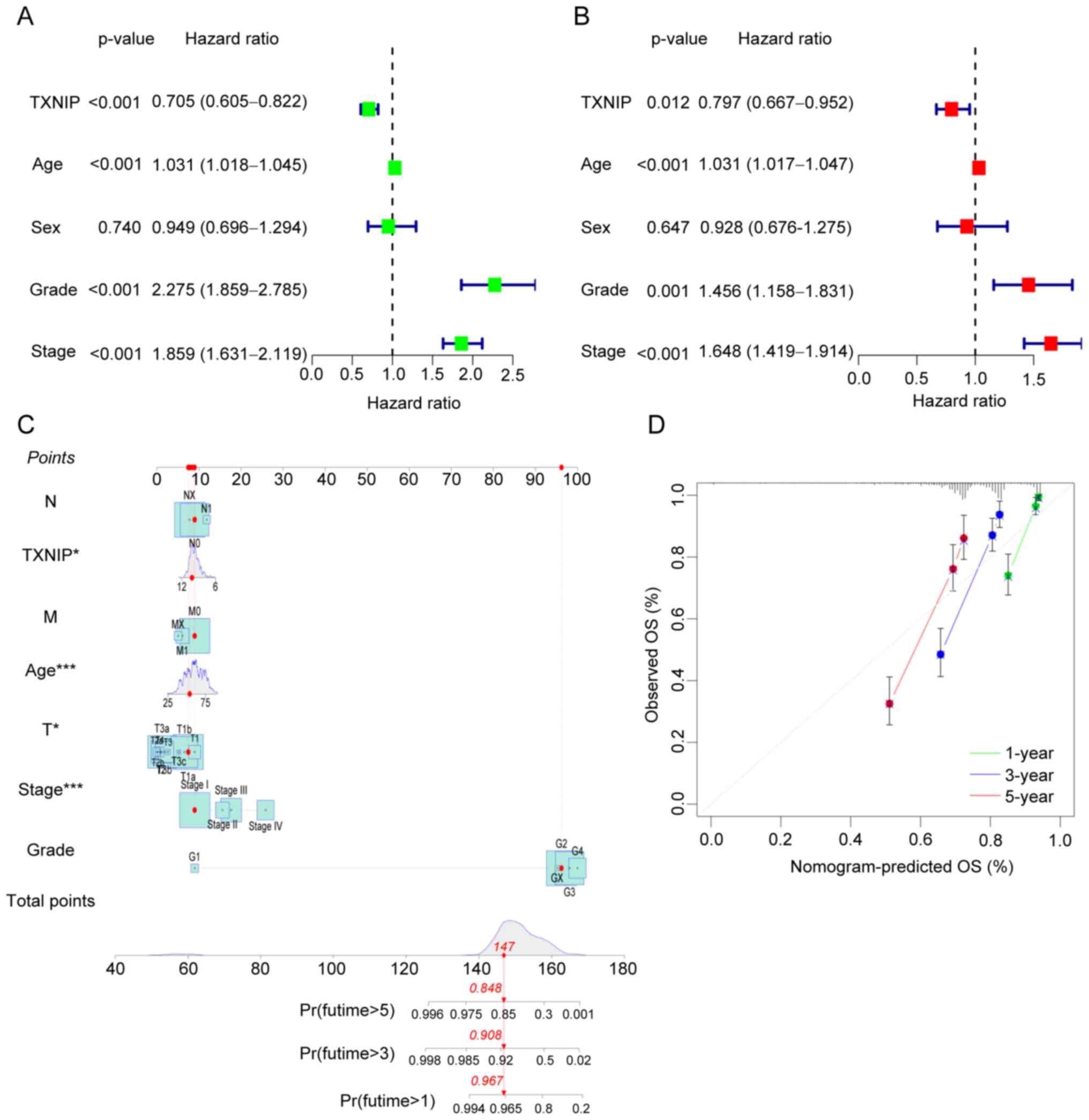
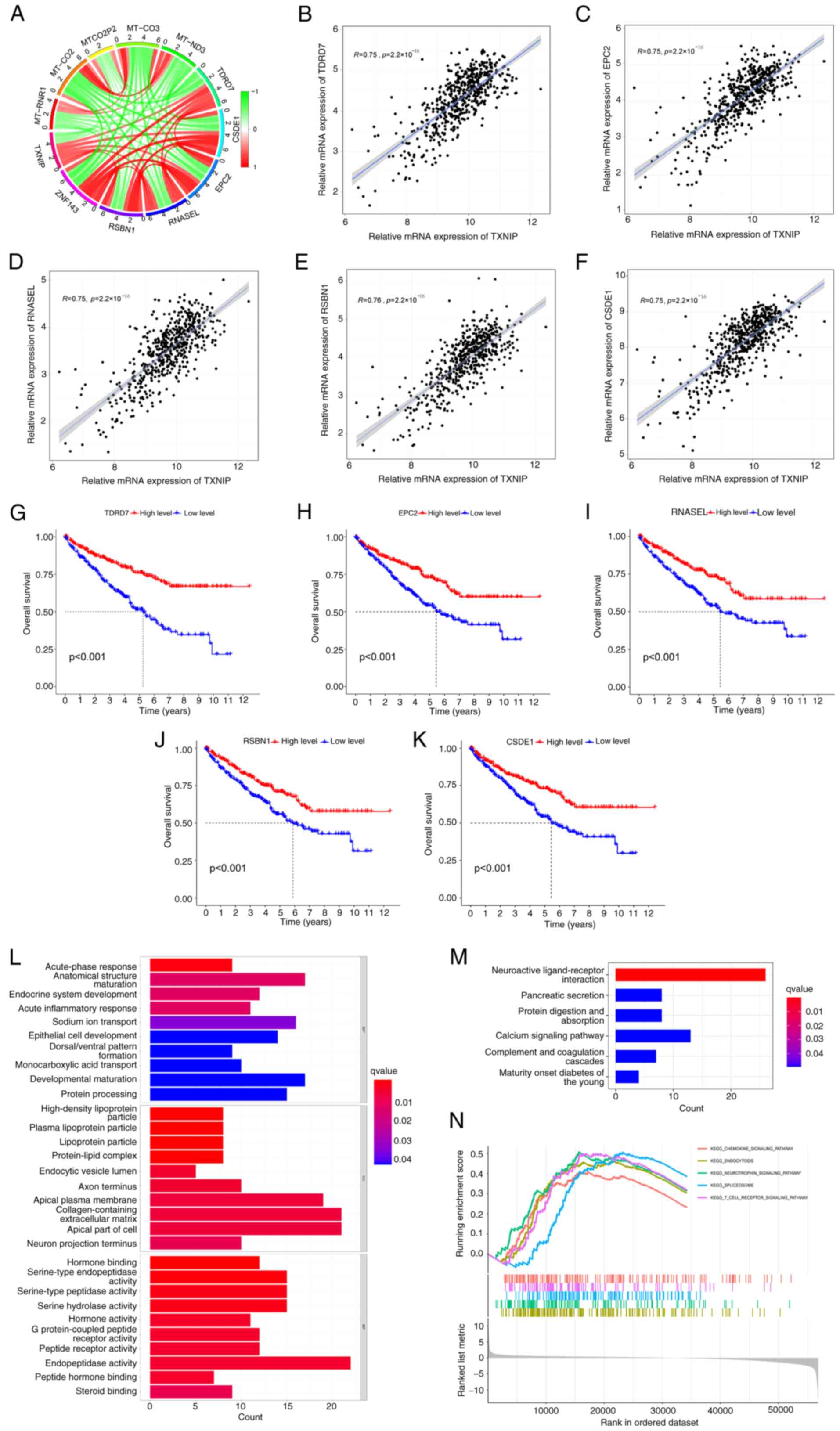
|
1
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2019. CA Cancer J Clin. 69:7–34. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Shuch B, Amin A, Armstrong AJ, Eble JN,
Ficarra V, Lopez-Beltran A, Martignoni G, Rini BI and Kutikov A:
Understanding pathologic variants of renal cell carcinoma:
Distilling therapeutic opportunities from biologic complexity. Eur
Urol. 67:85–97. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Sonpavde G, Choueiri TK, Escudier B,
Ficarra V, Hutson TE, Mulders PF, Patard JJ, Rini BI, Staehler M,
Sternberg CN and Stief CG: Sequencing of agents for metastatic
renal cell carcinoma: Can we customize therapy? Eur Urol.
