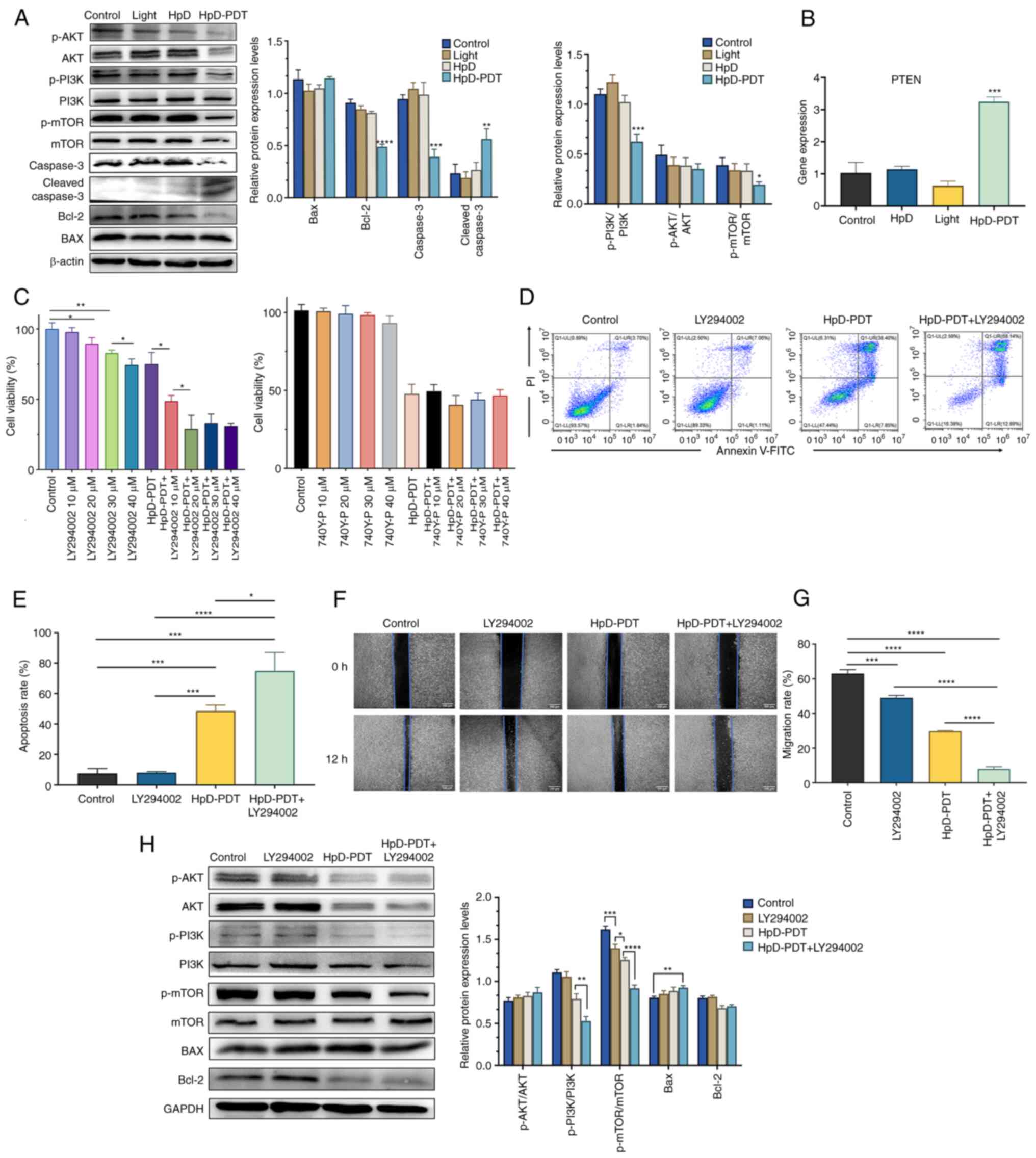
|
1
|
Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M,
Soerjomataram I, Jemal A and Bray F: Global Cancer Statistics 2020:
GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36
cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 71:209–249. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Morgan E, Soerjomataram I, Rumgay H,
Coleman HG, Thrift AP, Vignat J, Laversanne M, Ferlay J and Arnold
M: The global landscape of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma and
esophageal adenocarcinoma incidence and mortality in 2020 and
projections to 2040: New estimates from GLOBOCAN 2020.
