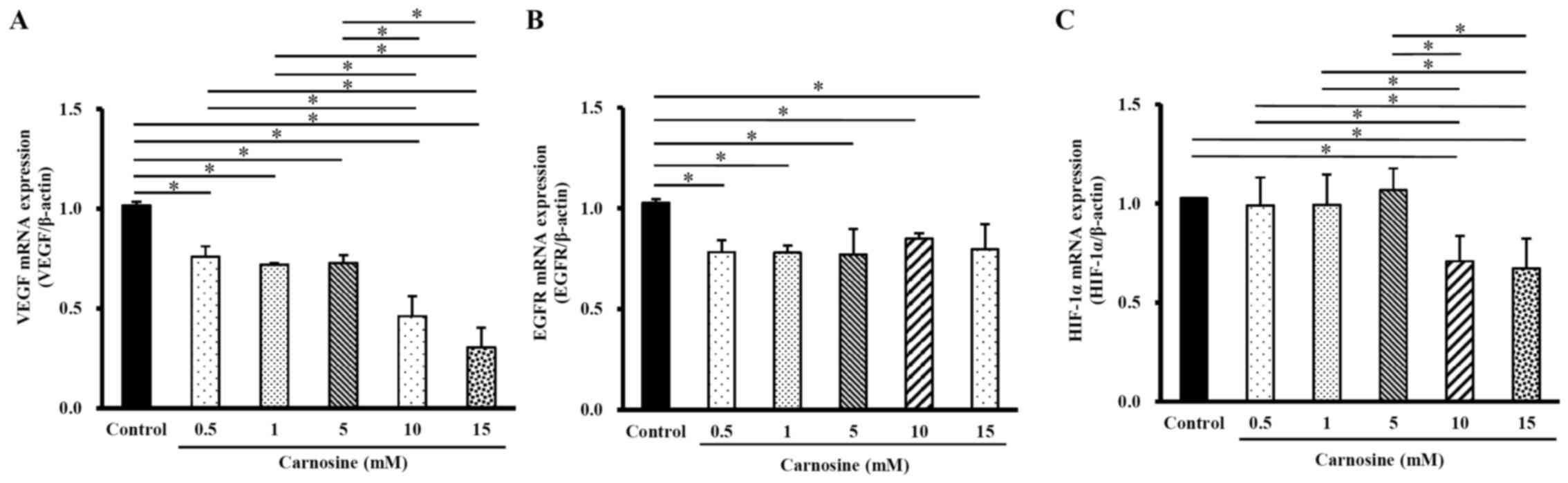
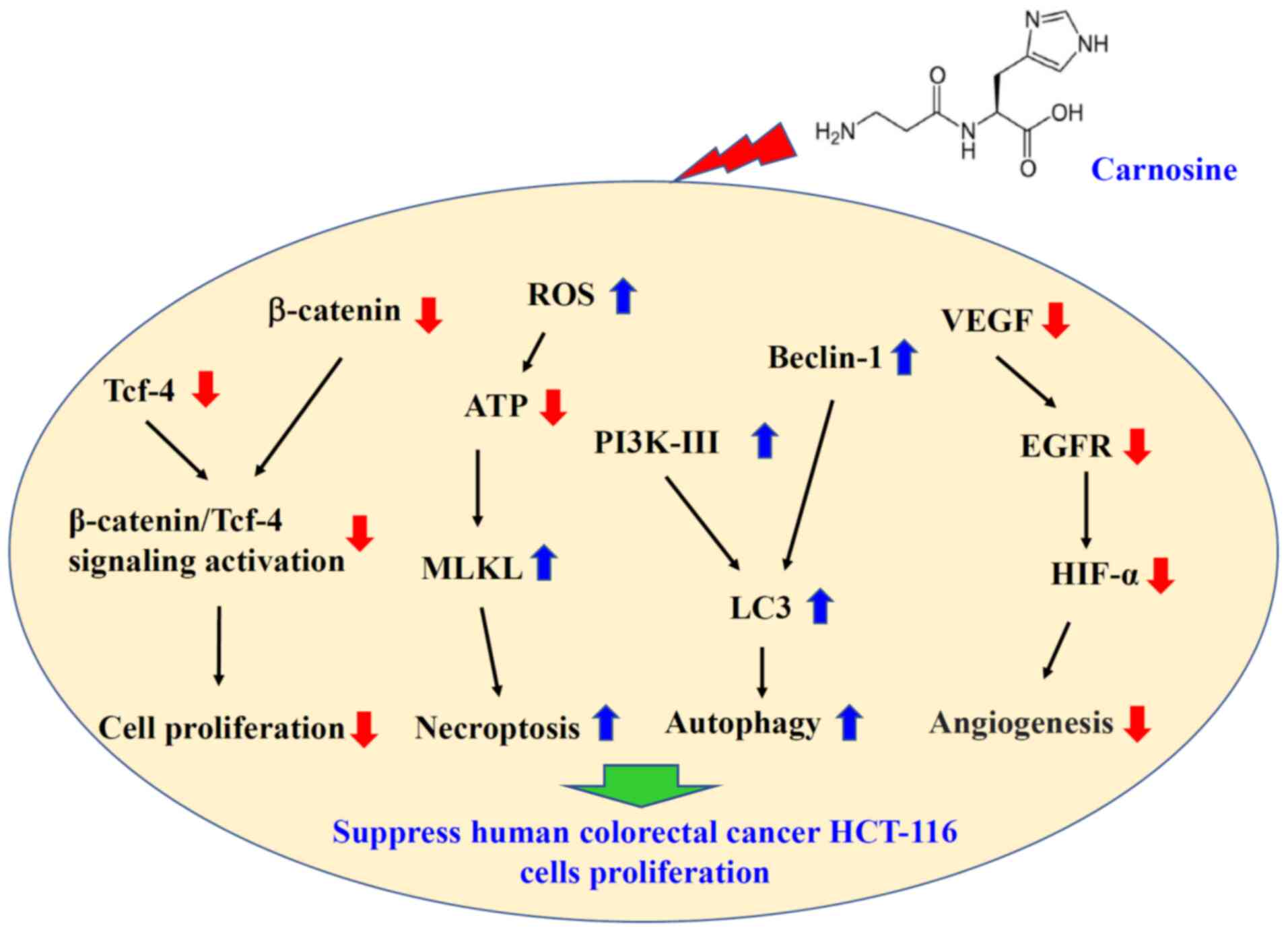
|
1
|
Boldyrev AA, Aldini G and Derave W:
Physiology and pathophysiology of carnosine. Physiol Rev.
93:1803–1845. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Hipkiss AR, Baye E and de Courten B:
Carnosine and the processes of ageing. Maturitas. 93:28–33. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Jain S, Kim ES, Kim D, Burrows D, De
Felice M, Kim M, Baek SH, Ali A, Redgrave J, Doeppner TR, et al:
Comparative cerebroprotective potential of d- and l-carnosine
following ischemic stroke in mice. Int J Mol Sci. 21:30532020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Prokopieva VD, Yarygina EG, Bokhan NA and
Ivanova SA: Use of carnosine for oxidative stress reduction in
different pathologies. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2016:29390872016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Caruso G, Fresta CG, Musso N, Giambirtone
M, Grasso M, Spampinato SF, Merlo S, Drago F, Lazzarino G, Sortino
MA, et al: Carnosine prevents Aβ-induced oxidative stress and
inflammation in microglial cells: A key role of TGF-β1. Cells.
8:642019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Bermúdez ML, Seroogy KB and Genter MB:
Evaluation of carnosine intervention in the Thy1-aSyn mouse model
of Parkinson's disease. Neuroscience. 411:270–278. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Hsieh SL, Hsieh S, Lai PY, Wang JJ, Li CC
and Wu CC: Carnosine suppresses human colorectal cell migration and
intravasation by regulating EMT and mMP expression. Am J Chin Med.
47:477–494. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Wu CC, Lai PY, Hsieh S, Cheng CC and Hsieh
SL: Suppression of carnosine on adhesion and extravasation of human
colorectal cancer cells. Anticancer Res. 39:6135–6144. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Zhang Z, Miao L, Wu X, Liu G, Peng Y, Xin
X, Jiao B and Kong X: Carnosine inhibits the proliferation of human
gastric carcinoma cells by retarding Akt/mTOR/p70S6K signaling. J
Cancer. 5:382–389. 2014. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Tamaki N, Funatsuka A, Fujimoto S and Hama
T: The utilization of carnosine in rats fed on a histidine-free
diet and its effect on the levels of tissue histidine and
carnosine. J Nutr Sci Vitaminol (Tokyo). 30:541–551. 1984.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Gariballa SE and Sinclair AJ: Carnosine:
Physiological properties and therapeutic potential. Age Ageing.