61:307–316. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Bella L, Zona S, Nestal de Moraes G and
Lam EW: Foxm1: A key oncofoetal transcription factor in health and
disease. Semin Cancer Biol. 29:32–39. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Mitchell TJ, Turajlic S, Rowan A, Nicol D,
Farmery JHR, O'Brien T, Martincorena I, Tarpey P, Angelopoulos N,
Yates LR, et al: Timing the landmark events in the evolution of
clear cell renal cell cancer: Tracerx Renal. Cell. 173:611–623.e17.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Bedke J, Gauler T, Grünwald V, Hegele A,
Herrmann E, Hinz S, Janssen J, Schmitz S, Schostak M, Tesch H, et
al: Systemic therapy in metastatic renal cell carcinoma. World J
Urol. 35:179–188. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Chatterjee N and Bivona TG: Polytherapy
and targeted cancer drug resistance. Trends Cancer. 5:170–182.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Noessner E, Brech D, Mendler AN, Masouris
I, Schlenker R and Prinz PU: Intratumoral alterations of
dendritic-cell differentiation and CD8(+) T-cell anergy are immune
escape mechanisms of clear cell renal cell carcinoma.
Oncoimmunology. 1:1451–1453. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Choueiri TK, Fishman MN, Escudier B,
McDermott DF, Drake CG, Kluger H, Stadler WM, Perez-Gracia JL,
McNeel DG, Curti B, et al: Immunomodulatory activity of nivolumab
in metastatic renal cell carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res. 22:5461–5471.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Lalani AA, McGregor BA, Albiges L,
Choueiri TK, Motzer R, Powles T, Wood C and Bex A: Systemic
treatment of metastatic clear cell renal cell carcinoma in 2018:
Current paradigms, use of immunotherapy, and future directions. Eur
Urol. 75:100–110. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Carlo MI, Voss MH and Motzer RJ:
Checkpoint inhibitors and other novel immunotherapies for advanced
renal cell carcinoma. Nat Rev Urol. 13:420–431. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Gill DM and Agarwal N: Cancer
immunotherapy: A paradigm shift in the treatment of advanced
urologic cancers. Urol Oncol. 35:676–677. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Martínez-Salamanca JI, Huang WC, Millán I,
Bertini R, Bianco FJ, Carballido JA, Ciancio G, Hernández C,
Herranz F, Haferkamp A, et al: Prognostic impact of the 2009
UICC/AJCC TNM staging system for renal cell carcinoma with venous
extension. Eur Urol. 59:120–127. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Brahmer JR, Drake CG, Wollner I, Powderly
JD, Picus J, Sharfman WH, Stankevich E, Pons A, Salay TM, McMiller
TL, et al: Phase I study of single-agent anti-programmed death-1
(MDX-1106) in refractory solid tumors: Safety, clinical activity,
pharmacodynamics, and immunologic correlates. J Clin Oncol.
28:3167–3175. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Lipson EJ, Sharfman WH, Drake CG, Wollner
I, Taube JM, Anders RA, Xu H, Yao S, Pons A, Chen L, et al: Durable
cancer regression off-treatment and effective reinduction therapy
with an anti-PD-1 antibody. Clin Cancer Res. 19:462–468. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Topalian SL, Hodi FS, Brahmer JR,
Gettinger SN, Smith DC, McDermott DF, Powderly JD, Carvajal RD,
Sosman JA, Atkins MB, et al: Safety, activity, and immune
correlates of anti-PD-1 antibody in cancer. N Engl J Med.
