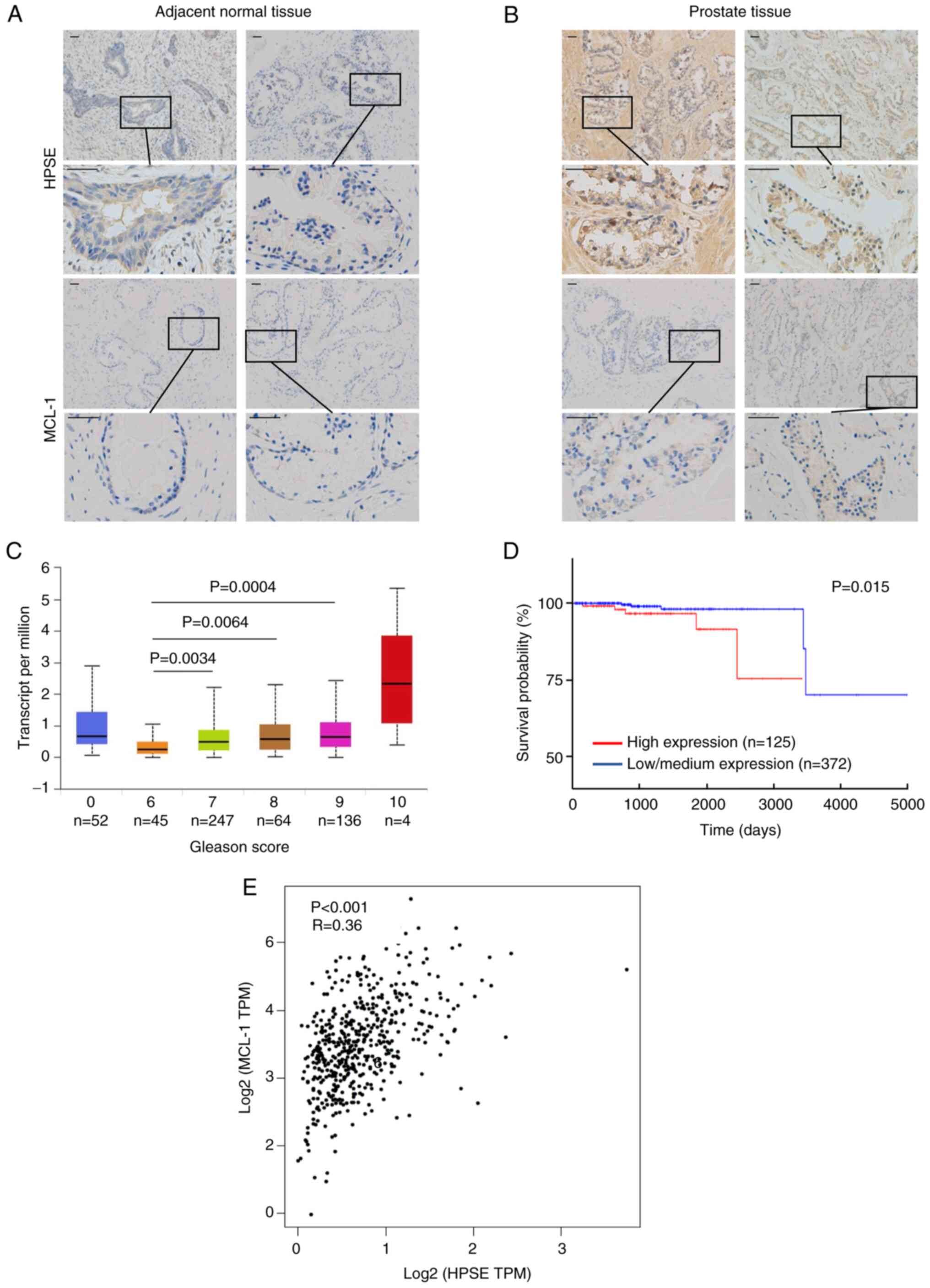
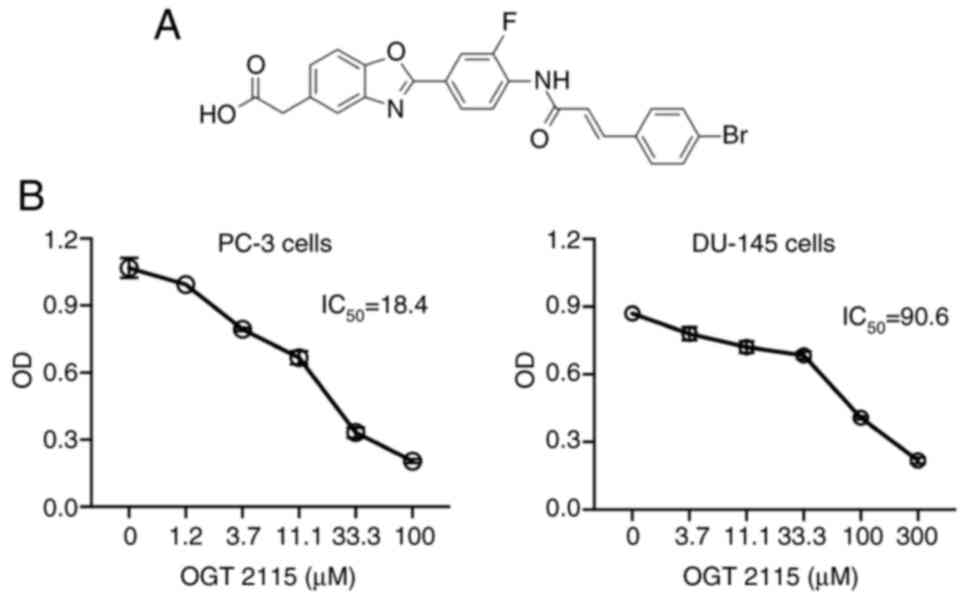
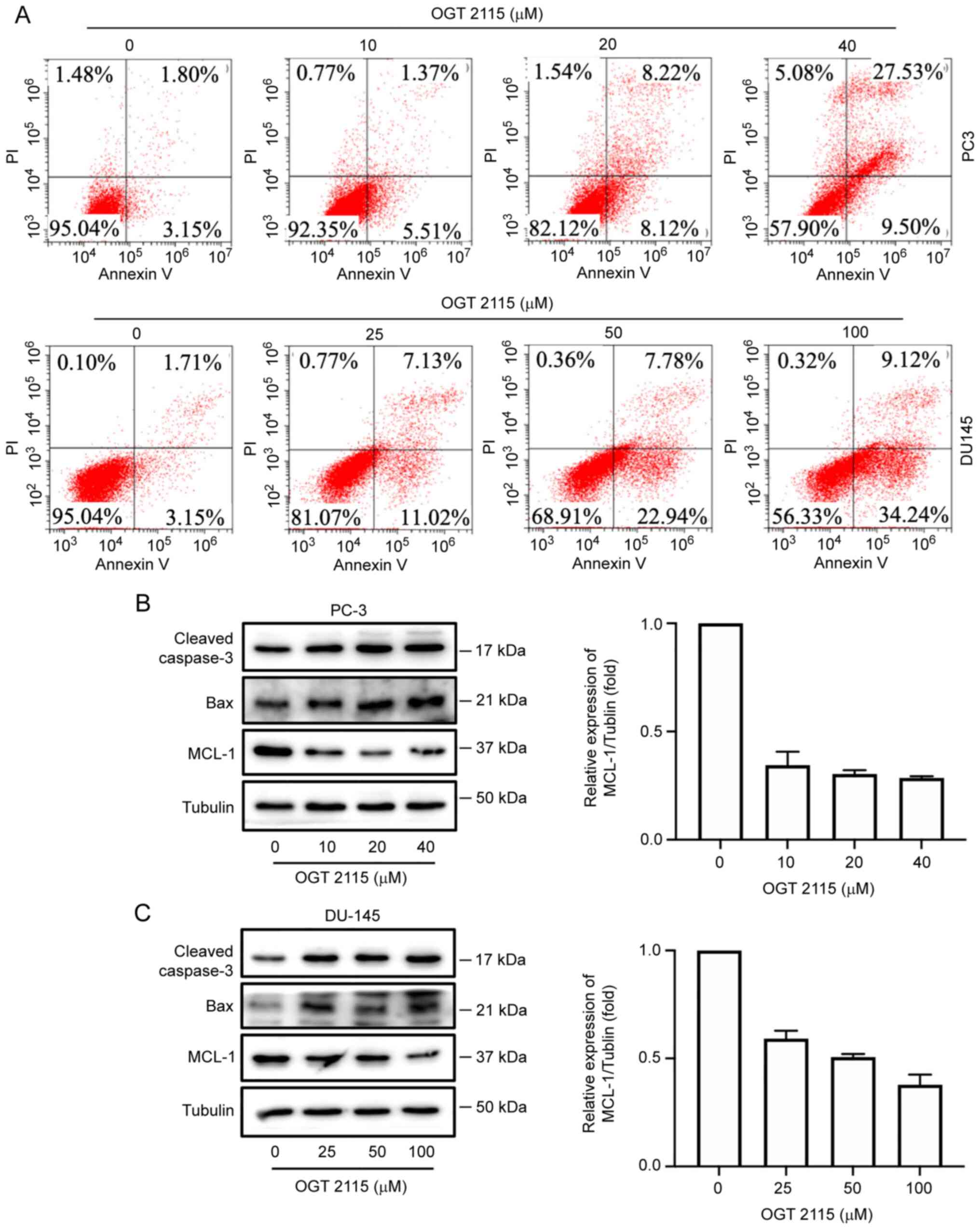
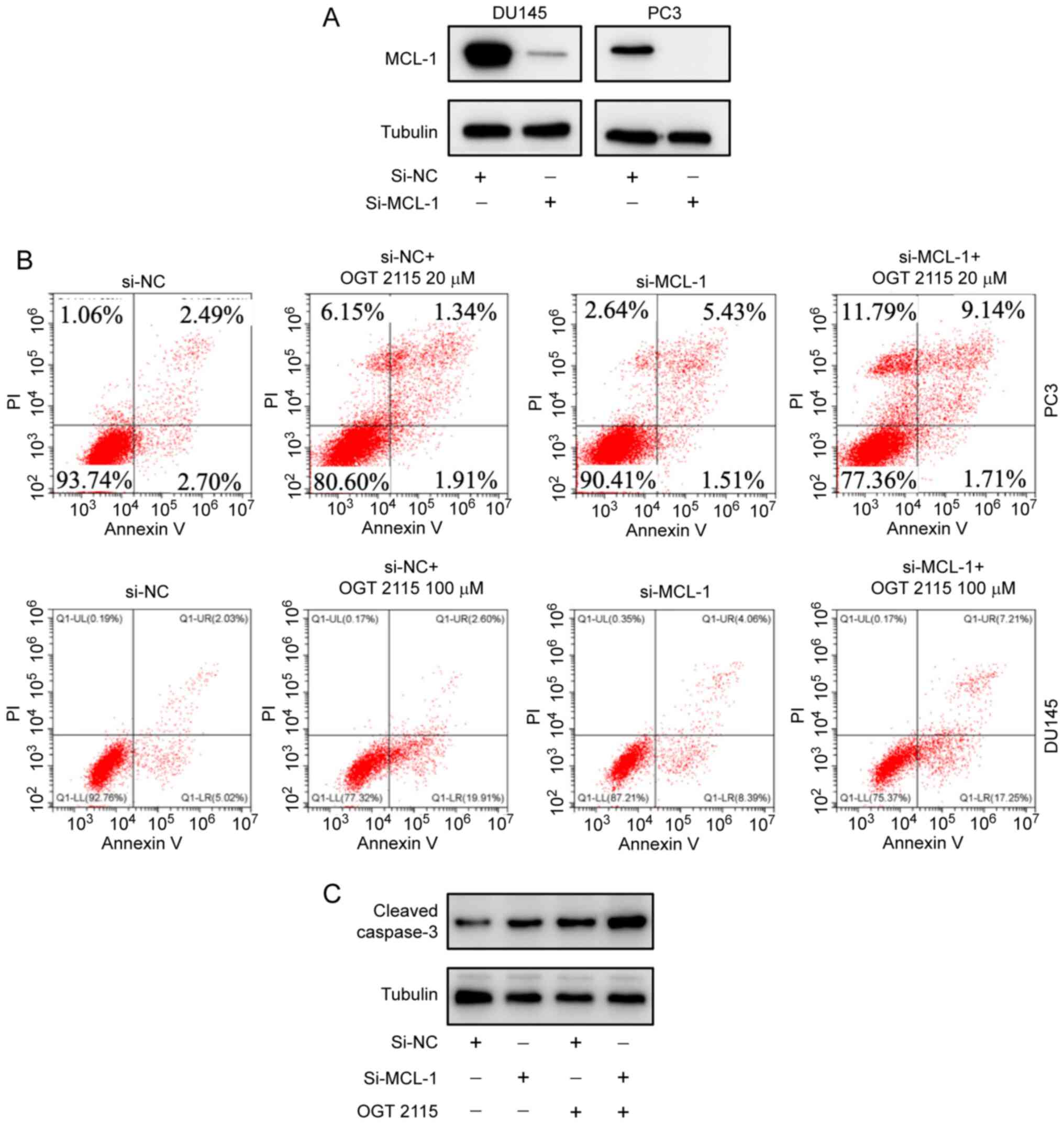
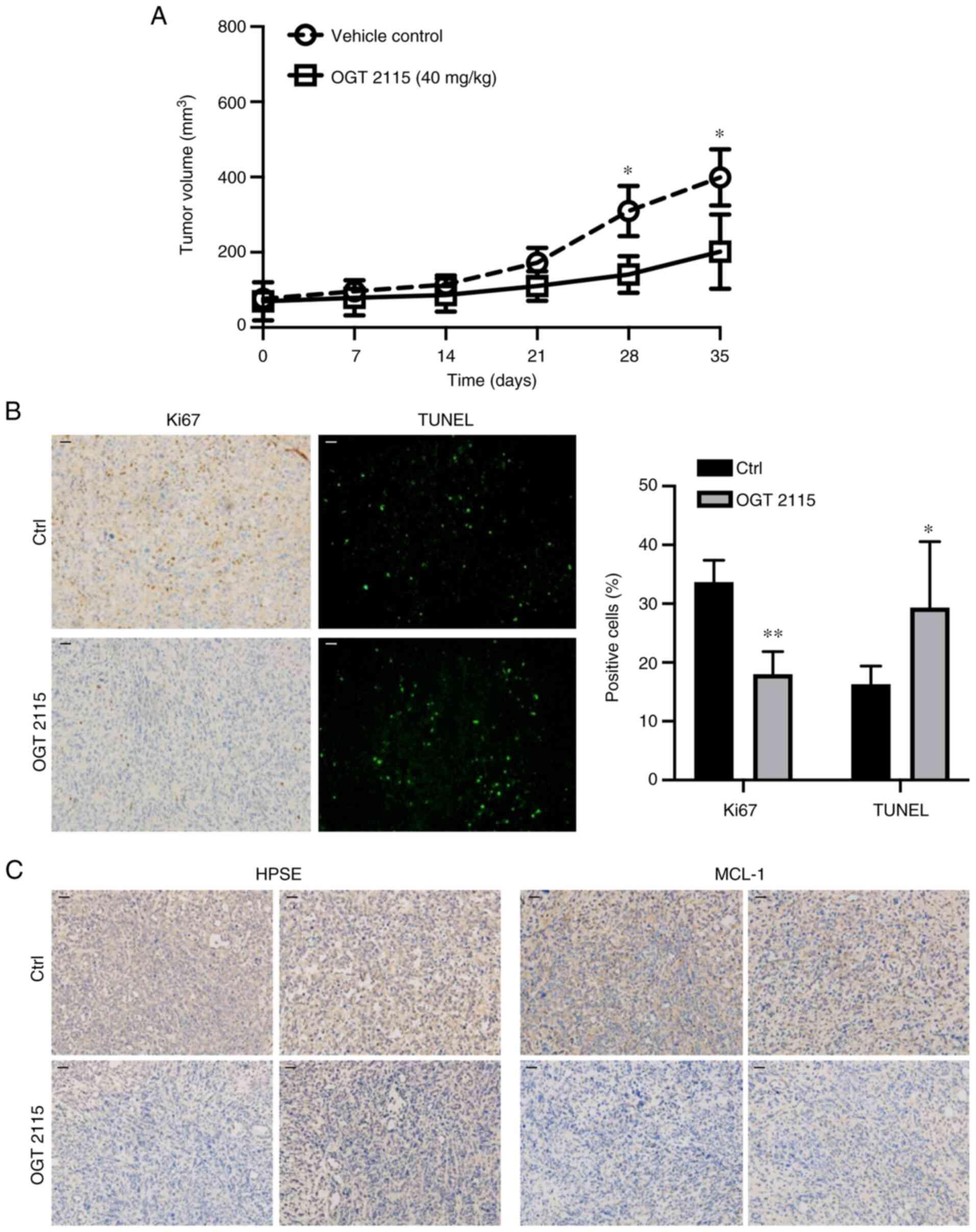
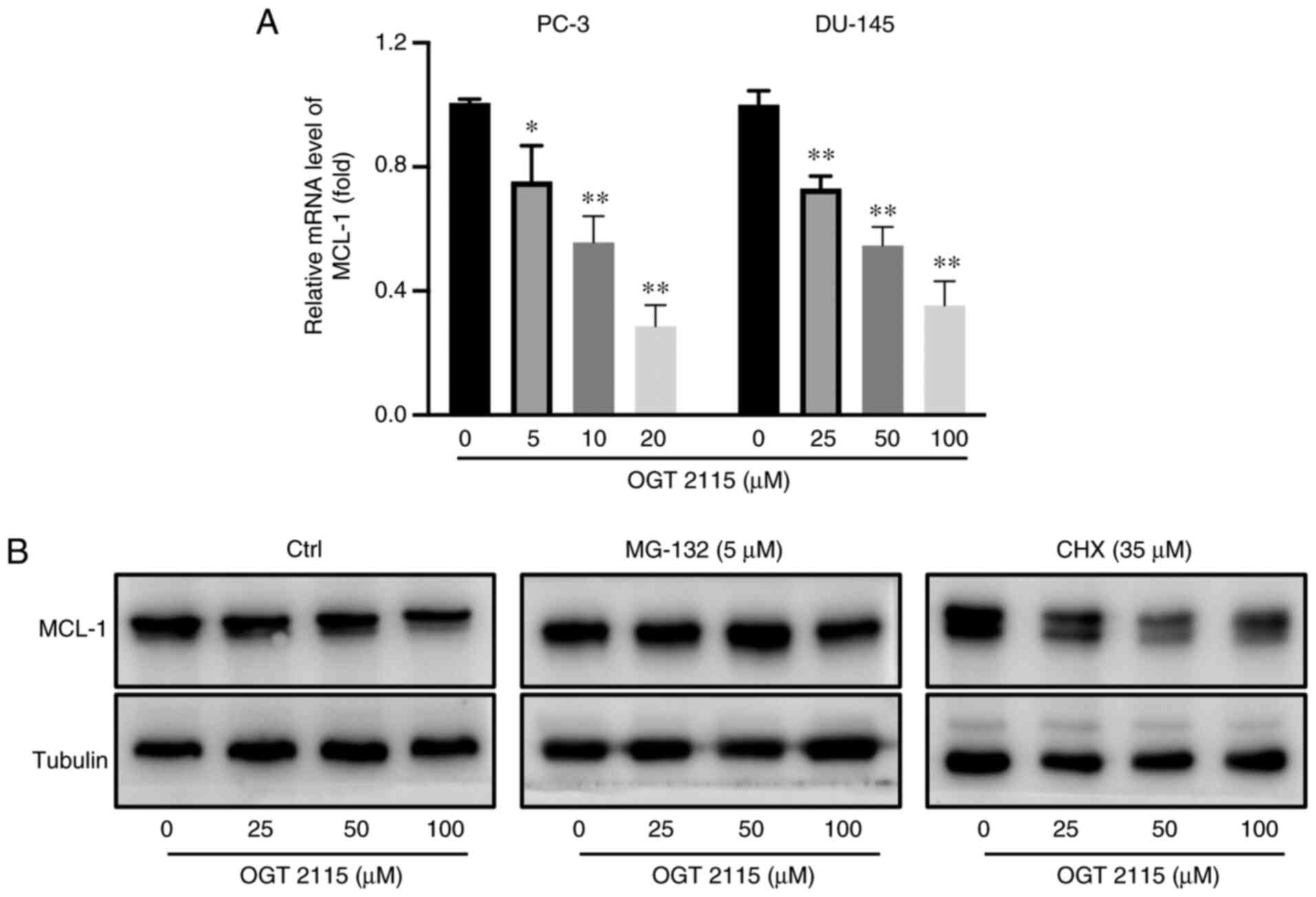
|
1
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD, Fuchs HE and Jemal
