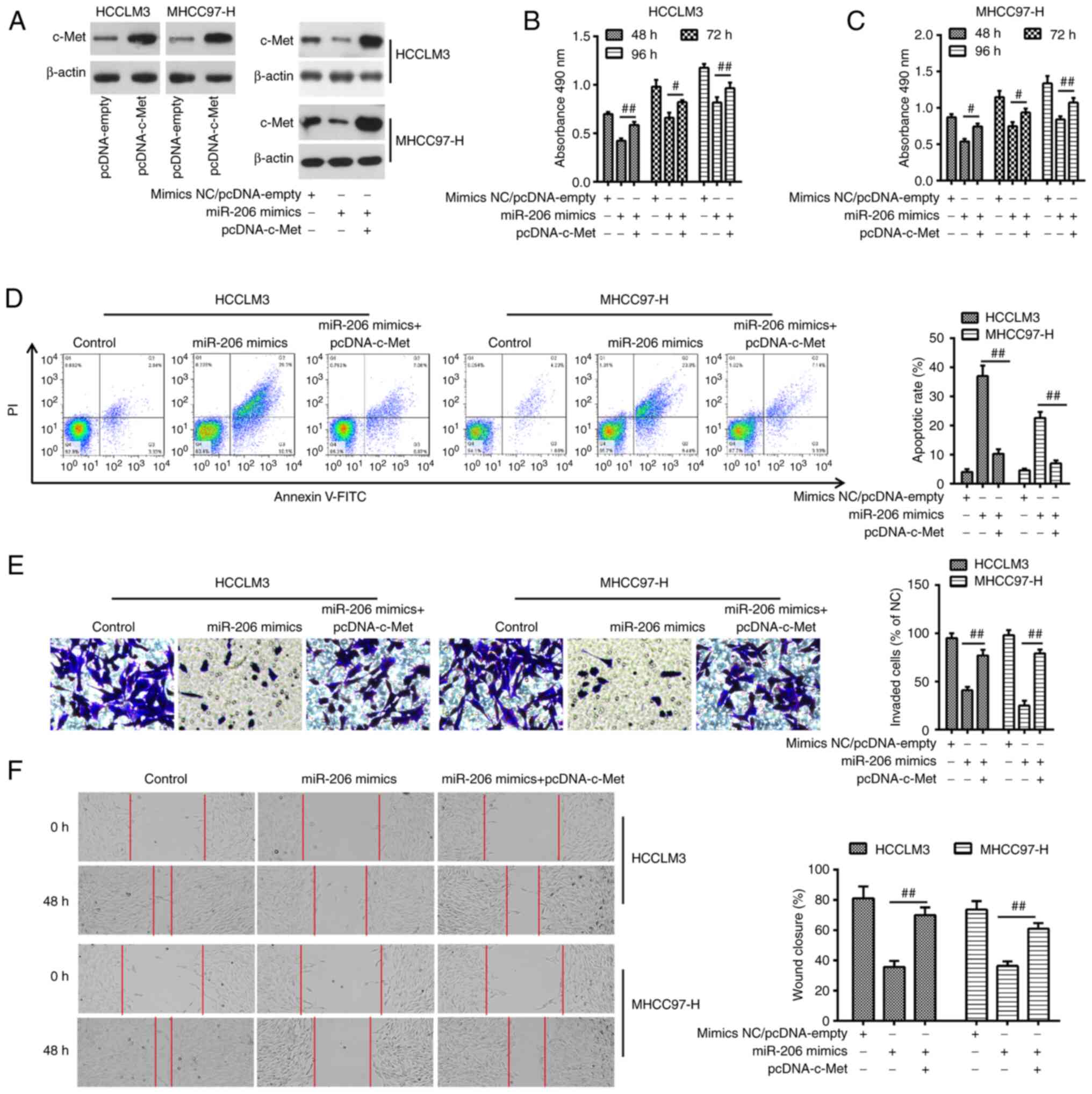
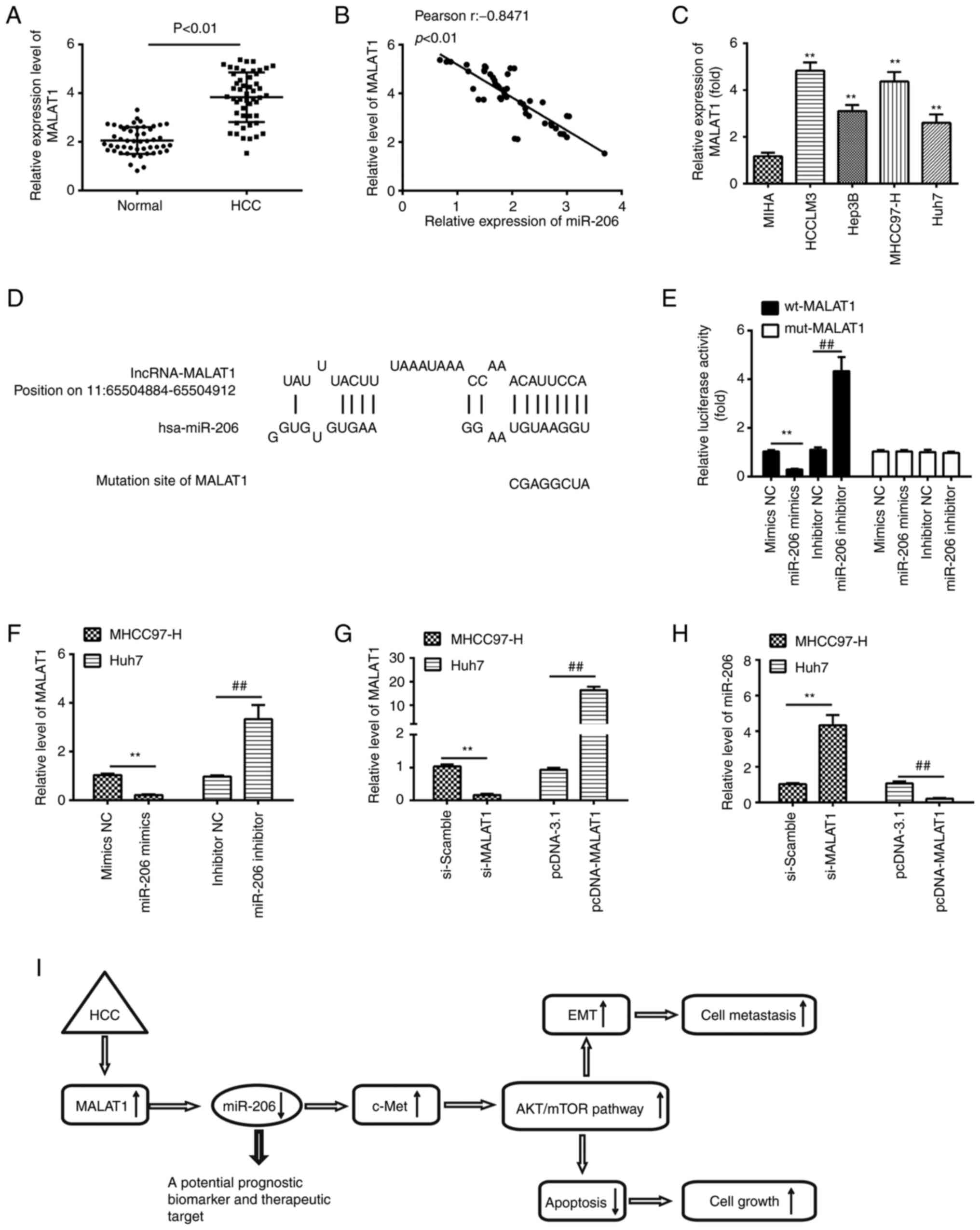
|
1
|
Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, Ferlay J,
Lortet-Tieulent J and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA
Cancer J Clin. 65:87–108. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Zhang J, Zhou ZG, Huang ZX, Yang KL, Chen
JC, Chen JB, Xu L, Chen MS and Zhang YJ: Prospective, single-center
cohort study analyzing the efficacy of complete laparoscopic
resection on recurrent hepatocellular carcinoma. Chin J Cancer.