366:2443–2454. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Motzer RJ, Rini BI, McDermott DF, Redman
BG, Kuzel TM, Harrison MR, Vaishampayan UN, Drabkin HA, George S,
Logan TF, et al: Nivolumab for metastatic renal cell carcinoma:
Results of a randomized phase ii trial. J Clin Oncol. 33:1430–1437.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Motzer RJ, Escudier B, McDermott DF,
George S, Hammers HJ, Srinivas S, Tykodi SS, Sosman JA, Procopio G,
Plimack ER, et al: Nivolumab versus everolimus in advanced
renal-cell carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 373:1803–1813. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Brahmer JR, Tykodi SS, Chow LQ, Hwu WJ,
Topalian SL, Hwu P, Drake CG, Camacho LH, Kauh J, Odunsi K, et al:
Safety and activity of anti-PD-L1 antibody in patients with
advanced cancer. N Engl J Med. 366:2455–2465. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
McDermott DF, Sosman JA, Sznol M, Massard
C, Gordon MS, Hamid O, Powderly JD, Infante JR, Fassò M, Wang YV,
et al: Atezolizumab, an anti-programmed death-ligand 1 antibody, in
metastatic renal cell carcinoma: Long-term safety, clinical
activity, and immune correlates from a phase Ia study. J Clin
Oncol. 34:833–842. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Yang JC, Hughes M, Kammula U, Royal R,
Sherry RM, Topalian SL, Suri KB, Levy C, Allen T, Mavroukakis S, et
al: Ipilimumab (anti-CTLA4 antibody) causes regression of
metastatic renal cell cancer associated with enteritis and
hypophysitis. J Immunother. 30:825–830. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Sharpe AH and Pauken KE: The diverse
functions of the PD1 inhibitory pathway. Nat Rev Immunol.
18:153–167. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Chen KS and DeLuca HF: Isolation and
characterization of a novel cDNA from HL-60 cells treated with
1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D-3. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1219:26–32. 1994.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Wu N, Zheng B, Shaywitz A, Dagon Y, Tower
C, Bellinger G, Shen CH, Wen J, Asara J, McGraw TE, et al:
Ampk-dependent degradation of TXNIP upon energy stress leads to
enhanced glucose uptake via GLUT1. Mol Cell. 49:1167–1175. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Shen L, O'Shea JM, Kaadige MR, Cunha S,
Wilde BR, Cohen AL, Welm AL and Ayer DE: Metabolic reprogramming in
triple-negative breast cancer through Myc suppression of TXNIP.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 112:5425–5430. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Han SH, Jeon JH, Ju HR, Jung U, Kim KY,
Yoo HS, Lee YH, Song KS, Hwang HM, Na YS, et al: Vdup1 upregulated
by TGF-beta1 and 1,25-dihydorxyvitamin d3 inhibits tumor cell
growth by blocking cell-cycle progression. Oncogene. 22:4035–4046.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Saxena G, Chen J and Shalev A:
Intracellular shuttling and mitochondrial function of
thioredoxin-interacting protein. J Biol Chem. 285:3997–4005. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Zhou R, Yazdi AS, Menu P and Tschopp J: A
role for mitochondria in NLRP3 inflammasome activation. Nature.
469:221–225. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Zhou R, Tardivel A, Thorens B, Choi I and
Tschopp J: Thioredoxin-interacting protein links oxidative stress
to inflammasome activation. Nat Immunol. 11:136–140. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Jiao D, Huan Y, Zheng J, Wei M, Zheng G,
Han D, Wu J, Xi W, Wei F, Yang AG, et al: UHRF1 promotes renal cell
carcinoma progression through epigenetic regulation of TXNIP.
Oncogene. 38:5686–5699. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Meszaros M, Yusenko M, Domonkos L, Peterfi
L, Kovacs G and Banyai D: Expression of TXNIP is associated with
angiogenesis and postoperative relapse of conventional renal cell
carcinoma. Sci Rep. 11:172002021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Gao Y, Qi JC, Li X, Sun JP, Ji H and Li
QH: Decreased expression of TXNIP predicts poor prognosis in
patients with clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Oncol Lett.
19:763–770. 2020.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Pan M, Zhang F, Qu K, Liu C and Zhang J:
TXNIP: A double-edged sword in disease and therapeutic outlook.
Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2022:78051152022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Hutter C and Zenklusen JC: The cancer
genome atlas: Creating lasting value beyond its data. Cell.