29:207–210. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Zhao K, Li Y, Wang Z, Han N and Wang Y:
Carnosine protects mouse podocytes from high glucose induced
apoptosis through PI3K/AKT and Nrf2 pathways. BioMed Res Int.
2019:43489732019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Lee J, Park JR, Lee H, Jang S, Ryu SM, Kim
H, Kim D, Jang A and Yang SR: L-carnosine induces apoptosis/cell
cycle arrest via suppression of NF-κB/STAT1 pathway in HCT116
colorectal cancer cells. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim. 54:505–512.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Joshi RK, Kim WJ and Lee SA: Association
between obesity-related adipokines and colorectal cancer: A
case-control study and meta-analysis. World J Gastroenterol.
20:7941–7949. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel
RL, Torre LA and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN
estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in
185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 68:394–424. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Chaabane W, User SD, El-Gazzah M, Jaksik
R, Sajjadi E, Rzeszowska-Wolny J and Los MJ: Autophagy, apoptosis,
mitoptosis and necrosis: Interdependence between those pathways and
effects on cancer. Arch Immunol Ther Exp (Warsz). 61:43–58. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Martinez-Font E, Pérez-Capó M, Ramos R,
Felipe I, Garcías C, Luna P, Terrasa J, Martín-Broto J, Vögler O,
Alemany R, et al: Impact of Wnt/β-Catenin Inhibition on Cell
Proliferation through CDC25A Downregulation in Soft Tissue
Sarcomas. Cancers (Basel). 12:25562020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Hikita H, Kodama T, Shimizu S, Li W,
Shigekawa M, Tanaka S, Hosui A, Miyagi T, Tatsumi T, Kanto T, et
al: Bak deficiency inhibits liver carcinogenesis: A causal link
between apoptosis and carcinogenesis. J Hepatol. 57:92–100. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Ahamed M, Akhtar MJ, Siddiqui MA, Ahmad J,
Musarrat J, Al-Khedhairy AA, AlSalhi MS and Alrokayan SA: Oxidative
stress mediated apoptosis induced by nickel ferrite nanoparticles
in cultured A549 cells. Toxicology. 283:101–108. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Galati S, Boni C, Gerra MC, Lazzaretti M
and Buschini A: Autophagy: A player in response to oxidative stress
and DNA damage. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2019:56929582019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Shimizu S, Yoshida T, Tsujioka M and
Arakawa S: Autophagic cell death and cancer. Int J Mol Sci.
15:3145–3153. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Robinson N, Ganesan R, Hegedűs C, Kovács
K, Kufer TA and Virág L: Programmed necrotic cell death of
macrophages: Focus on pyroptosis, necroptosis, and parthanatos.
Redox Biol. 26:1012392019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Wu W, Liu P and Li J: Necroptosis: An
emerging form of programmed cell death. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol.
82:249–258. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Manda G, Isvoranu G, Comanescu MV, Manea
A, Debelec Butuner B and Korkmaz KS: The redox biology network in
cancer pathophysiology and therapeutics. Redox Biol. 5:347–357.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Wang K, Liu R, Li J, Mao J, Lei Y, Wu J,
Zeng J, Zhang T, Wu H, Chen L, et al: Quercetin induces protective
autophagy in gastric cancer cells: Involvement of Akt-mTOR- and
hypoxia-induced factor 1α-mediated signaling. Autophagy. 7:966–978.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Fulda S: Cell death and survival signaling
in oncogenesis. Klin Padiatr. 222:340–344. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Denizot F and Lang R: Rapid colorimetric
assay for cell growth and survival. Modifications to the
tetrazolium dye procedure giving improved sensitivity and
reliability. J Immunol Methods. 89:271–277. 1986. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Chomczynski P and Sacchi N: Single-step
method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium
thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem.
162:156–159. 1987. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−ΔΔC(T)) Method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Cho YH, Ro EJ, Yoon JS, Mizutani T, Kang
DW, Park JC, Il Kim T, Clevers H and Choi KY: 5-FU promotes
stemness of colorectal cancer via p53-mediated WNT/β-catenin
pathway activation. Nat Commun. 11:53212020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Kanzawa T, Germano IM, Komata T, Ito H,
Kondo Y and Kondo S: Role of autophagy in temozolomide-induced
cytotoxicity for malignant glioma cells. Cell Death Differ.
