szymanski S, Fokt I, Dasgupta A, Madden T, et
al: Induction of cell-cycle arrest and apoptosis in glioblastoma
stem-like cells by WP1193, a novel small molecule inhibitor of the
JAK2/STAT3 pathway. J Neurooncol. 107:487–501. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|