173:283–285. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Subramanian A, Tamayo P, Mootha VK,
Mukherjee S, Ebert BL, Gillette MA, Paulovich A, Pomeroy SL, Golub
TR, Lander ES and Mesirov JP: Gene set enrichment analysis: A
knowledge-based approach for interpreting genome-wide expression
profiles. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 102:15545–15550. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Yu G, Wang LG, Han Y and He QY:
clusterProfiler: An R package for comparing biological themes among
gene clusters. OMICS. 16:284–287. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Chen B, Khodadoust MS, Liu CL, Newman AM
and Alizadeh AA: Profiling tumor infiltrating immune cells with
CIBERSORT. Methods Mol Biol. 1711:243–259. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Li B, Severson E, Pignon JC, Zhao H, Li T,
Novak J, Jiang P, Shen H, Aster JC, Rodig S, et al: Comprehensive
analyses of tumor immunity: Implications for cancer immunotherapy.
Genome Biol. 17:1742016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Shankavaram UT, Varma S, Kane D, Sunshine
M, Chary KK, Reinhold WC, Pommier Y and Weinstein JN: CellMiner: A
relational database and query tool for the NCI-60 cancer cell
lines. BMC Genomics. 10:2772009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Wu JH, Limmer AL, Narayanan D, Doan HQ,
Simonette RA, Rady PL and Tyring SK: The novel AKT inhibitor
afuresertib suppresses human Merkel cell carcinoma MKL-1 cell
growth. Clin Exp Dermatol. 46:1551–1554. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Trapani D, Esposito A, Criscitiello C,
Mazzarella L, Locatelli M, Minchella I, Minucci S and Curigliano G:
Entinostat for the treatment of breast cancer. Expert Opin Investig
Drugs. 26:965–971. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Athira KV, Sadanandan P and Chakravarty S:
Repurposing Vorinostat for the treatment of disorders affecting
brain. Neuromolecular Med. 23:449–465. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
James RG, Davidson KC, Bosch KA, Biechele
TL, Robin NC, Taylor RJ, Major MB, Camp ND, Fowler K, Martins TJ
and Moon RT: WIKI4, a novel inhibitor of tankyrase and
wnt/ß-catenin signaling. PLoS One. 7:e504572012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Yu J, Liu D, Sun X, Yang K, Yao J, Cheng
C, Wang C and Zheng J: CDX2 inhibits the proliferation and tumor
formation of colon cancer cells by suppressing Wnt/β-catenin
signaling via transactivation of GSK-3β and Axin2 expression. Cell
Death Dis. 10:262019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Haddadi MH and Negahdari B: Clinical and
diagnostic potential of regulatory T cell markers: From bench to
bedside. Transplant Immunol. 70:1015182022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Wang L, Zhu Y, Ren Z, Sun W, Wang Z, Zi T,
Li H, Zhao Y, Qin X, Gao D, et al: An immunogenic cell
death-related classification predicts prognosis and response to
immunotherapy in kidney renal clear cell carcinoma. Front Oncol.
13:11478052023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Sun Z, Tao W, Guo X, Jing C, Zhang M, Wang
Z, Kong F, Suo N, Jiang S and Wang H: Construction of a
Lactate-related prognostic signature for predicting prognosis,
tumor microenvironment, and immune response in kidney renal clear
cell carcinoma. Front Immunol. 13:8189842022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Zhou J, Yu Q and Chng WJ: TXNIP (VDUP-1,
TBP-2): A major redox regulator commonly suppressed in cancer by
epigenetic mechanisms. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 43:1668–1673. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Patwari P, Higgins LJ, Chutkow WA,
Yoshioka J and Lee RT: The interaction of thioredoxin with Txnip.
Evidence for formation of a mixed disulfide by disulfide exchange.
J Biol Chem. 281:21884–21891. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Zhang P, Wang C, Gao K, Wang D, Mao J, An
J, Xu C, Wu D, Yu H, Liu JO and Yu L: The ubiquitin ligase itch
regulates apoptosis by targeting thioredoxin-interacting protein
for ubiquitin-dependent degradation. J Biol Chem. 285:8869–8879.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Iqbal MA, Chattopadhyay S, Siddiqui FA, Ur
Rehman A, Siddiqui S, Prakasam G, Khan A, Sultana S and Bamezai RN:
Silibinin induces metabolic crisis in triple-negative breast cancer
cells by modulating EGFR-MYC-TXNIP axis: Potential therapeutic
implications. FEBS J. 288:471–485. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Chen D, Dang BL, Huang JZ, Chen M, Wu D,
Xu ML, Li R and Yan GR: Mir-373 drives the
epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and metastasis via the
mir-373-TXNIP-HIF1α-TWIST signaling axis in breast cancer.