Gastroenterology. 163:649–658.e2. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Kato H and Nakajima M: Treatments for
esophageal cancer: A review. Gen Thorac Cardiovasc Surg.
61:330–335. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Correia JH, Rodrigues JA, Pimenta S, Dong
T and Yang Z: Photodynamic Therapy review: Principles,
Photosensitizers, applications, and future directions.
Pharmaceutics. 13:13322021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Dobson J, de Queiroz GF and Golding JP:
Photodynamic therapy and diagnosis: Principles and comparative
aspects. Vet J. 233:8–18. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Agostinis P, Berg K, Cengel KA, Foster TH,
Girotti AW, Gollnick SO, Hahn SM, Hamblin MR, Juzeniene A, Kessel
D, et al: Photodynamic therapy of cancer: An update. CA Cancer J
Clin. 61:250–281. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Zahra M, Chota A, Abrahamse H and George
BP: Efficacy of green synthesized nanoparticles in photodynamic
therapy: A therapeutic approach. Int J Mol Sci. 24:109312023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Zhang X, Cai L, He J, Li X, Li L, Chen X
and Lan P: Influence and mechanism of 5-aminolevulinic
acid-photodynamic therapy on the metastasis of esophageal
carcinoma. Photodiagnosis Photodyn Ther. 20:78–85. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Lan M, Zhao S, Liu W, Lee CS, Zhang W and
Wang P: Photosensitizers for photodynamic therapy. Adv Healthc
Mater. 8:e19001322019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Kwiatkowski S, Knap B, Przystupski D,
Saczko J, Kędzierska E, Knap-Czop K, Kotlińska J, Michel O,
Kotowski K and Kulbacka J: Photodynamic therapy-mechanisms,
photosensitizers and combinations. Biomed Pharmacother.
106:1098–1107. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
van Gemert JC, Berenbaum MC and Gijsbers
GH: Wavelength and light-dose dependence in tumour phototherapy
with haematoporphyrin derivative. Br J Cancer. 52:43–49. 1985.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Kashyap D, Garg VK and Goel N: Intrinsic
and extrinsic pathways of apoptosis: Role in cancer development and
prognosis. Adv Protein Chem Struct Biol. 125:73–120. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Carpenter R and Brady MF: BAX Gene.
StatPearls [Internet] Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing;
2023
|
|
14
|
Cheung TH, Chung TK, Lo KW, Yu MY,
Krajewski S, Reed JC and Wong YF: Apotosis-related proteins in
cervical intraepithelial neoplasia and squamous cell carcinoma of
the cervix. Gynecol Oncol. 86:14–18. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Korsmeyer SJ: BCL-2 gene family and the
regulation of programmed cell death. Cancer Res. 59 (7
Suppl):1693s–1700s. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Thornberry NA and Lazebnik Y: Caspases:
Enemies within. Science. 281:1312–1316. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Kumar D, Haldar S, Gorain M, Kumar S,
Mulani FA, Yadav AS, Miele L, Thulasiram HV and Kundu GC:
Epoxyazadiradione suppresses breast tumor growth through
mitochondrial depolarization and caspase-dependent apoptosis by
targeting PI3K/Akt pathway. BMC Cancer. 18:522018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Huang L, Lin H, Chen Q, Yu L and Bai D:
MPPa-PDT suppresses breast tumor migration/invasion by inhibiting
Akt-NF-κB-dependent MMP-9 expression via ROS. BMC Cancer.
19:11592019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Kumar S, Patil HS, Sharma P, Kumar D,
Dasari S, Puranik VG, Thulasiram HV and Kundu GC: Andrographolide
inhibits osteopontin expression and breast tumor growth through
down regulation of PI3 kinase/Akt signaling pathway. Curr Mol Med.
12:952–966. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Liutkeviciute-Navickiene J, Mordas A,
Rutkovskiene L and Bloznelyte-Plesniene L: Skin and mucosal
fluorescence diagnosis with different light sources. Eur J
Dermatol. 19:135–40. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)). Method. 25:402–408. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Gupta S, Dwarakanath BS, Muralidhar K and
Jain V: Cellular uptake, localization and photodynamic effects of
haematoporphyrin derivative in human glioma and squamous carcinoma
cell lines. J Photochem Photobiol B. 69:107–120. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Pal M, Bhattacharya S, Kalyan G and Hazra
S: Cadherin profiling for therapeutic interventions in Epithelial
Mesenchymal Transition (EMT) and tumorigenesis. Exp Cell Res.