11:448–457. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Prieto-Domínguez N, Ordóñez R, Fernández
A, García-Palomo A, Muntané J, González-Gallego J and Mauriz JL:
Modulation of autophagy by sorafenib: Effects on treatment
response. Front Pharmacol. 7:1512016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Wu Y, Dong G and Sheng C: Targeting
necroptosis in anticancer therapy: Mechanisms and modulators. Acta
Pharm Sin B. 10:1601–1618. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Capozzi M, De Divitiis C, Ottaiano A, von
Arx C, Scala S, Tatangelo F, Delrio P and Tafuto S: Lenvatinib, a
molecule with versatile application: From preclinical evidence to
future development in anti-cancer treatment. Cancer Manag Res.
11:3847–3860. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Chao DL, Sanchez CA, Galipeau PC, Blount
PL, Paulson TG, Cowan DS, Ayub K, Odze RD, Rabinovitch PS and Reid
BJ: Cell proliferation, cell cycle abnormalities, and cancer
outcome in patients with Barrett's esophagus: A long-term
prospective study. Clin Cancer Res. 14:6988–6995. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Tiwari M: Apoptosis and survival. Indian J
Hum Genet. 17:120–125. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Loo G: Redox-sensitive mechanisms of
phytochemical-mediated inhibition of cancer cell proliferation
(review). J Nutr Biochem. 14:64–73. 2003.(review). View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Shi Y and Zhang CJ: The effects of
carnosine on high glucose-induced apoptosis of human umbilical vein
endothelial cells. Adv Mat Res. 345:365–369. 2011.
|
|
39
|
Mateyak MK, Obaya AJ and Sedivy JM: c-Myc
regulates cyclin D-Cdk4 and -Cdk6 activity but affects cell cycle
progression at multiple independent points. Mol Cell Biol.
19:4672–4683. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Tian Y, Wan H and Tan G: Cell
cycle-related kinase in carcinogenesis. Oncol Lett. 4:601–606.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Sebio A, Kahn M and Lenz HJ: The potential
of targeting Wnt/β-catenin in colon cancer. Expert Opin Ther
Targets. 18:611–615. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Sakoguchi-Okada N, Takahashi-Yanaga F,
Fukada K, Shiraishi F, Taba Y, Miwa Y, Morimoto S, Iida M and
Sasaguri T: Celecoxib inhibits the expression of survivin via the
suppression of promoter activity in human colon cancer cells.
Biochem Pharmacol. 73:1318–1329. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Shan BE, Wang MX and Li RQ: Quercetin
inhibit human SW480 colon cancer growth in association with
inhibition of cyclin D1 and survivin expression through
Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway. Cancer Invest. 27:604–612.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Ha T, Lou Z, Baek SJ and Lee SH:
Tolfenamic acid downregulates β-catenin in colon cancer. Int
Immunopharmacol. 35:287–293. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Han D, Cao C, Su Y, Wang J, Sun J, Chen H
and Xu A: Ginkgo biloba exocarp extracts inhibits
angiogenesis and its effects on Wnt/β-catenin-VEGF signaling
pathway in Lewis lung cancer. J Ethnopharmacol. 192:406–412. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Kang R, Zeh HJ, Lotze MT and Tang D: The
Beclin 1 network regulates autophagy and apoptosis. Cell Death
Differ. 18:571–580. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Mizushima N: Autophagy. FEBS Lett.
584:12792010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Klionsky DJ and Emr SD: Autophagy as a
regulated pathway of cellular degradation. Science. 290:1717–1721.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Ertmer A, Huber V, Gilch S, Yoshimori T,
Erfle V, Duyster J, Elsässer HP and Schätzl HM: The anticancer drug
imatinib induces cellular autophagy. Leukemia. 21:936–942. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Guamán-Ortiz LM, Romero-Benavides JC,
Suarez AI, Torres-Aguilar S, Castillo-Veintimilla P,
Samaniego-Romero J, Ortiz-Diaz K and Bailon-Moscoso N: Cytotoxic
property of Grias neuberthii extract on human colon cancer
cells: A crucial role of autophagy. Evid Based Complement Alternat
Med. 2020:15653062020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Hsieh LC, Hsieh SL, Chen CT, Chung JG,
Wang JJ and Wu CC: Induction of α-phellandrene on autophagy in
human liver tumor cells. Am J Chin Med. 43:121–136. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Hsieh SL, Chen CT, Wang JJ, Kuo YH, Li CC,
Hsieh LC and Wu CC: Sedanolide induces autophagy through the PI3K,
p53 and NF-κB signaling pathways in human liver cancer cells. Int J
Oncol. 47:2240–2246. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Rong L, Li Z, Leng X, Li H, Ma Y, Chen Y
and Song F: Salidroside induces apoptosis and protective autophagy
in human gastric cancer AGS cells through the PI3K/Akt/mTOR
pathway. Biomed Pharmacother. 122:1097262020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Galluzzi L, Kepp O, Chan FK and Kroemer G:
Necroptosis: Mechanisms and relevance to disease. Annu Rev Pathol.