Oncotarget. 6:32701–32712. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Cadenas C, Franckenstein D, Schmidt M,
Gehrmann M, Hermes M, Geppert B, Schormann W, Maccoux LJ, Schug M,
Schumann A, et al: Role of thioredoxin reductase 1 and thioredoxin
interacting protein in prognosis of breast cancer. Breast Cancer
Res. 12:R442010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Hamilton JP, Potter JJ, Koganti L, Meltzer
SJ and Mezey E: Effects of vitamin D3 stimulation of
thioredoxin-interacting protein in hepatocellular carcinoma.
Hepatol Res. 44:1357–1366. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Hong SY, Yu FX, Luo Y and Hagen T:
Oncogenic activation of the PI3K/AKT pathway promotes cellular
glucose uptake by downregulating the expression of
thioredoxin-interacting protein. Cell Signal. 28:377–383. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Woolston CM, Madhusudan S, Soomro IN, Lobo
DN, Reece-Smith AM, Parsons SL and Martin SG: Thioredoxin
interacting protein and its association with clinical outcome in
gastro-oesophageal adenocarcinoma. Redox Biol. 1:285–291. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Yang MH, Wu MZ, Chiou SH, Chen PM, Chang
SY, Liu CJ, Teng SC and Wu KJ: Direct regulation of TWIST by
HIF-1alpha promotes metastasis. Nat Cell Biol. 10:295–305. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Sheth SS, Bodnar JS, Ghazalpour A,
Thipphavong CK, Tsutsumi S, Tward AD, Demant P, Kodama T, Aburatani
H and Lusis AJ: Hepatocellular carcinoma in Txnip-deficient mice.
Oncogene. 25:3528–3536. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Grivennikov SI, Greten FR and Karin M:
Immunity, inflammation, and cancer. Cell. 140:883–899. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Picard E, Verschoor CP, Ma GW and Pawelec
G: Relationships between immune landscapes, genetic subtypes and
responses to immunotherapy in colorectal cancer. Front Immunol.
11:3692020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Wang SS, Liu W, Ly D, Xu H, Qu L and Zhang
L: Tumor-infiltrating B cells: Their role and application in
anti-tumor immunity in lung cancer. Cell Mol Immunol. 16:6–18.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Ribas A and Wolchok JD: Cancer
immunotherapy using checkpoint blockade. Science. 359:1350–1355.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Denkert C, von Minckwitz G, Brase JC, Sinn
BV, Gade S, Kronenwett R, Pfitzner BM, Salat C, Loi S, Schmitt WD,
et al: Tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes and response to neoadjuvant
chemotherapy with or without carboplatin in human epidermal growth
factor receptor 2-positive and triple-negative primary breast
cancers. J Clin Oncol. 33:983–991. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Ding Q, Lu P, Xia Y, Ding S, Fan Y, Li X,
Han P, Liu J, Tian D and Liu M: CXCL9: Evidence and contradictions
for its role in tumor progression. Cancer Med. 5:3246–3259. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Kokubo K, Hirahara K, Kiuchi M, Tsuji K,
Shimada Y, Sonobe Y, Shinmi R, Hishiya T, Iwamura C, Onodera A and
Nakayama T: Thioredoxin-interacting protein is essential for memory
T cell formation via the regulation of the redox metabolism. Proc
Natl Acad Sci USA. 120:e22183451202023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Zhu J and Han S: Histone deacetylase 10
exerts anti-tumor effects on cervical cancer via a novel
microRNA-223/TXNIP/Wnt/β-catenin pathway. IUBMB Life. Jan
22–2021.(Epub ahead of print). doi: 10.1002/iub.2448. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
68
|
Dong F, Dong S, Liang Y, Wang K, Qin Y and
Zhao X: Mir-20b inhibits the senescence of human umbilical vein
endothelial cells through regulating the Wnt/β-catenin pathway via
the TXNIP/NLRP3 axis. Int J Mol Med. 45:847–857. 2020.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Ao H, Li H, Zhao X, Liu B and Lu L: TXNIP
positively regulates the autophagy and apoptosis in the rat müller
cell of diabetic retinopathy. Life Sci. 267:1189882021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|