368:137–146. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Loh CY, Chai JY, Tang TF, Wong WF, Sethi
G, Shanmugam MK, Chong PP and Looi CY: The E-Cadherin and
N-Cadherin Switch in Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition:
Signaling, therapeutic implications, and challenges. Cells.
8:11182019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Glick D, Barth S and Macleod KF:
Autophagy: Cellular and molecular mechanisms. J Pathol. 221:3–12.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Mizushima N and Komatsu M: Autophagy:
Renovation of cells and tissues. Cell. 147:728–741. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Xie J, Wang S, Li Z, Ao C, Wang J, Wang L,
Peng X and Zeng K: 5-aminolevulinic acid photodynamic therapy
reduces HPV viral load via autophagy and apoptosis by modulating
Ras/Raf/MEK/ERK and PI3K/AKT pathways in HeLa cells. J Photochem
Photobiol B. 194:46–55. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Crowley LC and Waterhouse NJ: Detecting
cleaved caspase-3 in apoptotic cells by flow cytometry. Cold Spring
Harb Protoc. 2016:2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Li A, Qiu M, Zhou H, Wang T and Guo W:
PTEN, insulin resistance and cancer. Curr Pharm Des. 23:3667–3676.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Chen CY, Chen J, He L and Stiles BL: PTEN:
Tumor suppressor and metabolic regulator. Front Endocrinol
(Lausanne). 9:3382018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Chaussade C, Rewcastle GW, Kendall JD,
Denny WA, Cho K, Grønning LM, Chong ML, Anagnostou SH, Jackson SP,
Daniele N and Shepherd PR: Evidence for functional redundancy of
class IA PI3K isoforms in insulin signalling. Biochem J.
404:449–458. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Didamson OC and Abrahamse H: Targeted
photodynamic diagnosis and therapy for esophageal cancer: Potential
role of functionalized nanomedicine. Pharmaceutics. 13:19432021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Gallagher-Colombo SM, Finlay JC and Busch
T: Tumor Microenvironment as a Determinant of Photodynamic Therapy
Resistance. Resistance to Photodynamic Therapy in Cancer.
Resistance to Targeted Anti-Cancer Therapeutics. Rapozzi V and Jori
G: 5. Springer; Cham: pp. 65–97. 2015, View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Rapozzi V and Jori G: Resistance to
Photodynamic Therapy in Cancer. Resistance to Targeted Anti-Cancer
Therapeutics. 5. 1st edition. Springer; Cham: pp. p2482015
|
|
35
|
Rodrigues JA and Correia JH: Photodynamic
therapy for colorectal cancer: An update and a look to the future.
Int J Mol Sci. 24:122042023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Tahtamouni L, Ahram M, Koblinski J and
Rolfo C: Molecular regulation of cancer cell migration, invasion,
and metastasis. Anal Cell Pathol (Amst).
2019:13565082019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Mao W, Sun Y, Zhang H, Cao L, Wang J and
He P: A combined modality of carboplatin and photodynamic therapy
suppresses epithelial-mesenchymal transition and matrix
metalloproteinase-2 (MMP-2)/MMP-9 expression in HEp-2 human
laryngeal cancer cells via ROS-mediated inhibition of MEK/ERK
signalling pathway. Lasers Med Sci. 31:1697–1705. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Josefsen LB and Boyle RW: Unique
diagnostic and therapeutic roles of porphyrins and phthalocyanines
in photodynamic therapy, imaging and theranostics. Theranostics.
2:916–966. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Liu L, Ye Y and Zhu X: MMP-9 secreted by
tumor associated macrophages promoted gastric cancer metastasis
through a PI3K/AKT/Snail pathway. Biomed Pharmacother.