35:252016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
El-Serag HB and Rudolph KL: Hepatocellular
carcinoma: Epidemiology and molecular carcinogenesis.
Gastroenterology. 132:2557–2576. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Li X, Li C, Zhang L, Wu M, Cao K, Jiang F,
Chen D, Li N and Li W: The significance of exosomes in the
development and treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma. Mol Cancer.
19:12020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Rizzo A, Ricci AD, Gadaleta-Caldarola G
and Brandi G: First-line immune checkpoint inhibitor-based
combinations in unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma: Current
management and future challenges. Expert Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol.
15:1245–1251. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Rizzo A, Nannini M, Novelli M, Dalia Ricci
A, Scioscio VD and Pantaleo MA: Dose reduction and discontinuation
of standard-dose regorafenib associated with adverse drug events in
cancer patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Ther Adv
Med Oncol. 12:17588359209369322020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
De Lorenzo S, Tovoli F, Barbera MA, Garuti
F, Palloni A, Frega G, Garajovà I, Rizzo A, Trevisani F and Brandi
G: Metronomic capecitabine vs best supportive care in Child-Pugh B
hepatocellular carcinoma: A proof of concept. Sci Rep. 8:99972018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Rizzo A, Ricci AD, Di Federico A, Frega G,
Palloni A, Tavolari S and Brandi G: Predictive biomarkers for
checkpoint inhibitor-based immunotherapy in hepatocellular
carcinoma: Where do we stand? Front Oncol. 11:8031332021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Pahlavan Y, Mohammadi Nasr M, Dalir
Abdolahinia E, Pirdel Z, Razi Soofiyani S, Siahpoush S and Nejati
K: Prominent roles of microRNA-142 in cancer. Pathol Res Pract.
216:1532202020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Ali Syeda Z, Langden SSS, Munkhzul C, Lee
M and Song SJ: Regulatory mechanism of MicroRNA expression in
cancer. Int J Mol Sci. 21:17232020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Hussen BM, Hidayat HJ, Salihi A, Sabir DK,
Taheri M and Ghafouri-Fard S: MicroRNA: A signature for cancer
progression. Biomed Pharmacother. 138:1115282021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Fornari F, Gramantieri L, Callegari E,
Shankaraiah RC, Piscaglia F, Negrini M and Giovannini C: MicroRNAs
in animal models of HCC. Cancers (Basel). 11:19062019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Yin LC, Xiao G, Zhou R, Huang XP, Li NL,
Tan CL, Xie FJ, Weng J and Liu LX: MicroRNA-361-5p inhibits
tumorigenesis and the EMT of HCC by targeting Twist1. Biomed Res
Int. 2020:88918762020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Jiang T, Guan LY, Ye YS, Liu HY and Li R:
MiR-874 inhibits metastasis and epithelial-mesenchymal transition
in hepatocellular carcinoma by targeting SOX12. Am J Cancer Res.
7:1310–1321. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Li DP, Fan J, Wu YJ, Xie YF, Zha JM and
Zhou XM: MiR-155 up-regulated by TGF-β promotes
epithelial-mesenchymal transition, invasion and metastasis of human
hepatocellular carcinoma cells in vitro. Am J Transl Res.
9:2956–2965. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Komoll RM, Hu Q, Olarewaju O, von Döhlen
L, Yuan Q, Xie Y, Tsay HC, Daon J, Qin R, Manns MP, et al:
MicroRNA-342-3p is a potent tumour suppressor in hepatocellular
carcinoma. J Hepatol. 74:122–134. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Khare S, Khare T, Ramanathan R and Ibdah
JA: Hepatocellular carcinoma: The role of MicroRNAs. Biomolecules.