A: Cancer statistics, 2021. CA Cancer J Clin. 71:7–33. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Chen W, Zheng R, Baade PD, Zhang S, Zeng
H, Bray F, Jemal A, Yu XQ and He J: Cancer statistics in China,
2015. CA Cancer J Clin. 66:115–132. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Perlmutter MA and Lepor H: Androgen
deprivation therapy in the treatment of advanced prostate cancer.
Rev Urol. 9 (Suppl 1):S3–S8. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Limberger T, Schlederer M, Trachtová K,
Garces de Los Fayos Alonso I, Yang J, Högler S, Sternberg C, Bystry
V, Oppelt J, Tichý B, et al: KMT2C methyltransferase domain
regulated INK4A expression suppresses prostate cancer metastasis.
Mol Cancer. 21:892022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Smith MR, Saad F, Coleman R, Shore N,
Fizazi K, Tombal B, Miller K, Sieber P, Karsh L, Damião R, et al:
Denosumab and bone-metastasis-free survival in men with
castration-resistant prostate cancer: Results of a phase 3,
randomised, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet. 379:39–46. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Vlodavsky I, Ilan N and Sanderson RD:
Forty years of basic and translational heparanase research. Adv Exp
Med Biol. 1221:3–59. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Reynolds MR, Singh I, Azad TD, Holmes BB,
Verghese PB, Dietrich HH, Diamond M, Bu G, Han BH and Zipfel GJ:
Heparan sulfate proteoglycans mediate Aβ-induced oxidative stress
and hypercontractility in cultured vascular smooth muscle cells.