12:103–130. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Dhuriya YK and Sharma D: Necroptosis: A
regulated inflammatory mode of cell death. J Neuroinflammation.
15:1992018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Schenk B and Fulda S: Reactive oxygen
species regulate Smac mimetic/TNFα-induced necroptotic signaling
and cell death. Oncogene. 34:5796–5806. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Lee YJ, Park KS, Nam HS, Cho MK and Lee
SH: Apigenin causes necroptosis by inducing ROS accumulation,
mitochondrial dysfunction, and ATP depletion in malignant
mesothelioma cells. Korean J Physiol Pharmacol. 24:493–502. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Liu X, Zhang Y, Gao H, Hou Y, Lu JJ, Feng
Y, Xu Q, Liu B and Chen X: Induction of an MLKL mediated
non-canonical necroptosis through reactive oxygen species by
tanshinol A in lung cancer cells. Biochem Pharmacol.
171:1136842020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Jackson AL, Zhou B and Kim WY: HIF,
hypoxia and the role of angiogenesis in non-small cell lung cancer.
Expert Opin Ther Targets. 14:1047–1057. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Lichtenberger BM, Tan PK, Niederleithner
H, Ferrara N, Petzelbauer P and Sibilia M: Autocrine VEGF signaling
synergizes with EGFR in tumor cells to promote epithelial cancer
development. Cell. 140:268–279. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Huang KF, Zhang GD, Huang YQ and Diao Y:
Wogonin induces apoptosis and down-regulates survivin in human
breast cancer MCF-7 cells by modulating PI3K-AKT pathway. Int
Immunopharmacol. 12:334–341. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Zheng HL, Yang J, Hou Y, Sun B, Zhang Q,
Mou Y, Wand L and Wu C: Oligomer procyanidins (F2) isolated from
grape seeds inhibits tumor angiogenesis and cell invasion by
targeting HIF-1α in vitro. Int J Oncol. 46:708–720. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Quinn PJ, Boldyrev AA and Formazuyk VE:
Carnosine: Its properties, functions and potential therapeutic
applications. Mol Aspects Med. 13:379–444. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Hipkiss AR: Carnosine, a protective,
anti-ageing peptide? Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 30:863–868. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Sampathkumar SG, Jones MB, Meledeo MA,
Campbell CT, Choi SS, Hida K, Gomutputra P, Sheh A, Gilmartin T,
Head SR, et al: Targeting glycosylation pathways and the cell
cycle: Sugar-dependent activity of butyrate-carbohydrate cancer
prodrugs. Chem Biol. 13:1265–1275. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Fahie K and Zachara NE: Molecular
functions of glycoconjugates in autophagy. J Mol Biol.
428:3305–3324. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Cheng WK and Oon CE: How glycosylation
aids tumor angiogenesis: An updated review. Biomed Pharmacother.
103:1246–1252. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Hipkiss AR, Michaelis J and Syrris P:
Non-enzymatic glycosylation of the dipeptide L-carnosine, a
potential anti-protein-cross-linking agent. FEBS Lett. 371:81–85.
1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Hipkiss AR and Gaunitz F: Inhibition of
tumour cell growth by carnosine: some possible mechanisms. Amino
Acids. 46:327–337. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Li Y, Wang K, Chen L, Zhu X and Zhou J:
Quantification of mRNA Levels Using Real-Time Polymerase Chain
Reaction (PCR). Methods Mol Biol. 1406:73–79. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Deribe YL, Pawson T and Dikic I:
Post-translational modifications in signal integration. Nat Struct
Mol Biol. 17:666–672. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|