12:6452022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Wei L, Wang X, Lv L, Liu J, Xing H, Song
Y, Xie M, Lei T, Zhang N and Yang M: The emerging role of microRNAs
and long noncoding RNAs in drug resistance of hepatocellular
carcinoma. Mol Cancer. 18:1472019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Shao Y, Ye M, Li Q, Sun W, Ye G, Zhang X,
Yang Y, Xiao B and Guo J: LncRNA-RMRP promotes carcinogenesis by
acting as a miR-206 sponge and is used as a novel biomarker for
gastric cancer. Oncotarget. 7:37812–37824. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Ma F, Wang SH, Cai Q, Jin LY, Zhou D, Ding
J and Quan ZW: Long non-coding RNA TUG1 promotes cell proliferation
and metastasis by negatively regulating miR-300 in gallbladder
carcinoma. Biomed Pharmacother. 88:863–869. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Zhang CZ: Long non-coding RNA FTH1P3
facilitates oral squamous cell carcinoma progression by acting as a
molecular sponge of miR-224-5p to modulate fizzled 5 expression.
Gene. 607:47–55. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Song W, Wenhui Z, Ruiqiang Y, Hu X, Shi T,
Wang M and Zhang H: Long noncoding RNA PP7080 promotes
hepatocellular carcinoma development by sponging mir-601 and
targeting SIRT1. Bioengineered. 12:1599–1610. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Guan MM, Rao QX, Huang ML, Wang LJ, Lin
SD, Chen Q and Liu CH: Long noncoding RNA TP73-AS1 targets
MicroRNA-329-3p to regulate expression of the SMAD2 gene in human
cervical cancer tissue and cell lines. Med Sci Monit. 25:8131–8141.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Zhuang LK, Yang YT, Ma X, Han B, Wang ZS,
Zhao QY, Wu LQ and Qu ZQ: MicroRNA-92b promotes hepatocellular
carcinoma progression by targeting Smad7 and is mediated by long
non-coding RNA XIST. Cell Death Dis. 7:e22032016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Chen X, Tong ZK and Zhou JY, Yao YK, Zhang
SM and Zhou JY: MicroRNA-206 inhibits the viability and migration
of human lung adenocarcinoma cells partly by targeting MET. Oncol
Lett. 12:1171–1177. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Ren XL, He GY, Li XM, Men H, Yi LZ, Lu GF,
Xin SN, Wu PX, Li YL, Liao WT, et al: MicroRNA-206 functions as a
tumor suppressor in colorectal cancer by targeting FMNL2. J Cancer
Res Clin Oncol. 142:581–592. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Liang Z, Bian X and Shim H: Downregulation
of microRNA-206 promotes invasion and angiogenesis of triple
negative breast cancer. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 477:461–466.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Yunqiao L, Vanke H, Jun X and Tangmeng G:
MicroRNA-206, down-regulated in hepatocellular carcinoma,
suppresses cell proliferation and promotes apoptosis.
Hepatogastroenterology. 61:1302–1307. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Iwatsuki M, Mimori K, Yokobori T, Ishi H,
Beppu T, Nakamori S, Baba H and Mori M: Epithelial-mesenchymal
transition in cancer development and its clinical significance.
Cancer Sci. 101:293–299. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Chen QY, Jiao DM, Yan L, Wu YQ, Hu HZ,
Song J, Yan J, Wu LJ, Xu LQ and Shi JG: Comprehensive gene and
microRNA expression profiling reveals miR-206 inhibits MET in lung
cancer metastasis. Mol Biosyst. 11:2290–2302. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Chen QY, Jiao DM, Wu YQ, Chen J, Wang J,
Tang XL, Mou H, Hu HZ, Song J, Yan J, et al: MiR-206 inhibits
HGF-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition and angiogenesis in
non-small cell lung cancer via c-Met/PI3k/Akt/mTOR pathway.
Oncotarget. 7:18247–18261. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Zhang J, Fa X and Zhang Q: MicroRNA-206
exerts anti-oncogenic functions in esophageal squamous cell
carcinoma by suppressing the c-Met/AKT/mTOR pathway. Mol Med Rep.
19:1491–1500. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Yang H, Wen L, Wen M, Liu T, Zhao L, Wu B,
Yun Y, Liu W, Wang H, Wang Y and Wen N: FoxM1 promotes
epithelial-mesenchymal transition, invasion, and migration of
tongue squamous cell carcinoma cells through a c-Met/AKT-dependent
positive feedback loop. Anticancer Drugs. 29:216–226. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Dasgupta P, Kulkarni P, Majid S, Shahryari
V, Hashimoto Y, Bhat NS, Shiina M, Deng G, Saini S, Tabatabai ZL,
et al: MicroRNA-203 inhibits long noncoding RNA HOTAIR and
regulates tumorigenesis through epithelial-to-mesenchymal
transition pathway in renal cell carcinoma. Mol Cancer Ther.