Mol Neurodegener. 11:92016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Koganti R, Suryawanshi R and Shukla D:
Heparanase, cell signaling, and viral infections. Cell Mol Life
Sci. 77:5059–5077. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Cohen-Kaplan V, Jrbashyan J, Yanir Y,
Naroditsky I, Ben-Izhak O, Ilan N, Doweck I and Vlodavsky I:
Heparanase induces signal transducer and activator of transcription
(STAT) protein phosphorylation: preclinical and clinical
significance in head and neck cancer. J Biol Chem. 287:6668–6678.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Mahtouk K, Hose D, Raynaud P, Hundemer M,
Jourdan M, Jourdan E, Pantesco V, Baudard M, De Vos J, Larroque M,
et al: Heparanase influences expression and shedding of syndecan-1,
and its expression by the bone marrow environment is a bad
prognostic factor in multiple myeloma. Blood. 109:4914–4923. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Fletcher S: MCL-1 inhibitors-where are we
now (2019)? Expert Opin Ther Pat. 29:909–919. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Abdul Rahman SF, Azlan A, Lo KW, Azzam G
and Mohana-Kumaran N: Dual inhibition of anti-apoptotic proteins
BCL-XL and MCL-1 enhances cytotoxicity of Nasopharyngeal carcinoma
cells. Discov Oncol. 13:92022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Wang B, Ni Z, Dai X, Qin L, Li X, Xu L,
Lian J and He F: The Bcl-2/xL inhibitor ABT-263 increases the
stability of Mcl-1 mRNA and protein in hepatocellular carcinoma
cells. Mol Cancer. 13:982014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Carné Trécesson S, Souazé F, Basseville A,
Bernard AC, Pécot J, Lopez J, Bessou M, Sarosiek KA, Letai A,
Barillé-Nion S, et al: BCL-X(L) directly modulates RAS signalling
to favour cancer cell stemness. Nat Commun. 8:11232017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Wei AH, Roberts AW, Spencer A, Rosenberg
AS, Siegel D, Walter RB, Caenepeel S, Hughes P, McIver Z, Mezzi K,
et al: Targeting MCL-1 in hematologic malignancies: Rationale and
progress. Blood Rev. 44:1006722020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Yancey D, Nelson KC, Baiz D, Hassan S,
Flores A, Pullikuth A, Karpova Y, Axanova L, Moore V, Sui G and
Kulik G: BAD dephosphorylation and decreased expression of MCL-1
induce rapid apoptosis in prostate cancer cells. PLoS One.
8:e745612013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Cancer Genome Atlas Research Network, .
The molecular taxonomy of primary prostate cancer. Cell.
4:1011–1025. 2015.
|
|
18
|
Chandrashekar DS, Karthikeyan SK, Korla
PK, Patel H, Shovon AR, Athar M, Netto GJ, Qin ZS, Kumar S, Manne
U, et al: UALCAN: An update to the integrated cancer data analysis
platform. Neoplasia. 25:18–27. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Chandrashekar DS, Bashel B, Balasubramanya
SAH, Creighton CJ, Rodriguez IP, Chakravarthi BVSK and Varambally
S: UALCAN: A portal for facilitating tumor subgroup gene expression
and survival analyses. Neoplasia. 8:649–658. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Epstein JI, Egevad L, Amin MB, Delahunt B,
Srigley JR, Humphrey PA and Grading Committee: The 2014
international society of urological pathology (ISUP) consensus
conference on gleason grading of prostatic carcinoma: Definition of
grading patterns and proposal for a new grading system. Am J Surg
Pathol. 2:244–252. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
MacArthur Clark JA and Sun D: Guidelines
for the ethical review of laboratory animal welfare people's
republic of China national standard GB/T 35892-2018 (Issued 6
February 2018 Effective from 1 September 2018). Animal Model Exp
Med. 3:103–113. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Jiao W, Chen Y, Song H, Li D, Mei H, Yang
F, Fang E, Wang X, Huang K, Zheng L and Tong Q: HPSE enhancer RNA
promotes cancer progression through driving chromatin looping and
regulating hnRNPU/p300/EGR1/HPSE axis. Oncogene. 20:2728–2745.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Wang H, Guo M, Wei H and Chen Y: Targeting
MCL-1 in cancer: current status and perspectives. J Hematol Oncol.
1:672021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Sanderson RD, Elkin M, Rapraeger AC, Ilan
N and Vlodavsky I: Heparanase regulation of cancer, autophagy and
inflammation: New mechanisms and targets for therapy. FEBS J.