117:1090962019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Jung JS, Jung K, Kim DH and Kim HS:
Selective inhibition of MMP-9 gene expression by mangiferin in
PMA-stimulated human astroglioma cells: Involvement of PI3K/Akt and
MAPK signaling pathways. Pharmacol Res. 66:95–103. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Hwang YP, Yun HJ, Choi JH, Han EH, Kim HG,
Song GY, Kwon KI, Jeong TC and Jeong HG: Suppression of EGF-induced
tumor cell migration and matrix metalloproteinase-9 expression by
capsaicin via the inhibition of EGFR-mediated FAK/Akt, PKC/Raf/ERK,
p38 MAPK, and AP-1 signaling. Mol Nutr Food Res. 55:594–605. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Mathew R and White E: Autophagy in
tumorigenesis and energy metabolism: Friend by day, foe by night.
Curr Opin Genet Dev. 21:113–119. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
He C, Xia J, Gao Y, Chen Z and Wan X:
Chlorin A-mediated photodynamic therapy induced apoptosis in human
cholangiocarcinoma cells via impaired autophagy flux. Am J Transl
Res. 12:5080–5094. 2020.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Kma L and Baruah TJ: The interplay of ROS
and the PI3K/Akt pathway in autophagy regulation. Biotechnol Appl
Biochem. 69:248–264. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Xu Z, Han X, Ou D, Liu T, Li Z, Jiang G,
Liu J and Zhang J: Targeting PI3K/AKT/mTOR-mediated autophagy for
tumor therapy. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 104:575–587. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Heras-Sandoval D, Pérez-Rojas JM,
Hernández-Damián J and Pedraza-Chaverri J: The role of
PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway in the modulation of autophagy and the
clearance of protein aggregates in neurodegeneration. Cell Signal.
26:2694–2701. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Yan J, Dou X, Zhou J, Xiong Y, Mo L, Li L
and Lei Y: Tubeimoside-I sensitizes colorectal cancer cells to
chemotherapy by inducing ROS-mediated impaired autophagolysosomes
accumulation. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 38:3532019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Fan TJ, Han LH, Cong RS and Liang J:
Caspase family proteases and apoptosis. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin
(Shanghai). 37:719–727. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Elmore S: Apoptosis: A review of
programmed cell death. Toxicol Pathol. 35:495–516. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Wang H, Ewetse MP, Ma C, Pu W, Xu B, He P,
Wang Y, Zhu J and Chen H: The ‘Light Knife’ for gastric cancer:
Photodynamic therapy. Pharmaceutics. 15:1012022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Chen D, Wang B, Zhao Z, Zhang G, Wang P,
Zhang L, Liu X, Zhang H, Zeng Q and Wang X: Modified
5-aminolevulinic acid photodynamic therapy induces cutaneous
squamous cell carcinoma cell pyroptosis via the JNK signaling
pathway. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Res. 1871:1196032023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Li L, Song D, Qi L, Jiang M, Wu Y, Gan J,
Cao K, Li Y, Bai Y and Zheng T: Photodynamic therapy induces human
esophageal carcinoma cell pyroptosis by targeting the
PKM2/caspase-8/caspase-3/GSDME axis. Cancer Lett. 520:143–159.
2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Pan WL, Tan Y, Meng W, Huang NH, Zhao YB,
Yu ZQ, Huang Z, Zhang WH, Sun B and Chen JX:
Microenvironment-driven sequential ferroptosis, photodynamic
therapy, and chemotherapy for targeted breast cancer therapy by a
cancer-cell-membrane-coated nanoscale metal-organic framework.
Biomaterials. 283:1214492022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Zhang ZJ, Huang YP, Li XX, Liu ZT, Liu K,
Deng XF, Xiong L, Zou H and Wen Y: A Novel Ferroptosis-Related
4-Gene prognostic signature for cholangiocarcinoma and photodynamic
therapy. Front Oncol. 11:7474452021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Bartusik-Aebisher D, Osuchowski M,
Adamczyk M, Stopa J, Cieślar G, Kawczyk-Krupka A and Aebisher D:
Advancements in photodynamic therapy of esophageal cancer. Front
Oncol. 12:10245762022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Yamashita H, Kadota T, Minamide T,
Sunakawa H, Sato D, Takashima K, Nakajo K, Murano T, Shinmura K,
Yoda Y, et al: Efficacy and safety of second photodynamic therapy
for local failure after salvage photodynamic therapy for esophageal
cancer. Dig Endosc. 34:488–496. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|