17:1061–1069. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Tay Y, Rinn J and Pandolfi PP: The
multilayered complexity of ceRNA crosstalk and competition. Nature.
505:344–352. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Ren D, Zheng H, Fei S and Zhao JL: MALAT1
induces osteosarcoma progression by targeting miR-206/CDK9 axis. J
Cell Physiol. 234:950–957. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Wang SH, Zhang WJ, Wu XC, Zhang MD, Weng
MZ, Zhou D, Wang JD and Quan ZW: Long non-coding RNA Malat1
promotes gallbladder cancer development by acting as a molecular
sponge to regulate miR-206. Oncotarget. 7:37857–37867. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Li C, Miao R, Liu S, Wan Y, Zhang S, Deng
Y, Bi J, Qu K, Zhang J and Liu C: Down-regulation of miR-146b-5p by
long noncoding RNA MALAT1 in hepatocellular carcinoma promotes
cancer growth and metastasis. Oncotarget. 8:28683–28695. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Liu D, Zhu Y, Pang J, Weng X, Feng X and
Guo Y: Knockdown of long non-coding RNA MALAT1 inhibits growth and
motility of human hepatoma cells via modulation of miR-195. J Cell
Biochem. 119:1368–1380. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Chen L, Yao H, Wang K and Liu X: Long
non-coding RNA MALAT1 regulates ZEB1 expression by sponging
miR-143-3p and promotes hepatocellular carcinoma progression. J
Cell Biochem. 118:4836–4843. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Wu H, Tao J, Li X, Zhang T, Zhao L, Wang
Y, Zhang L, Xiong J, Zeng Z, Zhan N, et al: MicroRNA-206 prevents
the pathogenesis of hepatocellular carcinoma by modulating
expression of met proto-oncogene and cyclin-dependent kinase 6 in
mice. Hepatology. 66:1952–1967. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Ren J, Huang HJ, Gong Y, Yue S, Tang LM
and Cheng SY: MicroRNA-206 suppresses gastric cancer cell growth
and metastasis. Cell Biosci. 4:262014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Yang M, Wei S, Zhao H, Zhou D and Cui X:
The role of miRNA125b in the progression of hepatocellular
carcinoma. Clin Res Hepatol Gastroenterol. 45:1017122021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Wang L, Cui M, Cheng D, Qu F, Yu J, Wei Y,
Cheng L, Wu X and Liu X: miR-9-5p facilitates hepatocellular
carcinoma cell proliferation, migration and invasion by targeting
ESR1. Mol Cell Biochem. 476:575–583. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Li Z, Wu L, Tan W, Zhang K, Lin Q, Zhu J,
Tu C, Lv X and Jiang C: MiR-20b-5p promotes hepatocellular
carcinoma cell proliferation, migration and invasion by
down-regulating CPEB3. Ann Hepatol. 23:1003452021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Cao J, Liu J, Long J, Fu J, Huang L, Li J,
Liu C, Zhang X and Yan Y: microRNA-23b suppresses
epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) and metastasis in
hepatocellular carcinoma via targeting Pyk2. Biomed Pharmacother.
89:642–650. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Callegari E, Gramantieri L, Domenicali M,
D'Abundo L, Sabbioni S and Negrini M: MicroRNAs in liver cancer: A
model for investigating pathogenesis and novel therapeutic
approaches. Cell Death Differ. 22:46–57. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Janssen HLA, Reesink HW, Lawitz EJ, Zeuzem
S, Rodriguez-Torres M, Patel K, van der Meer AJ, Patick AK, Chen A,
Zhou Y, et al: Treatment of HCV infection by targeting microRNA. N
Engl J Med. 368:1685–1694. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Chang RM, Xiao S, Lei X, Yang H, Fang F
and Yang LY: miRNA-487a promotes proliferation and metastasis in
hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res. 23:2593–2604. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Liu F, Zhao X, Qian Y, Zhang J, Zhang Y
and Yin R: MiR-206 inhibits head and neck squamous cell carcinoma
cell progression by targeting HDAC6 via PTEN/AKT/mTOR pathway.