284:42–55. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Tumova S, Woods A and Couchman JR: Heparan
sulfate proteoglycans on the cell surface: versatile coordinators
of cellular functions. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 32:269–288. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Zhou Y, Song B, Qin WJ, Zhang G, Zhang R,
Luan Q, Pan TJ, Yang AG and Wang H: Heparanase promotes bone
destruction and invasiveness in prostate cancer. Cancer Lett.
268:252–259. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Li QW, Zhang GL, Hao CX, Ma YF, Sun X,
Zhang Y, Cao KX, Li BX, Yang GW and Wang XM: SANT, a novel Chinese
herbal monomer combination, decreasing tumor growth and
angiogenesis via modulating autophagy in heparanase overexpressed
triple-negative breast cancer. J Ethnopharmacol. 266:1134302021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Shteingauz A, Boyango I, Naroditsky I,
Hammond E, Gruber M, Doweck I, Ilan N and Vlodavsky I: Heparanase
enhances tumor growth and chemoresistance by promoting autophagy.
Cancer Res. 75:3946–3957. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Tatsumi Y, Miyake M, Shimada K, Fujii T,
Hori S, Morizawa Y, Nakai Y, Anai S, Tanaka N, Konishi N and
Fujimoto K: Inhibition of heparanase expression results in
suppression of invasion, migration and adhesion abilities of
bladder cancer cells. Int J Mol Sci. 21:37892020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Vlodavsky I, Beckhove P, Lerner I, Pisano
C, Meirovitz A, Ilan N and Elkin M: Significance of heparanase in
cancer and inflammation. Cancer Microenviron. 5:115–132. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Masola V, Zaza G, Onisto M, Lupo A and
Gambaro G: Impact of heparanase on renal fibrosis. J Transl Med.
13:1812015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Morciano G, Giorgi C, Balestra D, Marchi
S, Perrone D, Pinotti M and Pinton P: Mcl-1 involvement in
mitochondrial dynamics is associated with apoptotic cell death. Mol
Biol Cell. 27:20–34. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Luo W, Nagaria TS, Sun H, Ma J, Lombardo
JL, Bassett R, Cao AC and Tan D: Expression and potential
prognostic value of SOX9, MCL-1 and SPOCK1 in gastric
adenocarcinoma. Pathol Oncol Res. 28:16102932022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Vela L and Marzo I: Bcl-2 family of
proteins as drug targets for cancer chemotherapy: The long way of
BH3 mimetics from bench to bedside. Curr Opin Pharmacol. 23:74–81.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Bashari MH, Fan F, Vallet S, Sattler M,
Arn M, Luckner-Minden C, Schulze-Bergkamen H, Zörnig I, Marme F,
Schneeweiss A, et al: Mcl-1 confers protection of Her2-positive
breast cancer cells to hypoxia: Therapeutic implications. Breast
Cancer Res. 18:262016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Omari S, Waters M, Naranian T, Kim K,
Perumalsamy AL, Chi M, Greenblatt E, Moley KH, Opferman JT and
Jurisicova A: Mcl-1 is a key regulator of the ovarian reserve. Cell
Death Dis. 6:e17552015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Ma J, Zhao Z, Wu K, Xu Z and Liu K: MCL-1
is the key target of adjuvant chemotherapy to reverse the
cisplatin-resistance in NSCLC. Gene. 587:147–154. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Xiang W, Yang CY and Bai L: MCL-1
inhibition in cancer treatment. Onco Targets Ther. 11:7301–7314.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Leverson JD, Zhang H, Chen J, Tahir SK,
Phillips DC, Xue J, Nimmer P, Jin S, Smith M, Xiao Y, et al: Potent
and selective small-molecule MCL-1 inhibitors demonstrate on-target
cancer cell killing activity as single agents and in combination
with ABT-263 (navitoclax). Cell Death Dis. 6:e15902015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|