Biomed Pharmacother. 96:229–237. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Xiao H, Xiao W, Cao J, Li H, Guan W, Guo
X, Chen K, Zheng T, Ye Z, Wang J and Xu H: miR-206 functions as a
novel cell cycle regulator and tumor suppressor in clear-cell renal
cell carcinoma. Cancer Lett. 374:107–116. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Liu C, Li J, Wang W, Zhong X, Xu F and Lu
J: miR-206 inhibits liver cancer stem cell expansion by regulating
EGFR expression. Cell Cycle. 19:1077–1088. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Liu N, Steer CJ and Song G: MicroRNA-206
enhances antitumor immunity by disrupting the communication between
malignant hepatocytes and regulatory T cells in c-Myc mice.
Hepatology. 76:32–47. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Yin K, Yin W, Wang Y, Zhou L, Liu Y, Yang
G, Wang J and Lu J: MiR-206 suppresses epithelial mesenchymal
transition by targeting TGF-β signaling in estrogen receptor
positive breast cancer cells. Oncotarget. 7:24537–24548. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Zhang J and Babic A: Regulation of the MET
oncogene: Molecular mechanisms. Carcinogenesis. 37:345–355. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Marano L, Chiari R, Fabozzi A, De Vita F,
Boccardi V, Roviello G, Petrioli R, Marrelli D, Roviello F and
Patriti A: c-Met targeting in advanced gastric cancer: An open
challenge. Cancer Lett. 365:30–36. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Ho-Yen CM, Jones JL and Kermorgant S: The
clinical and functional significance of c-Met in breast cancer: A
review. Breast Cancer Res. 17:522015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Lyu J, Sun Y, Li X and Ma H: MicroRNA-206
inhibits the proliferation, migration and invasion of colorectal
cancer cells by regulating the c-Met/AKT/GSK-3β pathway. Oncol
Lett. 21:1472021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Dai C, Xie Y, Zhuang X and Yuan Z: MiR-206
inhibits epithelial ovarian cancer cells growth and invasion via
blocking c-Met/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway. Biomed Pharmacother.
104:763–770. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Wang Y, Tai Q, Zhang J, Kang J, Gao F,
Zhong F, Cai L, Fang F and Gao Y: MiRNA-206 inhibits hepatocellular
carcinoma cell proliferation and migration but promotes apoptosis
by modulating cMET expression. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai).
51:243–253. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Sun C, Liu Z, Li S, Yang C, Xue R, Xi Y,
Wang L, Wang S, He Q, Huang J, et al: Down-regulation of c-Met and
Bcl2 by microRNA-206, activates apoptosis, and inhibits tumor cell
proliferation, migration and colony formation. Oncotarget.
6:25533–25574. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Boccaccio C, Luraghi P and Comoglio PM:
MET-mediated resistance to EGFR inhibitors: An old liaison rooted
in colorectal cancer stem cells. Cancer Res. 74:3647–3651. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Shen SN, Li K, Liu Y, Yang CL, He CY and
Wang HR: Down-regulation of long noncoding RNA PVT1 inhibits
esophageal carcinoma cell migration and invasion and promotes cell
apoptosis via microRNA-145-mediated inhibition of FSCN1. Mol Oncol.
13:2554–2573. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Sun X, Luo L and Li J: LncRNA MALAT1
facilitates BM-MSCs differentiation into endothelial cells via
targeting miR-206/VEGFA axis. Cell Cycle. 19:3018–3028. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Wang S, Ren L, Shen G, Liu M and Luo J:
The knockdown of MALAT1 inhibits the proliferation, invasion and
migration of hemangioma endothelial cells by regulating
MiR-206/VEGFA axis. Mol Cell Probes. 51:1015402020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Zheng Z, Yan D, Chen X, Huang H, Chen K,
Li G, Zhou L, Zheng D, Tu L and Dong XD: MicroRNA-206: Effective
inhibition of gastric cancer progression through the c-Met pathway.
PLoS One. 10:e01287512015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|